





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (11): 5649-5659.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.11.024
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHAN Yige( ), LIU Yongning(
), LIU Yongning( ), ZHOU Shuang, LIU Qianlin, LI Yilin, DUAN Sizhang, AN Jian, ZHANG Jianjun*(
), ZHOU Shuang, LIU Qianlin, LI Yilin, DUAN Sizhang, AN Jian, ZHANG Jianjun*( )
)
Received:2024-10-08
Online:2025-11-23
Published:2025-11-27
Contact:
ZHANG Jianjun
E-mail:996813661@qq.com;1277887810@qq.com;zhjj339@163.com
CLC Number:
SHAN Yige, LIU Yongning, ZHOU Shuang, LIU Qianlin, LI Yilin, DUAN Sizhang, AN Jian, ZHANG Jianjun. Prokaryotic Expression and Immune Efficacy Evaluation of RON2L2ecto Protein from Eimeria tenella[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5649-5659.
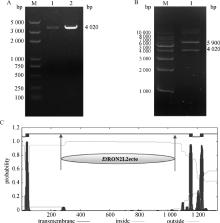
Fig. 2
PCR amplification of EtRON2L2 gene, double enzyme digestion identification of recombinant plasmids and transmembrane structure analysis of EtRON2L2 protein A. PCR amplification of EtRON2L2 gene: M. DL-5000 DNA Marker; 1-2. PCR amplification products of EtRON2L2. B. Double enzyme digestion identification of recombinant plasmids: M. DL-10000 DNA Marker; 1. Recombinant cloning vector of pET-32a(+)-EtRON2L2. C. Transmembrane structure analysis of EtRON2L2 protein"
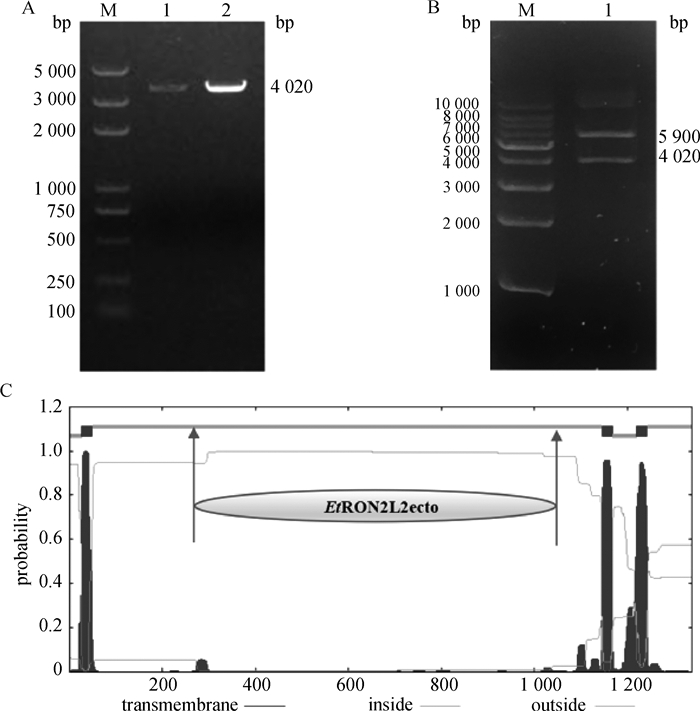
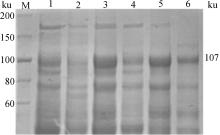
Fig. 3
Solubility analysis and purification result of rEtRON2L2ecto protein M. Protein Marker(30-200 ku); 1. Whole cell protein containing pET-28a (+) empty plasmid; 2. Whole cell protein before induction; 3. Whole cell protein after induction; 4. Supernatant after ultrasonic lysis; 5. Precipitation after ultrasonic lysis; 6. Purified rEtRON2L2ecto"
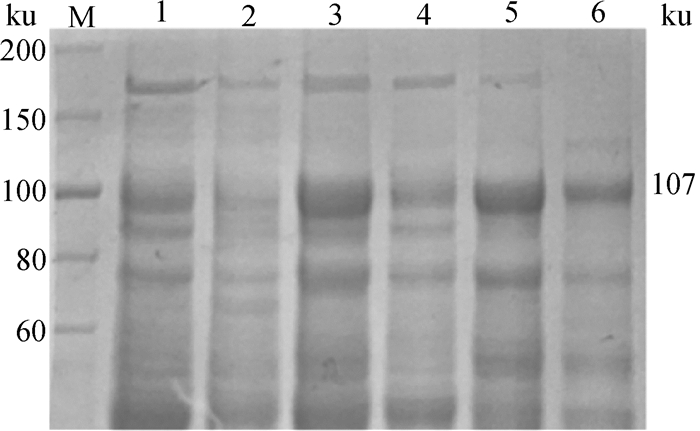
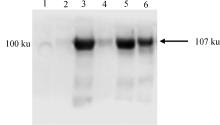
Fig. 4
Western blot identification result of rEtRON2L2ecto 1. Whole cell protein containing pET-28a (+) empty plasmid; 2. Whole cell protein before induction; 3. Whole cell protein after induction; 4. Supernatant after ultrasonic lysis; 5. Precipitation after ultrasonic lysis; 6. Purified rEtRON2L2ecto"
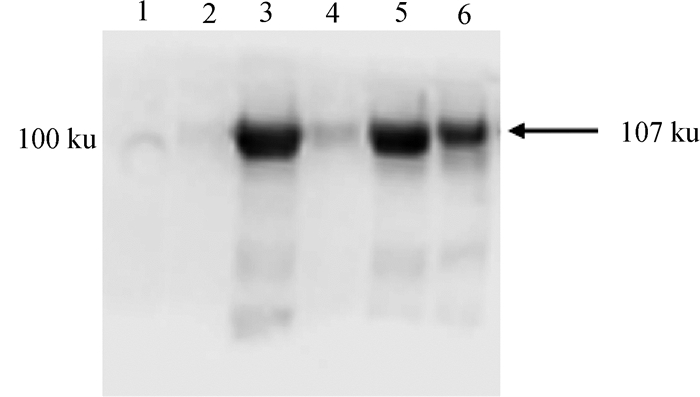
Table 1
Average weight gain and average OPG"
| 组别 Group | 平均体增重/g Average weight gain | 平均OPG/(×105·g-1) Average OPG |
| 不免疫不攻虫组 Negative control group | 65.29±1.32a | 0a |
| 不免疫攻虫组 Positive control group | 42.58±1.11b | 7.04±0.26b |
| 50 μg蛋白免疫组 50 μg rEtRON2L2ecto immune group | 41.87±0.75b | 4.01±0.27c |
| 100 μg蛋白免疫组 100 μg rEtRON2L2ecto immune group | 47.02±0.86c | 0.40±0.19d |
| 200 μg蛋白免疫组 200 μg rEtRON2L2ecto immune group | 46.83±1.26c | 0.24±0.06d |
Table 2
Score of cecal lesions"
| 组别 Group | 盲肠病变评分 Score of cecal lesions |
| 不免疫不攻虫组 Negative control group | 0a |
| 不免疫攻虫组 Positive control group | 1.5±0.53b |
| 50 μg蛋白免疫组 50 μg rEtRON2L2ecto immune group | 0.62±0.74ac |
| 100 μg蛋白免疫组 100 μg rEtRON2L2ecto immune group | 0.25±0.46ac |
| 200 μg蛋白免疫组 200 μg rEtRON2L2ecto immune group | 0.25±0.46ac |
Table 3
ACI"
| 组别 Group | 存活率/% Survival rate | 相对增重率/% Relative weight gain rate | 病变值 Lesion value | 卵囊值 Oocyst value | 抗球虫指数 ACI |
| 不免疫不攻虫组 Negative control group | 100 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 200 |
| 不免疫攻虫组 Positive control group | 100 | 65.2 | 15 | 40 | 110.2 |
| 50 μg蛋白免疫组 50 μg rEtRON2L2ecto immune group | 100 | 64.1 | 6.2 | 20 | 137.9 |
| 100 μg蛋白免疫组 100 μg rEtRON2L2ecto immune group | 100 | 72.0 | 2.5 | 5 | 164.5 |
| 200 μg蛋白免疫组 200 μg rEtRON2L2ecto immune group | 100 | 71.7 | 2.5 | 5 | 164.2 |
Table 4
Average Immune organ index mg·g-1"
| 组别 Group | 脾脏指数 Spleen index | 法氏囊指数 Bursa of Fabricius index |
| 不免疫不攻虫组 Negative control group | 21.8±1.0a | 52.6±2.2a |
| 不免疫攻虫组 Positive control group | 24.6±2.6a | 44.5±1.1b |
| 50 μg蛋白免疫组 50 μg rEtRON2L2ecto immune group | 29.7±1.5b | 31.0±1.9c |
| 100 μg蛋白免疫组 100 μg rEtRON2L2ecto immune group | 31.3±4.5b | 24.7±4.0d |
| 200 μg蛋白免疫组 200 μg rEtRON2L2ecto immune group | 33.8.±2.2b | 30.5±1.3c |
| 1 | SHIRLEY M W , SMITH A L , TOMLEY F M . The biology of avian Eimeria with an emphasis on their control by vaccination[J]. Adv Parasitol, 2005, 60, 285- 330. |
| 2 | SHIRLEY M W , SMITH A L , BLAKE D P . Challenges in the successful control of the avian coccidia[J]. Vaccine, 2007, 25 (30): 5540- 5547. |
| 3 | YUN C H , LILLEHOJ H S , CHOI K D . Eimeria tenella infection induces local gamma interferon production and intestinal lymphocyte subpopulation changes[J]. Infect Immun, 2000, 68 (3): 1282- 1288. |
| 4 | FERNANDO M A , LAWN A M , ROSE M E , et al. Invasion of chicken caecal and intestinal lamina propria by crypt epithelial cells infected with coccidia[J]. Parasitology, 1983, 86 (Pt 3): 391- 398. |
| 5 | AIKAWA M , MILLER L H , JOHNSON J , et al. Erythrocyte entry by malarial parasites. A moving junction between erythrocyte and parasite[J]. J Cell Biol, 1978, 77 (1): 72- 82. |
| 6 | SUSS-TOBY E , ZIMMERBERG J , WARD G E . Toxoplasma invasion: the parasitophorous vacuole is formed from host cell plasma membrane and pinches off via a fission pore[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1996, 93 (16): 8413- 8418. |
| 7 | LEBRUN M , MICHELIN A , EL HAJJ H , et al. The rhoptry neck protein RON4 re-localizes at the moving junction during Toxoplasma gondii invasion[J]. Cell Microbiol, 2005, 7 (12): 1823- 1833. |
| 8 | ALEXANDER D L , MITAL J , WARD G E , et al. Identification of the moving junction complex of Toxoplasma gondii: a collaboration between distinct secretory organelles[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2005, 1 (2): e17. |
| 9 | BESTEIRO S , MICHELIN A , PONCET J , et al. Export of a Toxoplasma gondii rhoptry neck protein complex at the host cell membrane to form the moving junction during invasion[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2009, 5 (2): e1000309. |
| 10 | STRAUB K W , CHENG S J , SOHN C S , et al. Novel components of the Apicomplexan moving junction reveal conserved and coccidia-restricted elements[J]. Cell Microbiol, 2009, 11 (4): 590- 603. |
| 11 | LAMARQUE M , BESTEIRO S , PAPOIN J , et al. The RON2-AMA1 interaction is a critical step in moving junction-dependent invasion by apicomplexan parasites[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2011, 7 (2): e1001276. |
| 12 | SRINIVASAN P , BEATTY W L , DIOUF A , et al. Binding of Plasmodium merozoite proteins RON2 and AMA1 triggers commitment to invasion[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011, 108 (32): 13275- 13280. |
| 13 | TYLER J S , BOOTHROYD J C . The C-terminus of Toxoplasma RON2 provides the crucial link between AMA1 and the host-associated invasion complex[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2011, 7 (2): e1001282. |
| 14 | JOHNSON J , REID W M . Anticoccidial drugs: lesion scoring techniques in battery and floor-pen experiments with chickens[J]. Exp Parasitol, 1970, 28 (1): 30- 36. |
| 15 | 郭致君, 刘澜, 布仁阿古达木. 克迪球预防人工感染鸡球虫病效果的观察[J]. 畜禽业, 2008 (2): 63- 64. |
| GUO Z J , LIU L , BUREN A G D M . Studies on the preventive effects of Kediqiu on coccidiosis in chickens[J]. Livestock and Poultry Industry, 2008 (2): 63- 64. | |
| 16 | 潘严, 姜子睿, 周超, 等. 肠道寄生虫粪便的病原学检查方法[J]. 中国医药科学, 2016, 6 (20): 213- 217. |
| PAN Y , JIANG Z R , ZHOU C , et al. Pathogenic examination methods of Intestinal parasite stool[J]. China Medicine and Pharmacy, 2016, 6 (20): 213- 217. | |
| 17 | 索勋, 李国清. 鸡球虫病学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1998. |
| SUO X , LI G Q . Coccidia and coccidiosis of domestic fowl[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1998. | |
| 18 | SHIRLEY M W , CHAPMAN H D , KUCERA J , et al. Enzyme variation and pathogenicity of recent field isolates of Eimeria tenella[J]. Res Vet Sci, 1989, 46 (1): 79- 83. |
| 19 | YAN M , CUI X , ZHAO Q , et al. Molecular characterization and protective efficacy of the microneme 2 protein from Eimeria tenella[J]. Parasite, 2018, 25, 60. |
| 20 | 刘贤勇, 索勋. 鸡球虫病及其控制策略[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2006 (5): 31- 37. |
| LIU X Y , SUO X . Chicken coccidiosis and the control strategies[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2006 (5): 31- 37. | |
| 21 | JEURISSEN S H . Structure and function of the chicken spleen[J]. Res Immunol, 1991, 142 (4): 352- 355. |
| 22 |
马锡慧, 肖漓. 淋巴细胞亚群成员研究进展[J]. 中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版), 2017, 7 (3): 168- 172.
doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-1221.2017.03.009 |
|
MA X H , XIAO L . Research progress in members of lymphocyte subsets[J]. Chinese Journal of Cells and Stem Cells (Electronic Edition), 2017, 7 (3): 168- 171.
doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-1221.2017.03.009 |
|
| 23 | 王莉. Th1/Th2极化: 多因素的参与和调控[J]. 上海免疫学杂志, 2001 (6): 376-378, 384. |
| WANG L . Th1/Th2 polarization: involvement and regulation of multiple factors[J]. Shanghai Journal of Immunology, 2001 (6): 376-378, 384. | |
| 24 | LILLEHOJ H S , TROUT J M . Avian gut-associated lymphoid tissues and intestinal immune responses to Eimeria parasites[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 1996, 9 (3): 349- 360. |
| 25 | LILLEHOJ H S , MIN W , DALLOUL R A . Recent progress on the cytokine regulation of intestinal immune responses to Eimeria[J]. Poult Sci, 2004, 83 (4): 611- 623. |
| [1] | DUAN Sizhang, LIU Yongning, SHAN Yige, LIU Qianlin, LI Yilin, AN Jian, ZHANG Jianjun. The Effect of Bidens pilosa on Intestinal Damage, Immune Function, and Antioxidant Capacity in Chicks Infected with Eimeria tenella [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5826-5838. |
| [2] | WANG Lele, WANG Liyue, CAI Weimin, KANG Xilong, FENG Qianqian, ZHANG Zhizhi, FAN Xuelian, ZHU Yu, LIU Dandan, XU Jinjun, PAN Zhiming, TAO Jianping. Immunoprotective Efficacy of Recombinant Protein rEnApiAP2 against Coccidia in Chicken [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1716-1727. |
| [3] | WANG He, GUO Zhiting, LI Jianxi, ZHANG Jingyan, WANG Lei, ZHANG Kang, SUN Jiwen, SHANG Xiaofen, MA Yonghua. Effect of Radix dichroa Powder on the Control of Eimeria tenella Infection in Chick at Different Developmental Stages [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1278-1289. |
| [4] | Junli NI, Xinchao LIU, Dong SUN, Siyun FANG, Dingai WANG, Hanqin SHEN, Zhuanqiang YAN, Nanshan QI, Mingfei SUN, Youfang GU. Construction, Expression and Preliminary Functional Analysis of the Eukaryotic Plasmid ET Seven, a 7-valent Multiepitope Chimeric Recombinant Antigen of Chicken Coccidia [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 5159-5172. |
| [5] | JIAO Yuzhou, YANG Huanhuan, LU Yao, SHI Congcong, XU Xiaojuan, CAI Xuwang. Effect of Enterococcus faecium on Growth Performance and Intestinal Barrier of Broilers Infected with Eimeria tenella [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(4): 1210-1219. |
| [6] | LIANG Shanshan, ZHU Shunhai, ZHAO Qiping, HUANG Bing, DONG Hui, YU Yu, WANG Qingjie, YU Shuilan, WANG Haixia, HAN Hongyu. Preliminary Study on the Function of Elongation Factor 1α of Eimeria tenella [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(12): 3111-3121. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||