





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (10): 5190-5201.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.10.038
• Basic Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Hao1,2( ), XU Qiaoyu1,2(
), XU Qiaoyu1,2( ), JIN Xiaohui1,2, CHEN Hongying1,2, LI Qinghao1,2, JIN Xin1,2, MA Junxing1,2,*(
), JIN Xiaohui1,2, CHEN Hongying1,2, LI Qinghao1,2, JIN Xin1,2, MA Junxing1,2,*( ), MA Shijie1,2,*(
), MA Shijie1,2,*( ), WEI Zhanyong1,2
), WEI Zhanyong1,2
Received:2024-11-13
Online:2025-10-23
Published:2025-11-01
Contact:
MA Junxing, MA Shijie
E-mail:15037382071@163.com;13037580584@163.com;majx@henau.edu.cn;participate2006@126.com
CLC Number:
LI Hao, XU Qiaoyu, JIN Xiaohui, CHEN Hongying, LI Qinghao, JIN Xin, MA Junxing, MA Shijie, WEI Zhanyong. Histopathological Changes of Immune Organs and Alterations of Cytokines in Piglets Infected with Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(10): 5190-5201.
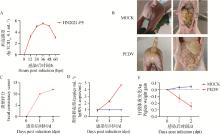
Fig. 1
Clinical symptoms and autopsy changes after PEDV infection in 5-day-old piglets A. One-step growth curve of PEDV on Vero cells; B. Clinical symptoms of piglets after challenge and pathological changes after necropsy; C. Stool viscosity score; D. Detoxification of piglet feces after challenge; E. Changes in piglet body weight after challenge"
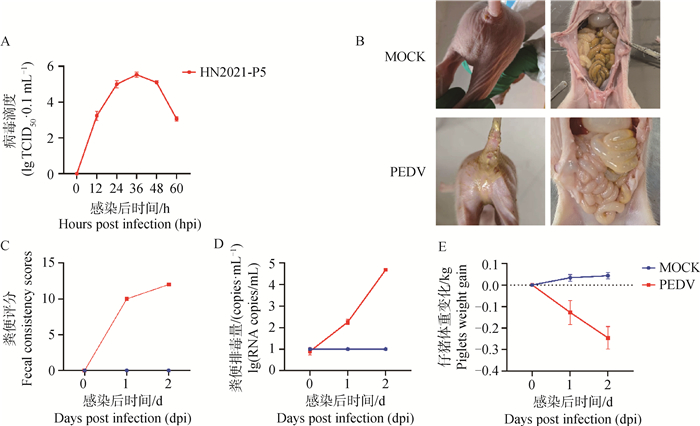
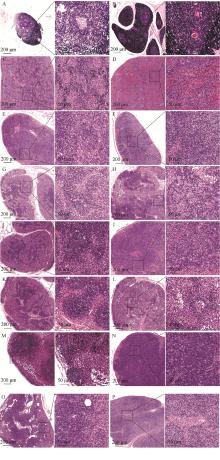
Fig. 2
Histopathological analysis of immune organs after PEDV infection in piglets A. Thymus in the control group; B. Thymus in the PEDV-infected group; C. Spleen of the control group; D. Spleen in PEDV-infected group; E. mesenteric lymph nodes in the control group; F. Mesenteric lymph nodes in the PEDV-infected group; G. Inferior iliac lymph nodes in the control group; H. Inferior iliac lymph nodes in PEDV-infected group; I. inguinal lymph nodes in the control group; J. Inguinal lymph nodes in the PEDV-infected group; K. Mandibular lymph nodes in the control group; L. Mandibular lymph nodes in the PEDV-infected group; M. Preshoulder lymph nodes in the control group; N. Preshoulder lymph nodes in PEDV-infected group; O. hilar lymph nodes in the control group; P. hilar lymph nodes in the PEDV-infected group"

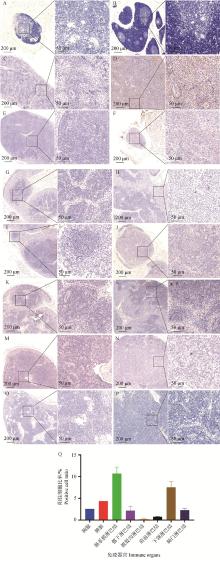
Fig. 3
Distribution and immunohistochemical analysis of PEDV in thymus and peripheral immune organs of piglets A. Thymus in the control group; B. Thymus in the PEDV-infected group; C. Spleen of the control group; D. Spleen in PEDV-infected group; E. mesenteric lymph nodes in the control group; F. Mesenteric lymph nodes in the PEDV-infected group; G. Inferior iliac lymph nodes in the control group; H. Inferior iliac lymph nodes in PEDV-infected group; I. inguinal lymph nodes in the control group; J. Inguinal lymph nodes in the PEDV-infected group; K. Mandibular lymph nodes in the control group; L. Mandibular lymph nodes in the PEDV-infected group; M. Preshoulder lymph nodes in the control group; N. Preshoulder lymph nodes in PEDV-infected group; O. Hilar lymph nodes in the control group; P. hilar lymph nodes in the PEDV-infected group; Q. Proportion of positive cells in each immune organ"

| 1 |
KOCHERHANSR,BRIDGENA,ACKERMANNM,et al.Completion of the porcine epidemic diarrhoea coronavirus (PEDV) genome sequence[J].Virus genes,2001,23(2):137-144.
doi: 10.1023/A:1011831902219 |
| 2 |
LIW T,LIH,LIUY B,et al.New variants of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, China, 2011[J].Emerg Infect Dis,2012,18(8):1350-1353.
doi: 10.3201/eid1803.120002 |
| 3 |
HAVEP,MOVINGV,SVANSSONV,et al.Coronavirus infection in mink (Mustela vison). Serological evidence of infection with a coronavirus related to transmissible gastroenteritis virus and porcine epidemic diarrhea virus[[J].Vet Microbiol,1992,31(1):1-10.
doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(92)90135-G |
| 4 |
PENSAERTMB,BOUCKP D.A new coronavirus-like particle associated with diarrhea in swine[J].Arch Virol,1978,58(3):243-247.
doi: 10.1007/BF01317606 |
| 5 | 杜坚,蒋玉雯,白安斌,等.广西猪流行性腹泻流行病学调查[J].动物科学与动物医学,2004,6,52-53. |
| DUJ,JIANGY W,BAIA B,et al.The epidemiological investigation of porcine epidemic diarrhea in Guangxi[J].Animal Science &Veterinary Medicine,2004,6,52-53. | |
| 6 |
SUNR Q,CAIR J,CHENY Q,et al.Outbreak of porcine epidemic diarrhea in suckling piglets, China[J].Emerg Infect Dis,2012,18(1):161-163.
doi: 10.3201/eid1801.111259 |
| 7 |
ZHANGH,ZOUC,PENGO,et al.Global dynamics of porcine enteric coronavirus PEDV epidemiology, evolution, and transmission[J].Mol Biol Evol,2023,40(3):msad052.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msad052 |
| 8 |
LIY,WUQ,HUANGL,et al.An alternative pathway of enteric PEDV dissemination from nasal cavity to intestinal mucosa in swine[J].Nat Commun,2018,9(1):3811.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06056-w |
| 9 |
SPRINGERT A.Adhesion receptors of the immune system[J].Nature,1990,346(6283):425-434.
doi: 10.1038/346425a0 |
| 10 | 卓秀萍,朱玲,乔小改,等.人工感染猪流行性腹泻病毒的哺乳仔猪的病理学观察[J].中国兽医科学,2015,45(2):202-207. |
| ZHUOX P,ZHUL,QIAOX G,et al.Pathological observation of suckling piglets infected with porcine epidemic diarrhea virus artificially[J].Chinese Veterinary Science,2015,45(2):202-207. | |
| 11 |
TAKAHASHIK,OKADAK,OHSHIMAK.An outbreak of swine diarrhea of a new-type associated with coronavirus-like particles in Japan[J].Nihon Juigaku Zasshi,1983,45(6):829-832.
doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.45.829 |
| 12 |
PANY,TIANX,LIW,et al.Isolation and characterization of a variant porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in China[J].Virology Journal,2012,9,195.
doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-195 |
| 13 | CIMAG.Viral disease affects U.S. pigs: porcine epidemic diarrhea found in at least 11 states[J].J Am Vet Med Assoc,2013,243(1):30-31. |
| 14 | CIMAG.PED virus reinfecting U.S. herds. Virus estimated to have killed 7 million-plus pigs[J].J Am Vet Med Assoc,2014,245(2):166-167. |
| 15 | 王金坡. 猪流行性腹泻病毒自然感染哺乳仔猪的病理学观察及肠道转录组学研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2020. |
| WANG J P. Pathological observation and intestinal transcriptomics study of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus naturally infected suckling piglets[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 16 |
贺叶青,左百姣,李庆豪,等.猪传染性胃肠炎病毒感染仔猪免疫器官的组织病理学观察[J].畜牧兽医学报,2023,54(11):4872-4879.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.11.041 |
|
HEY Q,ZUOB J,LIQ H,et al.Histopathological observation of immune organs of piglets infected with transmissible gastroenteritis virus[J].Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica,2023,54(11):4872-4879.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.11.041 |
|
| 17 | 左百姣,贺叶青,李庆豪,等.PDCoV感染对仔猪全身免疫器官的影响[J].中国兽医学报,2023,43(12):2412-2417. |
| ZUOB J,HEY Q,LIQ H,et al.Pathological damage of immune system in piglets infected with porcine deltacoronavirus[J].Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science,2023,43(12):2412-2417. | |
| 18 |
BRYCEC,GRIMESZ,PUJADASE,et al.Pathophysiology of SARS-CoV-2: the Mount Sinai COVID-19 autopsy experience[J].Mod Pathol,2021,34(8):1456-1467.
doi: 10.1038/s41379-021-00793-y |
| 19 |
HORIUCHIT,MITOMAH,HARASHIMAS,et al.Transmembrane TNF-alpha: structure, function and interaction with anti-TNF agents[J].Rheumatology,2010,49(7):1215-28.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keq031 |
| 20 |
DINARELLOC A.Interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory diseases[J].Blood,2011,117(14):3720-3732.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-07-273417 |
| 21 | CAMPBELLK J,PERKINSN D.Regulation of NF-kappaB function[J].Biochem Soc Symp,2006(73):165-180. |
| 22 |
ZHANGQ,MAJ,YOOD.Inhibition of NF-κB activity by the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus nonstructural protein 1 for innate immune evasion[J].Virology,2017,510,111-126.
doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2017.07.009 |
| 23 |
WUZ,CHENGL,XUJ,et al.The accessory protein ORF3 of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus inhibits cellular interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 productions by blocking the nuclear factor-κB p65 activation[J].Vet Microbiol,2020,251,108892.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2020.108892 |
| 24 |
ZHANGY H,LIH X,CHENX M,et al.Genetic characteristics and pathogenicity of a novel porcine epidemic diarrhea virus with a naturally occurring truncated ORF3 gene[J].Viruses,2022,14(3):487.
doi: 10.3390/v14030487 |
| 25 |
YUANC,LINY,WANGY,et al.Effects of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection on CD21+ B cells activation[J].Vet Microbiol,2024,293,110087.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2024.110087 |
| 26 | 周书亭,谢洋洋,丁思嘉,等.猪流行性腹泻病毒流行株感染小型猪的组织病理学观察[J].上海农业学报,2017,33(4):93-97. |
| ZHOUS T,XIEY Y,DINGS J,et al.The histopathological findings of miniature pigs infected with porcine epidemic diarrhea virus[J].Acta Agriculturae Shanghai,2017,33(4):93-97. | |
| 27 | 薄清如,郑兆荣,邱震东,等.猪流行性腹泻的病理学研究——人工感染仔猪病理组织学及小肠病理组织化学研究[J].兽医大学学报,1987(2):141-148. |
| BOQ R,ZHENGZ R,QIUZ D,et al.Experimental study on the pathology of porcine epizootic diarrhoea—histological and histochemical study[J].bulletin of veterinary college of PLA,1987(2):141-148. | |
| 28 |
WANGS,XUC,SHIJ,et al.Regulatory effect and mechanism of APN gene on porcine epidemic diarrhea virus resistance[J].Gene,2021,775,145448.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2021.145448 |
| 29 |
LIB X,GEJ W,LIY J.Porcine aminopeptidase N is a functional receptor for the PEDV coronavirus[J].Virology,2007,365(1):166-172.
doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.03.031 |
| [1] | QIN Yang, XIA Siting, HE Liuqin, WANG Tianli, LIU Yuyan, JIANG Xiaohan, LIU Zhihao, LIU Siwei, LI Tiejun, YIN Yulong. Effect of Chronic Oxidative Stress on Trace Elements in Organ Tissues of Weaned Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4452-4460. |
| [2] | RU Min, JIANG Xiaofeng, LUO Guosheng, WU Yonghou. Effects of Dietary Bacillus subtilis Supplementation on Growth Performance, Serum Immunity and Antioxidant Function, Intestinal Morphology and Microorganisms of Piglets Challenged with Escherichia coli [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4461-4471. |
| [3] | LI Huimin, LEI Mingkai, RUAN Shengnan, LI Panpan, LI Wentao, HE Qigai. Establishment of Fluorescent Microsphere Immunochromatographic Assay for Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Antigen Detection [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4572-4580. |
| [4] | MENG Yaxuan, LIU Yan, WANG Jing, CHEN Guoshun, FENG Tao. Effects of Glucosamine on Serum Anti-oxidation, Inflammatory Indexes and Intestinal Microbes in Weaned Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3908-3921. |
| [5] | TIAN Ru, FU Xingwei, HU Leyu, ZHU Mingjun, TONG Dewen. Isolation and Pathogenicity Analysis of a GⅡa Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 4101-4111. |
| [6] | WANG Nan, WANG Chengming, WANG Jing, LIN Xingtong, HE Lingyun. Effects of Phosphatidylethanolamine on Colonic Mucosal Barrier Function and Gut Microbiota in Postnatal Growth Retardation Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3305-3315. |
| [7] | LI Zhiqiang, CHEN Xueqing, ZHANG Yuanshu. Detection of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 in Intestinal Tissues of Clinically Infected Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Piglets and Analysis of Its Relationship with Intestinal Pathological Changes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3463-3473. |
| [8] | WANG Yunke, WANG Na, YUE Ke, HE Kunmiao, ZHANG Xing, LIU Yao, ZHANG Gaiping. Substances with Inhibitory Effects on Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2577-2589. |
| [9] | WU Chao, MING Wenhan, LU Shuwan, YANG Caimei, LIU Jinsong, MA Xiang, ZHANG Ruiqiang. Innate Immune Evasion Mechanisms of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and Advances in Prevention and Control Strategies [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2590-2599. |
| [10] | ZHOU Min, TANG Deyuan, ZENG Zhiyong, WANG Bin, HUANG Tao, HU Wenwen, MAO Yinming, ZHOU Piao, HE Song. Research Progress on the Interaction between Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Proteins and Host Proteins [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2600-2612. |
| [11] | LI Chengcheng, ZHAO Yongxiang, CAO Qiuxia, SONG Xu, LI Yupeng, FAN Baochao, GUO Rongli, XU Yefen, LI Bin. Tight Junction Protein CLDN4 Promotes Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2826-2835. |
| [12] | WU Peiling, LI Yixuan, WANG Haojie, LI Yafei, LIU Shaomeng, LIU Qingyun, WANG Xiangru. Research Progress of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Vaccine for Pigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1042-1058. |
| [13] | ZHOU Wentao, WANG Chenyu, ZHOU Hui, LIU Hongbiao, FENG Shuhuan, FAN Gaosheng, LI Tiejun, HE Liuqin. Effects of Tannic Acid on Muscle Morphology, Flavor Amino Acids, and Expression of Muscle Fiber-related Genes in Immunostressed Weaned Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1290-1301. |
| [14] | YU Xinya, HE Haijian, WANG Lei, NI Yuchen, DU Jing, ZHOU Yingshan, DONG Wanyu, WANG Xiaodu. Effect of lncRNA 18850 on Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1366-1375. |
| [15] | ZHANG Dongxuan, WANG Zhihao, QIAO Yan, ZHAO Xiaoxiao, FAN Songjie, ZHANG Chao. Prokaryotic Expression of S1 Protein in Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and Screening of Its Aptamers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 839-850. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||