





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (2): 839-850.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.02.032
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Dongxuan( ), WANG Zhihao, QIAO Yan, ZHAO Xiaoxiao, FAN Songjie, ZHANG Chao*(
), WANG Zhihao, QIAO Yan, ZHAO Xiaoxiao, FAN Songjie, ZHANG Chao*( )
)
Received:2024-03-13
Online:2025-02-23
Published:2025-02-26
Contact:
ZHANG Chao
E-mail:15138163667@163.com;chaozhang@henau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
ZHANG Dongxuan, WANG Zhihao, QIAO Yan, ZHAO Xiaoxiao, FAN Songjie, ZHANG Chao. Prokaryotic Expression of S1 Protein in Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and Screening of Its Aptamers[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 839-850.

Fig. 2
Soluble identification of recombinant proteins with different tags M. Protein marker; the different labels above the horizontal line correspond to different tag recombinant proteins; 1. Before induction; 2. After induction; 3. Supernatant after sonication; 4. Precipitation after sonication; red box marking the expression of recombinant proteins in the supernatant"

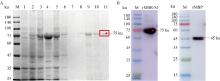
Fig. 3
Purification and Western blot detection of target protein A. Protein purification of the recombinant rMBP-S1 (M. Protein marker; 1. Before induction; 2. After induction; 3. Supernatant after sonication; 4. Precipitation after sonication; 5, 6. 20 mmol·L-1 imidazole washed twice; 7, 8. 50 mmol·L-1 imidazole washed twice; 9, 10. 250 mmol·L-1 imidazole eluted twice; 11. Protein after ultrafiltration; red box marked the target protein); B. Western blot identifies the recombinant rMBP-S1 and rMBP, arrows indicate the recombinant proteins rMBP-S1 and rMBP"


Fig. 4
IFA detected the biological activity of recombinant protein rMBP-S1 After 1 h incubation of different recombinant proteins for 4 ℃, IFA was performed, DMEM 4 ℃ was incubated for 1 h as a blank control group, and the binding to cells was observed by laser confocal microscopy, Dil staining the cell membrane (red), DAPI staining the nucleus (blue)"


Fig. 5
Enrichment was monitored by qPCR (A) and flow cytometry (B) A. Round 3 (light green), 7 (orange), 11 (blue) and 15 (red) input screening library melting curve, NC (dark green) for the initial random library control, the higher the melting chain temperature, the single enrichment degree higher; B. Rounds of input screening library incubation with target protein detection using flow cytometry. NC (dark green) for the initial random library control, with screening, fluorescence right shift, can combine with the target sequence, the higher the degree of enrichment"


Fig. 7
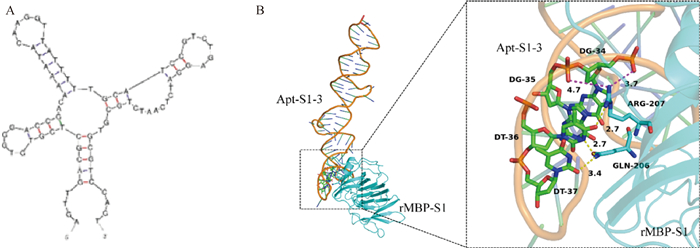
Prediction of secondary structure of aptamer Apt-S1-3 and molecular docking with the overall structure of target protein rMBP-S1 A. Secondary structure prediction results of aptamer Apt-S1-3;B. Molecular docking results of aptamer Apt-S1-3 (orange) and the overall structure of target protein rMBP-S1 (cyan)"
| 1 | 马茹梦, 赵玉梁, 马明爽, 等. 不同猪源受体菌表达猪流行性腹泻病毒保护性抗原S1诱导免疫应答的比较研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (5): 2090- 2099. |
| MA R M , ZHAO Y L , MA M S , et al. Comparative study on the immune response induced by the different porcine receptor bacteria with expressing the protective antigen S1 of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (5): 2090- 2099. | |
| 2 |
JUNG K , SAIF L J . Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection: etiology, epidemiology, pathogenesis and immunoprophylaxis[J]. Vet J, 2015, 204 (2): 134- 143.
doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2015.02.017 |
| 3 |
JUNG K , SAIF L J , WANG Q H . Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV): an update on etiology, transmission, pathogenesis, and prevention and control[J]. Virus Res, 2020, 286, 198045.
doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198045 |
| 4 |
LI W T , LI H , LIU Y B , et al. New variants of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, China, 2011[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2012, 18 (8): 1350- 1353.
doi: 10.3201/eid1803.120002 |
| 5 |
LEE C . Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: an emerging and re-emerging epizootic swine virus[J]. Virol J, 2015, 12, 193.
doi: 10.1186/s12985-015-0421-2 |
| 6 |
ANTAS M , OLECH M , SZCZOTKA-BOCHNIARZ A . Molecular characterization of porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus (PEDV) in Poland reveals the presence of swine enteric coronavirus (SeCoV) sequence in S gene[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16 (10): e0258318.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258318 |
| 7 |
LI W T , VAN KUPPEVELD F J M , HE Q G , et al. Cellular entry of the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus[J]. Virus Res, 2016, 226, 117- 127.
doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.05.031 |
| 8 |
VAN DIEP N , CHOIJOOKHUU N , FUKE N , et al. New tropisms of porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus (PEDV) in pigs naturally coinfected by variants bearing large deletions in the spike (S) protein and PEDVs possessing an intact S protein[J]. Transbound Emerg Dis, 2020, 67 (6): 2589- 2601.
doi: 10.1111/tbed.13607 |
| 9 |
LI Z W , MA Z Q , DONG L F , et al. Molecular mechanism of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus cell tropism[J]. mBio, 2022, 13 (2): e0373921.
doi: 10.1128/mbio.03739-21 |
| 10 |
PARK J E , CRUZ D J M , SHIN H J . Receptor-bound porcine epidemic diarrhea virus spike protein cleaved by trypsin induces membrane fusion[J]. Arch Virol, 2011, 156 (10): 1749- 1756.
doi: 10.1007/s00705-011-1044-6 |
| 11 |
HEALD-SARGENT T , GALLAGHER T . Ready, set, fuse! The coronavirus spike protein and acquisition of fusion competence[J]. Viruses, 2012, 4 (4): 557- 580.
doi: 10.3390/v4040557 |
| 12 |
WHITE J M , WHITTAKER G R . Fusion of enveloped viruses in endosomes[J]. Traffic, 2016, 17 (6): 593- 614.
doi: 10.1111/tra.12389 |
| 13 | XIONG X L , TORTORICI M A , SNIJDER J , et al. Glycan shield and fusion activation of a deltacoronavirus spike glycoprotein fine-tuned for enteric infections[J]. J Virol, 2018, 92 (4): e01628- 17. |
| 14 | SHANG J , ZHENG Y , YANG Y , et al. Cryo-electron microscopy structure of porcine deltacoronavirus spike protein in the prefusion state[J]. J Virol, 2018, 92 (4): e01556- 17. |
| 15 | 尹宝英, 朱小甫, 郑红青, 等. 猪流行性腹泻病毒逃逸宿主天然免疫研究进展[J]. 动物医学进展, 2023, 44 (10): 89- 94. |
| YIN B Y , ZHU X F , ZHENG H Q , et al. Progress on porcine epidemic diarrhea virus escaping from host innate immunity[J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 44 (10): 89- 94. | |
| 16 | 王巍, 贾凌云. 适配体筛选方法研究进展[J]. 分析化学, 2009, 37 (3): 454- 460. |
| WANG W , JIA L Y . Progress in aptamer screening methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 37 (3): 454- 460. | |
| 17 | 梁雨萱, 庞胜美, 刘梅, 等. 猪流行性腹泻疫苗研究进展[J]. 河南农业科学, 2023, 52 (8): 1- 10. |
| LIANG Y X , PANG S M , LIU M , et al. Research progress of porcine epidemic diarrhea vaccine for pigs[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 52 (8): 1- 10. | |
| 18 | WRAPP D , MCLELLAN J S . The 3. 1-angstrom cryo-electron microscopy structure of the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus spike protein in the prefusion conformation[J]. J Virol, 2019, 93 (23): e00923- 19. |
| 19 |
LI F , LI W H , FARZAN M , et al. Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor-binding domain complexed with receptor[J]. Science, 2005, 309 (5742): 1864- 1868.
doi: 10.1126/science.1116480 |
| 20 |
LU G W , HU Y W , WANG Q H , et al. Molecular basis of binding between novel human coronavirus MERS-CoV and its receptor CD26[J]. Nature, 2013, 500 (7461): 227- 231.
doi: 10.1038/nature12328 |
| 21 |
WANG N S , SHI X L , JIANG L W , et al. Structure of MERS-CoV spike receptor-binding domain complexed with human receptor DPP4[J]. Cell Res, 2013, 23 (8): 986- 993.
doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.92 |
| 22 |
WONG A H M , TOMLINSON A C A , ZHOU D X , et al. Receptor-binding loops in alphacoronavirus adaptation and evolution[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8 (1): 1735.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01706-x |
| 23 |
REGUERA J , SANTIAGO C , MUDGAL G , et al. Structural bases of coronavirus attachment to host aminopeptidase N and its inhibition by neutralizing antibodies[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2012, 8 (8): e1002859.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002859 |
| 24 |
DENG F , YE G , LIU Q Q , et al. Identification and comparison of receptor binding characteristics of the spike protein of two porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains[J]. Viruses, 2016, 8 (3): 55.
doi: 10.3390/v8030055 |
| 25 |
SHIRATO K , MAEJIMA M , ISLAM MT , et al. Porcine aminopeptidase N is not a cellular receptor of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, but promotes its infectivity via aminopeptidase activity[J]. J Gen Virol, 2016, 97 (10): 2528- 2539.
doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000563 |
| 26 |
SILWAL A P , THENNAKOON S K S , ARYA S P , et al. DNA aptamers inhibit SARS-CoV-2 spike-protein binding to hACE2 by an RBD-independent or dependent approach[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12 (12): 5522- 5536.
doi: 10.7150/thno.74428 |
| 27 | 李卫滨, 王开宇, 赵猛, 等. 人FcγRI特异性核酸适配体的体外筛选及鉴定[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2017, 33 (8): 818- 825. |
| LI W B , WANG K Y , ZHAO M , et al. In vitro selection and identification of aptamers against human FcγRI[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2017, 33 (8): 818- 825. | |
| 28 |
SUN M , LIU S W , WEI X Y , et al. Aptamer blocking strategy inhibits SARS-CoV-2 virus infection[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2021, 60 (18): 10266- 10272.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202100225 |
| 29 | 邹静娴, 孟慧, 潘朔楠, 等. 表达PEDV S蛋白重组仙台病毒的构建及其免疫原性研究[J]. 扬州大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2023, 44 (4): 43-50, 67. |
| ZOU J X , MENG H , PAN S N , et al. Construction and immunogenicity of a recombinant Sendai virus expressing S protein of PEDV[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University: Agricultural and Life Science Edition, 2023, 44 (4): 43-50, 67. | |
| 30 | 李洁森, 孙荣航, 邝燕齐, 等. 猪流行性腹泻病毒S1D蛋白的优化表达及其单克隆抗体的制备[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2021, 48 (12): 4641- 4651. |
| LI J S , SUN R H , KUANG Y Q , et al. Optimal expression of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus S1D protein and preparation of its monoclonal antibody[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 48 (12): 4641- 4651. | |
| 31 | 张天爱, 李婷婷, 陶晓莉, 等. 猪流行性腹泻病毒S蛋白原核表达及多克隆抗体的制备与鉴定[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2022, 49 (11): 4383- 4391. |
| ZHANG T A , LI T T , TAO X L , et al. Prokaryotic expression of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus S protein and preparation and identification of its polyclonal antibody[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 49 (11): 4383- 4391. | |
| 32 | 柏家果, 刘思雨, 杜琛, 等. 猪流行性腹泻病毒S蛋白的原核表达及其多克隆抗体的制备[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2022, 52 (11): 1415- 1421. |
| BAI J G , LIU S Y , DU C , et al. Prokaryotic expression and polyclonal antibody preparation of spike protein of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus[J]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 2022, 52 (11): 1415- 1421. | |
| 33 | 郭晓辉. 猪流行性腹泻病毒S重组蛋白的大肠杆菌表达及其免疫学评价的初步研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2023. |
| GUO X H. Expression and immunological evaluation of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus S recombinant protein in Escherichia coli[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | Weizhe LIU, Chenggang LUO, Rong YUAN, Yijie LIAO, Yimin WEN, Ying SUN, Enbo YU, Sanjie CAO, Xiaobo HUANG. Isolation and Identification of a Highly Pathogenic Strain of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3049-3063. |
| [2] | Dongliang LI, Guanmin ZHENG, Shuai LI, Hongsen ZHU, Chao WU. Differential Expression of Transcriptome in Jejunal of Piglets Infected with Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2652-2661. |
| [3] | WANG Jing, ZHANG Shujuan, HU Xia, LIU Xiangyang, ZHANG Xingcui, SONG Zhenhui. CD44 Regulates Na+/H+ Exchanger 3 Activity by Influencing Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2176-2185. |
| [4] | HU Zeqi, LI Runcheng, TAN Zuming, XIE Xiuyan, WANG Jiangping, QIN Lejuan, LI Rong, GE Meng. Establishment and Preliminary Application of PEDV, PoRVA and PDCoV TaqMan Triple RT-qPCR Assay [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2267-2272. |
| [5] | LIN Lili, ZHANG Mengdi, ZHU Linlin, MA Hailong, SUN Qi, HE Qigai, ZHANG Mengjia, LI Wentao. Establishment of Neutralizing Antibody Detection Method based on Recombinant Fluorescent Virus of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus GⅡb Strain [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1649-1660. |
| [6] | REN Lixin, ZHANG Jingyi, XU Shasha, YANG Liu, ZHANG Xingcui, SONG Zhenhui. Effect of ACE2 on Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells Infected with Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1238-1248. |
| [7] | ZHOU Jianhao, WANG Dongfang, LIU Ying, WANG Shujuan, MA Zhenyuan, XIE Caihua, ZHAO Xueli, YANG Haibo, FENG Guidan, KANG Taisheng, HU Yufeng, LI Bowen, YAN Ruoqian. Establishment and Preliminary Application of a Quantitative Droplet Digital PCR Assay for Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 413-418. |
| [8] | LIU Hua, YIN Dongdong, SHAO Ying, SONG Xiangjun, WANG Zhenyu, PAN Xiaocheng, TU Jian, HE Changsheng, ZHU Liangqiang, QI Kezong. Detection of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus by Recombinase Aided Amplification Combined with CRISPR/Cas13a [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(9): 3991-3997. |
| [9] | ZHANG Senhao, WANG Xueying, CAI Limeng, XIE Weichun, KUANG Hongdi, WANG Xiaona, LI Jiaxuan, CUI Wen, JIANG Yanping, ZHOU Han, SHAN Zhifu, WANG Li, QIAO Xinyuan, LI Yijing, TANG Lijie. Establishment and Application of Rapid Diagnosis Method for RPA of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(6): 2498-2508. |
| [10] | ZHAI Gang, GU Wenyuan, LIU Tao, LIU Ying, ZHANG Shuai, FAN Jinghui, ZUO Yuzhu. Establishment of TaqMan Detection Method of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and Analysis of Genetic Variation based on S Gene [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(2): 847-854. |
| [11] | TANG Rongfeng, FAN Qianjin, GUO Longjun, ZHANG Xin, SHI Da, SHI Hongyan, CHEN Jianfei, FENG Li. Screening and Identification of Host Proteins Interacting with PDCoV S1-CTD [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(7): 2260-2267. |
| [12] | HAO Jianwei, XUE Chunyi, CAO Yongchang. The Dose-titration Study of Inactivated Vaccine of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(5): 1536-1543. |
| [13] | WANG Tianyu, LI Zhiwei, YANG Ting, DONG Linfang, MA Zhiqian, BIANBA Ciren, XIAO Shuqi, LI Shuang. Screening and Identification of Nanobodies against Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus S Protein [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(9): 2589-2598. |
| [14] | ZHENG Hongqing, WU Xujin, ZHU Xiaofu, YIN Baoying, GAO Junhua, LI Yanzhi, ZHI Chanping. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Regulates Cell Apoptosis by miR-133c-3p/BCL2L2 Axis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(8): 2233-2243. |
| [15] | ZHANG Zhicheng, CHEN Meijuan, AI Jun. Bayesian Inference and Simulation on True Prevalence of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus in American Swine Population [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(7): 2013-2024. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||