





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (9): 4730-4740.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.09.049
• Clinical Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Wenzhe1( ), WANG Jinhao1, ZHAO Zichen1, ZHAO Tong1, PAN Feilong1, CHEN Fangfang1, SHAO Wenqi1, LIU Kexiang1,2, ZHAO Shuchen1,2, ZHAO Lijia1,2,*(
), WANG Jinhao1, ZHAO Zichen1, ZHAO Tong1, PAN Feilong1, CHEN Fangfang1, SHAO Wenqi1, LIU Kexiang1,2, ZHAO Shuchen1,2, ZHAO Lijia1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-11-25
Online:2025-09-23
Published:2025-09-30
Contact:
ZHAO Lijia
E-mail:1797333019@qq.com;ljzhao@neau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
YANG Wenzhe, WANG Jinhao, ZHAO Zichen, ZHAO Tong, PAN Feilong, CHEN Fangfang, SHAO Wenqi, LIU Kexiang, ZHAO Shuchen, ZHAO Lijia. Analysis of the Impact of Curcumin on the Ferroptosis Pathway in Alleviating the Inflammatory Response Induced by LPS in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4730-4740.
Table 1
Primers sequence for RT-PCR"
| 引物名称 Primer name | 基因登录号 Accession No. | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequence |
| TNF-α | NM_173966.3 | F: CTGGTTCAAACACTCAGGTCC R: CCATGAGGGCATTGGCATAC |
| IL-6 | NM_173923.2 | F: CAGATCCTGAAGCAAAAGATCGC R: TCAGGCTGAACTGCAGGAAAT |
| IL-1β | NM_174093.1 | F: CCTCCGACGAGTTTCTGTGT R: GCTCATGCAGAACACCACTTC |
| PTGS2 | NM_174445.2 | F: AGTCTTTTGGTCTGGTGCCTG R: GCCCCATTCTGGATGCTCTT |
| SLC7A11 | XM_024977578.2 | F: TCCCTTTACTCAGACCCA R: CATTCTTCGGAACCACTT |
| GPX4 | NM_001346430.1 | F: AATCCCAAGACCCGTGCG R: CTCATTGCGAGGCCACATTG |
| FTH1 | NM_174062.4 | F: TACGCCTCCTATGTCTACC R: TCTCAGCATGTTCCCTCT |
| ACSL4 | XM_015461587.3 | F: TGGCACAACAGAAAGGGGTA R: AATCGCTCCAGTTTCATGGT |
| iNOS | NM_001076799.1 | F: CAGAAGGCCAAAGGGGATCT R: GCCTCTTTGAAGGAGCCGTA |
| CXCL2 | NM_174299.3 | F: AAACCGAAGTCATAGCCACTC R: TCCACCTGGTCAGTTAGAGC |
| CCL2 | NM_174006.2 | F: CTCGCTGCAACATGAAGGTC R: TTGGGAGTTAATTGCATCTGGC |
| GAPDH | NM_001034034.2 | F: CGACCCTCAGAGATTAGCTT R: CGACCCTCAGAGATTAGCTT |
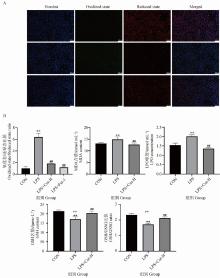
Fig. 1
Effect of Cur treatment on lipid peroxidation related indexes in MAC-T cell inflammation model A. Staining with BODIPY 581/591 C11; B. Detection of lipid peroxidation related kits (MDA, LPO, GSH, GSH/GSSG). * indicate significant differences between CON and LPS-treated groups (**. P < 0.01); # indicates significant differences between the LPS treatment group and the LPS+Cur/LPS+Cur+Erastin treatment group (##. P < 0.01)"
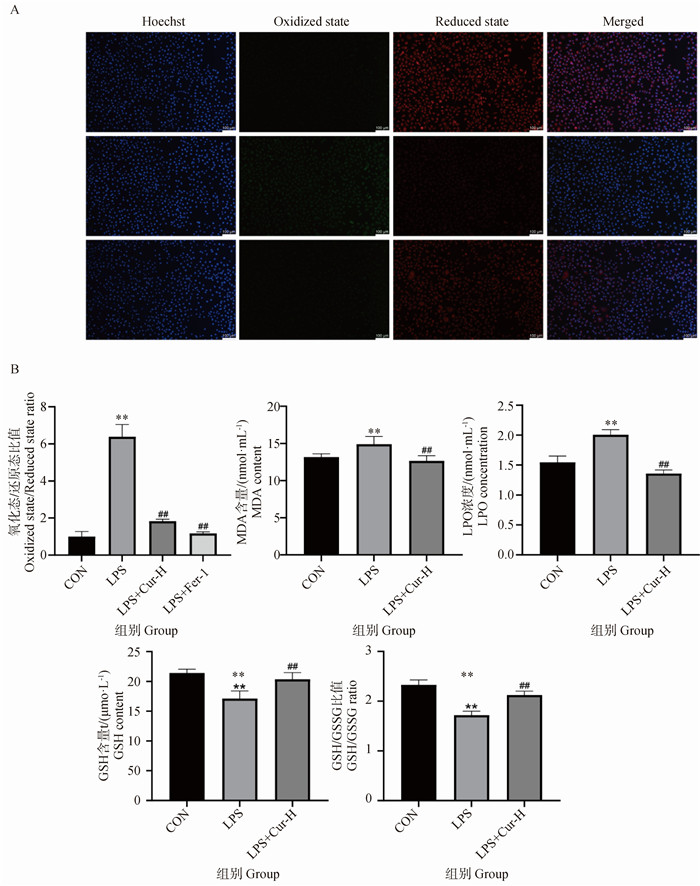
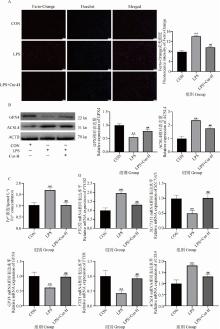
Fig. 2
Effect of Cur treatment on iron death related indicators in MAC-T cell inflammation model A. Staining with Ferro-Orange; B. Relative expression levels of GPX4 and ACSL4 proteins; C. Determination of Fe2+ content detection kit; D. mRNA expression levels of genes related to iron death. * indicate significant differences between CON and LPS-treated groups (**. P < 0.01); # indicates significant differences between the LPS treatment group and the LPS+Cur/LPS+Cur+Erastin treatment group (##. P < 0.01)"
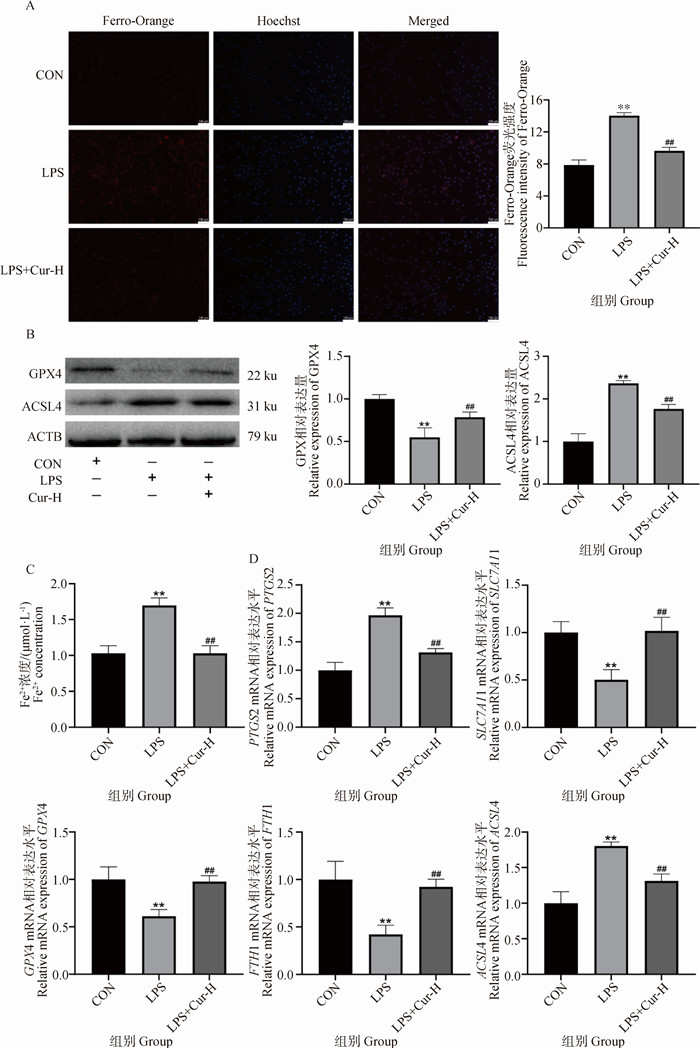
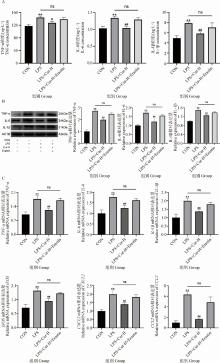
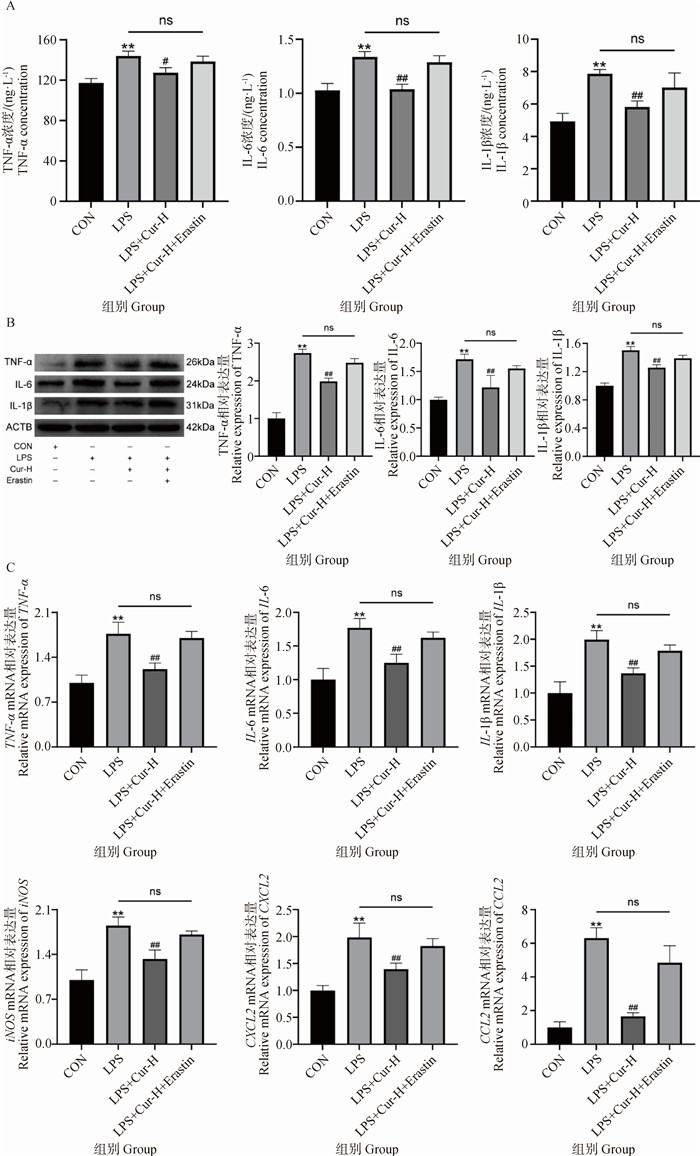
Fig. 3
Effects of iron death activator Erastin treatment on the anti-inflammatory effects of Cur A. Determination of inflammation-related kits; B. Relative expression levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β proteins; C. mRNA expression levels of genes associated with inflammation. * indicate significant differences between CON and LPS-treated groups(**. P < 0.01); # indicates significant differences between the LPS treatment group and the LPS+Cur/LPS+Cur+Erastin treatment group(#. P < 0.05, ##. P < 0.01)"
| 1 | JONEST.Treatment of clinical mastitis in dairy cattle[J].Vet Rec,2016,178(24):614. |
| 2 |
AIC,ZOUY,LIUH,et al.Traditional Chinese herbal medicine for allergic diseases: A review[J].Am J Chin Med,2023,51(4):779-806.
doi: 10.1142/S0192415X23500374 |
| 3 |
XUP,XUX,FOTINAH,et al.Anti-inflammatory effects of chlorogenic acid from Taraxacum officinale on LTA-stimulated bovine mammary epithelial cells via the TLR2/NF-κB pathway[J].PLoS One,2023,18(3):e0282343.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282343 |
| 4 |
HEX,WEIZ,ZHOUE,et al.Baicalein attenuates inflammatory responses by suppressing TLR4 mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced mastitis in mice[J].Int Immunopharmacol,2015,28(1):470-476.
doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.07.012 |
| 5 |
KASEKET B,CHIKWAMBIZ,GOMOC,et al.Antibacterial activity of medicinal plants on the management of mastitis in dairy cows: A systematic review[J].Vet Med Sci,2023,9(6):2800-2819.
doi: 10.1002/vms3.1268 |
| 6 |
KOTHAR R,LUTHRIAD L.Curcumin: biological, pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and analytical aspects[J].Molecules,2019,24(16):2930.
doi: 10.3390/molecules24162930 |
| 7 |
AJOSED J,OLUWARINDEB O,ABOLARINWAT O,et al.Combating bovine mastitis in the dairy sector in an era of antimicrobial resistance: Ethno-veterinary medicinal option as a viable alternative approach[J].Front Vet Sci,2022,9,800322.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.800322 |
| 8 | 徐进,敖日格乐,贾知锋,等.姜黄素对乳腺炎模型小鼠血清中抗炎因子的影响[J].中国农业大学学报,2018,23(4):69-74. |
| XUJ,AORIGELE,JIAZ F,et al.Effect of curcumin on anti-inflammatory factors in the serum of mice mastitis model[J].Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering,2018,23(4):69-74. | |
| 9 |
JIANGX,STOCKWELLB R,CONRADM.Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease[J].Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2021,22(4):266-282.
doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8 |
| 10 |
SUNY,CHENP,ZHAIB,et al.The emerging role of ferroptosis in inflammation[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2020,127,110108.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110108 |
| 11 |
XUS,HEY,LINL,et al.The emerging role of ferroptosis in intestinal disease[J].Cell Death Dis,2021,12(4):289.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03559-1 |
| 12 |
ZHANGY,XINL,XIANGM,et al.The molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and its role in cardiovascular disease[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2022,145,112423.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112423 |
| 13 | 李宇航. Gsta1在小鼠乳腺炎乳腺上皮细胞铁死亡中的作用及机制研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2023. |
| LI Y H. The role and mechanism of Gsta1 on ferroptosis of mammary epithelial cell in mouse mastitis[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 14 |
BAOL,ZHAOY,DUANS,et al.Ferroptosis is involved in Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis through autophagy activation by endoplasmic reticulum stress[J].Int Immunopharmacol,2024,140,112818.
doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112818 |
| 15 |
DEHZADM J,GHALANDARIH,NOURIM,et al.Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin/turmeric supplementation in adults: A GRADE-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J].Cytokine,2023,164,156144.
doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156144 |
| 16 | 王蕾,李强,姚书霞.汉黄芩素调节NF-κB/MAPK信号通路对心肌缺血再灌注损伤大鼠炎症损伤的影响[J].中国免疫学杂志,2024,40(11):2335-2342. |
| WANGL,LIQ,YAOS X.Impact of wogonin on inflammatory injury in rats with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway[J].Chinese Journal of Immunology,2024,40(11):2335-2342. | |
| 17 |
HEYDARIM,KHALILIM R,NOWROOZZADEHM H,et al.Therapeutic implications of curcumin in the treatment of inflammatory eye diseases: A review[J].Curr Pharm Biotechnol,2023,24(4):553-561.
doi: 10.2174/1389201023666220609085614 |
| 18 |
WANGX,WANGY,TANGT,et al.Curcumin-Loaded RH60/F127 mixed micelles: Characterization, biopharmaceutical characters and anti-inflammatory modulation of airway inflammation[J].Pharmaceutics,2023,15(12):2710.
doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15122710 |
| 19 |
KUNCHAM,NAIDUV G,SAHUB D,et al.Curcumin potentiates the anti-arthritic effect of prednisolone in Freund 's complete adjuvant-induced arthritic rats[J].J Pharm Pharmacol,2014,66(1):133-144.
doi: 10.1111/jphp.12156 |
| 20 |
MISEROCCHIE,GIUFFRÈC,CICINELLIM V,et al.Oral phospholipidic curcumin in juvenile idiopathic arthritis-associated uveitis[J].Eur J Ophthalmol,2020,30(6):1390-1396.
doi: 10.1177/1120672119892804 |
| 21 |
VAN BEERSE J,YANGY,RAGHAVACHARIN,et al.Iron, inflammation, and early death in adults with sickle cell disease[J].Circ Res,2015,116(2):298-306.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.304577 |
| 22 |
KUMARA,BROOKESM J.Iron therapy in inflammatory bowel disease[J].Nutrients,2020,12(11):3478.
doi: 10.3390/nu12113478 |
| 23 | 向艳茹. 基于铁死亡相关信号通路探讨姜黄素治疗溃疡性结肠炎的机制研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2023. |
| XANG Y R. Exploring the mechanism of curcumin in the treatment of ulcerative colitis based on ferroptosis-related signaling pathway[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 24 |
WANGY,LINH,HUANGW,et al.Curcumin attenuates periodontal injury via inhibiting ferroptosis of ligature-induced periodontitis in mice[J].Int J Mol Sci,2023,24(12):9835.
doi: 10.3390/ijms24129835 |
| 25 |
ZHAOY,LIY,ZHANGR,et al.The role of erastin in ferroptosis and its prospects in cancer therapy[J].Onco Targets Ther,2020,13,5429-5441.
doi: 10.2147/OTT.S254995 |
| [1] | WEN Xue, XU Wanxue, FU Yitong, YANG Jie, FU Hongyu, FAN Ruifeng. Research Progress on the Relationship between Ferroptosis and Inflammation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3666-3677. |
| [2] | WANG Miao, FU Tingshu, CHEN Mengwei, ZHOU Hongda, BAI Xiaonan, MA Baohua, PENG Sha. Study on the Repairing Effect of Exosomes Derived from Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Loaded with Curcumin on Skin Injury [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 4042-4052. |
| [3] | WANG Yi, HOU Lulu, FANG Fei, GAO Linying, XIE Shumin, WANG Yu. Fluoride Induced Small Intestine Oxidative Damage in Broilers via Autophagy and Ferroptosis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 442-454. |
| [4] | Hongyu FU, Yue LI, Han CUI, Jiuzhi LI, Wanxue XU, Xi WANG, Ruifeng FAN. The Mechanism of Long-Chain acyl-CoA Synthetase 4-mediated Ferroptosis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3792-3801. |
| [5] | Qilu ZHOU, Jinsong LIU, Chao WU, Caimei YANG, Yulan LIU, Ruiqiang ZHANG. Effects of Tannic Acid on Liver Tissue Function, Antioxidant Ability and Inflammatory Response in Lipopolysaccharide Stressed Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2519-2529. |
| [6] | SU Yiman, YE Jiali, QIU Wenyue, ZHANG Xinting, PANG Xiaoyue, WANG Rongmei, TANG Zhaoxin, SU Rongsheng. Asiatic Acid Alleviates LPS-induced Pyroptosis in Renal Cell by Inhibiting HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB Pathway in Broilers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1777-1786. |
| [7] | ZHANG Xinting, QIU Wenyue, PANG Xiaoyue, SU Yiman, YE Jiali, HUANG Jianjia, ZHOU Shuilian, TANG Zhaoxin, WANG Rongmei, SU Rongsheng. Effect of Asiatic Acid Alleviating Myocardial Injury Caused by Lipopolysaccharide through Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Ferroptosis in Broilers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1787-1799. |
| [8] | WANG Hao, XIAO Jinlong, SHEN Jue, ZHAO Jingang, WANG Shuai, LIU Gen, ZHAO Ru, XIAO Peng, GAO Hong. New Ways of Cell Death—Ferroptosis and Cuproptosis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 461-470. |
| [9] | QIU Wenyue, SU Yiman, YE Jiali, ZHANG Xinting, PANG Xiaoyue, WANG Rongmei, XIE Zimao, ZHANG Hui, TANG Zhaoxin, SU Rongsheng. Study on Asiatic Acid Alleviates LPS-induced Acute Kidney Injury by Regulating Apoptosis and Autophagy of Broilers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 809-821. |
| [10] | ZHANG Zixuan, ZHANG Ying, LI Zhijun, YANG Jingling, JIANG Zihao, HUANG Huamin, QI Xuefeng. The Effects of Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus (BVDV)-induced Ferroptosis on Virus Replication [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5716-5724. |
| [11] | XIONG Zhiwei, WANG Yun, CAO Huabin, PENG Chengcheng, YANG Fan, DAI Xueyan, XING Chenghong, LIU Lingli, LI Jingni, HU Aiming. Molybdenum and Cadmium Combined Exposure Mediates Oxidative Stress and Ferroptosis Induced Kidney Damage in Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5802-5812. |
| [12] | GAO Kangkang, YI Yanyan, ZHAO Yiteng, LIN Pengfei, CHEN Huatao, JIN Yaping. Protective Effect of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Preadaptation on LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response in Goat Endometrial Epithelial Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(8): 3546-3556. |
| [13] | MAO Peng, WANG Zhihao, LI Jianji, CUI Luying, ZHU Guoqiang, MENG Xia, DONG Junsheng, WANG Heng. Research Progress of Ferroptosis in Bacterial Infection [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(6): 2280-2287. |
| [14] | TIAN Yanhong, YU Jiangxu, JIAO Yuzhou, GAO Dongyang, CAI Xuwang. Research Progress on Structural Modification and Its Effects of Salmonella Lipopolysaccharides [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(4): 1392-1402. |
| [15] | ZHUO Ruhao, LIU Qingyang, ZHONG Xiang. Advances in the Roles of Curcumin on Regulating Gut Microbiota and Antiviral Effects [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(2): 473-483. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||