





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (7): 3210-3225.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.07.016
• Animal Genetics and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Yuqing( ), XING Ya, ZHOU Xiaoyi, GONG Haizhou, ZHAO Minmeng, LIU Long, GONG Daoqing, GE Jing*(
), XING Ya, ZHOU Xiaoyi, GONG Haizhou, ZHAO Minmeng, LIU Long, GONG Daoqing, GE Jing*( ), GENG Tuoyu*(
), GENG Tuoyu*( )
)
Received:2025-02-19
Online:2025-07-23
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
GE Jing, GENG Tuoyu
E-mail:15240007478@163.com;gejing@yzu.edu.cn;tygeng@yzu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
WANG Yuqing, XING Ya, ZHOU Xiaoyi, GONG Haizhou, ZHAO Minmeng, LIU Long, GONG Daoqing, GE Jing, GENG Tuoyu. Mitochondrial AMPK (mAMPK) Regulates Mitochondrial Function and Participates in the Formation of Goose Fatty Liver[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3210-3225.
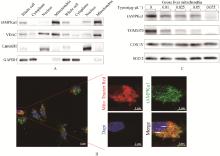
Fig. 2
Subcellular localization of tAMPKɑ1 A. The content of tAMPKɑ1 in whole cell samples, cytoplasmic samples, nuclear samples, and isolated mitochondrial samples of primary goose hepatocytes was detected by WB (n=2). VDAC, Lamin B1, and GAPDH were used as marker proteins for mitochondria, nucleus, and cytoplasm, respectively. B. Co-localization of tAMPKɑ1 with mitochondria in primary goose hepatocytes. Red (Mito-tracker Red) indicates mitochondria, green indicates tAMPKɑ1, blue (DAPI) indicates the nucleus, yellow (co-localization of red and green) indicates tAMPKɑ1 molecules bound to mitochondria. C. Immunoblot images of mitochondrial proteins isolated from goose liver treated with different concentrations of trypsin"
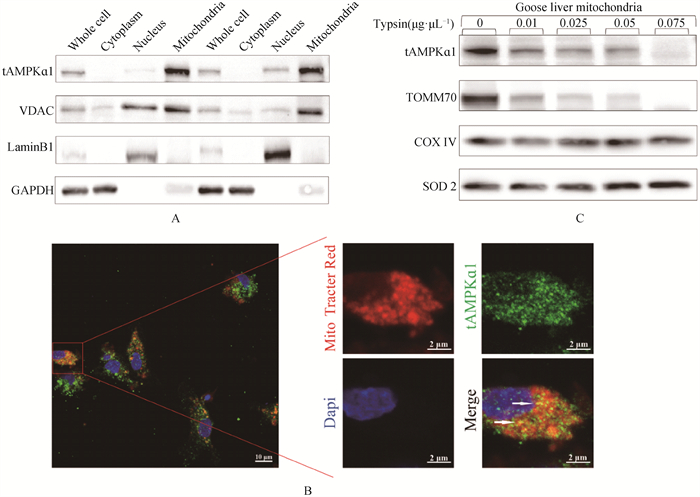
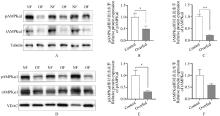
Fig. 3
The protein abundance of wAMPKα1 and mAMPKα1 in fatty liver and normal liver of goose A. Immunoblot images showing the protein abundance of p-wAMPKα1 and t-wAMPKα1 in whole cell lysates of fatty liver and normal liver of goose, n=3; B, C. The quantification of the protein abundance of p-wAMPKα1 and t-wAMPKα1 in whole cell lysates of fatty liver and normal liver of goose after immunoblot analysis; D. Immunoblot images showing the protein abundance of p-mAMPKα1 and t-mAMPKα1 in mitochondrial fractions of fatty liver and normal liver of goose, n=3; E, F. The quantification of the protein abundance of p-mAMPKα1 and t-mAMPKα1 in mitochondrial fractions of fatty liver and normal liver of goose. * indicates P < 0.05, ** indicates P < 0.01, the same as below"
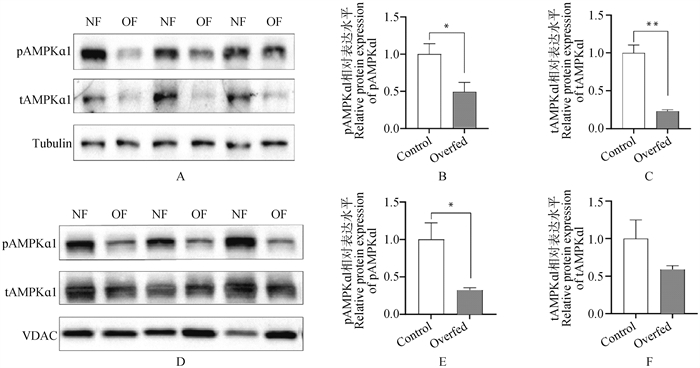
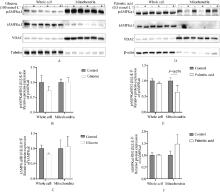
Fig. 4
The effect of glucose and palmitic acid treatment on the protein abundance of wAMPKα1 and mAMPKα1 in goose primary hepatocytes A. Immunoblot images showing the effect of glucose treatment on the protein abundance of t/p-wAMPKα1 and t/p-mAMPKα1 in primary goose hepatocytes. VDAC and Tubulin serve as loading controls for mitochondrial and whole cell lysates, respectively; B. Quantification of the protein abundance of p-wAMPKα1 and p-mAMPKα1 in glucose-treated and control groups of primary goose hepatocytes after immunoblot analysis, n=3; C. Quantification of the protein abundance of t-wAMPKα1 and t-mAMPKα1 in glucose-treated and control groups of primary goose hepatocytes after immunoblot analysis, n=3; D. Immunoblot images showing the effect of palmitic acid treatment on the protein abundance of t/p-wAMPKα1 and t/p-mAMPKα1 in primary goose hepatocytes; E. Quantification of the protein abundance of p-wAMPKα1 and p-mAMPKα1 in palmitic acid-treated and control groups of primary goose hepatocytes after immunoblot analysis, n=3; F. Quantification of the protein abundance of t-wAMPKα1 and t-mAMPKα1 in palmitic acid-treated and control groups of primary goose hepatocytes after immunoblot analysis, n=3"
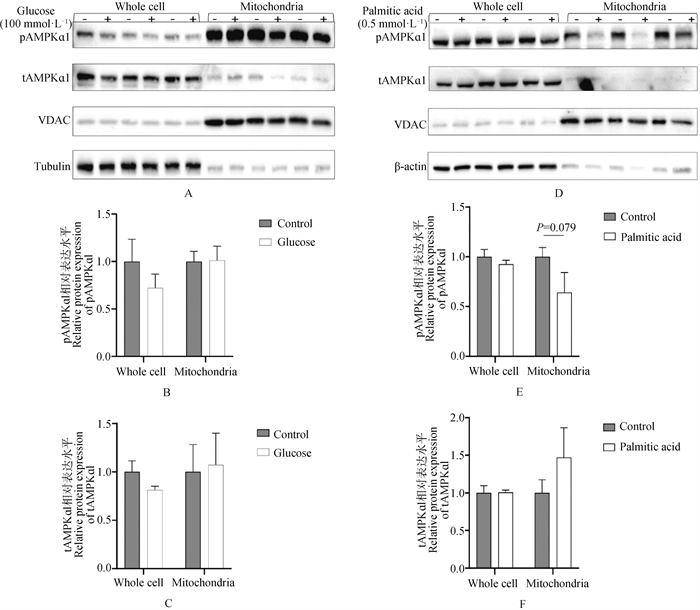
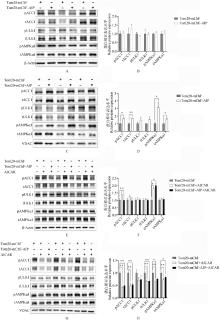
Fig. 5
The effect of mitoAIP overexpression on the abundance of AMPKα1 and its substrates ACC1 and ULK1 proteins A. Representative immunoblot images showing the effect of overexpressing mitoAIP on the protein abundance of AMPKα1 and its substrates ACC1 and ULK1 in whole cell lysates. β-Actin serves as the loading control for whole cell lysates; B. Quantification of the protein abundance of relevant proteins from the immunoblot images, n=6; C. Representative immunoblot images showing the effect of overexpressing mitoAIP on the protein abundance of AMPKα1 and its substrates ACC1 and ULK1 in mitochondrial fractions. VDAC serves as the loading control for mitochondrial fractions; D. Quantification of the protein abundance of relevant proteins from the immunoblot images, n=6; E. Representative immunoblot images showing the effect of overexpressing mitoAIP on the protein abundance of AMPKα1 and its substrates ACC1 and ULK1 in whole cell lysates under conditions where AMPKα1 is activated by AICAR; F. Quantification of the protein abundance of relevant proteins from the immunoblot images, n=6; G. Representative immunoblot images showing the effect of overexpressing pmitoAIP on the protein abundance of AMPKα1 and its substrates ACC1 and ULK1 in mitochondrial fractions under conditions where AMPKα1 is activated by AICAR; H. Quantification of the protein abundance of relevant proteins from the immunoblot images, n=6. Tom20-mChF denotes empty vector, while Tom20-mChF-AIP denotes mitoAIP overexpression vector. The significance of differences between the mean values of the Tom20-mChF group and the Tom20-mChF+AICAR group, as well as between the Tom20-mChF+AICAR group and the Tom20-mChF-AIP+AICAR group, was evaluated using the t-test method"

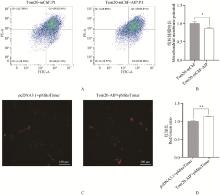
Fig. 6
The effect of overexpressing mitoAIP on indicators related to mitochondrial function A. The effect of overexpressing pmitoAIP on mitochondrial membrane potential was detected using flow cytometry and JC-1; B. Quantitative analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential, n=6; C. Immunofluorescence images of AML12 cells overexpressing pmitoAIP and mitoTimer; D. Quantitative analysis of immunofluorescence, n=3. Tom20-mChF and pcDNA3.1 denote empty vectors, while Tom20-mChF-AIP and Tom20-AIP denote mitoAIP overexpression vectors"
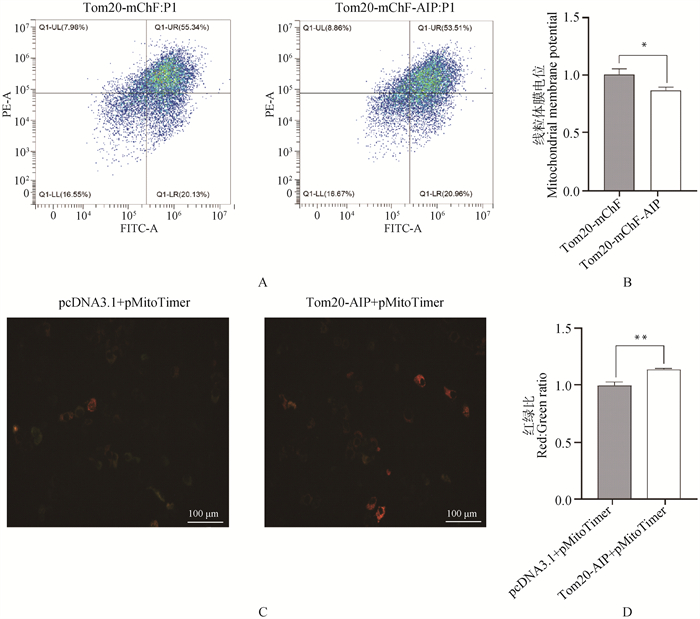
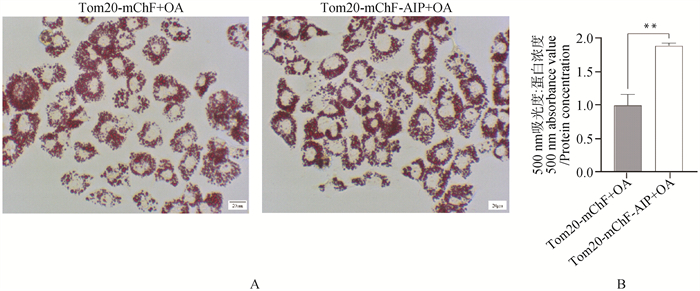
Fig. 7
The effect of overexpression of mitoAIP on fat content in AML12 cells A. Under the treatment with oleic acid, the representative images of Oil Red O staining for control group and overexpression group (400×); B. Quantification after Oil Red O staining, n=4. Tom20-mChF denotes empty vector, and Tom20-mChF-AIP denotes mitoAIP overexpression vector. OA represents oleic acid treatment"
| 1 | SEVASTIANOVA K , SANTOS A , KOTRONEN A , et al. Effect of short-term carbohydrate overfeeding and long-term weight loss on liver fat in overweight humans[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2012, 96 (4): 727- 734. |
| 2 | ZHU Y , WAN F , LIU J , et al. The critical role of lipid metabolism in health and diseases[J]. Nutrients, 2024, 16 (24): 4414. |
| 3 |
SMITH K , DENNIS K , HODSON L . The ins and outs of liver fat metabolism: The effect of phenotype and diet on risk of intrahepatic triglyceride accumulation[J]. Exp Physiol, 2025,
doi: 10.1113/EP092001 |
| 4 | BHAT N , MANI A . Dysregulation of lipid and glucose metabolism in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Nutrients, 2023, 15 (10): 2323. |
| 5 | 瞿浩, 王继文. 鹅肥肝形成的分子机理研究进展[J]. 四川畜牧兽医, 2003 (5): 33- 34. |
| QU H , WANG J W . Research progress on molecular mechanism of goose fatty liver formation[J]. Sichuan Animal Husbandry Veterinarian, 2003, 30 (5): 33- 34. | |
| 6 | UEHARA T , WAKUI H , TAMURA K . Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease reflects a significantly higher risk of hypertension than non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hypertens Res, 2023, 46 (5): 1165- 1167. |
| 7 | YOUNOSSI Z M , GOLABI P , PAIK J M , et al. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): a systematic review[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77 (4): 1335- 1347. |
| 8 | GUO Z , WU D , MAO R , et al. Global burden of MAFLD, MAFLD related cirrhosis and MASH related liver cancer from 1990 to 2021[J]. Sci Rep, 2025, 15 (1): 7083. |
| 9 | VAN HERCK M A , VONGHIA L , FRANCQUE S M . Animal models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-a starter's guide[J]. Nutrients, 2017, 9 (10): 1072. |
| 10 | HERMIER D , ROUSSELOT-PAILLEY D , PERESSON R , et al. Influence of orotic acid and estrogen on hepatic lipid storage and secretion in the goose susceptible to liver steatosis[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1994, 1211 (1): 97- 106. |
| 11 | HE H , LIU H H , WANG J W , et al. Molecular cloning of the goose ACSL3 and ACSL5 coding domain sequences and their expression characteristics during goose fatty liver development[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2014, 41 (4): 2045- 2053. |
| 12 | LIU L , WANG Q , WANG Q , et al. Role of miR29c in goose fatty liver is mediated by its target genes that are involved in energy homeostasis and cell growth[J]. BMC Vet Res, 2018, 14 (1): 325. |
| 13 | 柳序, 刘耀文, 匡佑华, 等. 鹅肥肝的形成及主要影响因素的研究进展[J]. 经济动物学报, 2019, 23 (4): 234- 239. |
| LIU X , LIU Y W , KUANG Y H , et al. Research progress on the formation of goose fatty liver and its main influencing factors[J]. Journal of Economic Zoology, 2019, 23 (4): 234- 239. | |
| 14 | GU W , WEN K , YAN C , et al. Maintaining intestinal structural integrity is a potential protective mechanism against inflammation in goose fatty liver[J]. Poult Sci, 2020, 99 (11): 5297- 5307. |
| 15 | XING Y , XU C , LIN X , et al. Complement C3 participates in the development of goose fatty liver potentially by regulating the expression of FASN and ETNK1[J]. Anim Sci J, 2021, 92 (1): e13527. |
| 16 | PENG K Y , WATT M J , RENSEN S , et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction-related lipid changes occur in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression[J]. J Lipid Res, 2018, 59 (10): 1977- 1986. |
| 17 | TAUIL R B , GOLONO P T , DE LIMA E P , et al. Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: the influence of oxidative stress, inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunctions, and the role of polyphenols[J]. Pharmaceuticals (Basel), 2024, 17 (10): 1354. |
| 18 | HU Z , YUE H , JIANG N , et al. Diet, oxidative stress and MAFLD: a mini review[J]. Front Nutr, 2025, 12, 1539578. |
| 19 | CLARE K , DILLON J F , BRENNAN P N . Reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of MAFLD[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2022, 10 (5): 939- 946. |
| 20 | LI Z , LI Y , ZHANG H X , et al. Mitochondria-mediated pathogenesis and therapeutics for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Mol Nutr Food Res, 2019, 63 (16): e1900043. |
| 21 | MARLAR-PAVEY M , TAPIAS-GOMEZ D , METTLEN M , et al. Compositionally unique mitochondria in filopodia support cellular migration[J]. Curr Biol, 2025, 35 (6): 1227- 1241.e6. |
| 22 | LIANG J , SHI J , SONG A , et al. Structures and mechanism of human mitochondrial pyruvate carrier[J]. Nature, 2025, 641 (8061): 258- 265. |
| 23 | WANG Y , HEKIMI S . Mitochondrial dysfunction and longevity in animals: Untangling the knot[J]. Science, 2015, 350 (6265): 1204- 1207. |
| 24 | SUN X , ALFORD J , QIU H . Structural and functional remodeling of mitochondria in cardiac diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22 (8): 4167. |
| 25 | BOUDABA N , MARION A , HUET C , et al. AMPK re-activation suppresses hepatic steatosis but its downregulation does not promote fatty liver development[J]. EBioMedicine, 2018, 28, 194- 209. |
| 26 | CAO Z , MA B , CUI C , et al. Protective effects of AdipoRon on the liver of Huoyan goose fed a high-fat diet[J]. Poult Sci, 2022, 101 (4): 101708. |
| 27 | TIAN W , GONZALES G B , WANG H , et al. Caffeic acid and chlorogenic acid mediate the ADPN-AMPK-PPARα pathway to improve fatty liver and production performance in laying hens[J]. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 2025, 16 (1): 49. |
| 28 | HERZIG S , SHAW R J . AMPK: guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2018, 19 (2): 121- 135. |
| 29 | LAKER R C , DRAKE J C , WILSON R J , et al. Ampk phosphorylation of Ulk1 is required for targeting of mitochondria to lysosomes in exercise-induced mitophagy[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8 (1): 548. |
| 30 | KIM J , KUNDU M , VIOLLET B , et al. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2011, 13 (2): 132- 141. |
| 31 | CHEN J , WONG H S , LEONG P K , et al. Ursolic acid induces mitochondrial biogenesis through the activation of AMPK and PGC-1 in C2C12 myotubes: a possible mechanism underlying its beneficial effect on exercise endurance[J]. Food Funct, 2017, 8 (7): 2425- 2436. |
| 32 | TOYAMA E Q , HERZIG S , COURCHET J , et al. Metabolism. AMP-activated protein kinase mediates mitochondrial fission in response to energy stress[J]. Science, 2016, 351 (6270): 275- 281. |
| 33 | REN X , ZHOU H , SUN Y , et al. MIRO-1 interacts with VDAC-1 to regulate mitochondrial membrane potential in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. EMBO Rep, 2023, 24 (8): e56297. |
| 34 | YIN L , DAI Y , WANG Y , et al. A mitochondrial outer membrane protein TOMM20 maintains protein stability of androgen receptor and regulates AR transcriptional activity in prostate cancer cells[J]. Oncogene, 2025, 44 (21): 1567- 1577. |
| 35 | MUTHUKUMAR G , STEVENS T A , INGLIS A J , et al. Triaging of α-helical proteins to the mitochondrial outer membrane by distinct chaperone machinery based on substrate topology[J]. Mol Cell, 2024, 84 (6): 1101- 1119.e9. |
| 36 | DRAKE J C , WILSON R J , LAKER R C , et al. Mitochondria-localized AMPK responds to local energetics and contributes to exercise and energetic stress-induced mitophagy[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2021, 118 (37): e2025932118. |
| 37 | OSMAN R H , LIU L , XIA L , et al. Fads1 and 2 are promoted to meet instant need for long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in goose fatty liver[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2016, 418 (1-2): 103- 117. |
| 38 | 洪胜辉, 张军, 张蕊, 等. 鹅原代肝细胞的简易、高纯分离及培养[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2012, 40 (4): 56- 58. |
| HONG S H , ZHANG J , ZHANG R , et al. Simple, high-purity isolation and culture of goose primary hepatocytes[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 40 (4): 56- 58. | |
| 39 | MOBIN M B , GERSTBERGER S , TEUPSER D , et al. The RNA-binding protein vigilin regulates VLDL secretion through modulation of Apob mRNA translation[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7, 12848. |
| 40 | 孙青云. 鹅肥肝中线粒体膜电位、抗氧化能力与细胞凋亡的研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2023. |
| SUN Q Y. Study on mitochondrial membrane potential, antioxidant capacity and Aapoptosis in goose fatty liver[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 41 | MIYAMOTO T , RHO E , SAMPLE V , et al. Compartmentalized AMPK signaling illuminated by genetically encoded molecular sensors and actuators[J]. Cell Rep, 2015, 11 (4): 657- 670. |
| 42 | LAKER R C , XU P , RYALL K A , et al. A novel MitoTimer reporter gene for mitochondrial content, structure, stress, and damage in vivo[J]. J Biol Chem, 2014, 289 (17): 12005- 12015. |
| 43 | FERREE A W , TRUDEAU K , ZIK E , et al. MitoTimer probe reveals the impact of autophagy, fusion, and motility on subcellular distribution of young and old mitochondrial protein and on relative mitochondrial protein age[J]. Autophagy, 2013, 9 (11): 1887- 1896. |
| 44 | HERNANDEZ G , THORNTON C , STOTLAND A , et al. MitoTimer: a novel tool for monitoring mitochondrial turnover[J]. Autophagy, 2013, 9 (11): 1852- 1861. |
| 45 | CHALASANI N , YOUNOSSI Z , LAVINE J E , et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guidance from the american association for the study of liver diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67 (1): 328- 357. |
| 46 | STOWE D F , CAMARA A K . Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production in excitable cells: modulators of mitochondrial and cell function[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2009, 11 (6): 1373- 1414. |
| 47 | WANG Q , SUN J , LIU M , et al. The new role of AMP-activated protein kinase in regulating fat metabolism and energy expenditure in adipose tissue[J]. Biomolecules, 2021, 11 (12): 1757. |
| 48 | ZHONG S , CHEN W , WANG B , et al. Energy stress modulation of AMPK/FoxO3 signaling inhibits mitochondria-associated ferroptosis[J]. Redox Biol, 2023, 63, 102760. |
| 49 | HAN H , LI X , GUO Y , et al. Plant sterol ester of α-linolenic acid ameliorates high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice: association with regulating mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress via activating AMPK signaling[J]. Food Funct, 2021, 12 (5): 2171- 2188. |
| 50 | BIAO Y , LI D , ZHANG Y , et al. Wulingsan alleviates MAFLD by activating autophagy via regulating the AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signaling pathway[J]. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2024, 2024, 9777866. |
| 51 | XING Y , GE J , WANG Y , et al. Mitochondrial HKDC1 suppresses oxidative stress and apoptosis by regulating mitochondrial function in goose fatty liver[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2024, 282 (Pt 4): 137222. |
| [1] | MIAO Junjie, ZHANG Riquan, WU Houyi, YOU Xinming, HUANG Yiwen, HUANG Xiaoying, GUO Zhenyang, LIU Jianlin, XIAO Weihua, GUO Tianhua, CHEN Hao, KANG Dongliu. Genome-Wide SNP Analysis Revealed the Characteristics of Germplasm Resources and Genetic Diversity of Jinggang Black-Palm Geese [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3199-3209. |
| [2] | LIU Siqi, YANG Zhen, YANG Yanan, CAI Yuan, ZHAO Shengguo. The Effect of Interfering with AdiopR2 on the Thermogenesis of Subcutaneous Inguinal Adipocytes in Tibetan Pigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2649-2660. |
| [3] | YAN Kai, XU Xiao, QING Zhe, BAI Lixia, LI Zhun, YANG Yajun, LIU Xiwang, LI Shihong, GE Wenbo, LI Jianyong, LI Cun. Preventive Effect of Aspirin Eugenol Ester on Fatty Liver Hemorrhagic Syndrome in Laying Hens [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2968-2977. |
| [4] | HOU Wanchen, XU Tong. Cannabidiol Antagonizes BPA-induced Apoptosis and Autophagy in Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells through the BRD4/AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1919-1933. |
| [5] | WAN Weican, HE Xu, LIU Yang, MA Yuyong, JIANG Yuzhang, DAI Qiuzhong, YAN Haifeng, JIANG Guitao, LI Chuang. Evaluation of Daozhou Gray Goose Conservation Based on Whole Genome Resequencing Analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 633-642. |
| [6] | LIANG Entang, LI Huaxuan, CHEN Shuaicheng, LI Guo, SUN Gege, ZAN Linsen. Effect of Genistein on Semen Cryopreservation of Bull [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 700-710. |
| [7] | LÜ Yongle, ZHENG Wen, WANG Qianhui, ZHU Jiaqi, HUANG Xiaoqi, CAO Zhongzan, LUAN Xinhong. Research Progress of Natural Active Substances against Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 45-62. |
| [8] | Shuo YANG, Min HUO, Zixuan SU, Yuxiang SHI. Research Progress on the Impact of Mitochondrial Quality Control on Oxidative Stress in Livestock and Poultry [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3769-3776. |
| [9] | Zijin YUAN, Wanxin WANG, Ya XING, Jiahui LI, Ying XUE, Jing GE, Minmeng ZHAO, Long LIU, Daoqing GONG, Tuoyu GENG. HDLBP Is Involved in Goose Fatty Liver Formation by Regulating the Level of Oxidative Stress and the Expression of Inflammatory Factors [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3897-3913. |
| [10] | Hongyan HUANG, Liyun ZHANG, Zhirong HUANG, Zhongping WU, Xumeng ZHANG, Hongjia OUYANG, Junpeng CHEN, Zhenping LIN, Yunbo TIAN, Xiujin LI, Yunmao HUANG. The Study on Population Genetic Diversity and Genome-wide Association Study of Body Weight and Size Traits for Lion-head Geese [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3914-3924. |
| [11] | Yi WANG, Jianfei GONG, Nuo HENG, Yingfan HU, Rui WANG, Huan WANG, Ni ZHU, Wei HE, Zhihui HU, Haisheng HAO, Huabin ZHU, Shanjiang ZHAO. Melatonin Alleviates Palmitic Acid-induced Damage in Bovine Endometrial Epithelial Cells by Improving Mitochondrial Dynamics [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3978-3987. |
| [12] | Jingxuan WANG, Lizhi DAI, Zhenyu WANG, Ying LIU, Tong YU, Min YAN, Ruilong WANG, Jianhua XIAO. Study on the Characteristics of Liver Energy Metabolism during the Induction of Insulin Resistance by High Fat Diet [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4172-4185. |
| [13] | Yan WANG, Yadong GAO, Chenghui JIANG, Qiaoying ZENG. Isolation and Pathogenicity of a Goose Derived Fowl Adenovirus Type 4 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4232-4240. |
| [14] | Yi WANG, Juan GAO, Yuemin HU, Yuefei YANG, Bojun FAN, Huiming JU. Effect of Transient Serum Starvation on Metabolism and Autophagy of Porcine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3408-3417. |
| [15] | Yao LI, Rui JIA, Jie LI, Shuangbao GUN, Qiaoli YANG, Longlong WANG, Pengxia ZHANG, Xiaoli GAO, Xiaoyu HUANG. Effects of Low Temperature on Adipose Tissue Morphology, Lipid Metabolism-Related Gene Expression and Enzyme Activities, and AMPK/PGC-1α Pathway in Hezuo Pigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3418-3426. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||