





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 2790-2800.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.06.023
• Animal Biotechnology and Reproduction • Previous Articles Next Articles
FU Yu( ), YANG Zhuo, ZHENG Hao, SUN Guohan, SHEN Wenjuan, HAN Xiaohong, TAO Jinzhong*(
), YANG Zhuo, ZHENG Hao, SUN Guohan, SHEN Wenjuan, HAN Xiaohong, TAO Jinzhong*( )
)
Received:2024-11-19
Online:2025-06-23
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
TAO Jinzhong
E-mail:fuyu771202@163.com;tao_jz@nxu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
FU Yu, YANG Zhuo, ZHENG Hao, SUN Guohan, SHEN Wenjuan, HAN Xiaohong, TAO Jinzhong. Correlation between Related Factors in Peripheral Plasma and Pregnancy Status of Dairy Cows in Early Breeding Period[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2790-2800.
Fig. 1
Concentrations of hormone in plasma with cows of different gestational status on day 7 after TAI A-F. Mean concentrations of plasma E2, P4, PGE2, PGF2α, MT, and COR in cows with different gestational status. P represents the pregnant group, NP represents the non-pregnant group, and RE represents the return estrus group.****. P < 0.000 1;***. P < 0.001;**. P < 0.01; *. P < 0.05; ns. P>0.05, the same as below"
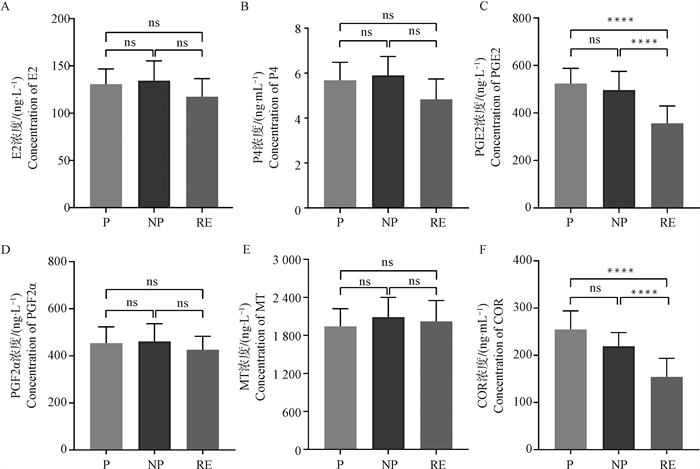
Fig. 4
Correlation analysis between hormone concentrations in plasma and pregnancy rate in dairy cows A-F. Correlation analysis of plasma concentrations of E2, P4, PGE2, PGF2α, MT, and COR with pregnancy rate in dairy cows on day 7 after TAI. According to the maximum and minimum concentrations of E2, P4, PGE2, PGF2α, MT and COR, they were divided into 5-6 concentration intervals on average"
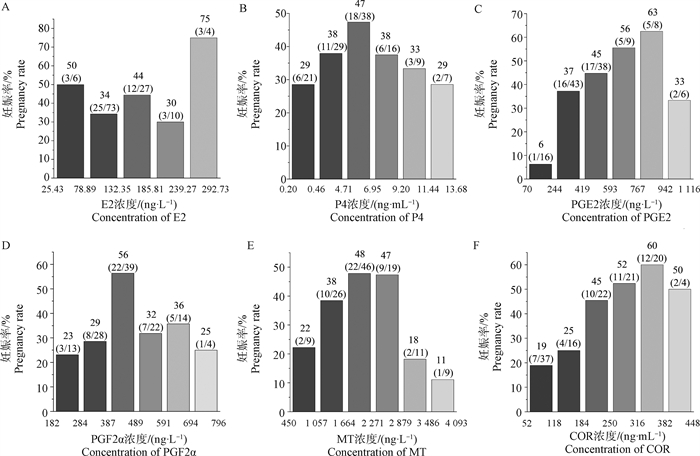
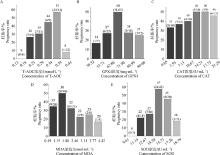
Fig. 5
Correlation analysis between plasma concentrations of oxidative stress indicators and pregnancy rate of cows A-E. Correlation analysis of plasma concentrations of T-AOC, GPX4, CAT, MDA and SOD with pregnancy rate in dairy cows on day 7 after TAI. According to the maximum and minimum concentrations of T-AOC, MDA, SOD, GPX4 and CAT, they were averaged into 5-6 concentration intervals"
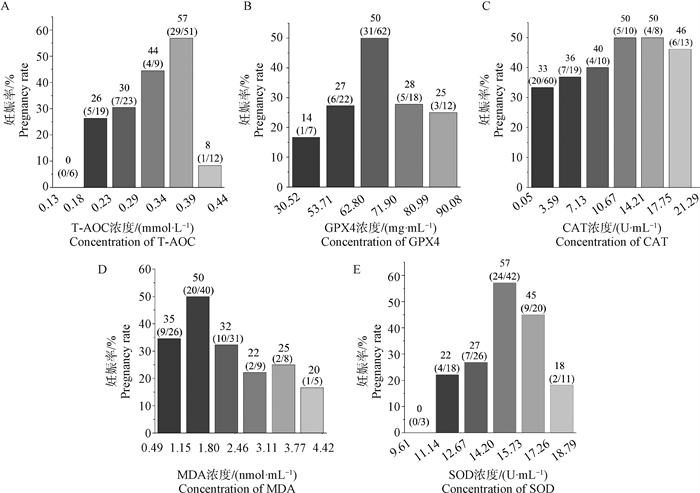
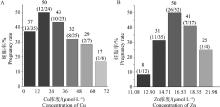
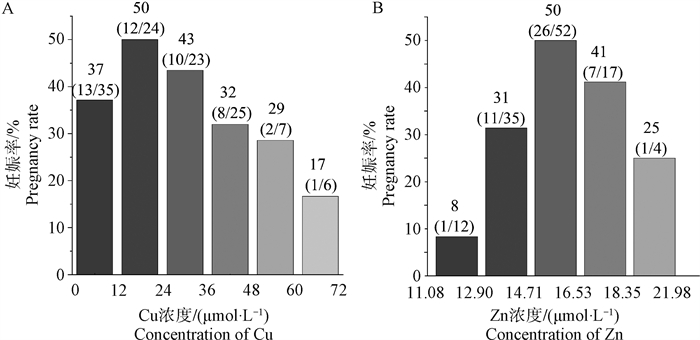
Fig. 6
Correlation analysis between plasma Cu and Zn concentrations and pregnancy rate of cows A-B. Correlation analysis of Cu and Zn concentrations in the plasma of dairy cows on day 7 after TAI with the pregnancy rate of dairy cows. According to the maximum and minimum concentrations of Cu and Zn, they were divided into 5-6 concentration intervals on average"
| 1 | MIGUEL Á L V , REBECA R R , AMALIA C N , et al. Embryonic losses between the early diagnosis and the confirmation of gestation in dairy cows from different farms for one year[J]. Agro productividad, 2023, 16 (5): 115- 120. |
| 2 | TINNING H , EDGE J C , DEBEM T H C , et al. Review: Endometrial function in pregnancy establishment in cattle[J]. Animal, 2023, 17 (Suppl 1): 100751. |
| 3 |
BERG D K , LEDGARD A , DONNISON M , et al. The first week following insemination is the period of major pregnancy failure in pasture-grazed dairy cows[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2022, 105 (11): 9253- 9270.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2021-21773 |
| 4 | SPECKHART S L , OLIVER M A , EALY A D . Developmental hurdles that can compromise pregnancy during the first month of gestation in cattle[J]. Animals(Basel), 2023, 13 (11): 1760. |
| 5 |
REESE S T , FRANCO G A , POOLE R K , et al. Pregnancy loss in beef cattle: A meta-analysis[J]. Anim Reprod Sci, 2020, 212, 106251.
doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2019.106251 |
| 6 |
SZENCI O . Recent possibilities for the diagnosis of early pregnancy and embryonic mortality in dairy cows[J]. Animals, 2021, 11 (6): 1666.
doi: 10.3390/ani11061666 |
| 7 | WILTBANK M C , MONTEIRO P L J , DOMINGUES R R , et al. Review: Maintenance of the ruminant corpus luteum during pregnancy: inte·rferon-tau and beyond[J]. Animal, 2023, 17 (Suppl 1): 100827. |
| 8 |
MAHER A D , HAYES B , COCKS B , et al. Latent biochemical relationships in the blood-milk metabolic axis of dairy cows revealed by statistical integration of 1H NMR spectroscopic data[J]. J Proteome Res, 2013, 12 (3): 1428- 1435.
doi: 10.1021/pr301056q |
| 9 |
薛鸿雁, 杨孟雨, 杨欢, 等. ALOX15B-JNK在热应激诱导支持细胞氧化应激和凋亡中的作用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (12): 5056- 5065.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.12.016 |
|
XUE H Y , YANG M Y , YANG H , et al. The role of ALOX15B-JNK in heat stress-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis of sertoli cells[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (12): 5056- 5065.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.12.016 |
|
| 10 |
BERNABUCCI U , RONCHI B , LACETERA N , et al. Influence of body condition score on relationships between metabolic status and oxidative stress in periparturient dairy cows[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2005, 88 (6): 2017- 2026.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(05)72878-2 |
| 11 | SAGRILLO-FAGUNDES L , SOLIMANA , VAILLANCOURT C . Maternal and placental melatonin: actions and implication for successful pregnancies[J]. Minerva Ginecol, 2014, 66 (3): 251- 266. |
| 12 | BHARTI V K , SRIVASTAVA R S , KUMAR H , et al. Effects of melatonin and epiphyseal proteins on fluoride-induced adverse changes in antioxidant status of heart, liver, and kidney of rats[J]. Adv Pharmacol Sci, 2014, 532969. |
| 13 | OLIVEIRA FILHO E F , LÓPEZ-ALONSO M , VIEIRA MARCOLINO G , et al. Factors affecting toxic and essential trace element concentrations in cow's milk produced in the state of pernambuco, brazil[J]. Animals(Basel), 2023, 13 (15): 2465. |
| 14 |
KASIMANICKAM R , KASIMANICKAM V , KASTELIC J P , et al. Metabolic biomarkers, body condition, uterine inflammation and response to superovulation in lactating Holstein cows[J]. Theriogenology, 2020, 146, 71- 79.
doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.02.006 |
| 15 | RAZA A , ABBAS K , SWANGCHAN-UTHAI T , et al. Behavioral adaptations in tropical dairy cows: insights into calving day predictions[J]. Animals (Basel), 2024, 14 (12): 1834. |
| 16 |
BAZER F W . Pregnancy recognition signaling mechanisms in ruminants and pigs[J]. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 2013, 4 (1): 23.
doi: 10.1186/2049-1891-4-23 |
| 17 |
孙国瀚, 郑浩, 杨卓, 等. 发情期和妊娠早期孕酮对奶牛繁殖的影响及调控方法[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (10): 4241- 4249.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.10.001 |
|
SUN G H , ZHENG H , YANG Z , et al. Effects and regulation methods of progesterone on reproduction in dairy cows during estrus and early pregnancy[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (10): 4241- 4249.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.10.001 |
|
| 18 | 张萌, 王俊奎, 杨玉东, 等. 人工授精后不同阶段葡萄糖、孕酮和雌二醇含量对奶牛妊娠预测的研究[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2020, 56 (10): 108- 111. |
| ZHANG M , WANG J K , YANG Y D , et al. Effects of different levels of glucose, progesterone and estradiol on the pregnancy of dairy cows after artificial insemination[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Scienc, 2020, 56 (10): 108- 111. | |
| 19 |
吕莲, 贾国慧, 王亮, 等. 奶牛妊娠早期血浆孕酮的变化规律[J]. 上海畜牧兽医通讯, 2009 (2): 48- 49.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7725.2009.02.027 |
|
LÜ L , JIA G H , WANG L , et al. Changing law of plasma progesterone in early pregnancy in dairy cows[J]. Shanghai Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2009 (2): 48- 49.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7725.2009.02.027 |
|
| 20 |
CONSTANTIN N T , BERCEA-STRUGARIU C M , BÎRT OIU D , et al. Predicting pregnancy outcome in dairy cows: the role of IGF-1 and progesterone[J]. Animals, 2023, 13, 1579.
doi: 10.3390/ani13101579 |
| 21 |
刘彩凤, 王婧卓, 王熙, 等. 外源褪黑素调控母牛繁殖性能的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (12): 5379- 5390.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.12.005 |
|
LIU C F , WANG J Z , WANG X , et al. Research progress on regulation of reproductive performance by exogenous melatonin in cows[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (12): 5379- 5390.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.12.005 |
|
| 22 |
REITER R J , MAYO J C , TAN D X , et al. Melatonin as an antioxidant: Under promises butover delivers[J]. J Pineal Res, 2016, 61, 253- 278.
doi: 10.1111/jpi.12360 |
| 23 |
EJAZ H , FIGARO J K , WOOLNER A M F , et al. Maternal serum melatonin increases during pregnancy and falls immediately after delivery implicating the placenta as a major source of melatonin[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2021, 11, 623038.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.623038 |
| 24 |
BROOKS K , BURNS G , SPENCER T E . Conceptus elongation in ruminants: roles of progesterone, prostaglandin, interferon tau and cortisol[J]. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 2014, 5 (1): 53.
doi: 10.1186/2049-1891-5-53 |
| 25 | DRUM J N , WILTBANK M C , MONTEIRO JR P L J , et al. Oxytocin-induced prostaglandin F2-alpha release is low in early bovine pregnancy but increases during the second month of pregnancy[J]. Biol Reprod, 2020, 102 (2): 412- 423. |
| 26 |
GINTHER O J . Uteroovarian pathway for embryo-empowered maintenance of the corpus luteum in farm animals[J]. Theriogenology, 2024, 216, 103- 110.
doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2023.12.028 |
| 27 | FARIA N , PACHECO-LIMA J , DA SILVA M H M , et al. Effects of cortisol levels on reproductive success in cattle of different temperaments during fixed-time artificial insemination (FTAI)[J]. J Anim Behav Biometeorol, 2024, 12 (1): 2024002. |
| 28 |
ULBRICH S E , SCHULKE K , GROEBNER A E , et al. Quantitative characterization of prostaglandins in the uterus of early pregnant cattle[J]. Reproduction, 2009, 138, 371- 382.
doi: 10.1530/REP-09-0081 |
| 29 |
LEE H Y , ACOSTA T J , TANIKAWA M , et al. The role of glucocorticoid in the regulation of prostaglandin biosynthesis in non-pregnant bovine endometrium[J]. J Endocrinol, 2007, 193, 127- 135.
doi: 10.1677/joe.1.06975 |
| 30 |
KOMIYAMA J , NISHIMURA R , LEE H Y , et al. Cortisol is a suppressor of apoptosis in bovine corpus luteum[J]. Biol Reprod, 2008, 78, 888- 895.
doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.107.065656 |
| 31 | 钟婧怡, 魏雨璠, 杨涔, 等. 皮质醇对原代奶牛子宫内膜上皮细胞Nrf2/HO-1通路的影响机制研究[J/OL]. 中国兽医科学, 1-8[2024-11-11]. https://doi.org/10.16656/j.issn.1673-4696.2025.0024. |
| ZHONG J Y, WEI Y F, YANG C, et al. The effect and mechanism of cortisol on the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in primary bovine endometrial epithelial cells[J/OL]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 1-8[2024-11-11]. https://doi.org/10.16656/j.issn.1673-4696.2025.0024. | |
| 32 |
DIRANDEH E , SAYYAR M A , ANSARI-PIRSARAEI Z , et al. Peripheral leucocyte molecular indicators of inflammation and oxidative stress are altered in dairy cows with embryonic loss[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11 (1): 12771.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91535-2 |
| 33 |
NAZARI A , DIRANDEH E , ANSARI-PIRSARAEI Z , et al. Antioxidant levels, copper and zinc concentrations were associated with postpartum luteal activity, pregnancy loss and pregnancy status in Holstein dairy cows[J]. Theriogenology, 2019, 133, 97- 103.
doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2019.04.034 |
| 34 |
DIRANDEH E , TOWHIDI A , ZEINOALDINI S , et al. Effects of different polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementations during the postpartum periods of early lactating dairy cows on milk yield, metabolic responses, and reproductive performances[J]. J Anim Sci, 2013, 91 (2): 713- 721.
doi: 10.2527/jas.2012-5359 |
| [1] | ZHAO Yunhai, ZHANG Yangyang, MA Haiyun, WANG Qing, HE Xiaoxiao, LIU Kai, ZHANG Yuting, LIU Yudong, YANG Yongning, WU Xiaochun, XING Xiaoyong, QUAN Guomei, ZHANG Zhixiong, BAO Shijun. Prokaryotic Expression and Adhesion Characteristics of Molecular Chaperone Dnak of Mycoplasma bovis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2868-2878. |
| [2] | ZHANG Junxing, SHENG Hui, HAN Liyun, ZHANG Hailiang, ZHANG Yi, CAI Bei, MA Yun, WANG Yachun. The Impact of Health Events on Important Economic Traits in Holstein Lactating Cows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2203-2218. |
| [3] | QIAO Yarui, MIAO Yuhang, HUANG Qian, ZHOU Xuezhang. Research on the Biological Characteristics of Enterococcus faecalis in Dairy Cow Mastitis in Ningxia [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2325-2339. |
| [4] | HAN Yangrui, XIA Luming, LI Ruifang, ZHANG Manyu, DU Jingying, SUN Qing, LI Zenqiang, ZHAO Hongjin, WANG Quan. Establishment of Lanthanide Microsphere Immunochromatographic Test Strips for the Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2353-2363. |
| [5] | XIE Yuehua, XIE Fujie, SUO Xun, YAN Wenchao. Application of the 3D Cell Culture System in the Study of Apicomplexa Protozoa [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1540-1548. |
| [6] | WANG Jiying, XIANG Shuhan, LI Zhiqiang, LI Shiyang, ZHANG Lei, XIE Qingyun, XIONG Qiyan, SHAO Guoqing, FENG Zhixin, YU Yanfei. Preliminary Study on the Inhibitory Effect of Plantamajoside on Inflammatory Response Induced by Mesomycoplasma hyopneumoniae [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1958-1968. |
| [7] | FAN Manting, HUANG Ruoting, SHE Yuanhang, GUO Jianchao, LIU Jianying, GUO Yongqing. Research Progress on the Application of Omics Technology in the Pathogenesis and Diagnosis of Mastitis in Dairy Cows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1076-1088. |
| [8] | ZHANG Shiqi, ZHENG Nan, WANG Jiaqi, ZHAO Shengguo. Effect of Dietary NFC/NDF Ratio on the Metabolic Flux of Microbial Urea Nitrogen in the Rumen of Dairy Cows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1302-1312. |
| [9] | WANG Chun, WANG Qing, WU Xiaoqian, HU Ting, CUI Weitao, PEI Jie, SONG Tieping, HU Sishun, ZHANG Wanpo, LI Zili, ZHOU Zutao. Analysis of Mycoplasma synoviae Infection in the Laying Hens in Hubei Province based on Fluorescence Quantitative PCR Detection and in situ Hybridization Technology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1396-1407. |
| [10] | LI Zhenya, LIU Jie, LI Yun, WANG Fei, KONG Yuanyuan, LI Yong, JIA Rongling. Biological Characteristics and Comparative Genomic Analysis of Virulent and Attenuated Strains of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 851-859. |
| [11] | WANG Jing, GUAN Shuwen, ZHAO Xiaobo, WANG Linwei, GUO Gang, JIANG Linshu. The Protective Effect of Bamboo Leaf Flavonoids on H2O2-induced Pyroptosis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 281-294. |
| [12] | Xu GUO, Xiaoxiao CHEN, Yiming CHI, Wenyu MA, Mengze DU, Jian AN, Qiuming LI, Deqi YIN. Research Progress of Toxoplasma gondii AP2 Family [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3824-3832. |
| [13] | Rui SHI, Shanshan LI, Hailiang ZHANG, Haibo LU, Qingxia YAN, Yi ZHANG, Shaohu CHEN, Yachun WANG. Genotype by Environment Interaction of Fertility Traits for the Holstein Cattle in China [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3968-3977. |
| [14] | Ruowei WANG, Xiyao XU, Xiaona TANG, Chunmei WANG, Feng ZHAO. Connective Tissue Growth Factor Regulates the Growth and Differentiation of Cows Mammary Epithelial Cells in Vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3446-3459. |
| [15] | Yiming GAO, Guosheng CHEN, Shiting NI, Ze TONG, Haonan WANG, Fan YANG, Lijun YANG, Yupeng MO, Chen TAN. Investigation and Analysis of Infection Status of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in Pigs in Selected Areas of Southern China, 2022 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3064-3074. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||