





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (12): 5527-5537.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.12.018
• Animal Genetics and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Miao1,2( ), PEI Fen3(
), PEI Fen3( ), JU Lin4, ZHAO Xiuxin3, YANG Jian3, XUE Guanghui3, XU Qianwen3, LIU Yan3, ZHANG Yuanpei3, CAI Gaozhan3, GAO Yundong1, YU Ying2,*(
), JU Lin4, ZHAO Xiuxin3, YANG Jian3, XUE Guanghui3, XU Qianwen3, LIU Yan3, ZHANG Yuanpei3, CAI Gaozhan3, GAO Yundong1, YU Ying2,*( ), WANG Xiao1,*(
), WANG Xiao1,*( ), LI Jianbin1,*(
), LI Jianbin1,*( )
)
Received:2024-06-19
Online:2024-12-23
Published:2024-12-27
Contact:
YU Ying, WANG Xiao, LI Jianbin
E-mail:zm13203163161@163.com;1615434703@qq.com;yuying@cau.edu.cn;xiaowangzntc@163.com;msdljb@163.com
CLC Number:
ZHANG Miao, PEI Fen, JU Lin, ZHAO Xiuxin, YANG Jian, XUE Guanghui, XU Qianwen, LIU Yan, ZHANG Yuanpei, CAI Gaozhan, GAO Yundong, YU Ying, WANG Xiao, LI Jianbin. Genetic Analysis of Milk Urea Nitrogen, Milk Production Traits, and Somatic Cell Score in First Lactation of Holstein Cattle[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5527-5537.
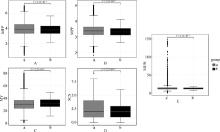
Fig. 1
The data boxplot of milk fat percentage, milk protein percentage, milk yield, somatic cell score and milk urea nitrogen before and after IQR quality control A. The data boxplot of milk fat percentage before and after IQR quality control; B. The data boxplot of milk protein percentage before and after IQR quality control; C. The data boxplot of milk production before and after IQR quality control; D. The data boxplot of somatic cell score before and after IQR quality control; E. The data boxplot of milk urea nitrogen before and after IQR quality control. a. IQR pre-control data; b. IQR post-control data"
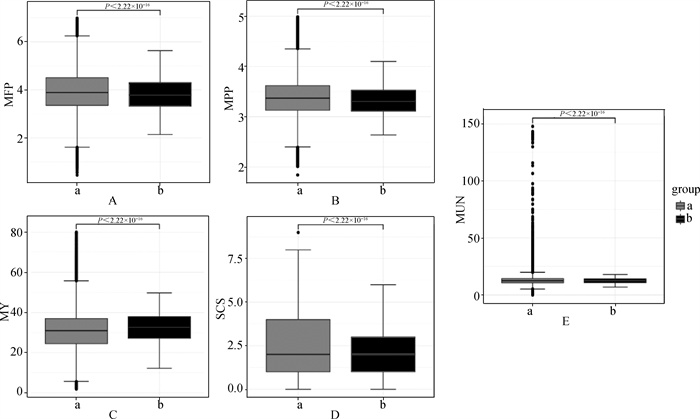

Fig. 2
The data distribution histogram of milk fat percentage, milk protein percentage, milk yield and milk urea nitrogen before and after IQR quality control MFP is milk fat percentage; MPP is milk protein percentage; MY is milk production; MUN is milk urea nitrogen. a is IQR pre-control data; b is IQR post-control data"
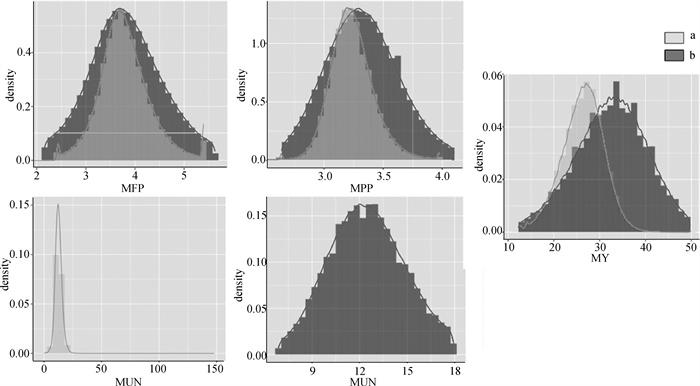
Table 3
Milk urea nitrogen levels in different cattle farms"
| 牛场 Herd | MUN平均值/ (mg·dL-1) Average | 标准差 SD | 数据记录量 Data record |
| 1 | 11.85h | 2.34 | 3 530 |
| 2 | 12.02f | 2.44 | 3 442 |
| 3 | 12.23f | 2.36 | 3 232 |
| 4 | 12.23f | 2.21 | 3 304 |
| 5 | 12.60d | 2.36 | 3 927 |
| 6 | 11.56i | 2.11 | 3 009 |
| 7 | 11.52i | 2.48 | 3 168 |
| 8 | 11.27j | 2.15 | 4 160 |
| 9 | 12.57d | 2.30 | 4 687 |
| 10 | 11.61i | 2.41 | 5 268 |
| 11 | 12.53de | 2.14 | 2 982 |
| 12 | 12.50d | 2.23 | 3 159 |
| 13 | 12.23f | 2.29 | 3 743 |
| 14 | 12.86c | 2.40 | 4 507 |
| 15 | 13.55a | 2.39 | 5 871 |
| 16 | 12.47e | 2.58 | 7 945 |
| 17 | 12.60d | 2.32 | 9 088 |
| 18 | 13.39b | 1.90 | 11 805 |
| 19 | 12.93c | 2.01 | 12 906 |
Table 4
Milk urea nitrogen levels at different calving years"
| 产犊年 Calving year | MUN平均值/ (mg·dL-1)Average | 标准差 SD | 数据记录量 Data records |
| 2015年 | 12.29d | 2.42 | 465 |
| 2016年 | 11.89d | 2.43 | 3 466 |
| 2017年 | 11.83e | 2.12 | 4 840 |
| 2018年 | 12.25d | 2.24 | 7 791 |
| 2019年 | 12.31d | 2.36 | 9 377 |
| 2020年 | 12.80b | 3.43 | 21 149 |
| 2021年 | 12.39c | 3.24 | 35 448 |
| 2022年 | 13.09a | 2.34 | 17 196 |
Table 7
Milk urea nitrogen levels at different lactation stages"
| 泌乳阶段/d Lactation stage | MUN平均值/ (mg·dL-1) Average | 标准差 SD | 数据记录量 Data record |
| 5~35 | 11.93e | 2.33 | 8 544 |
| 36~65 | 12.06d | 2.29 | 10 079 |
| 66~95 | 12.43c | 2.31 | 10 794 |
| 96~125 | 12.59b | 2.30 | 11 158 |
| 126~155 | 12.71c | 2.33 | 11 266 |
| 156~185 | 12.74a | 2.43 | 11 209 |
| 186~215 | 12.79a | 2.31 | 11 079 |
| 216~245 | 12.73a | 2.34 | 10 218 |
| 246~275 | 12.70a | 2.35 | 9 378 |
| 276~305 | 12.70a | 2.37 | 6 007 |
Table 8
The variance, heritability and repeatability statistics of milk urea nitrogen and each trait"
| 性状 Trait | 加性遗传方差 σa2 | 永久环境方差 σpe2 | 残差方差 σe2 | 遗传力 h2 | 重复力 r2 |
| 乳尿素氮MUN | 0.88 | 0.017 | 5.90 | 0.129 | 0.132 |
| 产奶量MY | 14.41 | 14.92 | 27.81 | 0.252 | 0.513 |
| 乳蛋白率MPP | 0.021 | 0.005 1 | 0.056 | 0.257 | 0.320 |
| 乳脂率MFP | 0.11 | 0.026 | 0.45 | 0.188 | 0.231 |
| 体细胞评分SCS | 0.24 | 0.50 | 1.45 | 0.110 | 0.339 |
| 1 |
王玲玲. 简述奶牛乳尿素氮产生机理及其影响因素[J]. 吉林畜牧兽医, 2021, 42 (5): 63- 64.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2078.2021.05.053 |
|
WANG L L . A brief description of the mechanism of milk urea nitrogen production in dairy cows and its influencing factors[J]. Jilin Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 42 (5): 63- 64.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2078.2021.05.053 |
|
| 2 | JONKER J S , KOHN R A . Using milk urea nitrogen to evaluate diet formulation and environmental impact on dairy farms[J]. Sci World J, 2001, 1 (Suppl 2): 852- 859. |
| 3 |
KESSLER E C , BRUCKMAIER R M , GROSS J J . Milk urea nitrogen concentration is higher in Brown Swiss than in Holstein dairy cows despite identical feeding[J]. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr, 2020, 104 (6): 1671- 1677.
doi: 10.1111/jpn.13408 |
| 4 | 韦科龙, 卢瑛, 李舒露, 等. 河流型水牛乳尿素氮影响因素分析[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2022, 58 (9): 294- 297. |
| WEI K L , LU Y , LI S L , et al. The influence factors of milk urea nitrogen of river buffalo[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2022, 58 (9): 294- 297. | |
| 5 |
HOJMAN D , GIPS M , EZRA E . Association between live body weight and milk urea concentration in Holstein cows[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2005, 88 (2): 580- 584.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(05)72721-1 |
| 6 | WEBB E C , DE BRUYN E . Effects of milk urea nitrogen (MUN) and climatological factors on reproduction efficiency of Holstein Friesian and Jersey cows in the subtropics[J]. Animals (Basel), 2021, 11 (11): 3068. |
| 7 |
HOF G , VERVOORN M D , LENAERS P J , et al. Milk urea nitrogen as a tool to monitor the protein nutrition of dairy cows[J]. J Dairy Sci, 1997, 80 (12): 3333- 3340.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(97)76309-4 |
| 8 |
NOUSIAINEN J , SHINGFIELD K J , HUHTANEN P . Evaluation of milk urea nitrogen as a diagnostic of protein feeding[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2004, 87 (2): 386- 398.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(04)73178-1 |
| 9 | JONKER J S , KOHN R A . Using milk urea nitrogen to evaluate diet formulation and environmental impact on dairy farms[J]. Sci World J, 2001, 1 (Suppl 2): 852- 859. |
| 10 |
王东卫, 曹志军, 李胜利, 等. 牛奶尿素氮含量与奶牛繁殖性能的关系[J]. 动物营养学报, 2010, 22 (6): 1509- 1514.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2010.06.007 |
|
WANG D W , CAO Z J , LI S L , et al. The relationship between content of milk urea nitrogen and reproductive performance of dairy cows[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2010, 22 (6): 1509- 1514.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2010.06.007 |
|
| 11 |
GODDEN S M , KELTON D F , LISSEMORE K D , et al. Milk urea testing as a tool to monitor reproductive performance in Ontario dairy herds[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2001, 84 (6): 1397- 1406.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(01)70171-3 |
| 12 |
KANANUB S , PECHKERD P , VANLEEUWEN J , et al. Evaluation of influence of milk urea nitrogen on reproductive performance in smallholder dairy farms[J]. Aust Vet J, 2020, 98 (8): 375- 379.
doi: 10.1111/avj.12946 |
| 13 |
POWELL J M , WATTIAUX M A , BRODERICK G A . Short communication: evaluation of milk urea nitrogen as a management tool to reduce ammonia emissions from dairy farms[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2011, 94 (9): 4690- 4694.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2011-4476 |
| 14 | LAVERY A , FERRIS C P . Proxy measures and novel strategies for estimating nitrogen utilisation efficiency in dairy cattle[J]. Animals (Basel), 2021, 11 (2): 343. |
| 15 |
MITCHELL R G , ROGERS G W , DECHOW C D , et al. Milk urea nitrogen concentration: heritability and genetic correlations with reproductive performance and disease[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2005, 88 (12): 4434- 4440.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(05)73130-1 |
| 16 |
STOOP W M , BOVENHUIS H , VAN ARENDONK J A M . Genetic parameters for milk urea nitrogen in relation to milk production traits[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2007, 90 (4): 1981- 1986.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2006-434 |
| 17 |
BOBBO T , PENASA M , ROSSONI A , et al. Short communication: genetic aspects of milk urea nitrogen and new indicators of nitrogen efficiency in dairy cows[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2020, 103 (10): 9207- 9212.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-18445 |
| 18 |
BEATSON P R , MEIER S , CULLEN N G , et al. Genetic variation in milk urea nitrogen concentration of dairy cattle and its implications for reducing urinary nitrogen excretion[J]. Animal, 2019, 13 (10): 2164- 2171.
doi: 10.1017/S1751731119000235 |
| 19 |
WOOD G M , BOETTCHER P J , JAMROZIK J , et al. Estimation of genetic parameters for concentrations of milk urea nitrogen[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2003, 86 (7): 2462- 2469.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(03)73840-5 |
| 20 | 杨海昱. 荷斯坦奶牛乳中尿素氮影响因素分析及遗传参数估计[D]. 邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2019. |
| YANG H Y. Analysis of affected factors and estimation of genetic parameters of urea nitrogen in Holstein cow milk[D]. Handan: Hebei University of Engineering, 2019. (in Chinese) | |
| 21 | 何开兵, 赵宗胜. 新疆石河子地区牛奶尿素氮数据统计分析及适宜范围研究[J]. 中国奶牛, 2021, (5): 34- 38. |
| HE K B , ZHAO Z S . Statistical analysis of milk urea nitrogen data and study of suitable range in Shihezi, Xinjiang[J]. China Dairy Cattle, 2021, (5): 34- 38. | |
| 22 | 周期. 牛奶尿素氮与奶牛繁殖性能关系的相关研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2014. |
| ZHOU Q. The association between milk urea nitrogen and reproductive performance of dairy cows[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese) | |
| 23 | 马建民, 孙健, 马国利, 等. 北京地区牛场乳尿素氮水平调查及分析[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2017, (10): 95- 97. |
| MA J M , SUN J , MA G L , et al. Survey and analysis of milk urea nitrogen in cattle farms in Beijing[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2017, (10): 95- 97. | |
| 24 |
黄文明, 王之盛, 王恬, 等. 牛奶尿素氮含量与奶牛胎次、泌乳天数、产奶量和乳成分的关系[J]. 中国奶牛, 2009, (12): 10- 14.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4264.2009.12.007 |
|
HUANG W M , WANG Z S , WANG T , et al. The relationship between milk urea nitrogen and parities, days in milk, milk production and composition[J]. China Dairy Cattle, 2009, (12): 10- 14.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4264.2009.12.007 |
|
| 25 |
FATEHI F , ZALI A , HONARVAR M , et al. Review of the relationship between milk urea nitrogen and days in milk, parity, and monthly temperature mean in Iranian Holstein cows[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2012, 95 (9): 5156- 5163.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2011-4349 |
| 26 |
ARUNVIPAS P , DOHOO I R , VANLEEUWEN J A , et al. The effect of non-nutritional factors on milk urea nitrogen levels in dairy cows in Prince Edward Island, Canada[J]. Prev Vet Med, 2003, 59 (1-2): 83- 93.
doi: 10.1016/S0167-5877(03)00061-8 |
| 27 |
CARLSSON J , BERGSTRÖM J , PEHRSON B . Variations with breed, age, season, yield, stage of lactation and herd in the concentration of urea in bulk milk and individual cow's milk[J]. Acta Vet Scand, 1995, 36 (2): 245- 254.
doi: 10.1186/BF03547693 |
| 28 |
YOON J T , LEE J H , KIM C K , et al. Effects of milk production, season, parity and lactation period on variation of milk urea nitrogen concentration and milk components of Holstein dairy cows[J]. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci, 2004, 17 (4): 479- 484.
doi: 10.5713/ajas.2004.479 |
| 29 |
VISSCHER P M , HILL W G , WRAY N R . Heritability in the genomics era—concepts and misconceptions[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2008, 9 (4): 255- 266.
doi: 10.1038/nrg2322 |
| 30 |
MUCHA S , STRANDBERG E . Genetic analysis of milk urea nitrogen and relationships with yield and fertility across lactation[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2011, 94 (11): 5665- 5672.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2010-3916 |
| 31 |
MIGLIOR F , SEWALEM A , JAMROZIK J , et al. Genetic analysis of milk urea nitrogen and lactose and their relationships with other production traits in Canadian Holstein cattle[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2007, 90 (5): 2468- 2479.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2006-487 |
| 32 |
PETERSON A B , FRENCH K R , RUSSEK-COHEN E , et al. Comparison of analytical methods and the influence of milk components on milk urea nitrogen recovery[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2004, 87 (6): 1747- 1750.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(04)73329-9 |
| 33 | 叶东东. 新疆呼图壁种牛场荷斯坦牛遗传参数估计和动物模型BLUP遗传评定研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2011. |
| YE D D. Studies of genetic parameter estimation and genetic evaluation using animal model BLUP in Holstein cattle in Xinjiang Hutubi herd farm[D]. Urumchi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2011. (in Chinese) | |
| 34 |
HAYES J F , NG-KWAI-HANG K F , MOXLEY J E . Heritability of milk casein and genetic and phenotypic correlations with production traits[J]. J Dairy Sci, 1984, 67 (4): 841- 846.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(84)81375-2 |
| 35 | 赵占龙. 武汉地区荷斯坦奶牛产奶和繁殖性状遗传分析[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2015. |
| ZHAO Z L. Analysis and evaluation of the milk production and fertility traits of Holstein herds in Wuhan[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese) | |
| 36 |
IKONEN T , AHLFORS K , KEMPE R , et al. Genetic parameters for the milk coagulation properties and prevalence of noncoagulating milk in Finnish dairy cows[J]. J Dairy Sci, 1999, 82 (1): 205- 214.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(99)75225-2 |
| 37 | 任小丽, 栗敏杰, 白雪利, 等. 中国荷斯坦牛头胎产奶量和乳成分遗传参数估计[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2019, 55 (7): 67- 70. |
| REN X L , LI M J , BAI X L , et al. Genetic parameters for test-day milk yield and milk composition in Chinese Holstein first Parity[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2019, 55 (7): 67- 70. | |
| 38 |
KOECK A , HERINGSTAD B , EGGER-DANNER C , et al. Genetic analysis of clinical mastitis and somatic cell count traits in Austrian Fleckvieh cows[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2010, 93 (12): 5987- 5995.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2010-3451 |
| 39 |
ALAM M , CHO C I , CHOI T J , et al. Estimation of genetic parameters for somatic cell scores of Holsteins using multi-trait lactation models in Korea[J]. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci, 2015, 28 (3): 303- 310.
doi: 10.5713/ajas.13.0627 |
| 40 |
MA L G , LUO H P , BRITO L F , et al. Estimation of genetic parameters and single-step genome-wide association studies for milk urea nitrogen in Holstein cattle[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2023, 106 (1): 352- 363.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2022-21857 |
| [1] | CAO Jinkang, ZHANG Chun, WANG Jiayao, LI Xiaotong, WANG Pengyu, FANG Yingyan, ZHANG Yu, DING Ning, JIANG Li. Proteomic Analysis of Sperm with Different Freezability in Chinese Holstein Bulls [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1052-1061. |
| [2] | LIANG Canxin, ZHENG Xiaoxue, SHU Xueli, ZHOU Wanyi, LIAO Ming, CAO Weisheng. Isolation of ALV-K Associated with Endothelial Hemangioma in Chicken and Analysis of gp85 Gene Evolution [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1127-1136. |
| [3] | SONG Yan, YUAN Yongfeng, QIAN Hongyu, LI Xincan, LUO Hongyan, WANG Zhiying, ZHOU Zuoyong. Identification and Partial Biological Characteristics Analysis of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Isolated from Goats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 680-687. |
| [4] | ZHOU Zhiyu, DU Jige, XIN Ruolan, ZHANG Jiawen, PAN Chenfan, YIN Chunsheng, CHEN Xiaoyun, ZHU Zhen. Isolation and Identification of Three Lumpy Skin Disease Viruses in China and Their GPCR Gene Analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5620-5630. |
| [5] | Wanyi LAI, Xinyue TAO, Gengxin YANG, Wenli YU, Shujing LI, Tahir USMAN, Ying YU. Application Study of Chinese Cow's SNPs Chip-Ⅰ in Chinese Holstein and Pakistani Indigenous Dairy Cattle Populations [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4489-4499. |
| [6] | WANG Zhiyuan, LIU Boqi, XU Zhiying, XU Sijia, XING Jiabao, ZHANG Guihong, WANG Heng, SUN Yankuo. Analysis of ORF5 Gene Variation of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus in Local Regions of China from 2021 to 2022 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(9): 3812-3823. |
| [7] | WANG Zhenyu, ZHANG Saibo, LIU Wenhui, LIANG Dong, REN Xiaoli, YAN Lei, YAN Yuefei, GAO Tengyun, ZHANG Zhen, HUANG Hetian. Genomic Inbreeding Coefficient Analysis and Functional Gene Screening in Different Dairy Farms Based on SNP Chip Data [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(7): 2848-2857. |
| [8] | CHEN Hongjian, CAO Yan, FAN Jie, GAN Rongxuan, SONG Wenbo, YU Shengwei, YANG Ting, ZHAO Yanxia, WEI Chunyan, XIE Rui, HUA Lin, PENG Zhong, WU Bin. Prevalence and Phylogenetic Analysis of Pseudorabies Virus within Pig Slaughterhouses in Hubei Province of China during 2020-2022 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(7): 2972-2981. |
| [9] | ZHANG Ao, TAN Bin, LIU Kexin, LIU Jiali, ZHANG Shuqin. Genomic Characterization Analysis of a H1N1 Subtype Swine Influenza Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(11): 4866-4871. |
| [10] | SUN Dongxiao, ZHANG Shengli, ZHANG Qin, LI Jiao, ZHANG Guixiang, LIU Chousheng, ZHENG Weijie. Application Progress on Genomic Selection Technology for Dairy Cattle in China [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(10): 4028-4039. |
| [11] | YANG Yang, ZHOU Ziwei, ZHANG Jingyi, YANG Shuo, WANG Boyu, GE Nan, LIN Ye, HOU Xiaoming. Analysis on SP1 Gene Structure and Its Function on Milk Fat Synthesis in Holstein Dairy Cows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(9): 2970-2981. |
| [12] | Lü Shiqi, MA Xiaofei, LI Bing, JIA Chunhui, WANG Yanchao, TIAN Shujun, ZHOU Rongyan, CHEN Xiaoyong. Genetics Analysis and Effects of Mitochondrial tRNA-Lys (T7719G) Variation on Litter Size of Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(6): 1759-1767. |
| [13] | SONG Yuetong, ZHANG Rumei, LI Yanqin, LI Rongling, GAO Yundong, ZHONG Jifeng, XUE Guanghui, WANG Yudong, LI Jianbin, SUN Dongxiao. Analysis of Genetic Parameters of Type Traits and Influence of Genealogical Generation of Holstein Cows in Shandong Province [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(5): 1384-1395. |
| [14] | LIU Jiamin, YU Baojun, MU Tong, ZHANG Di, FENG Xiaofang, ZHANG Juan, WANG Ying, WEN Wan, GU Yaling. Screening and Identification of Key miRNAs for Milk Fat Metabolism in Dairy Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(12): 4244-4257. |
| [15] | WAN Tao, WANG Ao, ZHANG Hailiang, HU Lirong, ZHAO Shanjiang, ZHANG Hanlin, WANG Yan, GUO Gang, YU Ying, WANG Yachun. Influencing Factors and Genetic Parameters of Plasma Anti-Müllerian Hormone Concentration in Holstein Cows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(1): 161-168. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||