





畜牧兽医学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 2070-2081.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.05.008
秦小霞1,2( ), 甘海清1, 佘高进1,2, 刘勇2, 黄兴国1,3, 陈丽蓉4,*(
), 甘海清1, 佘高进1,2, 刘勇2, 黄兴国1,3, 陈丽蓉4,*( ), 杨玲媛1,3,*(
), 杨玲媛1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-08
出版日期:2025-05-23
发布日期:2025-05-27
通讯作者:
陈丽蓉,杨玲媛
E-mail:2107427547@qq.com;466710831@qq.com;lyyang@hunan.edu.cn
作者简介:秦小霞(1999-),女,甘肃康乐人,硕士生,主要从事动物营养与饲料科学研究,E-mail: 2107427547@qq.com
基金资助:
QIN Xiaoxia1,2( ), GAN Haiqing1, SHE Gaojin1,2, LIU Yong2, HUANG Xingguo1,3, CHEN Lirong4,*(
), GAN Haiqing1, SHE Gaojin1,2, LIU Yong2, HUANG Xingguo1,3, CHEN Lirong4,*( ), YANG Lingyuan1,3,*(
), YANG Lingyuan1,3,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-08
Online:2025-05-23
Published:2025-05-27
Contact:
CHEN Lirong, YANG Lingyuan
E-mail:2107427547@qq.com;466710831@qq.com;lyyang@hunan.edu.cn
摘要:
油茶籽粕作为油茶籽提取茶油后的副产物,富含蛋白、脂肪、糖类等营养成分及皂苷类、黄酮类、蛋白酶、多糖和多酚等生物活性成分。这些功能成分具有显著的抗氧化、抗炎、抑菌、免疫调节、脂质代谢调节、降血糖和抗癌等功能。将油茶籽粕添加到畜禽饲料中,显示出提高畜禽生长性能、增强免疫力和改善肠道菌群结构与功能的巨大潜力。本文系统综述了油茶籽粕的生物活性成分及其生物学功能,并深入探讨了其在畜禽生产中的应用前景,为油茶籽粕在畜禽生产中广泛应用提供科学支撑。
中图分类号:
秦小霞, 甘海清, 佘高进, 刘勇, 黄兴国, 陈丽蓉, 杨玲媛. 油茶籽粕的活性成分、生物学功能及其在畜禽生产中的应用研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(5): 2070-2081.
QIN Xiaoxia, GAN Haiqing, SHE Gaojin, LIU Yong, HUANG Xingguo, CHEN Lirong, YANG Lingyuan. Research Progess in Active Components, Biological Functions of Camellia Seed Meal and Its Applications in Livestock and Poultry Production[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2070-2081.
表 1
油茶籽粕营养成分含量"
| 种类 Category | 产地 Origin | 加工方式 Processing methods | 粗蛋白质 CP | 糖类 TC | 粗纤维 CF | 粗脂肪 EE | 粗灰分 Ash | 参考文献 References |
| 油茶饼粕 Camellia oleifera cake | 贵州天柱 | 冷榨 | 8.9 | - | 18.98 | 9.4 | 4.03 | [ |
| 油茶饼粕 Camellia oleifera cake | 安徽六安 | 冷榨 | 15 | 40 | 6 | 5 | 6 | [ |
| 油茶饼粕 Camellia oleifera cake | 广东东菀 | - | 15.94 | 26.09 | 6 | 6.64 | - | [ |
| 油茶饼粕 Camellia oleifera cake | 海南琼海 | 热压 | 11.38 | 14.42 | 6.81 | 11.24 | 8.25 | [ |
| 油茶籽粕 Camellia seed meal | 湖南衡阳 | 低温压榨 | - | - | 46.18 | 5.35 | 1.72 | [ |
| 油茶籽粕 Camellia seed meal | 湖南长沙 | - | 15 | 40 | 6 | 5 | 14 | [ |
| 油茶籽粕 Camellia seed meal | 湖北通程 | 低温冷榨 | 13.00±2.02 | 11.19±0.86 | 14.77±3.19 | 2.15±0.55 | 11.30±0.05 | [ |
| 油茶籽粕 Camellia seed meal | 湖南浏阳 | 机榨浸提 | 9.19±1.55 | 10.05±1.24 | 17.92±1.58 | 2.90±0.01 | 9.08±0.02 | [ |
表 2
油茶籽粕中的主要活性物质提取方法"
| 提取方法 Extraction methods | 特点 Characteristics | 活性物质 Active components | 提取率 Extraction rate | 参考文献 References |
| 超声波辅助法 Ultrasonic-assisted | 提取效率高、时间短、适用性广、能耗和成本较低 | 多糖 | 14.56% | [ |
| 多酚 | 2.99% | [ | ||
| 茶皂素 | (22.79±1.16)% | [ | ||
| 超声波辅助水酶萃取法 Ultrasonic-assisted aqueous enzymatic extraction | 降低溶剂和能源消耗,提升提取效率 | 油茶籽粕蛋白 | (83.30±0.60)% | [ |
| 多酚 | 18.94 mg·g-1 | [ | ||
| 酶解法 Enzymolysis | 经酶解预处理,提取率高,但是消耗时间久 | 多糖 | 19.48% | [ |
| 油茶籽粕蛋白 | 80.83% | [ | ||
| 茶皂素 | 3.97% | [ | ||
| 微波辅助法 Microwave-assisted method | 简便、快速和高效,但对人体有辐射且耗能高 | 多酚 | (15.05±0.04)% | [ |
| 茶皂素 | 80.57% | [ | ||
| 水提醇沉法 Water extract alcohol precipitation method | 成本低,操作简单,但提取温度对提取率影响大 | 多糖 | 6.21% | [ |
| 茶皂素 | 25.24% | [ |
表 3
油茶籽粕中的主要生物活性物质及其功能特性"
| 活性物质 Active components | 主要成分 Essential component | 结构 Structure | 化学结构式 Chemical structural formula | 功能 Function | 参考文献 References |
| 皂苷类 Saponosides | 茶皂素、油茶皂苷 | 以皂苷元、糖体和有机酸为基本结构而构成的一种齐墩果烷型的五环三萜类皂苷化合物 | 茶皂素: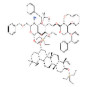 | 抗炎、抗氧化、抗癌、抑菌、降血糖等 | [ |
| 多糖类 Polyose | 甘露糖(30.06%)、半乳糖(22.92%)、阿拉伯糖(18.17%)、鼠李糖(11.39%)、葡萄糖(11.26%)和木糖(6.22%) | 由9个以上单糖分子脱水缩合而成,是由醛基和酮基通过糖苷键连接的高分子聚合物 | 多糖: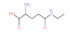 | 具有抗肿瘤、降血糖、降血脂、抗氧化、抗菌等功能 | [ |
| 多酚类 Polyphenols | 主要为儿茶素、黄酮、类黄酮醇、酚酸、单宁和山奈酚等大类化合物,其中以儿茶素类化合物含量最多 | 以α-苯基苯并吡喃为结构基础的类黄酮化合物 | 茶多酚: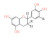 | 抗氧化、抗癌症、增加肠道有益菌、抑制和杀死引起腹泻的各种病原菌,还具有降血糖、清热解毒等功效 | [ |
EGCG: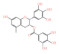 | |||||
| 蛋白类 Protide | 主要包括清蛋白、球蛋白、醇溶性蛋白以及谷蛋白 | ɑ螺旋占803%、β折叠占1%、β转角占64%、无规卷曲占158% | 油茶籽粕蛋白: | 具有降血压、降血脂、抗氧化、抗病菌、抗病毒功能 | [ |
表 4
日粮中添加油茶籽粕对畜禽生产性能的影响"
| 畜禽 Livestock and poultry | 阶段 Phase | 添加物 Supplement | 试验时间 Test time | 应用效果 Application effect | 文献 References |
| 蛋鸡 Laying hens | 26周龄 | 300或500 mg·kg-1油茶籽粕提取物和100 mg/kg粪肠球菌 | 12周 | 显著降低蛋形指数、哈氏单位和蛋壳强度,提高血清IgA和IgG水平,调节血清脂质代谢,增加盲肠菌群的多样性 | [ |
| 肉鸡 Broiler chickens | 15日龄 | 15%发酵油茶籽粕 | 28 d | 提高肉鸡的生长性能、屠体性能和改善肉品质,促进肉鸡免疫器官的发育,改善肉鸡小肠形态,调节肠道菌群 | [ |
| 生长猪 Growing pigs | 18 kg | 4%油茶籽粕 | 74 d | 显著降低了ADG和ADFI,提高了料肉比和SOD含量,提高猪的抗氧化能力 | [ |
| 生长猪 Growing pigs | (31.03±2.13) kg | 600 mg·kg-1油茶籽粕提取物 | 48 d | 显著提高ADFI、ADG和血清中的IgG水平及血清INF-γ水平,显著降低了F/G、血清尿素氮,改善了生长猪的生长性能, 增强了免疫功能 | [ |
| 泌乳期奶牛 Lactating dairy cows | - | 15%、30%、45%发酵油茶籽粕 | 30 d | 改善瘤胃内环境,增强奶牛对营养物质的消化吸收,显著提高产奶量、乳脂率,极显著提高乳蛋白率,降低血液尿素氮含量 | [ |
| 成年小尾寒羊 Adult small-tailed Han sheep | 50 kg | 油茶籽粕 | - | 提高生产性能和瘤胃内营养物质降解率,如摄入48 h后瘤胃内粗蛋白有效降解率高于棉籽粕、菜籽粕和棕榈仁粕 | [ |
| 成年湖羊 Adult Hu sheep | - | 25%发酵油茶籽粕 | - | 有利于瘤胃微生物繁殖,促进营养成分降解和发酵 | [ |
| 1 |
SHI T , WU G C , JIN Q Z , et al. Camellia oil authentication: a comparative analysis and recent analytical techniques developed for its assessment.a review[J]. Trends Food Sci Technol, 2020, 97, 88- 99.
doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.01.005 |
| 2 |
LUAN F , ZENG J S , YANG Y , et al. Recent advances in Camellia oleifera Abel: a review of nutritional constituents, biofunctional properties, and potential industrial applications[J]. J Funct Foods, 2020, 75, 104242.
doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.104242 |
| 3 |
LI G H , MA L , YAN Z P , et al. Extraction of oils and phytochemicals from Camellia oleifera seeds: trends, challenges, and innovations[J]. Processes, 2022, 10 (8): 1489.
doi: 10.3390/pr10081489 |
| 4 | 卫洋洋. 油茶籽粕生物改良及其在奶牛饲养上的应用[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2013. |
| WEI Y Y. Biological improvement of oil tea seed meal and its application in dairy cow feeding[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2013. (in Chinese) | |
| 5 | SARMAH K , DAS P , SAIKIA G K , et al. Biochemical characterization of tea (Camellia spp) seed oil cake[J]. Bull Environ Pharmacol Life Sci, 2018, 7 (9): 45- 49. |
| 6 |
ZHANG T , QIU F C , CHEN L , et al. Identification and in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of different forms of phenolic compounds in Camellia oleifera oil[J]. Food Chem, 2021, 344, 128660.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128660 |
| 7 |
LI X , DENG J L , SHEN S A , et al. Antioxidant activities and functional properties of enzymatic protein hydrolysates from defatted Camellia oleifera seed cake[J]. J Food Sci Technol, 2015, 52 (9): 5681- 5690.
doi: 10.1007/s13197-014-1693-z |
| 8 |
HU J L , NIE S P , HUANG D F , et al. Antimicrobial activity of saponin-rich fraction from Camellia oleifera cake and its effect on cell viability of mouse macrophage RAW 264.7[J]. J Sci Food Agric, 2012, 92 (12): 2443- 2449.
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.5650 |
| 9 |
ZHU C F , ZHANG M , TANG Q L , et al. Structure and activity of the Camellia oleifera sapogenin derivatives on growth and biofilm inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2019, 67 (51): 14143- 14151.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b03577 |
| 10 | ZHANG D D , NIE S P , XIE M Y , et al. Antioxidant and antibacterial capabilities of phenolic compounds and organic acids from Camellia oleifera cake[J]. Food Sci Biotechnol, 2019, 29 (1): 17- 25. |
| 11 |
罗彦玉, 王磊, 邹春霞, 等. 固态发酵降解油茶饼粕中茶皂素工艺优化及成分的分析[J]. 中国粮油学报, 2023, 38 (9): 150- 158.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2023.09.021 |
|
LUO Y Y , WANG L , ZOU C X , et al. Process optimi-zation and composition analysis of tea saponin in solidfemmentation degradation of Camellia oleifera cake meal[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Associatio, 2023, 38 (9): 150- 158.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2023.09.021 |
|
| 12 |
GAO C , CAI C Y , LIU J J , et al. Extraction and preliminary purification of polysaccharides from Camellia oleifera Abel.seed cake using a thermoseparating aqueous two-phase system based on EOPO copolymer and deep eutectic solvents[J]. Food Chem, 2020, 313, 126164.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126164 |
| 13 |
HONG C C , CHANG C , ZHANG H , et al. Identification and characterization of polyphenols in different varieties of Camellia oleifera seed cakes by UPLC-QTOF-MS[J]. Food Res Int, 2019, 126, 108614.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108614 |
| 14 | 张瑞麟, 杜超, 鞠雪莹, 等. 超声辅助提取3种油茶籽粕多糖及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国粮油学报, 2022, 37 (7): 122- 127. |
| ZHANG R L , DU C , JU X Y , et al. Ultrasonic assisted extraction of polysaccharides from three Camellia seed meal and their antioxidant activities[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2022, 37 (7): 122- 127. | |
| 15 |
ZHANG S Y , ZHENG L L , ZHENG X Y , et al. Effect of steam explosion treatments on the functional properties and structure of camellia (Camellia oleifera Abel.) seed cake protein[J]. Food Hydrocoll, 2019, 93, 189- 197.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.02.017 |
| 16 | 朱静, 吕静, 邢淑婕, 等. 光山油茶饼粕蛋白水解物的制备及功能活性分析[J]. 中国食品添加剂, 2023, 34 (9): 258- 265. |
| ZHU J , LV J , XING S J , et al. Preparation and functional activity analysis of protein hydrolysate from Guangshan oil tea cake[J]. China Food Additives, 2023, 34 (9): 258- 265. | |
| 17 | 梅华迪, 陈卫东, 马现永, 等. 油茶粕的营养特点、脱毒工艺及其在动物生产中的应用研究进展[J]. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35 (11): 6946- 6954. |
| MEI H D , CHEN W D , MA X Y , et al. Research progress on nutritional characteristics, detoxification process and application of Camellia oleifolia meal in animal production[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2019, 35 (11): 6946- 6954. | |
| 18 | QIAN B J , YIN L R , YAO X M , et al. Effects of fermentation on the hemolytic activity and degradation of Camellia oleifera saponins by Lactobacillus crustorum and Bacillus subtilis[J]. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 2018, 365 (7) |
| 19 | 曾斌, 唐敏, 唐伟, 等. 油茶副产物营养价值、生物活性功能及在动物养殖中的应用[J]. 饲料研究, 2023, 46 (23): 158- 162. |
| ZENG B , TANG M , TANG W , et al. The nutritional value, bioactive function and application in animal breeding of Camellia oleifera by-products[J]. Feed Research, 2023, 46 (23): 158- 162. | |
| 20 | GU M H , FAN R Y , DAI X , et al. Tannic acid induces intestinal dysfunction and intestinal microbial dysregulation in brandt's voles (Lasiopodomys brandtii)[J]. Animals (Basel), 2023, 13 (4): 586. |
| 21 |
LI Z M , LIU L , FAN Y , et al. Kinetic modeling for high voltage electrical discharge extraction based on discharge energy input[J]. Food Chem, 2020, 314, 126168.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126168 |
| 22 | 何玮. 油茶粕蛋白质的分离纯化及结构鉴定[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2019. |
| HE W. Purification and identification of protein from Camellia oleifera seed cake[D]. Haikou: Hainan Universityl, 2019. (in Chinese) | |
| 23 | 朱晓丽, 赵锦绣, 李富松, 等. 油茶籽粕发酵菌株的筛选鉴定及发酵产物特性分析[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 54 (2): 240- 250. |
| ZHU X L , ZHAO J X , LI F S , et al. Screening and identification of Camellia seed meal fermentation strains and analysis of fermentation product characteristics[J]. Journal of Northwest University(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 54 (2): 240- 250. | |
| 24 | 李梦丹, 杨伊磊, 陈力力, 等. 油茶籽粕的综合利用[J]. 粮食与油脂, 2016, 29 (1): 11- 14. |
| LI M D , YANG Y L , CHEN L L , et al. Comprehensive utilization of Camellia seed meal[J]. Cereals & Oils, 2016, 29 (1): 11- 14. | |
| 25 | 朱培, 钟海雁, 郑菲, 等. 不同油茶饼粕的营养成分比较与饲用可行性分析[J]. 经济林研究, 2011, 29 (1): 90- 93. |
| ZHU P , ZHONG H Y , ZHENG F , et al. Comparison of nutritional components and feeding feasibility analysis of different Camellia cakes[J]. Non-wood Forest Research, 2011, 29 (1): 90- 93. | |
| 26 |
SHEN S A , CHENG H R , LI X , et al. Effects of extraction methods on antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Camellia seed cake[J]. Eur Food Res Technol, 2014, 238, 1015- 1021.
doi: 10.1007/s00217-014-2183-2 |
| 27 |
谢阳姣, 何志鹏, 谢冬养, 等. 超声辅助乙醇提取油茶籽饼多酚工艺的优化[J]. 南方农业学报, 2012, 43 (4): 515- 519.
doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2012.04.515 |
|
XIE Y J , HE Z P , XIE D Y , et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted ethanol extraction of polyphenols from Camellia seed cake[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2012, 43 (4): 515- 519.
doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2012.04.515 |
|
| 28 |
ZHANG X L , MA H L , QUAISIE J , et al. Tea saponin extracted from seed pomace of Camellia oleifera Abel ameliorates DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis-like symptoms in BALB/c mice[J]. J Funct Foods, 2022, 91, 105001.
doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2022.105001 |
| 29 | 朱静, 吕静, 陈龙, 等. 超声波辅助酶法提取油茶粕蛋白工艺优化及其功能活性[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2023, 44 (18): 108- 115. |
| ZHU J , LV J , CHEN L , et al. Process optimization and functional activity of extraction of protein from Camellia oleifolia meal by ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic method[J]. Food Research and Development, 2023, 44 (18): 108- 115. | |
| 30 | 高群, 张智, 杨可心, 等. 超声波-酶法提取油茶多酚的工艺研究[J]. 中国林副特产, 2019 (5): 16- 20. |
| GAO Q , ZHANG Z , YANG K X , et al. Study on extraction of polyphenol from Camellia by ultrasonic-assisted complex enzyme method[J]. Forest by-Product and Speciality in China, 2019 (5): 16- 20. | |
| 31 | 何玮, 陈健, 赵一夫, 等. 油茶粕蛋白质提取工艺的研究[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 40 (3): 13- 19. |
| HE W , CHEN J , ZHAO Y F , et al. Study on protein extraction technology of Camellia meal[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 40 (3): 13- 19. | |
| 32 | 喻冬秀, 李晓江, 蔡斯琦, 等. 酶解法提取茶皂素的工艺研究[J]. 广东化工, 2017, 44 (13): 48- 50. |
| YU D X , LI X J , CAI S Q , et al. Sudy on the extrac-tion technology of tea saponin by enzymolysis method[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2017, 44 (13): 48- 50. | |
| 33 |
ZHANG L L , WANG Y M , WU D M , et al. Microwave-assisted extraction of polyphenols from Camellia oleifera fruit hull[J]. Molecules, 2011, 16 (6): 4428- 4437.
doi: 10.3390/molecules16064428 |
| 34 | 喻冬秀, 叶旅彬, 王秋怡, 等. 微波协同离子液体[J]. 化学试剂, 2023, 45 (5): 98- 105. |
| YU D X , YE L B , WANG Q Y , et al. Extraction of tea saponin from ionic liquid[J]. Chemical Reagents, 2023, 45 (5): 98- 105. | |
| 35 | 段丽萍, 苗丽坤, 孙炜炜, 等. 油茶多糖的提取及生物活性研究进展[J]. 粮食与油脂, 2020, 33 (11): 26- 28. |
| DUAN L P , MIAO L K , SUN W W , et al. Research progress on extraction and bioactivity of polysaccharides from Camellia oleifolia[J]. Cereals & Oils, 2019, 33 (11): 26- 28. | |
| 36 | ZHU L F , WANG S S , WAN F L , et al. Quantitative analysis of Camellia oleifera seed saponins and aqueous two-phase extraction and separation[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28 (5): 2132. |
| 37 | XIAO X M , HE L M , CHEN Y Y , et al. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects of Camellia oleifera Abel components[J]. Future Med Chem, 2017, 9 (17): 2069- 2079. |
| 38 | 黄祥元, 唐伟, 于桂阳, 等. 油茶籽粕对育肥猪生长性能、消化代谢及免疫能力的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2023 (14): 82- 85. |
| HUANG X Y , TANG W , YU G Y , et al. Effects of Camellia seed meal on growth performance, digestion, metabolism and immunity of finishing pigs[J]. China Feed, 2023 (14): 82- 85. | |
| 39 | 谭名洋, 杨媚, 王芳, 等. 糖萜素的生理功能及其在动物生产中的应用研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2022, 58 (11): 9- 13. |
| TAN M Y , YANG M , WANG F , et al. Research progress on the physiological function of saccharicterpenin and its application in animal production[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2022, 58 (11): 9- 13. | |
| 40 | 覃佐东, 全沁果, 敖艳, 等. 油茶不同部位黄酮的提取及活性研究进展[J]. 科技通报, 2016, 32 (7): 67- 71. |
| QIN Z D , QUAN Q G , AO Y , et al. The developmentsof flavonoids from differnt parts in Camellia oleifera[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2016, 32 (7): 67- 71. | |
| 41 | 古军旺, 周玉莹, 金海霞, 等. 油茶枯饼提取物主要生物活性成分及其对镉致大鼠学习记忆损伤的影响[J]. 中国油脂, 2022, 47 (3): 65- 70. |
| GU J W , ZHOU Y Y , JIN H X , et al. Main bioactive components of oil tea cake extract and their effects on learning and memory impairment induced by cadmium in rat s[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2022, 47 (3): 65- 70. | |
| 42 | 司喜艳, 王香玉, 皇甫新燕, 等. 油茶籽饼中茶皂苷的超声-微波辅助法提取工艺优化[J]. 中国油脂, 2023, 48 (7): 130- 136. |
| SI X Y , WANG X Y , HUANGFU X Y , et al. Optimi.zation on extraction technology of tea saponins from Camellia seed meal[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2023, 48 (7): 130- 136. | |
| 43 | WANG X Q , ZENG Q M , DEL MAR CONTRERAS M , et al. Profiling and quantification of phenolic compounds in Camellia seed oils: natural tea polyphenols in vegetable oil[J]. Food Res Int, 2017, 102, 184- 194. |
| 44 | 张善英, 徐鲁平, 郑丽丽, 等. 蒸汽爆破辅助提取油茶籽蛋白及其功能性质分析[J]. 中国油脂, 2019, 44 (9): 47- 53. |
| ZHANG S Y , XU L P , ZHENG L L , et al. Steam blasting assisted extraction of Camellia seed protein and its functional properties[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2019, 44 (9): 47- 53. | |
| 45 | 吴建宝, 马齐兵, 胡传荣, 等. 超声辅助水相酶法提取油茶籽油及蛋白的工艺优化[J]. 中国粮油学报, 2017, 32 (6): 91-95, 99. |
| WU J B , MA Q B , HU C R , et al. Optimization of extraction technology of Camellia oleifera seed oil and protein by ultrasonic assisted aqueous enzyme method[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2017, 32 (6): 91-95, 99. | |
| 46 | WU H , LI C Z , LI Z M , et al. Simultaneous extraction of oil and tea saponin from Camellia oleifera Abel.seeds under subcritical water conditions[J]. Fuel Process Technol, 2018, 174, 88- 94. |
| 47 | TSAI C E , LIN L H . DPPH scavenging capacity of extracts from Camellia seed dregs using polyol compounds as solvents[J]. Heliyon, 2019, 5 (8): e2315. |
| 48 | JIN X , NING Y . Antioxidant and antitumor activities of the polysaccharide from seed cake of Camellia oleifera Abel[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2012, 51 (4): 364- 368. |
| 49 | CHENG Y T , WU S L , HO C Y , et al. Beneficial effects of Camellia oil (Camellia oleifera Abel.) on ketoprofen-induced gastrointestinal mucosal damage through upregulation of HO-1and VEGF[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2014, 62 (3): 642- 650. |
| 50 | YE Y , XING H T , CHEN X L . Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of the hydrolyzed sasanquasaponins from the defatted seeds of Camellia oleifera[J]. Arch Pharm Res, 2013, 36 (8): 941- 951. |
| 51 | MATTERA R , BENVENUTO M , GIGANTI M G , et al. Effects of polyphenols on oxidative stress-mediated injury in cardiomyocytes[J]. Nutrients, 2017, 9 (5): 523. |
| 52 | YE Y , GUO Y , LUO Y T , et al. Isolation and free radical scavenging activities of a novel biflavonoid from the shells of Camellia oleifera Abel[J]. Fitoterapia, 2012, 83 (8): 1585- 1589. |
| 53 | LIU T , ZHANG L Y , JOO D , et al. NF-κB signaling in inflammation[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2017, 2, 17023. |
| 54 | LIU Y X , XIAO X M , JI L L , et al. Camellia cake extracts reduce burn injury through suppressing inflammatory responses and enhancing collagen synthesis[J]. Food Nutr Res, 2020, 64 |
| 55 | LIU X H , JIA L Y , GAO Y , et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of total flavonoids from seeds of Camellia oleifera Abel[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2014, 46 (10): 920- 922. |
| 56 | XIE C Q , LIN X Y , HU J W , et al. The polysaccharide from Camellia oleifera fruit shell enhances immune responses via activating MAPKs and NF-κB signaling pathways in RAW264.7 macrophages[J]. Food Nutr Res, 2022, 66 |
| 57 | WANG J , ZHANG M Y , GOU Z Y , et al. The effect of Camellia oleifera cake polysaccharides on growth performance, carcass traits, meat quality, blood profile, and caecum microorganisms in yellow broilers[J]. Animals (Basel), 2020, 10 (2): 266. |
| 58 | LI T T , MENG X Y , WU C E , et al. Anticancer activity of a novel glycoprotein from Camellia oleifera Abel seeds against hepatic carcinoma in vitro and in vivo[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2019, 136, 284- 295. |
| 59 | HUO G H , CHEN X T , LI Z M , et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of theasapogenol galactosides against Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. J Asian Nat Prod Res, 2018, 20 (2): 128- 138. |
| 60 | ZHANG X F , YANG S L , HAN Y Y , et al. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of triterpene saponins from tea seed pomace (Camellia oleifera Abel) and their activities against bacteria and fungi[J]. Molecules, 2014, 19 (6): 7568- 7580. |
| 61 | KUO P C , LIN T C , YANG C W , et al. Bioactive saponin from tea seed pomace with inhibitory effects against Rhizoctonia solani[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2010, 58 (15): 8618- 8622. |
| 62 | ZHANG S , LI X Z . Inhibition of alpha-glucosidase by polysaccharides from the fruit hull of Camellia oleifera Abel[J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2015, 115, 38- 43. |
| 63 | GAO J , MA L , YIN J , et al. Camellia (Camellia oleifera bel.) seed oil reprograms gut microbiota and alleviates lipid accumulation in high fat-fed mice through the mTOR pathway[J]. Food Funct, 2022, 13 (9): 4977- 4992. |
| 64 | 袁钟宇, 张石蕊, 贺喜, 等. 茶籽多糖及茶皂素对肉鸡生长性能和肠道微生物的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2010, 46 (7): 28- 31. |
| YUAN Z Y , ZHANG S R , HE X , et al. Effects of tea seed polysaccharide and tea saponin on growth performance and intestinal microorganisms of broilers[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2010, 46 (7): 28- 31. | |
| 65 | 曾李, 倪冬姣, 熊爱军, 等. 发酵茶籽粕对海兰褐蛋鸡产蛋性能、鸡蛋品质、血清生化指标和肠道菌群结构的影响[J]. 国外畜牧学(猪与禽), 2020, 40 (3): 75- 80. |
| ZENG L , NI D J , XIONG A J , et al. Effects of fermented tea seed meal on laying performance, egg quality, serum biochemical indexes and intestinal flora structure of Hy-Line Brown laying hens[J]. Animal Science Abroad(Pigs and Poultry), 2020, 40 (3): 75- 80. | |
| 66 | 陈作义, 江涛, 林晓邻, 等. 油茶粕脱茶皂素后的混菌发酵去毒工艺及饲养试验研究[J]. 广州化工, 2015, 43 (4): 77- 78. |
| CHEN Z Y , JIANG T , LIN X L , et al. Study on detoxification process and feeding experiment of mixed bacteria fermentation after tea saponin removal from Camellia seed meal[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2015, 43 (4): 77- 78. | |
| 67 | SONG D , WANG Y W , HOU Y J , et al. The effects of dietary supplementation of microencapsulated and the extract of seed on growth performance, immune functions, and serum biochemical parameters in broiler chickens[J]. J Anim Sci, 2016, 94 (8): 3271- 3277. |
| 68 | 樊庆山, 屠焰, 刁其玉, 等. 含棕榈仁粕、油茶籽粕或茶籽粕饲粮对3~5月龄犊牛生长性能、抗氧化能力及免疫性能的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2018, 54 (7): 76- 82. |
| FAN Q S , TU Y , DIAO Q Y , et al. Effects of diets containing palm kernel meal, Camellia seed meal or Camellia seed meal on growth performance, antioxidant capacity and immune performance of calves aged 3-5 months[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2018, 54 (7): 76- 82. | |
| 69 | SONG D , WANG Y W , LU Z X , et al. Effects of dietary supplementation of microencapsulated Enterococcus fecalis and the extract of Camellia oleifera seed on laying performance, egg quality, serum biochemical parameters, and cecal microflora diversity in laying hens[J]. Poult Sci, 2019, 98 (7): 2880- 2887. |
| 70 | 陈晓. 油茶粕生物饲料在肉鸡养殖中的应用研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2015. |
| CHEN X. Applied rsearch of the biological feed of Camellia oleifera seed meal in broiler breeding[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese) | |
| 71 | 岳龙, 叶小飞, 周玥, 等. 水酶法茶粕作为猪饲粮原料的试验效果研究[J]. 饲料工业, 2016, 37 (2): 42- 46. |
| YUE L , YE X F , ZHOU Y , et al. Experimental effect of water enzymatic method on tea meal as feed material for pigs[J]. Feed Industry, 2016, 37 (2): 42- 46. | |
| 72 | 朱良, 张石蕊, 贺喜, 等. 茶籽提取物对生长猪生长性能及血清生化指标的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2010 (17): 12- 14. |
| ZHU L , ZHANG S R , HE X , et al. Effects of tea seed extract on growth performance and serum biochemical indices of growing pigs[J]. China Feed, 2010 (17): 12- 14. | |
| 73 | 李媛, 刁其玉, 王世琴, 等. 2种粉碎粒度饼粕类饲料的瘤胃降解特性研究[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2017, 53 (12): 61-66, 118. |
| LI Y , DIAO Q Y , WANG S Q , et al. Study on rumen degradation characteristics of two kinds of crushed particle size cake feed[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2017, 53 (12): 61-66, 118. | |
| 74 | 武月雷, 陈忠法, 王佳堃. 油茶籽粕反刍动物饲料化利用价值初探[J]. 中国粮油学报, 2017, 32 (10): 111- 117. |
| WU Y L , CHEN Z F , WANG J K . Preliminary study on the utilization value of Camellia seed meal as ruminant feed[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2017, 32 (10): 111- 117. |
| [1] | 吴俊杰, 吕世明, 龙小霞, 王忠, 王立琦. 中药及活性成分抗耐药菌作用及其机制研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(4): 1632-1647. |
| [2] | 王恒泰, 吕浪, 蒋卉, 程君生, 刘铭赫, 储岳峰, 许健, 李朋, 丁家波. 牛种布鲁氏菌MgtC蛋白在抵抗低Mg2+环境中的生物学功能研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(1): 365-377. |
| [3] | 牛晓雨, 邢媛媛, 李大彪. 植物活性成分对动物肠道屏障功能的调控作用及其机制[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(4): 1467-1477. |
| [4] | 李艺璇, 牛静轶, 李港, 万超, 方仁东, 叶超. 伪狂犬病病毒编码的内膜蛋白生物学功能研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(3): 957-970. |
| [5] | 刘强, 牛小霞, 方敏, 刘艳玲, 高辉, 陈吉祥, 加华才让, 张思浓, 李勇. 牛冠状病毒刺突蛋白研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(3): 944-956. |
| [6] | 钟朱夏, 胡修忠, 向敏, 余婕, 刘辰晖, 赵胜兰, 万平民, 王定发, 周源, 程蕾. 妊娠相关糖蛋白的生物学功能及其在畜牧生产中的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(3): 874-881. |
| [7] | 郭艳丽, 李可强, 白少川, 王涛, 王德贺, 王麒, 李兰会. ALV-E的结构、活性调控以及对宿主功能的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(7): 2683-2691. |
| [8] | 夏春秋, 万发春, 刘磊, 沈维军, 肖定福. 缬氨酸的生物学功能及其在畜禽日粮中的应用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(11): 4502-4513. |
| [9] | 郭海康, 万发春, 沈维军, 王祚. 畜禽消化道细菌群体感应及相关调控技术研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53(6): 1678-1688. |
| [10] | 郑晓楠, 李婷婷, 王金磊, 郑文斌, 朱兴全. 弓形虫致密颗粒蛋白的生物学功能研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53(10): 3345-3357. |
| [11] | 王卫振, 邓占钊, 辛国省, 蔡正云, 顾亚玲, 张娟. 环状RNA的生物学功能及其在家禽中的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2021, 52(7): 1778-1788. |
| [12] | 刘一冰, 吴德群, 蔺哲广, 吉挺. 蜂王浆生物学功能研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2021, 52(6): 1498-1510. |
| [13] | 张然然, 刘华淼, 王洪亮, 李洋, 邢秀梅. 基于label-free技术的梅花鹿(Cervus nippon)茸角蛋白组分比较[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2019, 50(10): 2005-2012. |
| [14] | 张进威,龙科任,王讯,李明洲,马继登. 环状RNA研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2016, 47(11): 2151-2158. |
| [15] | 张松林,沈志强,刘磊,马永彪,刘吉山. 猪繁殖与呼吸综合征病毒结构和非结构蛋白生物学功能研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2012, 43(11): 1683-1696. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
