





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (10): 4863-4876.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.10.009
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Hengtai( ), JIANG Hui, LI Peng*(
), JIANG Hui, LI Peng*( ), DING Jiabo*(
), DING Jiabo*( )
)
Received:2025-01-10
Online:2025-10-23
Published:2025-11-01
Contact:
LI Peng, DING Jiabo
E-mail:17861509833@163.com;lipeng01@caas.cn;dingjiabo@caas.cn
CLC Number:
WANG Hengtai, JIANG Hui, LI Peng, DING Jiabo. Biosynthesis of Brucella Lipopolysaccharides and Their Biological Functions in Immune Evasion[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(10): 4863-4876.
Table 1
Comparison of homology between Brucella lipid A-related synthesis proteins and other gram-negative bacteria %"
| 蛋白 Protein | 与铜绿假单胞菌相似性 Similarity with Pseudomonas | 与沙门菌相似性 Similarity with Salmonella |
| LpxA | 38.43 | 39.22 |
| LpxC | 43.11 | 39.22 |
| LpxD | 38.30 | 37.74 |
| LpxB | 32.44 | 32.58 |
| LpxK | 36.49 | 34.81 |
| LpxL | 36.49 | 34.81 |
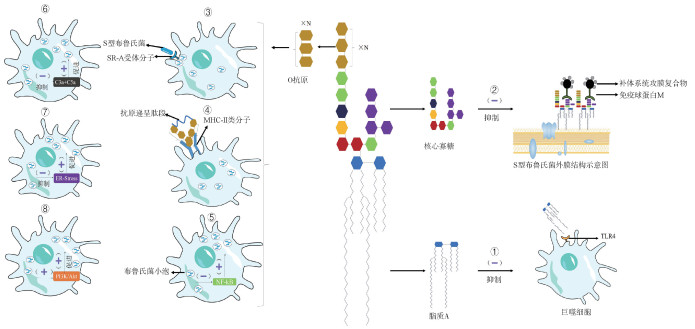
Fig. 1
Schematic diagram of the hypothetical biosynthesis process of Brucella LPS M6P. Mannose-6-phosphate; M1P.Mannose-1-phosphate; GDP-M. Guanosine diphosphate-mannose; GDP-G. Guanosine diphosphate-glucose; GDP-4-keto-6-dMan. Guanosine diphosphate-4-keto-6-deoxy-D-mannose; GDP-4-amino-4, 6-dMan. Guanosine diphosphate-4-amino-4, 6-dideoxy-D-mannose; GDP-Perosamine. Guanosine diphosphate-4-amino-4, 6-dideoxy-D-mannose"
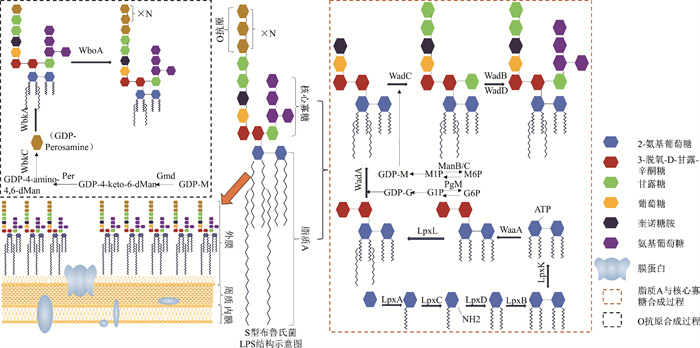
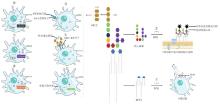
Fig. 2
The mechanism diagram of LPS in the immune evasion process of Brucella(S type) ①The long acyl chains of Brucella S-type LPS lipid A inhibit the recognition and binding of host TLR4/MD-2;②The low levels of phosphorylation and glycosylation of the core oligosaccharide of Brucella S-type LPS inhibit the binding of complement C1q;③The O-antigen of Brucella S-type LPS can bind to the scavenger receptor SR-A on host cell membranes, preventing early fusion with lysosomes, thereby ensuring the early survival of Brucella inside the cells; ④The O-antigen can spatially hinder the presentation process of MHC-Ⅱ, reducing the efficiency of antigen presentation; ⑤The O-antigen limits the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, promoting the survival of Brucella within cells; ⑥The O-antigen inhibits the formation of C3 convertase, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and decreasing complement-mediated lysis, which facilitates Brucella survival within cells; ⑦The O-antigen suppresses the ER-Stress signaling pathway, benefiting Brucella's survival inside the cells; ⑧The O-antigen activates the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in macrophages, promoting the survival of infected cells, which further enhances Brucella survival within cells. Here, C3a + C5a refers to the active peptides produced during the complement activation process—complement C3a and C5a fragments. PI3K/Akt refers to the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and protein kinase B (Akt) pathway, which is crucial for regulating cellular processes such as growth, metabolism, and survival. ER-Stress describes a state where the endoplasmic reticulum function is disrupted or damaged. As a response mechanism, cells initiate adaptive processes to restore ER homeostasis, ensuring proper protein folding and normal cellular function. NF-κB refers to a family of transcription factors involved in immune responses, inflammation, cell proliferation, survival, and stress reactions"
| 1 |
HUSSAIN A , HUSSAIN S , CHAUDHRY M , et al. Prevalence and herd-level risk factors associated with Brucella infection in small holders keeping large ruminants[J]. Res Vet Sci, 2025, 183, 105506.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2024.105506 |
| 2 |
QIN Y , ZHOU G , JIAO F , et al. Brucella mediates autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis to escape host killing[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2024, 14, 1408407.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1408407 |
| 3 | 王恒泰, 吕浪, 蒋卉, 等. 牛种布鲁氏菌MgtC蛋白在抵抗低Mg2+环境中的生物学功能研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56 (1): 365- 377. |
| WANG H T , LV L , JIANG H , et al. Biological function of MgtC protein in Brucella abortus in response to low Mg2+ environment[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56 (1): 365- 377. | |
| 4 |
LAPAQUE N , MORIYON I , MORENO E , et al. Brucella lipopolysaccharide acts as a virulence factor[J]. Curr Opin Microbiol, 2005, 8 (1): 60- 66.
doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2004.12.003 |
| 5 |
ZHAO Y , HANNIFFY S , ARCE-GORVEL V , et al. Immunomodulatory properties of Brucella melitensis lipopolysaccharide determinants on mouse dendritic cells in vitro and in vivo[J]. Virulence, 2018, 9 (1): 465- 479.
doi: 10.1080/21505594.2017.1386831 |
| 6 | MARCOS M . Smooth to rough dissociation in Brucella: The missing link to virulence[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2015, 5, 98. |
| 7 | AHMED M E , MOHAMED E I , RAMADAN K M , et al. Evaluation of the immunization of camels with Brucella abortus vaccine (RB51) in Egypt[J]. Open Vet J, 2024, 14 (1): 19- 24. |
| 8 |
CAI G H , GUO C Y , GUO K X , et al. Development of a competitive ELISA based on Brucella neotomae lipopolysaccharide for detecting brucellosis in livestock[J]. Anal Biochem, 2025, 703, 115880.
doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2025.115880 |
| 9 |
FUREVI A , UDEKWU K I , WIDMALM G . Structural elucidation of the O-antigen polysaccharide from Escherichia coli O125ac and biosynthetic aspects thereof[J]. Glycobiology, 2022, 32 (12): 1089- 1100.
doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwac061 |
| 10 |
BROWN H A , VINOGRADOV E , GILBERT M , et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex has a pathway for the biosynthesis of 4-formamido-4, 6-dideoxy-d-glucose[J]. Protein Sci, 2018, 27 (8): 1491- 1497.
doi: 10.1002/pro.3443 |
| 11 |
BUNDLE D R , CHERWONOGRODZKY J W , GINDNEY M A , et al. Definition of Brucella A and M epitopes by monoclonal typing reagents and synthetic oligosaccharides[J]. Infect Immun, 1989, 57 (9): 2829- 2836.
doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2829-2836.1989 |
| 12 |
BUNDLE D R , CHERWONOGRODZKY J W , PERRY M B . Structural elucidation of the Brucella melitensis M antigen by high-resolution NMR at 500 MHz[J]. Biochemistry, 1987, 26 (26): 8717- 8726.
doi: 10.1021/bi00400a034 |
| 13 |
WANG J , MA W , FANG Y , et al. Core oligosaccharide portion of lipopolysaccharide plays important roles in multiple antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2021, 65 (10): e0034121.
doi: 10.1128/AAC.00341-21 |
| 14 |
BAI Q , LI H , WU X , SHAO J , et al. Comparative analysis of the main outer membrane proteins of Brucella in the diagnosis of brucellosis[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2021, 560, 126- 131.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.04.127 |
| 15 |
FERGUSON G P , DATTA A , BAUMGARTNER J , et al. Similarity to peroxisomal-membrane protein family reveals that Sinorhizobium and Brucella BacA affect lipid-A fatty acids[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2004, 101 (14): 5012- 5017.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307137101 |
| 16 | MORIYÓN I , LÓPEZ-GOÑI I . Structure and properties of the outer membranes of Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis[J]. Int Microbiol, 1998, 1 (1): 19- 26. |
| 17 |
FONTANA C , CONDE-ÁLVAREZ R , STÁHLE J , et al. Structural studies of lipopolysaccharide-defective mutants from Brucella melitensis identify a core oligosaccharide critical in virulence[J]. J Biol Chem, 2016, 291 (14): 7727- 7741.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.701540 |
| 18 |
KAWAHARA K . Variation, modification and engineering of lipid A in endotoxin of gram-negative bacteria[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22 (5): 2281.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22052281 |
| 19 |
MORENO E , STACKEBRANDT E , DORSCH M , et al. Brucella abortus16S rRNA and lipid A reveal a phylogenetic relationship with members of the alpha-2 subdivision of the class proteobacteria[J]. J Bacteriol, 1990, 172 (7): 3569- 3576.
doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3569-3576.1990 |
| 20 |
ROJAS N , FREER E , WEINTRAUB A , et al. Immunochemical identification of Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharide epitopes[J]. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol, 1994, 1 (2): 206- 213.
doi: 10.1128/cdli.1.2.206-213.1994 |
| 21 |
ZHANG J D , WANG Q , HU H X , et al. Brucella lipopolysaccharide deficiency with lipid A induces robust T cells immune response[J]. Mol Immunol, 2025, 182, 11- 19.
doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2025.03.006 |
| 22 |
CASABUONO A C , CZIBENERr C , DEL GIUDICE MG , et al. New features in the lipid A structure of Brucella suis and Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharide[J]. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom, 2017, 28 (12): 2716- 2723.
doi: 10.1007/s13361-017-1805-x |
| 23 |
REEVES P R , HOBBS M , VALVANO M A , et al. Bacterial polysaccharide synthesis and gene nomenclature[J]. Trends Microbiol, 1996, 4 (12): 495- 503.
doi: 10.1016/S0966-842X(97)82912-5 |
| 24 | 张敏, 刘宗平, 于圣青. 布鲁氏菌脂多糖及其突变株的研究进展[J]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2013, 21 (3): 80- 86. |
| ZHANG M , LIU Z P , YU S Q . Research progress on Brucella lipopolysaccharides and its mutant strains[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Infectious Diseases, 2013, 21 (3): 80- 86. | |
| 25 |
MORONA R , STROEHER U H , KARAGEORGOS L E , et al. A putative pathway for biosynthesis of the O-antigen component, 3-deoxy-L-glycero-tetronic acid, based on the sequence of the vibrio cholerae O1 rfb region[J]. Gene, 1995, 166 (1): 19- 31.
doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00588-9 |
| 26 | 易德武. 羊种布鲁氏菌015株gmd、per和manb缺失株的构建及诊断抗原反应原性评价研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2015. |
| YI D W. Construction of gmd, per, and manb deletion mutants of Brucella ovis strain 015 and evaluation of diagnostic antigen reactogenicity[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2015. (in Chinese) | |
| 27 | 徐锦凤, 王震, 马旭升, 等. 布鲁氏菌脂多糖蛋白ManB和GMD的免疫原性比较[C]//中国兽医病理学2017年学术研讨会暨兽医病理学分会第九次全国会员代表大会. 锦州, 2017. |
| XU J F, WANG Z, MA X S, et al. Comparative immunogenicity of Brucella lipopolysaccharide proteins ManB and GMD[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 Academic Symposium on Veterinary Pathology and the 9th National Member Congress of the Veterinary Pathology Branch. Jinzhou, Liaoning, China, 2017. (in Chinese) | |
| 28 | CHAUDHURI P, SAMINATHAN M, ALI S A, et al. Immunization with Brucella abortus S19Δper conferred protection in water buffaloes against virulent challenge with B. abortus strain S544[J]. Vaccines (Basel), 2021, 9(12): 1423. |
| 29 | HANWEI J, NIE X, ZHU H, et al. miR-146b-5p plays a critical role in the regulation of autophagy in Δper Brucella melitensis-infected RAW264.7 cells[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 1953242. |
| 30 |
RIEGERT A S , CHANTIGIAN D P , THODEN J B , et al. Biochemical characterization of WbkC, an N-formyltransferase from Brucella melitensis[J]. Biochemistry, 2017, 56 (28): 3657- 3668.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00494 |
| 31 | DABRAL N, JAIN-GUPTA N, SELEEM M N, et al. Overexpression of Brucella putative glycosyltransferase WbkA in B. abortus RB51 leads to production of exopolysaccharide[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2015, 5: 54. |
| 32 |
LI Z Q , SHI J X , FU W D , et al. A Brucella melitensis M5-90 wboA deletion strain is attenuated and enhances vaccine efficacy[J]. Mol Immunol, 2015, 66 (2): 276- 283.
doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.04.004 |
| 33 |
VEMULAPALLI R , HE Y , BUCCOLO L S , et al. Complementation of Brucella abortus RB51 with a functional wboA gene results in O-antigen synthesis and enhanced vaccine efficacy but no change in rough phenotype and attenuation[J]. Infect Immun, 2000, 68 (7): 3927- 3932.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.7.3927-3932.2000 |
| 34 |
WANG X R , YAN G M , ZHANG R , et al. Immunogenic response induced by wzm and wzt gene deletion mutants from Brucella abortus S19[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2014, 9 (2): 653- 658.
doi: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1810 |
| 35 |
ALAIMO C , CATREIN I , MORF L , et al. Two distinct but interchangeable mechanisms for flipping of lipid-linked oligosaccharides[J]. Embo J, 2006, 25 (5): 967- 976.
doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601024 |
| 36 | 王秀然. 布鲁氏菌wzm/wzt基因对其毒力、免疫原性及蛋白质表达影响的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014. |
| WANG X R. The role of wzm/wzt gene on virulence, immunologicity, and protein expression of Brucella[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2014. (in Chinese) | |
| 37 |
CARDOSO P G , MACEDO G C , AZEVEDO V , et al. Brucella spp noncanonical LPS: structure, biosynthesis, and interaction with host immune system[J]. Microb Cell Fact, 2006, 5, 13.
doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-5-13 |
| 38 |
CZIBENER C , REY SERANTES D A , ROMANI A M , et al. Bm delta-pgm, a vaccine for the control of Brucella melitensis with cross-species protective properties[J]. Vaccine, 2023, 41 (23): 3534- 3543.
doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.04.076 |
| 39 |
UGALDE J E , CZIBENER C , FELDMAN M F , et al. Identification and characterization of the Brucella abortus phosphoglucomutase gene: role of lipopolysaccharide in virulence and intracellular multiplication[J]. Infect Immun, 2000, 68 (10): 5716- 5723.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.10.5716-5723.2000 |
| 40 |
ZHANG Y , LI T , ZHANG J , et al. The Brucella melitensis M5-90 phosphoglucomutase (PGM) mutant is attenuated and confers protection against wild-type challenge in BALB/c mice[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2016, 32 (4): 58.
doi: 10.1007/s11274-016-2015-6 |
| 41 |
ZHANG J , YIN S , YI D , et al. The Brucella melitensis M5-90ΔmanB live vaccine candidate is safer than M5-90 and confers protection against wild-type challenge in BALB/c mice[J]. Microb Pathog, 2017, 112, 148- 155.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.09.016 |
| 42 |
ZYGMUNT M S , BLASCO J M , LETESSON J J , et al. DNA polymorphism analysis of Brucella lipopolysaccharide genes reveals marked differences in O-polysaccharide biosynthetic genes between smooth and rough Brucella species and novel species-specific markers[J]. BMC Microbiol, 2009, 9, 92.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-92 |
| 43 |
MONREAL D , GRILLÓ M J , GONZÁLEZ D , Et al . Characterization of Brucella abortus O-polysaccharide and core lipopolysaccharide mutants and demonstration that a complete core is required for rough vaccines to be efficient against Brucella abortus and Brucella ovis in the mouse model[J]. Infect Immun, 2003, 71 (6): 3261- 3271.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.6.3261-3271.2003 |
| 44 |
WEN L , ZHENG Y , LI T , et al. Enzymatic synthesis of 3-deoxy-d-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO) and its application for LPS assembly[J]. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2016, 26 (12): 2825- 2828.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.04.061 |
| 45 |
ELAMIN A A , STEINICKE S , OEHLMANN W , et al. Novel drug targets in cell wall biosynthesis exploited by gene disruption in Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12 (10): e0186801.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186801 |
| 46 | SOLER-LLORÉNS P , GIL-RAMÍREZ Y , ZABALZA-BARANGUÁ A , et al. Mutants in the lipopolysaccharide of Brucella ovis are attenuated and protect against B. ovis infection in mice[J]. Vet Res, 2014, 45, 72. |
| 47 |
GIL-RAMÍREZ Y , CONDE-ÁLVAREZ R , PALACIOS-CHAVES L , et al. The identification of wadB, a new glycosyltransferase gene, confirms the branched structure and the role in virulence of the lipopolysaccharide core of Brucella abortus[J]. Microb Pathog, 2014, 73, 53- 59.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2014.06.002 |
| 48 |
SALVADOR-BESCÓS M , GIL-RAMÍREZ Y , ZÚÑIGA-RIPA A , et al. WadD, a new Brucella lipopolysaccharide core glycosyltransferase identified by genomic search and phenotypic characterization[J]. Front Microbiol, 2018, 9, 2293.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02293 |
| 49 |
IZQUIERDO L , ABITIU N , CODERCH N , et al. The inner-core lipopolysaccharide biosynthetic waaE gene: function and genetic distribution among some Enterobacteriaceae[J]. Microbiology (Reading), 2002, 148, 3485- 3496.
doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-11-3485 |
| 50 | HONE D M , POWELL J , CROWLEY R W , et al. Lipopolysaccharide from an Escherichia coli htrB msbB mutant induces high levels of MIP-1 alpha and MIP-1 beta secretion without inducing TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta[J]. J Hum Virol, 1998, 1 (4): 251- 256. |
| 51 | EMIOLA A , GEORGE J , ANDREWS S S . A complete pathway model for lipid A biosynthesis in Escherichia coli[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 10 (4): e0121216. |
| 52 |
ZHAO M , ZHU Y , WANG H , et al. Efficient production of N-acetylneuraminic acid in Escherichia coli based on the UDP-N-acetylglucosamine biosynthetic pathway[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2023, 71 (28): 10701- 10709.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c02432 |
| 53 |
BRANDTZAEG P . Host response to Neisseria meningitidis lacking lipopolysaccharides[J]. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther, 2003, 1 (4): 589- 596.
doi: 10.1586/14787210.1.4.589 |
| 54 |
SHARMA S , BANERJEE T , YADAV G , et al. Mutations at novel sites in pmrA/B and lpxA/D genes and absence of reduced fitness in colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii from a tertiary care hospital, India[J]. Microb Drug Resist, 2021, 27 (5): 628- 636.
doi: 10.1089/mdr.2020.0023 |
| 55 |
KUMAR PAL S , KUMAR S . LpxC (UDP-3-O-(R-3-hydroxymyristoyl)-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase) inhibitors: A long path explored for potent drug design[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2023, 234, 122960.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.179 |
| 56 |
KRAUSE K M , HAGLUND C M , HEBNER C , et al. Potent LpxC inhibitors with in vitro activity against multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2019, 63 (11): e00977-19.
doi: 10.1128/AAC.00977-19 |
| 57 |
BARTLING C M , RAETZ C R . Crystal structure and acyl chain selectivity of Escherichia coli LpxD, the N-acyltransferase of lipid A biosynthesis[J]. Biochemistry, 2009, 48 (36): 8672- 8683.
doi: 10.1021/bi901025v |
| 58 |
ALTINOK I , OZTURK R C , KAHRAMAN U C , et al. Protection of rainbow trout against yersiniosis by lpxD mutant Yersinia ruckeri[J]. Fish Shellfish Immunol, 2016, 55, 21- 27.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.04.018 |
| 59 |
BOHL H O , SHI K , LEE J K , et al. Crystal structure of lipid A disaccharide synthase LpxB from Escherichia coli[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9 (1): 377.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02712-9 |
| 60 |
METZGER L E , RAETZ C R . Purification and characterization of the lipid A disaccharide synthase (LpxB) from Escherichia coli, a peripheral membrane protein[J]. Biochemistry, 2009, 48 (48): 11559- 11571.
doi: 10.1021/bi901750f |
| 61 |
EMPTAGE R P , PEMBLE C W , YORK J D , et al. Mechanistic characterization of the tetraacyldisaccharide-1-phosphate 4'-kinase LpxK involved in lipid A biosynthesis[J]. Biochemistry, 2013, 52 (13): 2280- 2290.
doi: 10.1021/bi400097z |
| 62 |
WEI J R , RICHIE D L , MOSTAFAVI M , et al. LpxK is essential for growth of Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606: Relationship to toxic accumulation of lipid A pathway intermediates[J]. mSphere, 2017, 2 (4): e00199-17.
doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00199-17 |
| 63 |
WU J , JIANG L , SHAO Q , et al. Comparison of the safety and efficacy of the wild-type and lpxL/lpxM mutant inactivated vaccine against the avian pathogenic Escherichia coli O1, O2, and O78 challenge[J]. Vaccine, 2024, 42 (10): 2707- 2715.
doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.03.038 |
| 64 |
GORZELAK P , KLEIN G , RAINA S . Molecular basis of essentiality of early critical Steps in the lipopolysaccharide biogenesis in Escherichia coli K-12: Requirement of MsbA, Cardiolipin, LpxL, LpxM and GcvB[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22 (10): 5099.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22105099 |
| 65 |
ZHU L , LI Y , WANG J , et al. Identification of two secondary acyltransferases of lipid A in Pseudomonas putida KT2442[J]. J Appl Microbiol, 2017, 123 (2): 478- 490.
doi: 10.1111/jam.13499 |
| 66 |
FISSEHA M , CHEN P , BRANDT B , et al. Characterization of native outer membrane vesicles from lpxL mutant strains of Neisseria meningitidis for use in parenteral vaccination[J]. Infect Immun, 2005, 73 (7): 4070- 4080.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.7.4070-4080.2005 |
| 67 |
OKUDA S , SHERMAN D J , SILHAVY T J , et al. Lipopolysaccharide transport and assembly at the outer membrane: the PEZ model[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2016, 14 (6): 337- 345.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.25 |
| 68 |
SALMON-DIVON M , KORNSPAN D . Transcriptomic analysis of smooth versus rough Brucella melitensis Rev.1 vaccine strains reveals insights into virulence attenuation[J]. Int J Med Microbiol, 2020, 310 (1): 151363.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2019.151363 |
| 69 |
MANTEROLA L , MORIYóN I , MORENO E , et al. The lipopolysaccharide of Brucella abortus BvrS/BvrR mutants contains lipid A modifications and has higher affinity for bactericidal cationic peptides[J]. J Bacteriol, 2005, 187 (16): 5631- 5639.
doi: 10.1128/JB.187.16.5631-5639.2005 |
| 70 |
FERNANDEZ-PRADA C M , NIKOLICH M , VEMULAPALLI R , et al. Deletion of wboA enhances activation of the lectin pathway of complement in Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis[J]. Infect Immun, 2001, 69 (7): 4407- 4416.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.7.4407-4416.2001 |
| 71 |
KIM S , WATARAI M , SUZUKI H , et al. Lipid raft microdomains mediate class A scavenger receptor-dependent infection of Brucella abortus[J]. Microb Pathog, 2004, 37 (1): 11- 19.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2004.04.002 |
| 72 |
ZHANG M , HAN X , LIU H , et al. Inactivation of the ABC transporter ATPase gene in Brucella abortus strain 2308 attenuated the virulence of the bacteria[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2013, 164 (3-4): 322- 329.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.02.017 |
| 73 |
PEI J , TURSE J E , FICHT T A . Evidence of Brucella abortus OPS dictating uptake and restricting NF-kappaB activation in murine macrophages[J]. Microbes Infect, 2008, 10 (6): 582- 590.
doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2008.01.005 |
| 74 |
LI P , TIAN M , BAO Y , et al. Brucella rough mutant induce macrophage death via activating IRE1α pathway of endoplasmic reticulum stress by enhanced T4SS secretion[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2017, 7, 422.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00422 |
| 75 |
刘爱军, 黄晓兵, 张传亮, 等. 布鲁氏菌与宿主天然免疫信号通路相互作用的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56 (4): 1561- 1574.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.04.009 |
|
LIU A J , HUANG X B , ZHANG C L , et al. Progress on the interactions of Brucella with host innate immunity signaling pathways[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56 (4): 1561- 1574.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.04.009 |
|
| 76 |
EISENSCHENK F C , HOULE J J , HOFFMANN E M . Mechanism of serum resistance among Brucella abortus isolates[J]. Vet Microbiol, 1999, 68 (3-4): 235- 244.
doi: 10.1016/S0378-1135(99)00075-9 |
| 77 | HAJIZADEH SISAKHT B , KHALEDI M , AFKHAMI H , et al. Bactericidal activity of serum by Brucella Abortus RB51 outer membrane protein's combined by Brucella Abortus S99 lipopolysaccharide induction[J]. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol, 2024, 16 (3): 187- 192. |
| 78 |
BARQUERO-CALVO E , CHAVES-OLARTE E , WEISS D S , et al. Brucella abortus uses a stealthy strategy to avoid activation of the innate immune system during the onset of infection[J]. PLoS One, 2007, 2 (7): e631.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000631 |
| 79 | 尤留超, 尹号, 陶政宇, 等. 布鲁氏菌毒力因子与胞内存活机制研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56 (4): 1575- 1593. |
| YOU L C , YIN H , TAO Z Y , et al. Research progress in the virulence factors and intracellular survival mechanism of Brucella[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56 (4): 1575- 1593. | |
| 80 |
CAMPOS M A , ROSINHA G M , ALMEIDA I C , et al. Role of Toll-like receptor 4 in induction of cell-mediated immunity and resistance to Brucella abortus infection in mice[J]. Infect Immun, 2004, 72 (1): 176- 186.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.1.176-186.2004 |
| 81 |
SCHMIDINGER B , PETRI K , LETTL C , et al. Helicobacter pylori binds human annexins via lipopolysaccharide to interfere with Toll-like receptor 4 signaling[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2022, 18 (2): e1010326.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010326 |
| 82 |
DUEÑAS A I , ORDUÑA A , CRESPO M S , et al. Interaction of endotoxins with Toll-like receptor 4 correlates with their endotoxic potential and may explain the proinflammatory effect of Brucella spp. LPS[J]. Int Immunol, 2004, 16 (10): 1467- 1475.
doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh148 |
| 83 |
BARQUERO-CALVO E , MORA-CARTíN R , ARCE-GORVEL V , et al. Brucella abortus induces the premature death of human neutrophils through the action of its lipopolysaccharide[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2015, 11 (5): e1004853.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004853 |
| 84 |
LI Z , ZHANG H , ZHANG J , et al. Brucella abortus phosphoglyceromutase and dihydrodipicolinate reductase induce Th1 and Th2-related immune responses[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2018, 34 (2): 22.
doi: 10.1007/s11274-017-2405-4 |
| 85 |
CLOECKAERT A , WEYNANTS V , GODFROID J , et al. O-polysaccharide epitopic heterogeneity at the surface of Brucella spp. studied by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and flow cytometry[J]. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol, 1998, 5 (6): 862- 870.
doi: 10.1128/CDLI.5.6.862-870.1998 |
| 86 |
SURENDRAN N , HILTBOLD E M , HEID B , et al. Role of TLRs in Brucella mediated murine DC activation in vitro and clearance of pulmonary infection in vivo[J]. Vaccine, 2012, 30 (8): 1502- 1512.
doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.12.036 |
| 87 |
LI X , HE Y . Caspase-2-dependent dendritic cell death, maturation, and priming of T cells in response to Brucella abortus infection[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7 (8): e43512.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043512 |
| 88 |
BARRIONUEVO P , CASSATARO J , DELPINO M V , et al. Brucella abortus inhibits major histocompatibility complex class Ⅱ expression and antigen processing through interleukin-6 secretion via Toll-like receptor 2[J]. Infect Immun, 2008, 76 (1): 250- 262.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.00949-07 |
| 89 |
STRANAHAN L W , ARENAS-GAMBOA A M . When the going gets rough: The significance of Brucella lipopolysaccharide phenotype in host-pathogen interactions[J]. Front Microbiol, 2021, 12, 713157.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.713157 |
| 90 |
IM Y B , PARK W B , JUNG M , et al. Evaluation of Th1/Th2-related immune response against recombinant proteins of Brucella abortus infection in mice[J]. J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2016, 26 (6): 1132- 1139.
doi: 10.4014/jmb.1512.12046 |
| 91 |
SWEENEY R P , LOWARY T L . New insights into lipopolysaccharide assembly and export[J]. Curr Opin Chem Biol, 2019, 53, 37- 43.
doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2019.07.004 |
| [1] | LIU Yuxin, CHEN Si, GAO Yang, GU Deyuan, PENG Haitao, ZHANG Dong, ZHANG Ru, XU Huihui, LIU Yaqiao, YANG Yanling. Proteomic Analysis and Immunogenicity Evaluation of Outer Membrane Vesicles of Brucella melitensis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3378-3389. |
| [2] | LIU Aijun, HUANG Xiaobing, ZHANG Chuanliang, ZHANG Hongli. Progress on the Interactions of Brucella with Host Innate Immunity Signaling Pathways [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1561-1574. |
| [3] | YOU Liuchao, YIN Hao, TAO Zhengyu, HUANG Rong, FU Lei, CHU Yuefeng. Research Progress in the Virulence Factors and Intracellular Survival Mechanism of Brucella [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1575-1593. |
| [4] | WU Tingting, GUAN Feihu, GUO Jia, ZHANG Lu, ZHU Dexin, SUN Zhihua, CAO Shuzhu, XU Yimei, ZHANG Hui, DENG Xingmei. Construction of Brucella Secretory Protein BPE005 Deletion Strain and Its Effect on GPR126/ADGRG6 Protein [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(10): 5104-5114. |
| [5] | ZHANG Yunlong, WANG Jinglei, ZHU Yajie, ZHANG Mingjie, KANG Ao, ZHOU Xiang, WEI Kai, CAO Hongfang, LI Qiang, WANG Yong, SU Feng. Establishment and Application of a Nucleic Acid Detection Method for Brucella based on RAA-DETECTOR System [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(10): 5115-5124. |
| [6] | XU Zhenyu, DENG Xiaoyu, WANG Yueli, SUN Can, WU Aodi, CAO Jian, YI Jihai, WANG Yong, WANG Zhen, CHEN Chuangfu. Biological Characteristics of Brucella abortus A19ΔBtpA Deletion Strain and Its Immunogenicity Study [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2135-2145. |
| [7] | WU Shangjie, LUAN Yuanyuan, WANG Mingkun, ZHANG Hechun, YU Bo, MA Yuehui, JIANG Lin, HE Xiaohong. Advances of Disease-Resistant Breeding on Ovine Brucellosis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 882-893. |
| [8] | ZHAI Yunyi, YUAN Ye, LI Junmei, TIAN Lulu, DIAO Ziyang, LI Bin, CHEN Jialu, ZHOU Dong, JIN Yaping, WANG Aihua. Preparation and Preliminary Application of Monoclonal Antibody to Brucella Outer Membrane Protein 16 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 2083-2091. |
| [9] | LONG Qinqin, WEI Min, WANG Yuting, WEN Ming, PANG Feng. The Battle between Orf Virus and Host: Immune Response and Viral Immune Evasion Mechanisms [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 1845-1853. |
| [10] | XIANG Caixia, WANG Xiangguo, LI Junmei, ZHI Feijie, FANG Jiaoyang, ZHENG Weifang, CHEN Jialu, JIN Yaping, WANG Aihua. The Influence of Brucella Type IV Secretes System Effector Protein VceC on Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Gonadal Hormone Secretory in Goat Trophoblast Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(3): 1210-1220. |
| [11] | WANG Yang, CUI Shuai, XIN Ting, WANG Xixi, YU Hainan, CHEN Shiyu, JIANG Yajun, GAO Xintao, PANG Zhongbao, JIANG Yitong, GUO Xiaoyu, JIA Hong, ZHU Hongfei. ASFV MGF360-14L Interacts with MAVS and Inhibit the Expression of Type Ⅰ Interferon [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(9): 3272-3278. |
| [12] | FENG Xin, WANG Mingshu, CHENG Anchun. The Role of Alpha Herpesvirus Envelope Glycoprotein C on Virus Infection and Replication [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(9): 2867-2876. |
| [13] | LI Yang, ZHOU Dong, YIN Yanlong, ZHANG Guangdong, XIANG Caixia, ZHI Feijie, BAI Furong, LIN Pengfei, JIN Yaping, WANG Aihua. Effects of Brucella Outer Membrane Protein 16 on Apoptosis and Immune Activity of RAW264.7 Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(8): 2642-2651. |
| [14] | YANG Qin, DENG Xiaoyu, XIE Shanshan, YI Jihai, WANG Yong, ZHANG Qian, WANG Zhen, CHEN Chuangfu. Effects of Brucella bovis Type IV Secretion System on Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis of Macrophages [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(4): 1192-1200. |
| [15] | WANG Fei, YANG Jie, Lü Qingjie, WANG Mixue, LIU Peng, ZHANG Ruoyu, SHI Congcong, WANG Xueying, LIN Lin, HUA Lin, SONG Wenbo, LIANG Wan, CHEN Huanchun, WU Bin, PENG Zhong. Isolation and Genomic Characterization of a Meningitis Causing Pasteurella multocida [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(12): 4346-4355. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||