





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 2340-2352.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.05.031
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Jinxiang( ), SU Jinbo, FU Huanru, SUN Shikun, GAO Chengfang, CHEN Dongjin, SANG Lei, XIE Xiping*(
), SU Jinbo, FU Huanru, SUN Shikun, GAO Chengfang, CHEN Dongjin, SANG Lei, XIE Xiping*( )
)
Received:2024-07-14
Online:2025-05-23
Published:2025-05-27
Contact:
XIE Xiping
E-mail:wjx841227@126.com;xxp702@163.com
CLC Number:
WANG Jinxiang, SU Jinbo, FU Huanru, SUN Shikun, GAO Chengfang, CHEN Dongjin, SANG Lei, XIE Xiping. Pathogenicity and Genomic Features of Rabbit Sourced Serogroup A Pasteurella multocida Isolates Pm3 and Pm6[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2340-2352.
Table 1
Groups and treatment of the experimental rabbits"
| 组别 Group | 试验兔数量/只 No. of rabbit | 攻毒菌株 Infection strain | 攻毒剂量a/CFU Infection dose | 攻毒方式b Infection rout |
| Pm3攻毒组 Pm3 infected group | 6 | Pm3 | 6.0×104 | 滴鼻 Intranasal inoculation |
| Pm6攻毒组 Pm6 infected group | 6 | Pm6 | 6.0×104 | 滴鼻 Intranasal inoculation |
| 对照组 Control group | 6 | 生理盐水 Normal saline | 100 μL | 滴鼻 Intranasal inoculation |
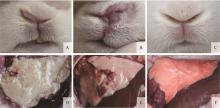
Fig. 1
Clinical signs and pathologic lesions of the rabbits A. Serosity nasal discharge of the infected rabbits; B. Purulent nasal discharge of the infected rabbits; C. No nasal discharge was observed in the control rabbits; D. Fibrinopurulent pleuropneumonia of the infected rabbits that were caught up in the endpoint of the experiment; E. Hemorrhagic pneumonia and pulmonary consolidation of the rabbits that survived the experiment; F. No pathologic lesions were observed in the lungs of control rabbits"
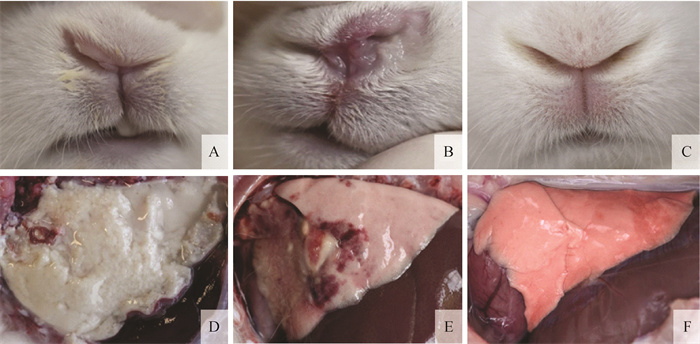
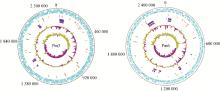
Fig. 2
Circular maps of the Pm3 and Pm6 genomes From the outside to the inside: circle 1 (black) shows the DNA base position; circle 2 and 3 (cyan-blue) show protein-coding regions in forward and reverse strands, respectively; circle 4 (red) shows the tRNA; circle 5 (green) shows the rRNA; circle 6 (blue) shows the genomic island; circle 7 (purple) shows the prophage sequence; the two innermost circles represent the G+C content and GC skew, respectively"
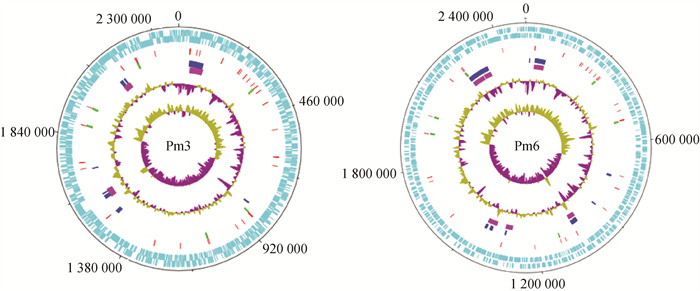
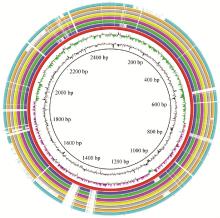
Fig. 5
Comparative analysis of the genomes of Pm3 and Pm6 with the low-virulent (s4 and AH09) and high-virulent (PF1, PF2, PF11 and PF15) rabbit-sourced P. multocida strains From the outside to the inside: circle 1 (cyan-blue) represents s4; circle 2 (orange) represents AH09; circle 3 (gray) represents PF1; circle 4 (yellow) represents PF2; circle 5 (purple) represents PF11; circle 6 (green) represents PF15; circle 7 (blue) represents Pm3; circle 8 (red) represents Pm6; the three innermost circles represent the GC skew, G+C content and DNA base position, respectively"
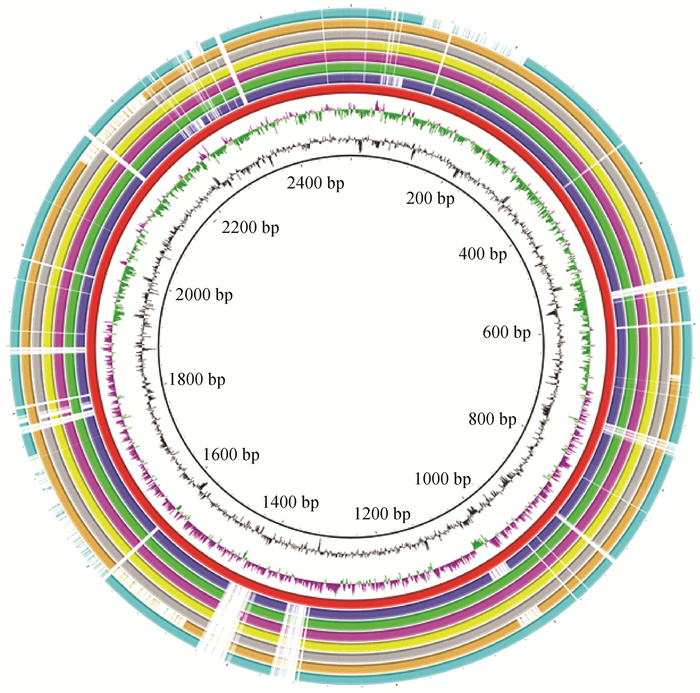
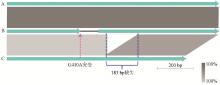
Fig. 8
Comparative analyses of the natC gene from the P. multocida of LPS genotype L3 A. Represents the majority of P. multocida, such as the Pm70; B. Represents the HN07 (swine), F (bovine), 36502 (chicken) and SD11 (rabbit); C. Represents all of the rabbit-sourced P. multocida strains (except for SD11)"
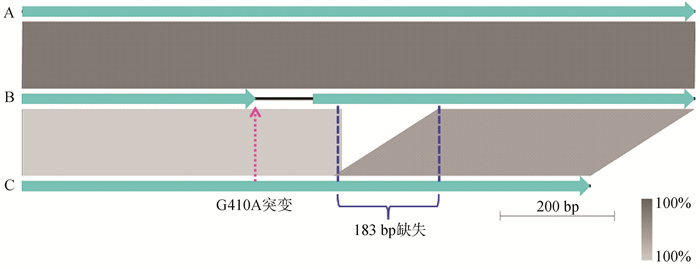
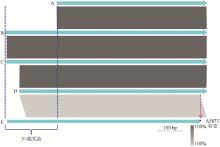
Fig. 9
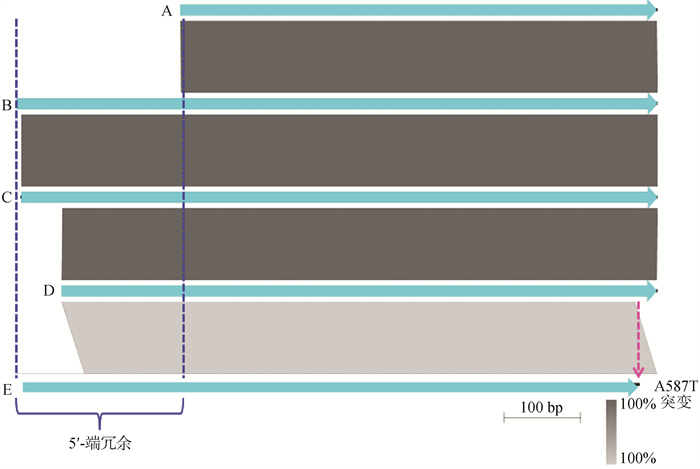
Comparative analyses of the gatF gene from the P. multocida of LPS genotype L3 A. Pm70; B. Represents some of the P. multocida strans, such as HN07 (swine), CQ6 (bovine), RCAD0726 (avian), CIRMBP-0873 (rabbit) and 9N (rodent); C. Represents some of the P. multocida strans, such as the P1933 (bovine), 36502 (avian) and SD11 (rabbit); D. Represents the F (bovine) and Pm-3 (bovine); E. Represents the CIRMBP-0884 (rabbit)"
| 1 |
HARPERM,BOYCEJ D,ADLERB.Pasteurella multocida pathogenesis: 125 years after Pasteur[J].FEMS Microbiol Lett,2006,265(1):1-10.
doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00442.x |
| 2 | PENGZ,WANGX R,ZHOUR,et al.Pasteurella multocida: genotypes and genomics[J].Microbiol Mol Biol Rev,2019,83(4):e00014-19. |
| 3 | OMALEKIL,BLACKALLP J,CUDDIHYT,et al.Phase variation in the glycosyltransferase genes of Pasteurella multocida associated with outbreaks of fowl cholera on free-range layer farms[J].Microb Genom,2022,8(3):000772. |
| 4 |
ALHAMAMIT,CHOWDHURYP R,VENTERH,et al.Genomic profiling of Pasteurella multocida isolated from feedlot cases of bovine respiratory disease[J].Vet Microbiol,2023,283,109773.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2023.109773 |
| 5 |
罗素贤,周红,蔺辉星,等.我国中东部主要养猪地区死亡育肥猪呼吸道病原菌的流行病学调查及猪多杀性巴氏杆菌的特性鉴定[J].中国农业科学,2024,57(11):2254-2264.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2024.11.016 |
|
LUOS X,ZHOUH,LINH X,et al.Epidemiological investigation of respiratory pathogens in deceased fattening pigs in major pig farming area of middle and eastern China and characterization of Pasteurella multocida[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2024,57(11):2254-2264.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2024.11.016 |
|
| 6 |
YANGW H,LIM T,ZHANGC C,et al.Pathogenicity, colonization, and innate immune response to Pasteurella multocida in rabbits[J].BMC Vet Res,2022,18(1):416.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03517-9 |
| 7 |
TOWNSENDK M,BOYCEJ D,CHUNGJ Y,et al.Genetic organization of Pasteurella multocida cap loci and development of a multiplex capsular PCR typing system[J].J Clin Microbiol,2001,39(3):924-929.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.3.924-929.2001 |
| 8 |
HARPERM,JOHNM,TURNIC,et al.Development of a rapid multiplex PCR assay to genotype Pasteurella multocida strains by use of the lipopolysaccharide outer core biosynthesis locus[J].J Clin Microbiol,2015,53(2):477-485.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.02824-14 |
| 9 |
WANGJ X,SANGL,SUNS K,et al.Characterization of Pasteurella multocida isolated from dead rabbits with respiratory disease in Fujian, China[J].BMC Vet Res,2019,15(1):438.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-019-2191-3 |
| 10 |
WANGJ X,SUNS K,CHENY F,et al.Pathogenic and genomic characterisation of a rabbit sourced Pasteurella multocida serogroup F isolate s4[J].BMC Vet Res,2022,18(1):288.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03381-7 |
| 11 |
WANGJ X,SUNS K,CHEND J,et al.Pathogenic and genomic characterization of rabbit-sourced Pasteurella multocida serogroup F isolates recovered from dead rabbits with respiratory disease[J].Microbiol Spectr,2024,12(4):e0365423.
doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03654-23 |
| 12 | D'AMICOF,MESSINAD,CASALINOG,et al.Characterisation of Pasteurella multocida strains from different lesions in rabbits[J].Animals (Basel),2024,14(11):1569. |
| 13 |
GARCÍA-ALVAREZA,CHAVESF,FERNÁNDEZA,et al.An ST11 clone of Pasteurella multocida, widely spread among farmed rabbits in the Iberian Peninsula, demonstrates respiratory niche association[J].Infect, Genet Evol,2015,34,81-87.
doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2015.07.018 |
| 14 | 王锦祥,桑雷,孙世坤,等.一株兔源多杀性巴氏杆菌的分离鉴定及荚膜血清分型[J].中国养兔,2019(1):4-6, 13. |
| WANGJ X,SANGL,SUNS K,et al.Identification and capsule serotyping of a Pasteurella multocida isolated from rabbit[J].Chinese Journal of Rabbit Farming,2019(1):4-6, 13. | |
| 15 |
JAGLICZ,JEKLOVAE,LEVAL,et al.Experimental study of pathogenicity of Pasteurella multocida serogroup F in rabbits[J].Vet Microbiol,2008,126(1-3):168-177.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2007.06.008 |
| 16 |
BERTELLIC,LAIRDM R,WILLIAMSK P,et al.IslandViewer 4: expanded prediction of genomic islands for larger-scale datasets[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2017,45(W1):W30-W35.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx343 |
| 17 |
ARNDTD,GRANTJ R,MARCUA,et al.PHASTER: a better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2016,44(W1):W16-W21.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw387 |
| 18 |
CARVERT,THOMSONN,BLEASBYA,et al.DNAPlotter: circular and linear interactive genome visualization[J].Bioinformatics,2009,25(1):119-120.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn578 |
| 19 |
FOGGINC M,ROSENL E,HENTONM M,et al.Pasteurella sp. Associated with fatal septicaemia in six African elephants[J].Nat Commun,2023,14(1):6398.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41987-z |
| 20 |
MAHBOOBS,ULLAHN,UL HAQUEM F,et al.Genomic characterization and comparative genomic analysis of HS-associated Pasteurella multocida serotype B: 2 strains from Pakistan[J].BMC Genomics,2023,24(1):546.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09626-5 |
| 21 |
CAMACHOC,COULOURISG,AVAGYANV,et al.BLAST+: architecture and applications[J].BMC Bioinformatics,2009,10,421.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-421 |
| 22 |
DARLINGA C E,MAUB,BLATTNERF R,et al.Mauve: multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements[J].Genome Res,2004,14(7):1394-1403.
doi: 10.1101/gr.2289704 |
| 23 |
ALIKHANN F,PETTYN K,BEN ZAKOURN L,et al.BLAST ring image generator (BRIG): simple prokaryote genome comparisons[J].BMC Genomics,2011,12,402.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-402 |
| 24 |
SULLIVANM J,PETTYN K,BEATSONS A.Easyfig: a genome comparison visualizer[J].Bioinformatics,2011,27(7):1009-1010.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr039 |
| 25 |
QIUR L,WEIH J,HUB,et al.Experimental pathogenicity and comparative genome analysis of high- and low-virulence strains of rabbit-origin Pasteurella multocida[J].Comp Immunol, Microbiol Infect Dis,2022,90-91,101889.
doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2022.101889 |
| 26 |
MAYB J,ZHANGQ,LIL L,et al.Complete genomic sequence of Pasteurella multocida, Pm70[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2001,98(6):3460-3465.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.051634598 |
| 27 |
CASALINOG,D'AMICOF,BOZZOG,et al.In field evaluation of impact on clinical signs of an inactivated autogenous vaccine against Pasteurella multocida in rabbits[J].Int J Vet Sci Med,2024,12(1):39-47.
doi: 10.1080/23144599.2024.2348900 |
| 28 |
WEIX Y,ZHANGJ,ZHANGY,et al.Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic evaluation of gamithromycin against rabbit pasteurellosis[J].BMC Vet Res,2024,20,147.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-03988-y |
| 29 | 季权安,徐翔飞,鲍国连,等.两株兔源多杀性巴氏杆菌分离鉴定及荚膜血清分型[J].浙江农业学报,2024,36(5):1041-1046. |
| JIQ A,XUX F,BAOG L,et al.Identification and capsule serotyping of two strains of Pasteurella multocida isolated from rabbit[J].Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2024,36(5):1041-1046. | |
| 30 |
GAOP Y,WANGL B,WANGS,et al.The activity of hyaD contributed to the virulence of avian Pasteurella multocida[J].Microb Pathog,2024,193,106768.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106768 |
| 31 |
FEGANJ E,WAECKERLINR C,TESFAWL,et al.Developing a PmSLP3-based vaccine formulation that provides robust long-lasting protection against hemorrhagic septicemia-causing serogroup B and E strains of Pasteurella multocida in cattle[J].Front Immunol,2024,15,1392681.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1392681 |
| 32 |
LIN Z,FENGT,WANGY L,et al.A single point mutation in the hyaC gene affects Pasteurella multocida serovar A capsule production and virulence[J].Microb Pathog,2021,159,105145.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105145 |
| 33 |
ZHAOX X,YANGF X,SHENH,et al.Immunogenicity and protection of a Pasteurella multocida strain with a truncated lipopolysaccharide outer core in ducks[J].Vet Res,2022,53(1):17.
doi: 10.1186/s13567-022-01035-y |
| 34 |
YANGY,HUP,GAOL X,et al.Deleting qseC downregulates virulence and promotes cross-protection in Pasteurella multocida[J].Vet Res,2021,52(1):140.
doi: 10.1186/s13567-021-01009-6 |
| 35 |
GULLIVERE L,SYB M,WONGJ L,et al.The role and targets of the RNA-binding protein ProQ in the Gram-negative bacterial pathogen Pasteurella multocida[J].J Bacteriol,2022,204(4):e0059221.
doi: 10.1128/jb.00592-21 |
| 36 |
MÉGROZM,KLEIFELDO,WRIGHTA,et al.The RNA-binding chaperone Hfq is an important global regulator of gene expression in Pasteurella multocida and plays a crucial role in production of a number of virulence factors, including hyaluronic acid capsule[J].Infect Immun,2016,84(5):1361-1370.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.00122-16 |
| 37 |
HARPERM,BOYCEJ D.The myriad properties of Pasteurella multocida lipopolysaccharide[J].Toxins (Basel),2017,9(8):254.
doi: 10.3390/toxins9080254 |
| 38 |
PENGZ,LIANGW,WANGY G,et al.Experimental pathogenicity and complete genome characterization of a pig origin Pasteurella multocida serogroup F isolate HN07[J].Vet Microbiol,2017,198,23-33.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.11.028 |
| [1] | WANG Yanan, GUO Yaru, JIANG Yanping, CUI Wen, LI Jiaxuan, LI Yijing, WANG Li. Isolation, Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of Porcine Rotavirus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2259-2269. |
| [2] | GE Lei, QIU Rulong, FAN Zhiyu, HU Bo, WEI Houjun, CHEN Mengmeng, SONG Yanhua, LI Yiming, XU Weizhong, WANG Fang. Construction and Biological Characterization of ompW Gene Deletion and Complemented Strain of Salmonella Typhimurium [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1865-1875. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yingying, GUO Jiaye, XU Huiyan, WU Yayun, WU Longfei, SUN Songying, ZHAO Wenchao, ZHANG Longxian, ZHANG Sumei, LI Junqiang. Analysis of the Pathogenicity of Giardia duodenalis to Mongolian gerbils [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1408-1418. |
| [4] | LI Zhenya, LIU Jie, LI Yun, WANG Fei, KONG Yuanyuan, LI Yong, JIA Rongling. Biological Characteristics and Comparative Genomic Analysis of Virulent and Attenuated Strains of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 851-859. |
| [5] | WU Pingxian, WANG Junge, DIAO Shuqi, CHAI Jie, ZHA Lin, GUO Zongyi, CHEN Hongyue, LONG Xi. Analysis of Genetic Architecture Characteristics and Selection Signature by Imputed Whole Genome Sequencing Data in Rongchang Pigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 147-158. |
| [6] | LIU Jianhua, SA Ruixue, ZHANG Siyu, LI Yintao, DENG Zhichao, JIA Handuo, ZHAO Min, FU Yu, YANG Yiming, RAN Duoliang, JA Erken. Pathogenicity of Equine Herpesvirus Type 1 Isolates to Syrian Golden Hamsters [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 327-334. |
| [7] | FAN Wei, LIU Xinxin, ZHAI Yilu, ZHANG Xinyu, WANG Wei, FU Jiaqi, SUN Fuliang. Isolation and Identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae of Sheep Origin and Establishment of a Method for the Extraction of Its Outer Membrane Vesicles [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 353-364. |
| [8] | WANG Hao, WANG Shiyu, XIAO Jinlong, SHEN Jue, PAN Tianling, ZHANG Jingsong, XIAO Peng, GAO Hong. Evolutionary Analysis of High Pathogenicity Virulence Island Structure Gene of Escherichia coli from Pigs and Its Effect on TNF/NF-κB Pathway [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 392-403. |
| [9] | Shan ZHANG, Dahu LIU, Baojing LIU, Lin LIANG, Ruiying LIANG, Xinming TANG, Xusheng QIU, Chan DING, Jiabo DING, Shaohua HOU. Isolation, Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of a Pigeon Paramyxovirus-1 Strain [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4051-4060. |
| [10] | Bilin XIE, Zhimin LIN, Binbin LIN, Yijuan XU, Fengqiang LIN, Lu YAN, Huini WU, Cuiting LI, Haiou ZHOU, Zhaolong LI. Isolation, Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of Riemerella anatipestifer Strain LC1 and CX1 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4196-4203. |
| [11] | Yan WANG, Yadong GAO, Chenghui JIANG, Qiaoying ZENG. Isolation and Pathogenicity of a Goose Derived Fowl Adenovirus Type 4 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4232-4240. |
| [12] | Fanfan ZHANG, Jiemao LI, Jia TAN, Jiangnan HUANG, Ling WU, Qipeng WEI, Zhaofeng KANG. Research Progress on Avian Metapneumovirus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3344-3353. |
| [13] | Yudian SUN, Ziyue SONG, Hongliang ZHANG, Zhihua QIN, Hu SHAN, Ruimei YANG. Isolation and ldentification of Duckling Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3623-3630. |
| [14] | Weizhe LIU, Chenggang LUO, Rong YUAN, Yijie LIAO, Yimin WEN, Ying SUN, Enbo YU, Sanjie CAO, Xiaobo HUANG. Isolation and Identification of a Highly Pathogenic Strain of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3049-3063. |
| [15] | Wangqing BAN MA, Xi CHEN, Yi YUE, Yurong SU, Hua YUE, Cheng TANG. Isolation, Identification and Partial Biological Characteristics of a Bovine Respiratory Coronavirus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3094-3104. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||