





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 1712-1721.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.04.020
• Animal Genetics and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Xiaowei( ), TIAN Wei, LIU Yuan, LI Huixia*(
), TIAN Wei, LIU Yuan, LI Huixia*( )
)
Received:2024-10-08
Online:2025-04-23
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
LI Huixia
E-mail:lixiaowei@stu.njau.edu.cn;lihuixia@njau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
LI Xiaowei, TIAN Wei, LIU Yuan, LI Huixia. Study on the Difference of m6A Methylation Modification in Ovarian Granulosa Cells of Hu Sheep under Heat Stress[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1712-1721.
Table 1
IP and input library sequencing data"
| 样品 Sample | 原始序列/条 Raw reads | 原始测序量/G Raw bases | 有效序列/条 Valid reads | 有效测序量/G Valid bases | 有效碱基比例/% Valid base proportion | Q20/% | Q30/% | GC% |
| CON_IP | 47 365 524 | 7.10 | 41 455 642 | 6.21 | 87.52 | 98.29 | 94.97 | 52.09 |
| CON_input | 54 530 712 | 8.18 | 49 710 036 | 7.46 | 91.16 | 98.54 | 95.56 | 53.01 |
| HS_IP | 48 938 176 | 7.34 | 42 650 390 | 6.40 | 87.15 | 98.31 | 95.02 | 51.66 |
| HS_input | 51 379 578 | 7.71 | 46 873 704 | 7.03 | 91.23 | 98.61 | 95.73 | 52.66 |
Table 2
The alignment of valid data to Hu sheep"
| 样品 Sample | 有效序列/条 Valid reads | 比对序列/条 Mapped reads | 唯一比对序列/条 Unique mapped reads | 多比对序列/条 Multi mapped reads | PE比对序列/条 PE mapped reads |
| CON_IP | 41 455 642 | 37 148 104 (89.61%) | 34 601 443 (83.47%) | 2 546 661 (6.14%) | 35 690 352 (86.09%) |
| CON_input | 49 710 036 | 44 628 418 (89.78%) | 41 778 005 (84.04%) | 2 850 413 (5.73%) | 43 358 814 (87.22%) |
| HS_IP | 42 650 390 | 38 034 618 (89.18%) | 35 149 335 (82.41%) | 2 885 283 (6.76%) | 36 482 296 (85.54%) |
| HS_input | 46 873 704 | 41 651 352 (88.86%) | 38 810 303 (82.80%) | 2 841 049 (6.06%) | 40 355 184 (86.09%) |
| 样品 Sample | 序列比对到正义链/条 Reads map to sense strand | 序列比对到负义链/条 Reads map to antisense strand | 非拼接序列/条 Non-splice reads | 拼接序列/条 Splice reads | |
| CON_IP | 17 289 541 (41.71%) | 17 311 902 (41.76%) | 18 036 150 (43.51%) | 16 565 293 (39.96%) | |
| CON_input | 20 876 469 (42.00%) | 20 901 536 (42.05%) | 20 787 178 (41.82%) | 20 990 827 (42.23%) | |
| HS_IP | 17 561 443 (41.18%) | 17 587 892 (41.24%) | 18 303 008 (42.91%) | 16 846 327 (39.50%) | |
| HS_input | 19 373 947 (41.33%) | 19 436 356 (41.47%) | 19 136 673 (40.83%) | 19 673 630 (41.97%) | |
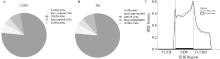
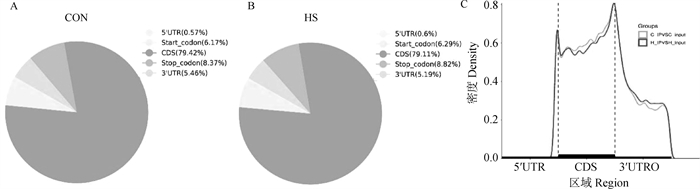
Fig. 1
Characterization of m6A methylation modifications in ovarian granulosa cells of Hu sheep A. The proportion of m6A peak distribution in different regions of mRNA in CON group; B. The proportion of m6A peak distribution in different regions of mRNA in HS group; C.m6A peak distribution in CON and HS groups"
| 1 |
ZHOU R , LIU D . The function of exosomes in ovarian granulosa cells[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2023, 394 (2): 257- 267.
doi: 10.1007/s00441-023-03820-3 |
| 2 |
RUSSELL D L , ROBKER R L . Molecular mechanisms of ovulation: co-ordination through the cumulus complex[J]. Hum Reprod Update, 2007, 13 (3): 289- 312.
doi: 10.1093/humupd/dml062 |
| 3 |
HSUEH A J , KAWAMURA K , CHENG Y , et al. Intraovarian control of early folliculogenesis[J]. Endocr Rev, 2015, 36 (1): 1- 24.
doi: 10.1210/er.2014-1020 |
| 4 |
ZHANG C H , LIU X Y , WANG J . Essential role of granulosa cell glucose and lipid metabolism on oocytes and the potential metabolic imbalance in polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (22): 16247.
doi: 10.3390/ijms242216247 |
| 5 |
WANG S J , LIU W J , WU C J , et al. Melatonin suppresses apoptosis and stimulates progesterone production by bovine granulosa cells via its receptors (MT1 and MT2)[J]. Theriogenology, 2012, 78 (7): 1517- 1526.
doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2012.06.019 |
| 6 |
CARABATSOS M J , SELLITTO C , GOODENOUGH D A , et al. Oocyte-granulosa cell heterologous gap junctions are required for the coordination of nuclear and cytoplasmic meiotic competence[J]. Dev Biol, 2000, 226 (2): 167- 179.
doi: 10.1006/dbio.2000.9863 |
| 7 |
VAN WETTERE W H E J , CULLEY S , SWINBOURNE A M F , et al. Heat stress from current and predicted increases in temperature impairs lambing rates and birth weights in the Australian sheep flock[J]. Nat Food, 2024, 5 (3): 206- 210.
doi: 10.1038/s43016-024-00935-w |
| 8 |
VAN WETTERE W H E J , KIND K L , GATFORD K L , et al. Review of the impact of heat stress on reproductive performance of sheep[J]. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 2021, 12 (1): 26.
doi: 10.1186/s40104-020-00537-z |
| 9 |
MANABE N , GOTO Y , MATSUDA-MINEHATA F , et al. Regulation mechanism of selective atresia in porcine follicles: regulation of granulosa cell apoptosis during atresia[J]. J Reprod Dev, 2004, 50 (5): 493- 514.
doi: 10.1262/jrd.50.493 |
| 10 |
MU H , CAI S , WANG X , et al. RNA binding protein IGF2BP1 meditates oxidative stress-induced granulosa cell dysfunction by regulating MDM2 mRNA stability in an m6A-dependent manner[J]. Redox Biol, 2022, 57, 102492.
doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102492 |
| 11 | ZHU L , ZHANG H , ZHANG X , et al. RNA m6A methylation regulators in sepsis[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2023, 479 (9): 2165- 2180. |
| 12 |
SAMMAD A , LUO H , HU L , et al. Transcriptome reveals granulosa cells coping through redox, inflammatory and metabolic mechanisms under acute heat stress[J]. Cells, 2022, 11 (9): 1443.
doi: 10.3390/cells11091443 |
| 13 | LU Z , LIU J , YUAN C , et al. m(6)A mRNA methylation analysis provides novel insights into heat stress responses in the liver tissue of sheep[J]. Genomics, 2021, 113 (1 Pt 2): 484- 492. |
| 14 |
LU Z , MA Y , LI Q , et al. The role of N(6)-methyladenosine RNA methylation in the heat stress response of sheep (Ovis aries)[J]. Cell Stress Chaperones, 2019, 24 (2): 333- 342.
doi: 10.1007/s12192-018-00965-x |
| 15 |
CHEN B , YUAN C , GUO T , et al. Molecular mechanism of m6A methylation modification genes METTL3 and FTO in regulating heat stress in sheep[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (15): 11926.
doi: 10.3390/ijms241511926 |
| 16 |
ZHANG Y , YAN C , XIE Q , et al. Exposure to bisphenol A affects transcriptome-wide N6-methyladenine methylation in ovarian granulosa cells[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2024, 272, 116071.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116071 |
| 17 |
LIU K , ZHOU X , LI C , et al. YTHDF2 as a Mediator in BDNF-Induced Proliferation of Porcine Follicular Granulosa Cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25 (4): 2343.
doi: 10.3390/ijms25042343 |
| 18 |
CAO M , CHEN X , WANG Y , et al. The reduction of the m(6)A methyltransferase METTL3 in granulosa cells is related to the follicular cysts in pigs[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2024, 239 (6): e31289.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.31289 |
| 19 |
CAO M , YUAN C , CHEN X , et al. METTL3 deficiency leads to ovarian insufficiency due to IL-1beta overexpression in theca cells[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2024, 222, 72- 84.
doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.05.048 |
| 20 | LIU Z , ZHOU L , LI D , et al. N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase METTL3 modulates the cell cycle of granulosa cells via CCND1 and AURKB in Haimen goats[J]. FASEB J, 2023, 37 (11): e31289. |
| 21 |
DING H , LI Z , LI X , et al. FTO Alleviates CdCl(2)-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress via the AKT/Nrf2 pathway in bovine granulosa cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (9): 4948.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23094948 |
| 22 |
LU J , ZHAO P , DING X , et al. N-acetylcysteine stimulates the proliferation and differentiation in heat-stressed skeletal muscle cells[J]. J Therm Biol, 2024, 124, 103958.
doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2024.103958 |
| 23 |
GAO M , SHEN H , LI Q , et al. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) induces apoptosis and autophagy by inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in human granulosa cell line KGN[J]. Environ Pollut, 2024, 344, 123333.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2024.123333 |
| 24 | DENG X , NING Z , LI L , et al. High expression of miR-22-3p in chicken hierarchical follicles promotes granulosa cell proliferation, steroidogenesis, and lipid metabolism via PTEN/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2023, 253 (Pt 7): 127415. |
| 25 |
ZHANG T Y , SUN X F , LI L , et al. Ochratoxin A Exposure Impairs Porcine Granulosa Cell Growth via the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2019, 67 (9): 2679- 2690.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b06361 |
| 26 |
FRANCO R , CIDLOWSKI J A . Apoptosis and glutathione: beyond an antioxidant[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2009, 16 (10): 1303- 1314.
doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.107 |
| 27 |
WANG H X , LI T Y , KIDDER G M . WNT2 regulates DNA synthesis in mouse granulosa cells through beta-catenin[J]. Biol Reprod, 2010, 82 (5): 865- 875.
doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.109.080903 |
| 28 | HABARA O , LOGAN C Y , KANAI-AZUMA M , et al. Self-activation of Wnt signaling in pre-granulosa cells is required for ovarian folliculogenesis[J]. Development, 2020, 148 (9): dev198846. |
| 29 |
LI L , JI S Y , YANG J L , et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling regulates follicular development by modulating the expression of Foxo3a signaling components[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2014, 382 (2): 915- 925.
doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.11.007 |
| 30 |
WANG L J , XUE Y , HUO R , et al. N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase METTL3 affects the phenotype of cerebral arteriovenous malformation via modulating Notch signaling pathway[J]. J Biomed Sci, 2020, 27 (1): 62.
doi: 10.1186/s12929-020-00655-w |
| 31 |
JING J , JIANG X , CHEN J , et al. Notch signaling pathway promotes the development of ovine ovarian follicular granulosa cells[J]. Anim Reprod Sci, 2017, 181, 69- 78.
doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2017.03.017 |
| 32 |
FLORKE GEE R R , CHEN H , LEE A K , et al. Emerging roles of the MAGE protein family in stress response pathways[J]. J Biol Chem, 2020, 295 (47): 16121- 16155.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.008029 |
| 33 |
LIU X L , WU R Y , SUN X F , et al. Mycotoxin zearalenone exposure impairs genomic stability of swine follicular granulosa cells in vitro[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2018, 14 (3): 294- 305.
doi: 10.7150/ijbs.23898 |
| [1] | WANG Ying, ZHANG Jiaojiao, WANG Xianzhong, QUAN Fusheng. Advances in Autophagy of Ovarian Granulosa Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1508-1517. |
| [2] | WANG Xinxin, LIU Xiaoying, WANG Yi, WANG Fang, ZHAO Han, DU Zhiqiang, YANG Caixia. Acute Heat Stress Affects the Functions of Porcine Sertoli Cells via Decreasing Taurine Level [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1779-1790. |
| [3] | HE Yu, WANG Xiangyu, DI Ran, CHU Mingxing, LIANG Chen. BMP4/SMAD4 Downregulates GJA1 Gene Expression to Affect the Gap Junctional Intercellular Communication Activity in Sheep Ovarian Granulosa Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 679-688. |
| [4] | LIANG Hui, ZHAO Jing, WANG Yanya, LONG Runze, LIU Xuyang, WU Yingjie, LIU Ning, QIN Yinghe. Effects of Dietary Chlorogenic Acid on Reproductive Performance of Female Rabbits and Growth of Suckling Rabbits under Heat Stress Conditions [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 755-764. |
| [5] | LI Wei, WU Xilong, ZHAO Xingrui, XU Lanjiao, YANG Xiaobin, SONG Xiaozhen. Effects of Chinese Medicine Jianpisiwei Formulas on Growth Performance, Rumen Fermentation and Microbiota Composition of Weaned Hu Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 466-478. |
| [6] | Yongjie WU, Yinghuan XU, Tengfei LIU, Lin MA, Hong CHEN, Yongping XU. Effect of Scrotal Hyperthermia on Structure and Function of Blood-testis Barrier in Goats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2973-2982. |
| [7] | Mingliang HE, Xiaoyang LÜ, Yongqing JIANG, Zhenghai SONG, Yeqing WANG, Huiguo YANG, Shanhe WANG, Wei SUN. Function Analysis of SOX18 in Hu Sheep Hair Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells Based on Transcriptome Sequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2409-2420. |
| [8] | Xiaoyi FENG, Peipei ZHANG, Hang ZHANG, Haisheng HAO, Weihua DU, Huabin ZHU, Kai CUI, Xueming ZHAO. Effects of Heat Stress on Epigenetic Modifications and Developmental Competence of Bovine Oocytes and Their Embryos [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2460-2473. |
| [9] | Hang ZHANG, Peipei ZHANG, Baigao YANG, Xiaoyi FENG, Yifan NIU, Zhou YU, Jianhua CAO, Pengcheng WAN, Xueming ZHAO. Combination of IGF1, CoQ10 and MT Alleviated the Effects of Heat Stress on Bovine IVF Blastocysts [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2474-2485. |
| [10] | Ji WANG, Xinyan ZHOU, Fangrui GUO, Qiurong XU, Dongyi WU, Yan MAO, Zhihang YUAN, Jin'e YI, Lixin WEN, Jing WU. Viola yedoensis Makino Improves the Growth Performance, Meat Quality, and Gut Microbiota of Broilers Exposed to Heat Stress [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2761-2774. |
| [11] | WANG Xiao, ZHANG Hao, LUAN Qingjiang, LI Hui, YANG Ding, WANG Tingyue, TIAN Jing, ZHAO Meng, CHEN Lu, TIAN Rugang. A Comprehensive Review of the Impact of Cold and Heat Stress on the Physiological Parameters and Gene Expression in Beef Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 894-904. |
| [12] | LIU Yangguang, ZHANG Huibin, WEN Haoyu, XIE Fan, ZHAO Shiming, DING Yueyun, ZHENG Xianrui, YIN Zongjun, ZHANG Xiaodong. SNP/Indel Screening Analysis of Porcine Ovarian Granulosa Cells Treated with Follicular Fluid Exosomes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 576-586. |
| [13] | HUO Yuannan, QIU Meijia, ZHANG Jiaojiao, YANG Weirong, WANG Xianzhong. Arginine and Its Metabolites Attenuate Heat Stress-induced Apoptosis of Immature Boar Sertoli Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 587-597. |
| [14] | Liwa ZHANG, Yaojing YUE, Xuejiao AN, Jianye LI, Bohui YANG, Zhenfei XU, Jinxia ZHANG, Zhiguang GENG, Yanli GUO, Rui ZHANG. Comparative Analysis of the Contents of Amino Acids, Fatty Acids and Volatile Flavor Compounds in the Muscles of Hu Sheep and Their Different Hybrid Combinations [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4428-4442. |
| [15] | Yongqing LIU, Gang ZHANG, Yanling XIONG, Zhongxin SUN, Fan GAO, Ting LIU, Hui LI. Effects of Heat Stress on Duodenal Mucosal Structure, HIF-1 and Its Related Protein Expression in Congjiang Xiang Pigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4690-4699. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||