





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (10): 4311-4324.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.10.007
• Animal Genetics and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
Qingzhen SHI1( ), Hongyang XU2, Yan ZHANG3, Yi ZHANG1, Yachun WANG1, Jianyong HAN2, Li JIANG1,*(
), Hongyang XU2, Yan ZHANG3, Yi ZHANG1, Yachun WANG1, Jianyong HAN2, Li JIANG1,*( )
)
Received:2024-04-03
Online:2024-10-23
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Li JIANG
E-mail:sqz20000515@163.com;lijiang@cau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Qingzhen SHI, Hongyang XU, Yan ZHANG, Yi ZHANG, Yachun WANG, Jianyong HAN, Li JIANG. Detection and Comparative Analysis of Genomic Genetic Variations in Trace Cells Using Different Methods[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4311-4324.
Table 1
DNA concentration of 7 and 10 cells obtained using different reagent kits ng ·μL-1"
| 细胞数 Cell number | EasyPure Micro Genomic DNA Kit | TIANamp Micro DNA Kit | MagicPure Microbiome DNA Isolation Kit | MALBAC® Single Cell WGA Kit | GenomePlex® Whole Genome Amplification | REPLI-g® Single Cell Kit |
| 7 | 0.05±0.06de | 0.25±0.03d | 0.04±0.03e | 14.03±0.40b | 8.86±0.87c | 747.33±25.17a |
| 10 | 0.01±0.00b | 0.24±0.05b | 0.12±0.03b | 17.07±5.68b | 26.33±6.71b | 800.67±79.41a |

Fig. 2
The results of agarose gel electrophoresis of genomic DNA obtained from 7 and 10 cells using different WGA kits Sample lane order 1-3 is genomic DNA obtained from 7 cells using MALBAC® Single Cell WGA Kit; 4-6 is genomic DNA obtained from 10 cells using MALBAC® Single Cell WGA Kit; 7-9 is genomic DNA obtained from 7 cells using REPLI-g® Single Cell Kit; 10-12 is genomic DNA obtained from 10 cells using REPLI-g® Single Cell Kit; 13-15 is genomic DNA obtained from 7 cells using GenomePlex® Whole Genome Amplification; 16-18 is genomic DNA obtained from 10 cells using GenomePlex® Whole Genome Amplification"
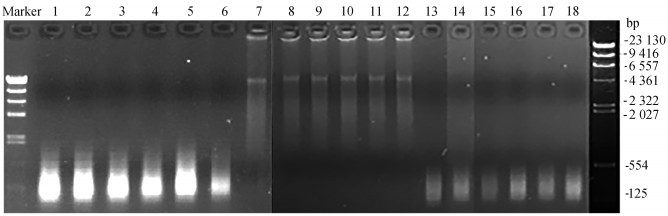
Table 2
Quantity and quality of sequencing data of 7 cells"
| 项目 Item | EasyPure Micro Genomic DNA Kit | TIANamp Micro DNA Kit | MagicPure Microbiome DNA Isolation Kit | MALBAC® Single Cell WGA Kit | GenomePlex® Whole Genome Amplification | REPLI-g® Single Cell Kit |
| 原始碱基数/Gb Raw bases | 5.57±1.94 | 6.60±9.94 | 5.01±6.65b | 7.83±3.86 | 7.10±1.54 | 8.96±1.10a |
| 过滤后碱基/Gb Clean bases | 5.55±1.93 | 6.00±9.27 | 4.79±5.83b | 7.43±2.50 | 7.00±1.52 | 8.87±1.08a |
| 过滤后比例/% Clean rate | 99.58±0.15 | 91.04±3.95 | 95.56±1.19 | 94.93±1.92 | 98.56±0.31 | 98.95±0.27 |
| Q20/% | 96.35±0.17a | 96.64±0.13a | 96.84±0.24a | 96.89±0.06a | 94.43±0.96b | 96.89±0.31a |
| GC/% | 46.58±0.84abc | 48.20±5.68 | 41.95±1.12 | 46.30±0.59b | 41.49±0.28c | 40.08±0.26d |
Table 3
Quantity and quality of sequencing data of 10 cells"
| 项目 Item | EasyPure Micro Genomic DNA Kit | TIANamp Micro DNA Kit | MagicPure Microbiome DNA Isolation Kit | MALBAC® Single Cell WGA Kit | GenomePlex® Whole Genome Amplification | REPLI-g® Single Cell Kit |
| 原始碱基数/Gb Raw bases | 6.60±3.50 | 6.35±1.47 | 5.76±6.46 | 9.19±1.36 | 8.13±1.57 | 7.71±1.09 |
| 过滤后碱基/Gb Clean bases | 6.54±3.30 | 5.66±1.46 | 5.47±6.25 | 8.44±1.37 | 7.96±1.52 | 7.64±1.08 |
| 过滤后比例/% Clean rate | 99.12±0.48a | 88.87±3.93 | 94.92±0.26b | 91.63±2.30 | 97.92±0.28a | 99.07±0.16a |
| Q20/% | 95.92±1.01ab | 96.53±0.23a | 96.88±0.19a | 97.03±0.17a | 94.30±0.12b | 97.01±0.04a |
| GC/% | 41.45±0.10bc | 48.78±1.54 | 42.55±0.22b | 46.44±0.13a | 41.35±0.07bc | 39.95±0.32c |
Table 4
Quality evaluation of reference genome alignment for sequencing data of 7 cells"
| 项目 Item | EasyPure Micro Genomic DNA Kit | TIANamp Micro DNA Kit | MagicPure Microbiome DNA Isolation Kit | MALBAC® Single Cell WGA Kit | GenomePlex® Whole Genome Amplification | REPLI-g® Single Cell Kit |
| 平均深度/X Mean | 1.45±0.78bc | 0.58±0.41c | 1.45±0.62bc | 2.78±0.08ab | 2.53±0.55ab | 3.53±0.44a |
| 覆盖度/% Coverage | 38.33±18.73 | 2.03±0.95d | 35.87±14.19 | 51.87±1.22b | 35.10±1.10c | 83.53±1.75a |
| 比对率/% Mapped rate | 68.97±13.59 | 38.51±16.15 | 78.43±24.07 | 98.19±0.16 | 97.44±0.49 | 98.81±0.14 |
| 双端比对率/% Pair mapped rate | 62.34±14.20 | 32.51±14.22 | 74.40±24.00 | 84.99±1.74 | 86.94±1.63 | 88.22±0.26 |
Table 5
Quality evaluation of reference genome alignment for sequencing data of 10 cells"
| 项目 Item | EasyPure Micro Genomic DNA Kit | TIANamp Micro DNA Kit | MagicPure Microbiome DNA Isolation Kit | MALBAC® Single Cell WGA Kit | GenomePlex® Whole Genome Amplification | REPLI-g® Single Cell Kit |
| 平均深度/X Mean | 1.33±0.51b | 1.04±0.11c | 1.96±0.26 | 3.14±0.51a | 2.85±0.56a | 3.04±0.43a |
| 覆盖度/% Coverage | 14.83±5.00c | 2.37±0.47c | 43.20±12.55 | 51.67±1.88b | 54.90±4.67b | 80.23±4.50a |
| 比对率/% Mapped rate | 58.00±14.12 | 56.13±11.63 | 90.90±1.90 | 98.03±0.58 | 97.77±0.17b | 98.84±0.09a |
| 双端比对率/% Pair mapped rate | 50.74±14.83 | 50.99±11.07 | 86.74±2.08 | 85.11±0.59b | 84.45±1.06 | 88.17±0.42a |

Fig. 3
DNA concentrations obtained from 3, 5, 7, and 10 cells using different kits Different letters indicate significant difference between different cell numbers under the same treatment (P < 0.05), while the same letter or no letter indicate no significant differences (P>0.05). The same as the following figures"

Table 6
Variation detection results of 3, 5, 7, and 10 cells using different reagent kits"
| 细胞数 Cell number | 项目 Item | TIANamp Micro DNA Kit | MagicPure Microbiome DNA Isolation Kit | REPLI-g® Single Cell Kit |
| 3 | 检出的SNP数量Number of detected SNPs | 11 928 | 1 456 232 | 10 496 024 |
| 占dbSNP库比例/% Percentage of dbSNP | 49.86 | 73.34 | 82.40 | |
| 5 | 检出的SNP数量Number of detected SNPs | 50 271 | 329 523 | 11 264 639 |
| 占dbSNP库比例/% Percentage of dbSNP | 61.91 | 68.21 | 81.94 | |
| 7 | 检出的SNP数量Number of detected SNPs | 51 742 | 1 547 788 | 11 190 573 |
| 占dbSNP库比例/% Percentage of dbSNP | 47.56 | 70.55 | 82.40 | |
| 10 | 检出的SNP数量Number of detected SNPs | 80 375 | 2 050 007 | 10 387 060 |
| 占dbSNP库比例/% Percentage of dbSNP | 54.86 | 72.69 | 82.46 |
Table 7
Variants detection results of bovine blastocyst 5 and 7 cells using sequencing data"
| 细胞数 Cell number | 检出SNPs数量 Number of detected SNPs | 检出INDELs数量 Number of detected INDELs | 占dbSNP库比例/% Percentage of dbSNP |
| 5 | 2 670 902±1 639 522 | 418 698±253 237 | 87.98±1.93 |
| 7 | 3 976 749±414 046 | 628 196±52 588 | 89.26±0.93 |
Table 8
GGP-100K SNP detection results of bovine blastocyst 5 and 7 cells"
| 细胞数 Cell number | 样品名 Sample name | 检出SNPs位点数 Number of detected SNPs | 检出率/% Call rate | 平均检出率/% Mean call rate |
| 5 | 5-1 | 73 319 | 76.97 | 74.09±12.08 |
| 5-2 | 57 940 | 60.83 | ||
| 5-3 | 80 475 | 84.48 | ||
| 7 | 7-1 | 68 707 | 72.13 | 81.52±8.19 |
| 7-2 | 83 092 | 87.23 | ||
| 7-3 | 81 151 | 85.19 |

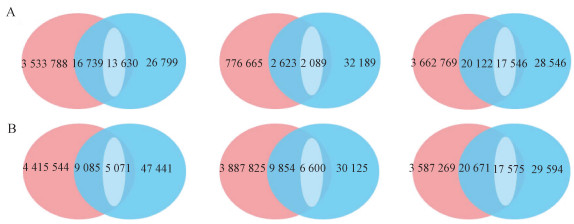
Fig. 9
Venn plots of SNP detection results for bovine blastocyst 5 and 7 cells using sequencing and SNP chip A. Three samples of 5 cells; B. Three samples of 7 cells. Red represents SNP detection result of sequencing data; Blue represents SNP detection result of GGP-100K chip; White represents the same SNP loci with consistent genotypes"
| 1 | 王腾飞, 张燕, 王彦平, 等. 奶牛活体采卵-体外受精效率的影响因素研究[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2021, 48 (2): 574- 580. |
| WANG T F , ZHANG Y , WANG Y P , et al. Study on the influencing factors of in vitro fertilization efficiency in dairy cows[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 48 (2): 574- 580. | |
| 2 | 徐华, 车瑞香, 朱捷. 牛OPU-IVF技术发展现状和趋势[J]. 中国奶牛, 2023, (2): 19- 24. |
| XU H , CHE R X , ZHU J . Status and trends in the development of OPU-IVF technology in cattle[J]. China Dairy Cattle, 2023, (2): 19- 24. | |
| 3 | VIANA J H M . 2020 statistics of embryo production and transfer in domestic farm animals[J]. Embryo Technol Newsl, 2021, 39 (4): 24- 38. |
| 4 |
FUJⅡ T , NAITO A , HIRAYAMA H , et al. Potential of preimplantation genomic selection for carcass traits in Japanese Black cattle[J]. J Reprod Dev, 2019, 65 (3): 251- 258.
doi: 10.1262/jrd.2019-009 |
| 5 |
BOGLIOTTI Y S , WU J , VILARINO M , et al. Efficient derivation of stable primed pluripotent embryonic stem cells from bovine blastocysts[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2018, 115 (9): 2090- 2095.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1716161115 |
| 6 |
HOU Z C , AN L , HAN J Y , et al. Revolutionize livestock breeding in the future: an animal embryo-stem cell breeding system in a dish[J]. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 2018, 9, 90.
doi: 10.1186/s40104-018-0304-7 |
| 7 |
GOSZCZYNSKI D E , CHENG H , DEMYDA-PEYRÁS S , et al. In vitro breeding: application of embryonic stem cells to animal production[J]. Biol Reprod, 2019, 100 (4): 885- 895.
doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioy256 |
| 8 | 高山凤, 肖轩, 张玲羽, 等. 单细胞测序技术在生殖研究中的应用[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报, 2020, 42 (12): 2234- 2243. |
| GAO S F , XIAO X , ZHANG L Y , et al. The application of single-cell sequencing technology in reproductive research[J]. Chinese Journal of Cell Biology, 2020, 42 (12): 2234- 2243. | |
| 9 |
RHEE M , LIGHT Y K , MEAGHER R J , et al. Digital droplet multiple displacement amplification (ddMDA) for whole genome sequencing of limited DNA samples[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11 (5): e0153699.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153699 |
| 10 |
SHOJAEI SAADI H A , VIGNEAULT C , SARGOLZAEI M , et al. Impact of whole-genome amplification on the reliability of pre-transfer cattle embryo breeding value estimates[J]. BMC Genomics, 2014, 15 (1): 889.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-889 |
| 11 |
TELENIUS H , CARTER N P , BEBB C E , et al. Degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR: general amplification of target DNA by a single degenerate primer[J]. Genomics, 1992, 13 (3): 718- 725.
doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90147-K |
| 12 |
DEAN F B , NELSON J R , GIESLER T L , et al. Rapid amplification of plasmid and phage DNA using Phi29 DNA polymerase and multiply-primed rolling circle amplification[J]. Genome Res, 2001, 11 (6): 1095- 1099.
doi: 10.1101/gr.180501 |
| 13 |
DEAN F B , HOSONO S , FANG L H , et al. Comprehensive human genome amplification using multiple displacement amplification[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2002, 99 (8): 5261- 5266.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.082089499 |
| 14 | 汤志成, 梁伟锦. FW-超微量磁珠法提取石蜡包埋胚胎组织DNA检验1例[J]. 广东公安科技, 2024, 32 (1): 61- 62. |
| TANG Z C , LIANG W J . A case of DNA testing of paraffin-embedded embryonic tissue extracted by FW-ultra-micro magnetic bead method[J]. Guangdong Gongan Keji, 2024, 32 (1): 61- 62. | |
| 15 |
TURNER K J , SILVESTRI G , BLACK D H , et al. Karyomapping for simultaneous genomic evaluation and aneuploidy screening of preimplantation bovine embryos: the first live-born calves[J]. Theriogenology, 2019, 125, 249- 258.
doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2018.11.014 |
| 16 |
SILVESTRI G , CANEDO-RIBEIRO C , SERRANO-ALBAL M , et al. Preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy improves live birth rates with in vitro produced bovine embryos: a blind retrospective study[J]. Cells, 2021, 10 (9): 2284.
doi: 10.3390/cells10092284 |
| 17 |
HOU Y , FAN W , YAN L Y , et al. Genome analyses of single human oocytes[J]. Cell, 2013, 155 (7): 1492- 1506.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.040 |
| 18 |
LI H , HANDSAKER B , WYSOKER A , et al. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools[J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25 (16): 2078- 2079.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352 |
| 19 |
LI H , DURBIN R . Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform[J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25 (14): 1754- 1760.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324 |
| 20 | VAN DER AUWERA G A , CARNEIRO M O , HARTL C , et al. From FastQ data to high confidence variant calls: the Genome Analysis Toolkit best practices pipeline[J]. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics, 2013, 43 (1110): 11.10.1- 11.10.33. |
| 21 |
DANECEK P , MCCARTHY S A . BCFtools/csq: haplotype-aware variant consequences[J]. Bioinformatics, 2017, 33 (13): 2037- 2039.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx100 |
| 22 |
PURCELL S , NEALE B , TODD-BROWN K , et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses[J]. Am J Hum Genet, 2007, 81 (3): 559- 575.
doi: 10.1086/519795 |
| 23 | LIU Y , LIANG S M , WANG B , et al. Advances in single-cell sequencing technology and its application in poultry science[J]. Genes (Basel), 2022, 13 (12): 2211. |
| 24 | YAO K , GONZÁLEZ-ESCALONA N , HOFFMANN M . Multiple displacement amplification as a solution for low copy number plasmid sequencing[J]. Front Microbiol, 2021, 12, 617487. |
| 25 | 于婷, 王云云, 费嘉, 等. 3种单细胞全基因组扩增方法对1~4 Mb拷贝数变异检测性能的研究[J]. 分子诊断与治疗杂志, 2022, 14 (9): 1549- 1553. |
| YU T , WANG Y Y , FEI J , et al. The performance of three commonly single-cell whole genome amplification methods for the detection of 1~4 Mb copy number variation[J]. Journal of Molecular Diagnostics and Therapy, 2022, 14 (9): 1549- 1553. | |
| 26 | HE F , ZHOU W J , CAI R , et al. Systematic assessment of the performance of whole-genome amplification for SNP/CNV detection and β-thalassemia genotyping[J]. J Hum Genet, 2018, 63 (4): 407- 416. |
| 27 | ZHANG X Y , LIANG B , XU X Y , et al. The comparison of the performance of four whole genome amplification kits on ion proton platform in copy number variation detection[J]. Biosci Rep, 2017, 37 (4): BSR20170252. |
| 28 | 胡智辉, 王欢, 衡诺, 等. 高通量SNP芯片在牛体外早期胚胎染色体质量鉴定中的初步应用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53 (11): 3866- 3879. |
| HU Z H , WANG H , HENG N , et al. Preliminary application of high throughput SNP chip in chromosome quality identification of bovine early in vitro embryos[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53 (11): 3866- 3879. | |
| 29 | 李钰华, 黄杰, 姬晓伟, 等. NGS panel与全基因组SNP芯片在胚胎植入前地贫检测中的应用比较[J]. 分子诊断与治疗杂志, 2022, 14 (11): 1832-1835, 1840. |
| LI Y H , HUANG J , JI X W , et al. Comparative study of NGS panel and whole genome SNP microarray in pre-implantation genetic testing of thalassemia[J]. Journal of Molecular Diagnostics and Therapy, 2022, 14 (11): 1832-1835, 1840. | |
| 30 | CHEN C Y , XING D , TAN L Z , et al. Single-cell whole-genome analyses by Linear Amplification via Transposon Insertion (LIANTI)[J]. Science, 2017, 356 (6334): 189- 194. |
| 31 | CHU W K , EDGE P , LEE H S , et al. Ultraaccurate genome sequencing and haplotyping of single human cells[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2017, 114 (47): 12512- 12517. |
| 32 | ZHOU Y , JIA E T , QIAO Y , et al. Low bias multiple displacement amplification with confinement effect based on agarose gel[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2021, 413 (17): 4397- 4405. |
| 33 | ZHOU X X , XU Y , ZHU L B , et al. Comparison of multiple displacement amplification (MDA) and multiple annealing and looping-based amplification cycles (MALBAC) in limited DNA sequencing based on tube and droplet[J]. Micromachines (Basel), 2020, 11 (7): 645. |
| [1] | Siyu LIU, Man ZHANG, Yan ZHANG, Zhitong WEI, Xinglei QI, Tengyun GAO, Xian LIU, Dong LIANG, Tong FU. Evaluation of the Conservation Effect in Nanyang Cattle Based on Resequencing Data [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3876-3886. |
| [2] | Kangning ZHAO, Zhonglong YANG, Yi CHEN, Chuncheng ZHU, Yunfei GUO, Yuncong YIN, Tao QIN, Sujuan CHEN, Daxin PENG. Genetic Variation Analysis of Sixteen Novel H3N3 Subtype Avian Influenza Viruses [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4029-4040. |
| [3] | Shuying DAI, Qing LIU, Aiguo LI, Bo YU, Hongbo CHEN. Research Progress on Culture Medium Additives in Bovine In Vitro Embryo Production [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3309-3320. |
| [4] | Tao ZHANG, Jiaqi LI, Lei XU, Dan WANG, Menghua ZHANG, Tao ZHANG, Mengjie YAN, Weitao WANG, Shoumin FAN, Xixia HUANG. Detection and Population Structure Analysis of Genomic Structural Variation in Xinjiang Brown Cattle Based on Whole Genome Resequencing Data [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3427-3435. |
| [5] | Yifan NIU, Chongyang LI, Baigao YANG, Peipei ZHANG, Hang ZHANG, Xiaoyi FENG, Jianhua CAO, Zhou YU, Youji MA, Xueming ZHAO. Evaluation of the Effect of Different Single Cell Whole Genome Amplification Systems on the Amplification of Bovine Trace Blood DNA [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3436-3445. |
| [6] | Zijiao GUO, Weijie ZHENG, Wei SUN, Baojiang WU, Xiangnan BAO, Qi ZHANG, Jinfeng HE, Siqin BAO, Gaoping ZHAO, Zixin WANG, Bo HAN, Xihe LI, Dongxiao SUN. Study on Genomic Selection of Embryos in Holstein Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2940-2950. |
| [7] | Ying CHEN, Dayong CHEN, Riga WU, Chunjuan QIU, Lihong FAN, Meirong BAO, Yuan YUE, Hongyan LIANG, Jiaxin ZHANG, Jianhui TIAN, Lei AN, Liqin WANG. Influence of Meat Sheep Varieties on the Scale Application of in vitro Embryo Production Technology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2451-2459. |
| [8] | Hang ZHANG, Peipei ZHANG, Baigao YANG, Xiaoyi FENG, Yifan NIU, Zhou YU, Jianhua CAO, Pengcheng WAN, Xueming ZHAO. Combination of IGF1, CoQ10 and MT Alleviated the Effects of Heat Stress on Bovine IVF Blastocysts [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2474-2485. |
| [9] | DENG Gunan, ZHANG Jiaqi, BAO Zhipeng, CHEN Taoyun, YU Qisheng, DING Lu, ZHU Chenxi, WANG Yi, REN Yupeng, HE Chao, ZHANG Bin. Detection of Feline Herpesvirus Type 1 and Pathogenicity of an Isolated Strain [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2253-2258. |
| [10] | LAN Xinrui, ZHAO Baobao, ZHANG Bihan, LIN Xiaoyu, MA Huiming, WANG Yongsheng. Effects of β-sitosterol on Porcine Oocyte Maturation and Embryonic Development in Vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1629-1637. |
| [11] | LI Yujun, HE Honghong, YANG Lixue, YANG Xiaogeng, LI Jian, ZHANG Huizhu. Advances in Regulation of Mammalian Embryonic Development by Mitochondrial Autophagy [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 905-912. |
| [12] | SONG Kelin, YAN Zunqiang, WANG Pengfei, CHENG Wenhao, LI Jie, BAI Yaqin, SUN Guohu, GUN Shuangbao. Analysis on Genetic Diversity and Genetic Structure Based on SNP Chips of Huixian Qingni Black Pig [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 995-1006. |
| [13] | SU Wennan, LIU Jiaqi, ZHONG Jiacheng, CHEN Jidang, ZHU Wanjun, ZHANG Yishan, ZHANG Jipei. Complete Genome Re-sequence and Comparative Genomic Analysis of Avibacterium paragallinarum from Geese [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1208-1216. |
| [14] | REN Yuwei, CHEN Xing, LIN Yanning, HUANG Xiaoxian, HONG Lingling, WANG Feng, SUN Ruiping, ZHANG Yan, LIU Hailong, ZHENG Xinli, CHAO Zhe. Investigating the Influencing Factors of Egg Laying Performance in Wenchang Chickens Based on Whole Genome Resequencing [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 502-514. |
| [15] | ZHANG Chenjian, LI Yinxia, DING Qiang, LIU Weijia, WANG Huili, HE Nan, WU Jiashun, CAO Shaoxian. Efficient Preparation of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Goat SOCS2 Gene Edited Embryos [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 129-141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||