





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 1919-1933.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.04.039
• Basic Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2024-05-20
Online:2025-04-23
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
XU Tong
E-mail:wanchenhouneau@163.com;tongxu@neau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
HOU Wanchen, XU Tong. Cannabidiol Antagonizes BPA-induced Apoptosis and Autophagy in Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells through the BRD4/AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1919-1933.
Table 1
Primer sequence."
| 引物名称 Primer name | 上游引物(5′→3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′→3′) Reverse primer |
| Bcl-2 | TCTTTGAGTTCGGTGGGGTC | CTCCACAAAGGCATCCCAGC |
| Bax | GGCCCTTTTGCTTCAGGGTTTC | GTCCACGGCTGCGATCAT |
| caspase-3 | GCTGTAGAACTCTAACTGGCAAACC | CCCACTGTCCGTCTCAATCCC |
| Nrf2 | TAAGGGTGCTCCTTTGCGAG | CGGGCTAAGTTCAGTCGCTT |
| Keap-1 | CCATGAAGCATCGGCGAAGC | CGCTCCAGGTGTCCGTGTC |
| LC3 | TGTCAACATGAGCGAGTTGGT | CTGCTCATAGATGTCCGCGAT |
| P62 | AAGAACGTAGGGGAGAGTGTG | TTGCTAGGGTCGGAAGAGCA |
| LAMP1 | CTCCACAAAGGCATCCCAGC | TCTTGCTGGCTGAAGCTGTT |
| BRD4 | ACAGCAACACAAGCAAGAAGGA | GCTGCCGCTTTTCATCATAACTCA |
| AMPK | CGACAGCCGAGAAGCAGAAAC | TTTGCCAACCTTCACTTTGCC |
| mTOR | ACTGTGCGGATCACTTCCTG | GGTTATCCCAACCACGAGCA |
| β-actin | GACGATATTGCTGCGCTCGTG | TCAGGATGCCTCTCTTGCTCT |
Table 2
Antibody information used in Western blot"
| 抗体 Antibodies | 稀释比例 Dilution ratio | 公司 Company |
| Bcl-2 | 1∶1 000 | Wanleibio |
| Bax | 1∶1 000 | Wanleibio |
| caspase-3 | 1∶1 000 | Wanleibio |
| Nrf2 | 1∶800 | Wanleibio |
| Keap1 | 1∶1 000 | Wanleibio |
| LC3 | 1∶1 000 | ABclonal |
| P62 | 1∶1 000 | ABclonal |
| ATG5 | 1∶1 000 | Wanleibio |
| LAMP1 | 1∶1 000 | Wanleibio |
| BRD4 | 1∶400 | ABclonal |
| AMPK | 1∶1 000 | ABclonal |
| mTOR | 1∶1 000 | ABclonal |
| β-actin | 1∶1 000 | ABclonal |
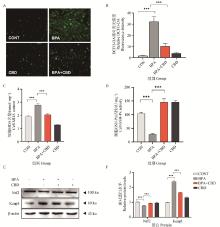
Fig. 2
Effect of BPA or/and CBD on oxidative stress A. DCFH-DA fluorescence intensity detection; B. Numerical analysis of fluorescence intensity of DCFH-DA; C. Numerical analysis of MDA content; D. Numerical analysis of GSH-Px activity; E. The levels of oxidative stress-related proteins were detected by Western blot; F. Gray value analysis. "ns". No significant difference; *. P < 0.05; **. P < 0.01; ***. P < 0.001 and ****. P < 0.000 1"

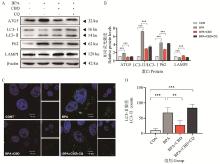
Fig. 3
Effect of BPA or/and CBD on autophagy of IPEC-J2 cells A. The expression levels of autophagy related proteins were detected by Western blot; B. Gray value analysis; C. The expression level of LC3-Ⅱ was detected by immunofluorescence; D. Numerical analysis of LC3-Ⅱ expression level. "ns" indicates no significant difference, *. P < 0.05; **. P < 0.01; ***. P < 0.001 and ****. P < 0.000 1"
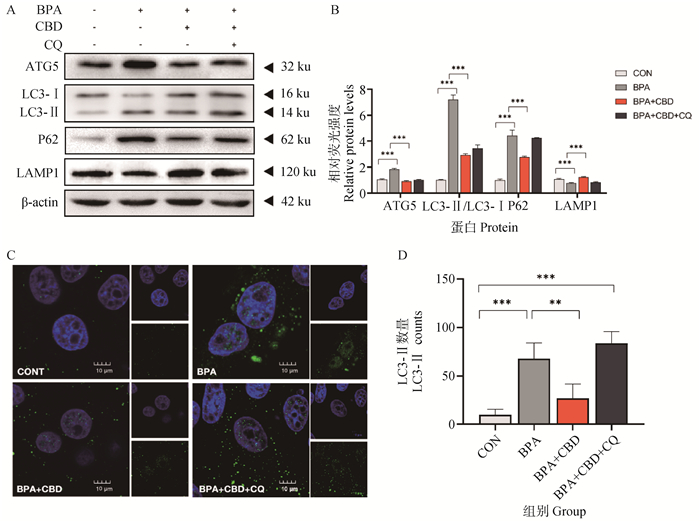
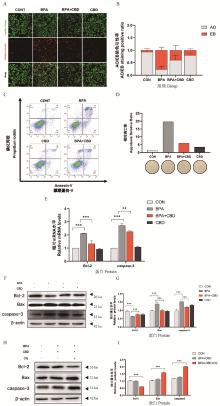
Fig. 4
Effects of BPA or/and CBD exposure on apoptosis of IPEC-J2 cells A. The apoptosis rate was detected by AO/EB staining; B. Numerical analysis of AO/EB staining positive rate; C. The apoptosis rate was detected by flow cytometry; D. Numerical analysis of apoptosis rate; F and H. Apoptosis-related proteins were detected by Western blot; G and I. Gray value analysis. "ns" indicate no significant difference; *. P < 0.05; **. P < 0.01; ***. P < 0.001 and ****. P < 0.000 1"

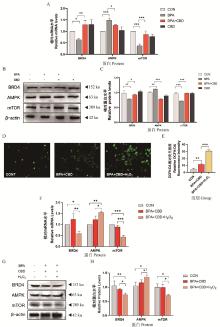
Fig. 5
Effects of BPA or/and CBD exposure on mRNA and protein expression levels of BRD4/AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in IPEC-J2 cells A. Numerical analysis of relative mRNA levels; B. The expression levels of pathway-related proteins were detected by Western blot; C. Gray value analysis. D. DCFH-DA fluorescence intensity detection; E. Numerical analysis of fluorescence intensity of DCFH-DA; F. Numerical analysis of relative mRNA levels; G. The expression levels of pathway-related proteins were detected by Western blot; H. Gray value analysis. "ns" indicate no significant difference; *. P < 0.05; **. P < 0.01; ***. P < 0.001 and ****. P < 0.0001"
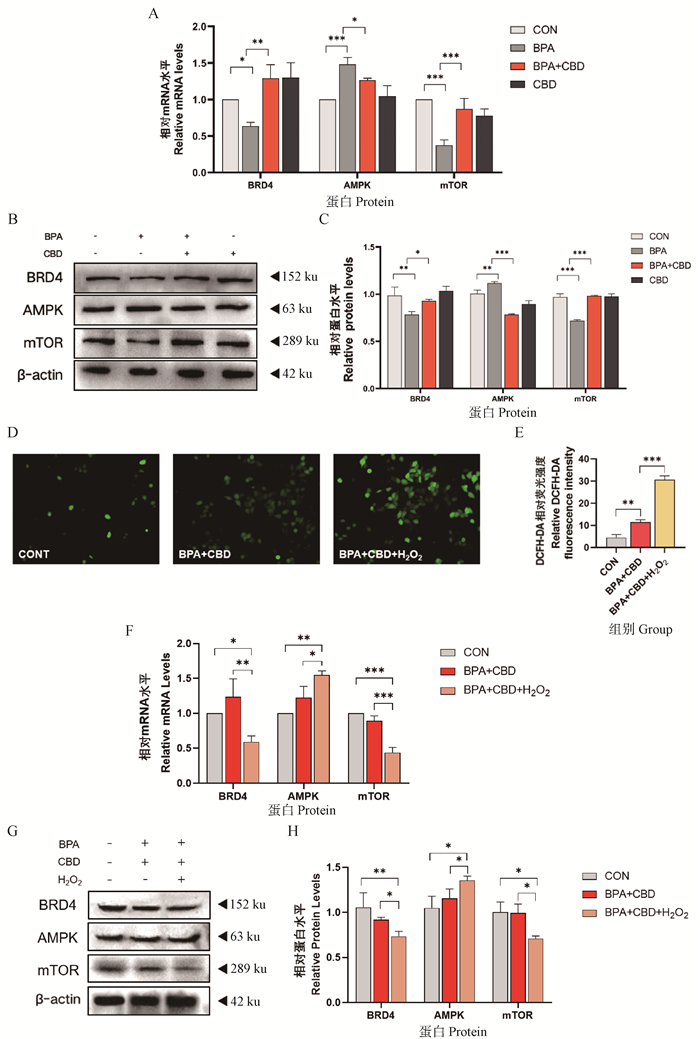
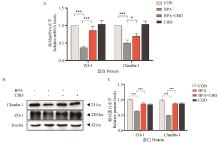
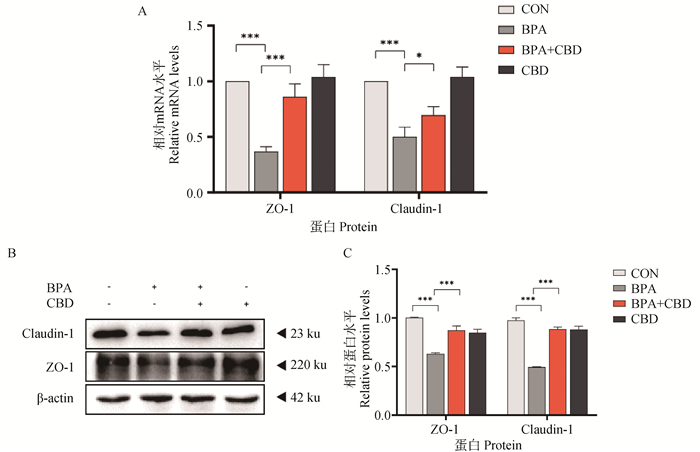
Fig. 6
Effects of BPA and/or CBD on intestinal compact junction mRNA and protein in IPEC-J2 cells. A. Numerical analysis of relative mRNA levels; B. The expression levels of intestinal tight junction related proteins were detected by Western blot; C. Gray value analysis. ns indicate no significant difference; *. P < 0.05; **. P < 0.01; ***. P < 0.001 and ****. P < 0.0001"
| 1 |
FRIQUES A G F , SANTOS F D N , ANGELI D B , et al. Bisphenol A contamination in infant rats: molecular, structural, and physiological cardiovascular changes and the protective role of kefir[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2020, 75, 108254.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.108254 |
| 2 |
CIMMINO I , FIORY F , PERRUOLO G , et al. Potential mechanisms of bisphenol A (BPA) contributing to human disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21 (16): 5761.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21165761 |
| 3 | 蔡家星, 李桢, 代娟, 等. 4-壬基酚联合双酚A通过抑制Akt/mTOR通路诱导F1代大鼠睾丸细胞自噬和精子发生障碍[J]. 中华男科学杂志, 2022, 28 (3): 195- 202. |
| CAI J X , LI Z , DAI J , et al. 4-nonylphenol combined with bisphenol A induces testicular autophagy and spermatogenic impairment by inhibiting the Akt/mTOR pathway in F1 male offspring rats[J]. National Journal of Andrology, 2022, 28 (3): 195- 202. | |
| 4 |
FENG L , CHEN S J , ZHANG L J , et al. Bisphenol A increases intestinal permeability through disrupting intestinal barrier function in mice[J]. Environ Pollut, 2019, 254, 112960.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.112960 |
| 5 |
FENG D , ZHANG H M , JIANG X , et al. Bisphenol A exposure induces gut microbiota dysbiosis and consequent activation of gut-liver axis leading to hepatic steatosis in CD-1 mice[J]. Environ Pollut, 2020, 265, 114880.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114880 |
| 6 |
WEN X , KLIONSKY D J . BRD4 is a newly characterized transcriptional regulator that represses autophagy and lysosomal function[J]. Autophagy, 2017, 13 (11): 1801- 1803.
doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1364334 |
| 7 |
GUI D , CUI Z M , ZHANG L , et al. Salidroside attenuates hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis resistance by upregulating autophagy through the AMPK-mTOR-ULK1 pathway[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2017, 17 (1): 191.
doi: 10.1186/s12890-017-0477-4 |
| 8 |
WANG L P , YUAN D , ZHENG J , et al. Chikusetsu saponin IVa attenuates isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis in mice through activation autophagy mediated by AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signaling[J]. Phytomedicine, 2019, 58, 152764.
doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.11.024 |
| 9 | 林任. mTOR介导自噬和脂代谢异常参与生命早期双酚A和果糖暴露致非酒精性脂肪肝发生发展中的作用机制研究[D]. 沈阳: 中国医科大学, 2020. |
| LIN R. Study on the mechanism of abnormal autophagy and lipid metabolism mediated by mTOR in the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by bisphenol A and fructose exposure in early life[D]. Shenyang: China Medical University, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 10 |
CHEN Q , KANG J , FU C Y . The independence of and associations among apoptosis, autophagy, and necrosis[J]. Sig Transduct Target Ther, 2018, 3 (1): 18.
doi: 10.1038/s41392-018-0018-5 |
| 11 |
EISENBERG-LERNER A , BIALIK S , SIMON H U , et al. Life and death partners: apoptosis, autophagy and the cross-talk between them[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2009, 16 (7): 966- 975.
doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.33 |
| 12 |
COCETTA V , GOVERNA P , BORGONETTI V , et al. Cannabidiol isolated from Cannabis sativa L. protects intestinal barrier from in vitro inflammation and oxidative stress[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12, 641210.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.641210 |
| 13 |
SUN M D , ZHANG F Y , LU F , et al. Integrating fecal metabolomics and intestinal microbiota to study the mechanism of cannabidiol in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2024, 15, 1358626.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1358626 |
| 14 |
GONG X L , JIANG L , LI W , et al. Curcumin induces apoptosis and autophagy inhuman renal cell carcinoma cells via Akt/mTOR suppression[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12 (1): 5017- 5027.
doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1960765 |
| 15 | 米杨. 大麻二酚在大鼠蛛网膜下腔出血早期脑损伤中促进自噬反应的研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州医科大学, 2021. |
| MI Y. Cannabinol promotes autophagy in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou Medical University, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| 16 |
LIAO C Y , LIU F , GUO Y , et al. Occurrence of eight bisphenol analogues in indoor dust from the united states and several asian countries: implications for human exposure[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2012, 46 (16): 9138- 9145.
doi: 10.1021/es302004w |
| 17 |
SALIM S Y , KAPLAN G G , MADSEN K L . Air pollution effects on the gut microbiota A link between exposure and inflammatory disease[J]. Gut Microbes, 2014, 5 (2): 215- 219.
doi: 10.4161/gmic.27251 |
| 18 |
ATALAY S , JAROCKA-KARPOWICZ I , SKRZYDLEWSKA E . Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties of cannabidiol[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2019, 9 (1): 21.
doi: 10.3390/antiox9010021 |
| 19 |
BACALIA K M A , TVETER K M , PALMER H , et al. Cannabidiol decreases intestinal inflammation in the ovariectomized murine model of postmenopause[J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 11 (1): 74.
doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11010074 |
| 20 |
SIES H . Oxidative stress: oxidants and antioxidants[J]. Exp Physiol, 1997, 82 (2): 291- 295.
doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1997.sp004024 |
| 21 |
ZHANG Y Y , MI K H , XUE W , et al. Acute BPA exposure-induced oxidative stress, depressed immune genes expression and damage of hepatopancreas in red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii[J]. Fish Shellfish Immunol, 2020, 103, 95- 102.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2020.04.032 |
| 22 |
DE TERNAY J , NAASSILA M , NOURREDINE M , et al. Therapeutic prospects of cannabidiol for alcohol use disorder and alcohol-related damages on the liver and the brain[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10, 627.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00627 |
| 23 | 范港, 黄鑫, 张伟伟, 等. 大麻二酚对脂多糖诱导的小鼠乳腺上皮细胞氧化损伤的保护作用[J]. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35 (2): 1298- 1307. |
| FAN G , HUANG X , ZHANG W W , et al. Protective effects of cannabidiol on oxidative damage of mouse mammary epithelial cells induced by lipopolysaccharide[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2023, 35 (2): 1298- 1307. | |
| 24 |
SYKIOTIS G P , HABEOS I G , SAMUELSON A V , et al. The role of the antioxidant and longevity-promoting Nrf2 pathway in metabolic regulation[J]. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care, 2011, 14 (1): 41- 48.
doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32834136f2 |
| 25 |
OUYANG L , ZHANG L , LIU J , et al. Discovery of a small-molecule bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) inhibitor that induces AMP-activated protein kinase-modulated autophagy-associated cell death in breast cancer[J]. J Med Chem, 2017, 60 (24): 9990- 10012.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00275 |
| 26 |
ANAND S K , SHARMA A , SINGH N , et al. Activation of autophagic flux via LKB1/AMPK/mTOR axis against xenoestrogen Bisphenol-A exposure in primary rat hepatocytes[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2020, 141, 111314.
doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111314 |
| 27 |
BAO L J , ZHAO C J , FENG L J , et al. Ferritinophagy is involved in Bisphenol A-induced ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through the activation of the AMPK-mTOR-ULK1 pathway[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2022, 163, 112909.
doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2022.112909 |
| 28 |
SHRIVASTAVA A , KUZONTKOSKI P M , GROOPMAN J E , et al. Cannabidiol induces programmed cell death in breast cancer cells by coordinating the cross-talk between apoptosis and autophagy[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2011, 10 (7): 1161- 1172.
doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-1100 |
| 29 |
GIACOPPO S , POLLASTRO F , GRASSI G , et al. Target regulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway by cannabidiol in treatment of experimental multiple sclerosis[J]. Fitoterapia, 2017, 116, 77- 84.
doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2016.11.010 |
| 30 | PENG L Q , LU Y , ZHONG J Y , et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide promotes proliferation of human melanocytes via activating the Nrf2/p62 signaling pathway by inducing autophagy in vitro[J]. J Food Biochem, 2022, 46 (10): e14301. |
| 31 | 曹炜炜, 张欢, 张月梅, 等. 丙泊酚后处理在高糖环境下改善H9c2心肌细胞缺氧/复氧诱导的凋亡和自噬[J]. 中国心血管病研究, 2024, 22 (2): 185- 192. |
| CAO W W , ZHANG H , ZHANG Y M , et al. Propofol postconditioning ameliorates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis and autophagy in H9c2 cardiomyocytes under high glucose environment[J]. Chin J Cardiovasc Res, 2024, 22 (2): 185- 192. | |
| 32 | 周康. 红景天苷通过AMPK/mTOR信号通路激活海绵体平滑肌细胞自噬治疗海绵体神经损伤大鼠勃起功能障碍[D]. 杭州: 浙江中医药大学, 2022. |
| ZHOU K. Salidroside activates autophagy of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle cells through AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway to treat erectile dysfunction in rats with cavernous nerve injury[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 33 | 李桢. Akt/mTOR通路介导的细胞自噬在4-壬基酚与双酚A致雄性子代生殖障碍中的作用[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2020. |
| LI Z. 4-nonylphenol and bisphenol A induces reproductive disorders by cell autophagy via Akt/mTOR pathway in F1 male rat[D]. Hubei: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 34 | 刘暑霞, 张玲, 柳赟昊, 等. PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP通路在双酚A诱导小鼠睾丸支持细胞凋亡中的作用[J]. 卫生研究, 2023, 52 (4): 591- 597. |
| LIU S X , ZHANG L , LIU Y H , et al. The role of PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP pathway in the apoptosis of TM4 cells induced by bisphenol A[J]. Journal of Hygiene Research, 2023, 52 (4): 591- 597. | |
| 35 |
RUNWAL G , STAMATAKOU E , SIDDIQI F H , et al. LC3-positive structures are prominent in autophagy-deficient cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9 (1): 10147.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46657-z |
| 36 |
JEONG S J , ZHANG X Y , RODRIGUEZ-VELEZ A , et al. p62/SQSTM1 and selective autophagy in cardiometabolic diseases[J]. Antioxid Redox Signaling, 2019, 31 (6): 458- 471.
doi: 10.1089/ars.2018.7649 |
| 37 |
HUANG F M , CHANG Y C , LEE S S , et al. Bisphenol A exhibits cytotoxic or genotoxic potential via oxidative stress-associated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in murine macrophages[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2018, 122, 215- 224.
doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2018.09.078 |
| 38 |
LIU T , DI Q N , SUN J H , et al. Effects of nonylphenol induced oxidative stress on apoptosis and autophagy in rat ovarian granulosa cells[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 261, 127693.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127693 |
| 39 | 胡莹莹, 丁珊珊, 林雪娟, 等. 促卵合剂调控AMPK/mTOR/HIF-1/VEGF通路改善卵泡发育不良大鼠氧化应激及凋亡的作用机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2024, 30 (16): 76- 84. |
| HU Y Y , DING S S , LIN X J , et al. Mechanism of Culuan Heji in regulating AMPK/mTOR/HIF-1/VEGF pathway to improve oxidative stress and apoptosis in rats with follicular maldevelopment[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2024, 30 (16): 76- 84. | |
| 40 |
CAO W Y , LI J H , YANG K P , et al. An overview of autophagy: mechanism, regulation and research progress[J]. Bull Cancer, 2021, 108 (3): 304- 322.
doi: 10.1016/j.bulcan.2020.11.004 |
| 41 |
MENG D X , LI Z , WANG G C , et al. Carvedilol attenuates liver fibrosis by suppressing autophagy and promoting apoptosis in hepatic stellate cells[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 108, 1617- 1627.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.005 |
| 42 |
ZHONG J Y , FANG L , CHEN R , et al. Polysaccharides from sporoderm-removed spores of Ganoderma lucidum induce apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells via disruption of autophagic flux[J]. Oncol Lett, 2021, 21 (5): 425.
doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12686 |
| [1] | WANG Ying, ZHANG Jiaojiao, WANG Xianzhong, QUAN Fusheng. Advances in Autophagy of Ovarian Granulosa Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1508-1517. |
| [2] | YE Rungen, LIU Yuanbo, LU Lili, Collins Amponsah Asiamah, SU Ying*. Expression of miR-215-5p in Leizhou Black Duck Tissues and Its Effect on Follicular Granulosa Cells Proliferation and Apoptosis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1722-1730. |
| [3] | PANG Siyao, ZHANG Jinlong, SUN Yuhang. Proteomic Analysis of 3D4/21 Cells Infected with H1N1 Swine Influenza Virus under Non-cytotoxic Concentration of AFB1 Exposure [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1947-1957. |
| [4] | LIU Chenlong, JI Huayuan, LU Dan, WAN Mingchun, HU Yao, ZHOU Quanyong. Effect of FST on Proliferation, Apoptosis and Hormone Secretion of Porcine Ovarian Granulosa Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1242-1251. |
| [5] | WANG Lei, BAI Shaocheng, WANG Sen, BAO Zhiyuan, CAI Jiawei, LIU Yan, ZHAO Bohao, WU Xinsheng, CHEN Yang. Effect of SRD5A2 on the Expression of Genes Related to Proliferation, Apoptosis and Steroid Hormone Synthesis in Rabbit Granulosa Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 259-268. |
| [6] | WANG Yi, HOU Lulu, FANG Fei, GAO Linying, XIE Shumin, WANG Yu. Fluoride Induced Small Intestine Oxidative Damage in Broilers via Autophagy and Ferroptosis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 442-454. |
| [7] | Xiangchen LI, Linnan WANG, Zhengqing YU, Li ZHANG, Chenchen YANG, Liangli SONG. Quercetin Inhibits Autophagy to Restore LTA-induced Tight Junction Function in Mammary Alveolar Cells-large T Antigen [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3887-3896. |
| [8] | 古丽米热·阿布都热依木, Xinru ZHANG, Yangsheng WU, Ying CHEN, Liqin WANG, Xinming XU, Juncheng HUANG, Jiapeng LIN. Effects of FKBP5 on Function of Sheep Follicular Granulosa Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3947-3956. |
| [9] | Yi WANG, Jianfei GONG, Nuo HENG, Yingfan HU, Rui WANG, Huan WANG, Ni ZHU, Wei HE, Zhihui HU, Haisheng HAO, Huabin ZHU, Shanjiang ZHAO. Melatonin Alleviates Palmitic Acid-induced Damage in Bovine Endometrial Epithelial Cells by Improving Mitochondrial Dynamics [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3978-3987. |
| [10] | Yi WANG, Juan GAO, Yuemin HU, Yuefei YANG, Bojun FAN, Huiming JU. Effect of Transient Serum Starvation on Metabolism and Autophagy of Porcine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3408-3417. |
| [11] | Zenghua LU, Yan CUI, Sijiu YU, Xuefeng BAI, Hongqin LU, Junfeng HE, Kai LU, Guoliang ZHAI, Zhengman QI. Effect of Erythropoietin on the Expression of Apoptotic Factor in Yak Renal Interstitial Fibroblasts [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3460-3471. |
| [12] | Xinyu CAO, Jiawei CAI, Zhiyuan BAO, Shuyu YAO, Yunpeng LI, Yang CHEN, Xinsheng WU, Bohao ZHAO. The Function Analysis of ATG14 Regulates the Autophagy Process in Rabbit Hair Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3472-3481. |
| [13] | Tong ZHAO, Wenzhe YANG, Feilong PAN, Shuchen ZHAO, Kexiang LIU, Zhanjun LÜ, Lijia ZHAO. Bisphenol A Inhibits Testosterone Synthesis in TM3 Cells by Upregulating Apoa1 Gene Expression [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3516-3525. |
| [14] | Zuhua YU, Mengru GAO, Lei HE, Ying WEI, Jian CHEN, Songbiao CHEN, Ke DING. Effects of mdv1-miR-M4-5p Encoded by MDV on Proliferation and Apoptosis of MDCC-MSB1 Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3678-3687. |
| [15] | Milan MA, Qi WANG, Qiu YAN, Tianan LI, Xingxu ZHAO, Yong ZHANG. Expression of HIG1 Hypoxia Inducible Domain Family Member 1C in Cryptorchidism of Yak and Its Regulatory Mechanism [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2983-2994. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
