





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (11): 5247-5258.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.11.040
• Basic Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yao TANG( ), Tao WANG, Mengqing XUE, Wenyu ZHANG, Mei SHI, Xianzhong WANG, Jiaojiao ZHANG*(
), Tao WANG, Mengqing XUE, Wenyu ZHANG, Mei SHI, Xianzhong WANG, Jiaojiao ZHANG*( )
)
Received:2024-01-11
Online:2024-11-23
Published:2024-11-30
Contact:
Jiaojiao ZHANG
E-mail:1264142767@qq.com;zhangjjff@126.com
CLC Number:
Yao TANG, Tao WANG, Mengqing XUE, Wenyu ZHANG, Mei SHI, Xianzhong WANG, Jiaojiao ZHANG. Thiazolidinedione Inhibits Chicken Growth via Adiponectin-mediated AMPK Signaling Pathway[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 5247-5258.
Table 1
Primer sequences for RT-PCR"
| 基因 Gene | 序列号 Sequence number | 序列位置 Sequence position | 序列长度/bp Product length | 退火温度/℃ Annealing temperature | 序列(5′→3′) Sequence |
| β-actin | NM_205518.1 | 625-818 | 194 | 58 | F: GTGCGTGACATCAAGGAGAAGC R: CCACAGGACTCCATACCCAAGA |
| ADIPOQ | AY523637.1 | 309-473 | 165 | 58 | F: TTCCTCCTTTGCTCACTGCT R: TCCATCTTTTCCATCCTTGC |
| ADIPOR1 | NM_001031027 | 280-523 | 244 | 57 | F: GTGATCCCCTACGATGTGCT R: TCCCAAACACAACCTTCTCC |
| ADIPOR2 | NM_001007854 | 711-915 | 205 | 57 | F: TGTGCAGGAGAAAGTGGTTG R: AGGCTGAGGGTTGCAGTAGA |
| AMPKα2 | NM_001039605.1 | 726-943 | 218 | 57 | F: GGAGGCGTGTTTTACATCCC R: AACTTCTCACAGACCTCCCG |
| mTOR | XM_417614.4 | 119-309 | 191 | 57 | F: TGAAGGGGTCAAGGCAATCC R: GGCGAGCAGTGGTTGTGGAT |
| IGF1 | NM_001004384.2 | 188-316 | 129 | 58 | F: AGTTCGTATGTGGAGACAGAGGC R: CCAGCCTCCTCAGGTCACAAC |
| IGF1R | NM_205032.1 | 2 961-3 114 | 154 | 57 | F: TTGTGCTCCCCATTGCTTTC R: GGAACGTACACATCCGAAGC |
| INS | NM_205222 | 126-308 | 183 | 59 | F: CACTGCCTCTTCTGGCTCTC R: GCAAGGGACTGCTCACTAGG |
| INSR | XM_001233398 | 2 303-2 462 | 160 | 57 | F: TGAGAGTGCAGAGGAGCAGA R: GGCACTGACATAAGCTGCAA |
| PIK3CA | NM_001004410 | 3 006-3 155 | 150 | 57 | F: AACATCTGGCAAAACCAAGG R: CTGCAATGCTCCCTTTAAGC |
| AKT1 | NM_205055.1 | 1 156-1 328 | 173 | 57 | F: AACGGAGGGGAGTTGTTTTT R: ATGTGCCCGTCTTTATCCAG |
| p21 | NM_204396 | 530-684 | 155 | 58 | F: TTTCCCTGCCCTGTACTGTC R: AGTCCTCCTCAGTCCCTTCC |
| p27 | NM_204256.2 | 922-1 102 | 181 | 58 | F: AGGCCGAAAGACTGATGTTG R: CGATTTCTTGGGTGTTTGCT |
| CDK2 | NM_001199857.1 | 386-562 | 177 | 58 | F: AACCCCAGAACCTCCTCATC R: TCCAGATGTCCACAGCAGTC |
| Cyclin E1 | NM_001031358.1 | 1 481-1 642 | 162 | 58 | F: CGCCAGCCACTTAAAAGAAC R: TGTCAACAGGGGACAGCATA |
Table 2
Primary and secondary antibodies and their respective dilutions"
| 抗体 Antibody | 目标蛋白 Target | 抗体名称 Name of antibody | 来源 Source and reference | 种属;克隆性 Species raised in; clonality | 稀释度 Dilution used |
| 一抗 Primary antibodies | p-AMPKα2 | Anti-phospho-AMPK alpha2 (Thr172) | Bioss Antibodies Inc., Woburn, MA, USA | Rabbit; polyclonal | 1∶300 |
| AMPKα2 | Anti-AMPK alpha2 | Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA | Rabbit; polyclonal | 1∶500 | |
| p-mTOR | Anti-mTOR (phosphor S2448) | Abcam | Rabbit; monoclonal | 1∶1 000 | |
| mTOR | Anti-mTOR | Abcam | Rabbit; polyclonal | 1∶1 000 | |
| Adiponectin | Anti-Adiponectin | Abcam | Rabbit; polyclonal | 1∶300 | |
| IGF1R | Anti-IGF1R | Bioss | Rabbit; polyclonal | 1∶500 | |
| INSR | Anti-Insulin Receptor | Bioss | Rabbit; polyclonal | 1∶500 | |
| PIK3CA | Anti-PIK3CA | Bioss | Rabbit; polyclonal | 1∶500 | |
| AKT1 | Anti-AKT1 | Abcam | Rabbit; polyclonal | 1∶500 | |
| p21 | p21 Polyclonal Antibody | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA | Rabbit; polyclonal | 1∶500 | |
| p27 | Anti-CDKN1B/p27 KIP 1 | Bioss | Rabbit; polyclonal | 1∶500 | |
| CDK2 | Anti-CDK2 | Bioss | Rabbit; polyclonal | 1∶500 | |
| Cyclin E1 | Anti-Cyclin E1 | Bioss | Rabbit; polyclonal | 1∶500 | |
| Beta-actin | Beta-actin (AC-15) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, Texas, USA | Rabbit; polyclonal | 1∶1 000 | |
| 二抗 Secondary antibodies | Goat IgG | Anti-rabbit IgG H & L (HRP) | Abcam | Goat; polyclonal | 1∶5 000 |
| Goat IgG | Anti-mouse IgG-HRP | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Goat; polyclonal | 1∶5 000 |

Fig. 1
Effects of TZD on chicken growth and related hormones A. Effect of TZD on the growth of chicks. ADFI. Average daily feed intake; AGD. Average daily gain; F/G ratio. Feed/gain ratio; Data are expressed as "$\bar x \pm s$" (n=40 for each group), compared with the control group, according to t test, *. P < 0.05; B. Serum ATP level; C. Serum adiponectin level; D. Serum insulin (INS) level; E. Serum levels of growth hormone (GH), insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 (IGFBP2); Data are represented as $\bar x \pm s$ (n=20 per group). For the female treatment group compared with the female control group, according to the t test *. P < 0.05, **. P < 0.01; for the male treatment group compared with the male control group, according to the t test, #. P < 0.05, ##. P < 0.01"


Fig. 2
Effects of TZD on ATP level and mitochondrial respiratory enzymes in the liver, kidney, and muscle of chicks A. ATP level; B. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide hydrogen (NADH) level; C. Cytochrome C oxidase activity; D. ATP synthase activity; Data are represented as "$\bar x \pm s$" (n=10 per group). For the female treatment group compared with the female control group according to the t test, *. P < 0.05 **. P < 0.01; for the male treatment group compared with the male control group according to the t test, #. P < 0.05, ##. P < 0.01"


Fig. 3
Effects of TZD on mRNA transcriptional level of growth-related genes in the liver, kidney, and muscle of chicks A. Relative mRNA levels of adiponectin (ADIPOQ), adiponectin receptor 1 (ADIPOR1), adiponectin receptor 2 (ADIPOR2), AMP-activated protein kinase α2 (AMPKα2), and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in the liver of TZD-treated chicks; B. Relative mRNA levels of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1), insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R), insulin (INS), insulin receptor (INSR), phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA), and AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 (AKT1) in the liver of TZD-treated chicks; C. Relative mRNA levels of p21, p27, Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), and Cyclin E1 in the liver of TZD-treated chicks; D-F and G-I show relative mRNA levels of above genes in the kidney and muscle respectively; Data are represented as $\bar x \pm s$ (n=3 per group). For the female treatment group compared with the female control group according to the t test, *. P < 0.05, **. P < 0.01; for the male treatment group compared with the male control group according to the t test, #. P < 0.05, ##. P < 0.01"

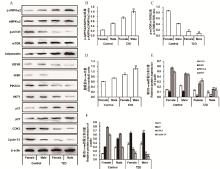
Fig. 4
Effects of TZD on growth-related protein expression in the muscle of chicks A. Western blot analysis of protein bands; B. p-AMPKα2/AMPKα2 ratio; C. p-mTOR/mTOR ratio; D. Relative protein level of adiponectin; E. Relative protein levels of IGF1R, INSR, PIK3CA, and AKT1; F. Relative protein levels of p21, p27, CDK2, and Cyclin E1; Data are represented as "$\bar x \pm s$" (n=3 per group). For the female treatment group compared with the female control group according to the t test, *. P < 0.05, **. P < 0.01; for the male treatment group compared with the male control group according to the t test, #. P < 0.05, ##. P < 0.01"

| 1 |
DATAR S P , BHONDE R R . Modeling chick to assess diabetes pathogenesis and treatment[J]. Rev Diabet Stud, 2011, 8 (2): 245- 253.
doi: 10.1900/RDS.2011.8.245 |
| 2 |
SWEAZEA K L . Revisiting glucose regulation in birds-a negative model of diabetes complications[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol, 2022, 262, 110778.
doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2022.110778 |
| 3 |
YU J G , JAVORSCHI S , HEVENER A L , et al. The effect of thiazolidinediones on plasma adiponectin levels in normal, obese, and type 2 diabetic subjects[J]. Diabetes, 2002, 51 (10): 2968- 2674.
doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.10.2968 |
| 4 |
INZUCCHI S E , BERGENSTAL R M , BUSE J B , et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach: position statement of the American diabetes association (ADA) and the European association for the study of diabetes (EASD)[J]. Diabetes Care, 2012, 35 (6): 1364- 1379.
doi: 10.2337/dc12-0413 |
| 5 |
LI Y W , KS N , BYRAN G , et al. Identification of selective PPAR-γ modulators by combining pharmacophore modeling, molecular docking, and adipogenesis assay[J]. Appl Biochem Biotechnol, 2023, 195 (2): 1014- 1041.
doi: 10.1007/s12010-022-04190-2 |
| 6 |
POURAZADI L , SHARAFI M , TORSHIZI M A K , et al. Modulatory effects of pioglitazone as a ligand for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor on semen quality and fertility potential of broiler breeder roosters[J]. Poult Sci, 2022, 101 (5): 101795.
doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101795 |
| 7 |
JIN C L , ZENG H R , XIE W Y , et al. Dietary supplementation with pioglitazone hydrochloride improves intramuscular fat, fatty acid profile, and antioxidant ability of thigh muscle in yellow-feathered chickens[J]. J Sci Food Agric, 2020, 100 (2): 665- 671.
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10062 |
| 8 |
QUARESMA P G F , REENCOBER N , ZANOTTO T M , et al. Pioglitazone treatment increases food intake and decreases energy expenditure partially via hypothalamic adiponectin/adipoR1/AMPK pathway[J]. Int J Obes (Lond), 2016, 40 (1): 138- 146.
doi: 10.1038/ijo.2015.134 |
| 9 |
TANYANSKIY D A , SHAVVA V S , DIZHE E B , et al. Adiponectin stimulates apolipoprotein A-1 gene expression in HepG2 cells via AMPK, PPARα, and LXRs signaling mechanisms[J]. Biochemistry (Mosc), 2022, 87 (11): 1252- 1259.
doi: 10.1134/S0006297922110049 |
| 10 | FANG H , JUDD R L . Adiponectin regulation and function[J]. Compr Physiol, 2018, 8 (3): 1031- 1063. |
| 11 |
INVERNIZZI M , LIPPI L , FOLLI A , et al. Integrating molecular biomarkers in breast cancer rehabilitation. What is the current evidence?A systematic review of randomized controlled trials[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2022, 9, 930361.
doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.930361 |
| 12 |
LI X R , ZHANG D Y , VATNER D F , et al. Mechanisms by which adiponectin reverses high fat diet-induced insulin resistance in mice[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2020, 117 (51): 32584- 32593.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922169117 |
| 13 |
FRANCISCHETTI E A , DEZONNE R S , PEREIRA C M , et al. Insights into the controversial aspects of adiponectin in cardiometabolic disorders[J]. Horm Metab Res, 2020, 52 (10): 695- 707.
doi: 10.1055/a-1239-4349 |
| 14 |
REIS M , VENEZIANI L P , PORTO F L , et al. Intrathymic somatotropic circuitry: consequences upon thymus involution[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14, 1108630.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1108630 |
| 15 |
ORRÙ S , NIGRO E , MANDOLA A , et al. A Functional Interplay between IGF-1 and adiponectin[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18 (10): 2145.
doi: 10.3390/ijms18102145 |
| 16 |
SCHINDLER M , PENDZIALEK M , GRYBEL K J , et al. Adiponectin stimulates lipid metabolism via AMPK in rabbit blastocysts[J]. Hum Reprod, 2017, 32 (7): 1382- 1392.
doi: 10.1093/humrep/dex087 |
| 17 |
PARDINA E , FERRER R , BAENA-FUSTEGUERAS J A , et al. The relationships between IGF-1 and CRP, NO, leptin, and adiponectin during weight loss in the morbidly obese[J]. Obes Surg, 2010, 20 (5): 623- 632.
doi: 10.1007/s11695-010-0103-5 |
| 18 |
GUEVARA-AGUIRRE J , ROSENBLOOM A L , GUEVARA A , et al. Divergent metabolic phenotypes in two genetic syndromes of low insulin secretion[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2023, 196, 110228.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2022.110228 |
| 19 |
SATO T , SEGAWA M , SEKINE S , et al. Mild depolarization is involved in troglitazone-induced liver mitochondrial membrane permeability transition via mitochondrial iPLA2 activation[J]. J Toxicol Sci, 2019, 44 (11): 811- 820.
doi: 10.2131/jts.44.811 |
| 20 |
WU S N , ZOU M H . AMPK, mitochondrial function, and cardiovascular disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21 (14): 4987.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21144987 |
| 21 |
WANG S T , HO H J , LIN J T , et al. Simvastatin-induced cell cycle arrest through inhibition of STAT3/SKP2 axis and activation of AMPK to promote p27 and p21 accumulation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2017, 8 (2): e2626.
doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.472 |
| 22 |
JOUBERT R , MÉTAYER COUSTARD S , SWENNEN Q , et al. The beta-adrenergic system is involved in the regulation of the expression of avian uncoupling protein in the chicken[J]. Domest Anim Endocrinol, 2010, 38 (2): 115- 125.
doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2009.08.002 |
| 23 |
YADAV U , VANJARI Y , LAXMIKESHAV K , et al. Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of phenanthrene linked 2, 4- thiazolidinediones as potential anticancer agents[J]. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 2021, 21 (9): 1127- 1140.
doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200714142931 |
| 24 |
ZHANG J J , LI Y Q , SHI M , et al. 17β-estradiol rescues the damage of thiazolidinedione on chicken Sertoli cell proliferation via adiponectin[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2022, 233, 113308.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113308 |
| 25 |
GIANNINI S , SERIO M , GALLI A . Pleiotropic effects of thiazolidinediones: taking a look beyond antidiabetic activity[J]. J Endocrinol Invest, 2004, 27 (10): 982- 991.
doi: 10.1007/BF03347546 |
| 26 |
HU X Y , LIU L , SONG Z G , et al. Effects of feed deprivation on the AMPK signaling pathway in skeletal muscle of broiler chickens[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol, 2016, 191, 146- 154.
doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2015.10.007 |
| 27 |
ZHANG J J , WANG X Z , LUONG DO H , et al. MicroRNA-7450 regulates non-thermal plasma-induced chicken Sertoli cell apoptosis via adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activation[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8 (1): 8761.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27123-8 |
| 28 |
JIAO Z J , YI W , RONG Y W , et al. MicroRNA-1285 regulates 17β-estradiol-inhibited immature boar sertoli cell proliferation via adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activation[J]. Endocrinology, 2015, 156 (11): 4059- 4070.
doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1982 |
| 29 |
MACVANIN M , GLUVIC Z , RADOVANOVIC J , et al. New insights on the cardiovascular effects of IGF-1[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2023, 14, 1142644.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1142644 |
| 30 |
BIONDO L A , TEIXEIRA A A S , DE O S FERREIRA K C , et al. Pharmacological strategies for insulin sensitivity in obesity and cancer: thiazolidinediones and metformin[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2020, 26 (9): 932- 945.
doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200122124116 |
| 31 |
SEGAWA M , SEKINE S , SATO T , et al. Increased susceptibility to troglitazone-induced mitochondrial permeability transition in type 2 diabetes mellitus model rat[J]. J Toxicol Sci, 2018, 43 (5): 339- 351.
doi: 10.2131/jts.43.339 |
| 32 | SEYDI E , SERVATI T , SAMIEI F , et al. Toxicity of pioglitazone on mitochondria isolated from brain and heart: an analysis for probable drug-induced neurotoxicity and cardiotoxicity[J]. Drug Res (Stuttg), 2020, 70 (2-3): 112- 118. |
| 33 |
JIANG Q X , JI A D , LI D C , et al. Mitochondria damage in ambient particulate matter induced cardiotoxicity: roles of PPAR alpha/PGC-1 alpha signaling[J]. Environ Pollut, 2021, 288, 117792.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117792 |
| 34 |
QI Y B , HU M Y , QIU Y , et al. Mitoglitazone ameliorates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via targeting mitoNEET[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2023, 465, 116440.
doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2023.116440 |
| 35 |
JEON K I , KUMAR A , CALLAN C L , et al. Blocking mitochondrial pyruvate transport alters corneal myofibroblast phenotype: a new target for treating fibrosis[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2023, 64 (13): 36.
doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.13.36 |
| 36 |
BOVA M P , TAM D , MCMAHON G , et al. Troglitazone induces a rapid drop of mitochondrial membrane potential in liver HepG2 cells[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2005, 155 (1): 41- 50.
doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2004.08.009 |
| 37 |
HU D , WU C Q , LI Z J , et al. Characterizing the mechanism of thiazolidinedione-induced hepatotoxicity: an in vitro model in mitochondria[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2015, 284 (2): 134- 141.
doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.02.018 |
| 38 |
MANIERI E , HERRERA-MELLE L , MORA A , et al. Adiponectin accounts for gender differences in hepatocellular carcinoma incidence[J]. J Exp Med, 2019, 216 (5): 1108- 1119.
doi: 10.1084/jem.20181288 |
| 39 |
GURU B , TAMRAKAR A K , MANJULA S N , et al. Novel dual PPARα/γ agonists protect against liver steatosis and improve insulin sensitivity while avoiding side effects[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2022, 935, 175322.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175322 |
| 40 |
FRÖHLICH E , MACHICAO F , WAHL R . Action of thiazolidinediones on differentiation, proliferation and apoptosis of normal and transformed thyrocytes in culture[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2005, 12 (2): 291- 303.
doi: 10.1677/erc.1.00973 |
| 41 | EGGLETON J S I . Thiazolidinediones[M]. Treasure Island: StatPearls Publishing, 2023. |
| 42 |
BODEN G , ZHANG M J . Recent findings concerning thiazolidinediones in the treatment of diabetes[J]. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 2006, 15 (3): 243- 250.
doi: 10.1517/13543784.15.3.243 |
| 43 |
YAMAUCHI T , NIO Y , MAKI T , et al. Targeted disruption of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 causes abrogation of adiponectin binding and metabolic actions[J]. Nat Mede, 2007, 13 (3): 332- 339.
doi: 10.1038/nm1557 |
| 44 | SUGIYAMA M , TAKAHASHI H , HOSONO K , et al. Adiponectin inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth through the AMPK/mTOR pathway[J]. Int J Oncol, 2009, 34 (2): 339- 44. |
| 45 |
QI H P , LIU Y , LI S Z , et al. Activation of AMPK attenuated cardiac fibrosis by inhibiting CDK2 via p21/p27 and miR-29 family pathways in rats[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2017, 8, 277- 290.
doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.07.004 |
| 46 |
SINAGRA T , TAMBURELLA A , URSO V , et al. Reversible inhibition of vasoconstriction by thiazolidinediones related to PI3K/Akt inhibition in vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2013, 85 (4): 551- 559.
doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.11.013 |
| 47 |
STRELECKIENE G , INCIURAITE R , JUZENAS S , et al. miR-20b and miR-451a are involved in gastric carcinogenesis through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway: data from gastric cancer patients, cell lines and ins-gas mouse model[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21 (3): 877.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21030877 |
| 48 |
ALZAHRANI A S . PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in cancer: at the bench and bedside[J]. Seminars in cancer biology, 2019, 59, 125- 132.
doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.07.009 |
| 49 | LEE S M , MURATALLA J , SIERRA-CRUZ M , et al. Role of hepatic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Endocrinol, 2023, 257 (1): e220155. |
| 50 | COUGHLAN K A , VALENTINE R J , RUDERMAN N B , et al. AMPK activation: a therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes?[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes, 2014, 7, 241- 253. |
| 51 | QIU H , YANG J K , CHEN C . Influence of insulin on growth hormone secretion, level and growth hormone signalling[J]. Acta Physiol Sin, 2017, 69 (5): 541- 556. |
| 52 |
YOSHIDA T , DELAFONTAINE P . Mechanisms of IGF-1-mediated regulation of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy[J]. Cells, 2020, 9 (9): 1970.
doi: 10.3390/cells9091970 |
| 53 |
KUAI M Y , LI Y , SUN X , et al. A novel formula Sang-Tong-Jian improves glycometabolism and ameliorates insulin resistance by activating PI3K/AKT pathway in type 2 diabetic KKAy mice[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2016, 84, 1585- 1594.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.10.101 |
| [1] | Yao LI, Rui JIA, Jie LI, Shuangbao GUN, Qiaoli YANG, Longlong WANG, Pengxia ZHANG, Xiaoli GAO, Xiaoyu HUANG. Effects of Low Temperature on Adipose Tissue Morphology, Lipid Metabolism-Related Gene Expression and Enzyme Activities, and AMPK/PGC-1α Pathway in Hezuo Pigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3418-3426. |
| [2] | Yi WANG, Juan GAO, Yuemin HU, Yuefei YANG, Bojun FAN, Huiming JU. Effect of Transient Serum Starvation on Metabolism and Autophagy of Porcine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3408-3417. |
| [3] | Ya’nan LI, Tianwen MA, Yuhui MA, Chengwei WEI. Bilobalide Regulates Mitochondrial Biogenesis Mediated by AMPK-SIRT3 Positive Feedback Loop and Improves Inflammatory Damage of ATDC5 Chondrocytes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3714-3724. |
| [4] | ZHAO Huiying, YU Shiqiang, ZHAO Yuchao, JIANG Linshu. Mechanism of Liver-Adipose Tissue Crosstalk in the Development of Fatty Liver in Periparturient Cows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(10): 4105-4116. |
| [5] | ZHU Wenjun, CHEN Xingyong, LIU Le, LIU Zhengquan, ZHAO Yutong, GENG Zhaoyu. Fatty Acid Composition and Gene Expression of AMPK Signaling Pathway in Liver of Muscovy Duck at Different Egg-laying Stages [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(9): 2429-2438. |
| [6] | WANG Qi, WANG Changjian, WEI Zongyou, LU Hanxi, YAO Xiaolei, YANG Hua, WANG Feng, ZHANG Yanli. Study on the Role of AMPK Activator in Cryopreservation of Sheep Semen [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(12): 3033-3045. |
| [7] | CHEN Miaomiao, TONG Xishuai, ZHENG Jiaming, ZHAO Hongyan, GU Jianhong, LIU Zongping. Effects of 5-amino-imidazole-4-carboxamide Nucleotide on Autophagy and Differentiation in Osteoclasts [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2019, 50(11): 2339-2347. |
| [8] | YAO Xiao-lei, HUANG Xin-ai, XIAO Shen-hua, ZHENG Lin-feng, FAN Li-jie, JIN Yu-yue, LIU Zi-fei, ZHANG Yan-li, WANG Jie, WANG Feng. Expression Patterns and Correlation of Adiponectin Receptors and Testosterone Secretion Related-genes Expression in Male Reproductive Organs at Different Developmental Stages of Hu Sheep [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2018, 49(8): 1642-1650. |
| [9] | LI Kan, LIU Wen-zhong, ZHANG Rui-xin, LI Qian, ZHANG Ting, QIN Xu-ze, ZHANG Jian-xin, ZHAO Jun-xing. AMPK Regulates Sheep Muscle Derived Preadipocytes Differentiation [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2018, 49(8): 1594-1604. |
| [10] | TANG Ni, WANG Shu-yao, QI Jin-wen, WU Yuan-bing, LI Zhi-qiong. Research Progress on Adiponectin Regulating Lipid Metabolism [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2018, 49(12): 2550-2557. |
| [11] | ZHOU Hua-jin, HU Xi-yi, YANG Jia-chang, DING Xiang-wen, WANG Yu, SONG Zhi-gang. Effects of Heat Stress on Gene Expression of AMPKα1 and Lipid Metabolism Related Molecules in the Liver of Broiler Chickens [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2018, 49(1): 102-110. |
| [12] | SHEN Liu-hong,JIANG Tao,WU Xiao-feng,JIANG Si-xun,XIAO Jin-bang,CAO Sui-zhong,YU Shu-min,DENG Jun-liang,ZUO Zhi-cai,PENG Guang-neng,MA Xiao-ping,ZHONG Zhi-jun,REN Zhi-hua,WANG Ya,HU Yan-chun. The Correlation between Adiponectin,Leptin,Visfatin in Placenta and Calf Birth Weight [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2017, 48(1): 185-192. |
| [13] | LIU Aisha;LI Yan;HU Wenfeng;WU Tongshan;LI Jiaqi;CHEN Zhenwei;JIANG Guanyao;LI Li . Expression of Porcine Globular Adiponectin Gene in Lactococcus lactis [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2012, 43(3): 353-357. |
| [14] | YANG Ye, SONG Jiao, FU Rui-qi, LI Ying-ying, GOU Zhong-yong, SUI Yan-fa, ZHAO Gui-ping, WEN Jie. The Expression of Beijing-You Chicken AMPK Gene and Its Effects on the Adipogenesis in the Muscle and Adipocyte [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2012, 43(11): 1703-1709. |
| [15] | SHAO Kang;ZHOU Jie;WU Xiaoxue;SHU Baoping;LUO Lianhui;SHENG Sheng;ZHANG Jia;LI Weixin;YIN Zongjun. Developmental Patterns and Correlation of Adiponectin Receptors,LHR,CYP11A1 and StAR mRNA Expression in Testis of Wannan Hua Pigs [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2011, 42(12): 1680-1685. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||