





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (10): 4489-4499.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.10.021
• Animal Biotechnology and Reproduction • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wanyi LAI1( ), Xinyue TAO1, Gengxin YANG2, Wenli YU2, Shujing LI2, Tahir USMAN3, Ying YU1,*(
), Xinyue TAO1, Gengxin YANG2, Wenli YU2, Shujing LI2, Tahir USMAN3, Ying YU1,*( )
)
Received:2024-04-07
Online:2024-10-23
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Ying YU
E-mail:laiwanyi@cau.edu.cn;yuying@cau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Wanyi LAI, Xinyue TAO, Gengxin YANG, Wenli YU, Shujing LI, Tahir USMAN, Ying YU. Application Study of Chinese Cow's SNPs Chip-Ⅰ in Chinese Holstein and Pakistani Indigenous Dairy Cattle Populations[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4489-4499.

Fig. 2
Single-locus association analysis results of Chinese Holstein (least squares mean±standard error) A. SCC is the quantitative variable; B. SCS is the quantitative variable. *. Significant difference (P < 0.05); **. Extremely significant difference (P < 0.01). The figure shows only the models with the least AIC"


Fig. 3
Single-locus association analysis results of Chinese Holstein (SCC is the categorical variable) 0 and 1 represent cows with subclinical mastitis and healthy cows, with SCC≥100 000 ·mL-1 as the dividing criteria; The figure shows only the models with the least AIC; When OR > 1, it was considered that the genotype had no resistance to mastitis; When OR < 1, the genotype was considered to have mastitis resistance; When OR=1, the genotype was not considered to be associated with mastitis resistance. The same as Figure 5"

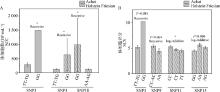
Fig. 4
Single-locus association analysis results of Pakistani Holstein and indigenous Achai (least squares mean±standard error) A. SCC is the quantitative variable; B. SCS is the quantitative variable. *. Significant difference (P < 0.05); Near significant difference when P < 0.1. The figure shows only the models with the least AIC"

Table 1
Pairwise SNP association analysis of Chinese Holstein"
| 成对位点Pairwise SNP | 基因1 Gene1 | 基因2 Gene2 | 模式 Model | P值 P-value | 优势基因型 Advantage genotype | |
| 位点1 SNP1 | 位点2 SNP2 | |||||
| SNP4 | SNP9 | JAK2 | STAT5A | DD_int_rr_1vs0 | 0.002 8 | TC+CC/CA+AA |
| SNP6 | SNP8 | JAK2 | JAK2 | RD_int_ro_1vs0 | 0.000 1 | CC/CC |
| SNP8 | SNP11 | JAK2 | CD4 | DD_int_oo_1vs0 | 0.002 0 | CT+TT/CT+TT |
| SNP8 | SNP15 | JAK2 | DGAT1 | DD_int_or_1vs0 | 0.005 4 | CT+TT/AA |
| SNP11 | SNP15 | CD4 | DGAT1 | RD_int_or_1vs0 | 0.004 7 | CC+CT/AG+GG |
| SNP11 | SNP17 | CD4 | DGAT1 | DD_int_ro_1vs0 | 0.002 1 | CT+TT/TT |
| SNP15 | SNP19 | DGAT1 | TRAPPC9 | DD_int_rr_1vs0 | 0.000 6 | AG+GG/GA+AA |
| SNP15 | SNP20 | DGAT1 | PTK2 | DD_int_rr_1vs0 | 0.000 7 | AG+GG/GA+AA |
Table 2
Pairwise SNP association analysis of Chinese Holstein in Hebei province"
| 成对位点Pairwise SNP | 基因1 Gene1 | 基因2 Gene2 | 模式 Model | P值 P-value | 优势基因型 Advantage genotype | |
| 位点1 SNP1 | 位点2 SNP2 | |||||
| SNP6 | SNP18 | JAK2 | TRAPPC9 | RD_int_rr_1vs0 | 0.006 7 | TT+TC/GG |
| SNP6 | SNP19 | JAK2 | TRAPPC9 | AA_int_ro_12 | 0.003 9 | TT/AA |
| SNP6 | SNP20 | JAK2 | PTK2 | AA_int_ro_12 | 0.003 3 | TT/AA |
| SNP9 | SNP19 | STAT5A | TRAPPC9 | AA_int_rr_12 | 0.001 5 | AA/AA |
| SNP9 | SNP20 | STAT5A | PTK2 | AA_int_rr_12 | 0.001 5 | AA/AA |
| SNP11 | SNP15 | CD4 | DGAT1 | AA_int_ro_12 | 0.008 9 | CC/GG |
| SNP11 | SNP18 | CD4 | TRAPPC9 | DD_int_rr_1vs0 | 0.004 8 | CT+TT/AG+GG |
| SNP12 | SNP15 | LAG3 | DGAT1 | AA_int_rr_12 | 0.002 2 | AA/GG |
| SNP12 | SNP17 | LAG3 | DGAT1 | AA_int_rr_12 | 0.002 8 | AA/CC |
Table 3
Pairwise SNP association analysis of Pakistani indigenous Achai and Holstein"
| 品种 Breed | 成对位点Pairwise SNP | 基因1 Gene1 | 基因2 Gene2 | 模式 Model | P值 P-value | 优势基因型 Advantage genotype | |
| 位点1 SNP1 | 位点2 SNP2 | ||||||
| 阿卡牛Achai | SNP3 | SNP11 | TRAPPC9 | CD4 | DD_int_rr_1vs0 | 0.043 7 | TT/TT |
| SNP3 | SNP15 | TRAPPC9 | DGAT1 | AA_int_rr_12 | 0.032 5 | TT/GG | |
| SNP16 | SNP17 | DGAT1 | DGAT1 | DD_int_rr_1vs0 | 0.010 0 | GG/CC | |
| SNP17 | SNP18 | DGAT1 | TRAPPC9 | DR_int_or_1vs0 | 0.015 4 | CC/GG | |
| SNP17 | SNP19 | DGAT1 | TRAPPC9 | DR_int_rr_1vs0 | 0.015 4 | CC/GG+GA | |
| 巴基斯坦荷斯坦牛 | SNP2 | SNP11 | TRAPPC9 | CD4 | AA_int_ro_12 | 0.015 0 | CC/TT |
| Pakistani Holstein | SNP4 | SNP11 | JAK2 | CD4 | AA_int_ro_12 | 0.003 9 | TT/TT |
| SNP8 | SNP11 | JAK2 | CD4 | AA_int_ro_12 | 0.004 4 | CC/TT | |
| SNP8 | SNP15 | JAK2 | DGAT1 | DD_int_ro_1vs0 | 0.019 6 | CC/AG+GG | |
| SNP8 | SNP19 | JAK2 | TRAPPC9 | AA_int_ro_12 | 0.026 2 | CC/AA | |
| SNP8 | SNP20 | JAK2 | PTK2 | DD_int_rr_1vs0 | 0.034 5 | CC/GG | |
| SNP9 | SNP11 | STAT5A | CD4 | AA_int_oo_12 | 0.008 9 | AA/TT | |
| SNP9 | SNP19 | STAT5A | TRAPPC9 | AA_int_oo_12 | 0.009 2 | AA/AA | |
| SNP11 | SNP12 | CD4 | LAG3 | AA_int_rr_12 | 0.012 5 | TT/AA | |
| SNP11 | SNP16 | CD4 | DGAT1 | RD_int_oo_1vs0 | 0.008 8 | TT/AG+GG | |
| SNP11 | SNP19 | CD4 | TRAPPC9 | AA_int_rr_12 | 0.003 4 | TT/AA | |
| SNP12 | SNP16 | LAG3 | DGAT1 | DD_int_or_1vs0 | 0.032 6 | GA+AA/AA | |
| SNP15 | SNP16 | DGAT1 | DGAT1 | DD_int_or_1vs0 | 0.028 1 | AG+GG/AA | |
| SNP17 | SNP19 | DGAT1 | TRAPPC9 | AA_int_ro_12 | 0.016 1 | TT/AA | |
| SNP18 | SNP19 | TRAPPC9 | TRAPPC9 | DD_int_ro_1vs0 | 0.028 1 | AA/GA+AA | |
| SNP19 | SNP20 | TRAPPC9 | PTK2 | DD_int_or_1vs0 | 0.000 3 | GA+AA/GG | |
| 1 |
DODDF H,HOARER J T.Progress in the control of bovine mastitis[J].Aust Vet J,1985,62(S1):37-40.
doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1985.tb13887.x |
| 2 |
MEKTRIRATR,CHUAMMITRIP,NAVATHONGD,et al.Exploring the potential immunomodulatory effects of gallic acid on milk phagocytes in bovine mastitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus[J].Front Vet Sci,2023,10,1255058.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1255058 |
| 3 | 叶雯,麻柱,俞英,等.我国奶牛乳房炎发病现状及防治措施[J].中国畜牧杂志,2023,59(9):343-348. |
| YEW,MAZ,YUY,et al.Incidence status of mastitis in dairy cows and its prevention and treatment measures in China[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Science,2023,59(9):343-348. | |
| 4 |
WANGM Q,LIANGY,IBEAGHA-AWEMUE M,et al.Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of mammary gland tissues from Chinese Holstein cows with Staphylococcus aureus induced mastitis[J].Front Genet,2020,11,550515.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.550515 |
| 5 |
MARTINP,BARKEMAH W,BRITOL F,et al.Symposium review: novel strategies to genetically improve mastitis resistance in dairy cattle[J].J Dairy Sci,2018,101(3):2724-2736.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13554 |
| 6 |
YUANZ R,CHUG Y,DANY,et al.BRCA1:a new candidate gene for bovine mastitis and its association analysis between single nucleotide polymorphisms and milk somatic cell score[J].Mol Biol Rep,2012,39(6):6625-6631.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1467-5 |
| 7 |
MAGOTRAA,GUPTAI D,AHMADT,et al.Polymorphism in DNA repair gene BRCA1 associated with clinical mastitis and production traits in indigenous dairy cattle[J].Res Vet Sci,2020,133,194-201.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2020.09.013 |
| 8 | WANGC F,LIUM,LIQ L,et al.Three novel single-nucleotide polymorphisms of MBL1 gene in Chinese native cattle and their associations with milk performance traits[J].Vet Immunol Immunopathol,2011,139(2/4):229-236. |
| 9 |
LIUJ B,JUZ H,LIQ L,et al.Mannose-binding lectin 1 haplotypes influence serum MBL-A concentration, complement activity, and milk production traits in Chinese Holstein cattle[J].Immunogenetics,2011,63(11):727-742.
doi: 10.1007/s00251-011-0548-2 |
| 10 |
KAMALDEEP,MAGOTRAA,PANDERB L,et al.Evaluation of candidate genotype of immune gene MBL1 associated with udder health and performance traits in dairy cattle and buffalo of India[J].Trop Anim Health Prod,2021,53(4):429.
doi: 10.1007/s11250-021-02865-2 |
| 11 | BEECHERC,DALYM,CHILDSS,et al.Polymorphisms in bovine immune genes and their associations with somatic cell count and milk production in dairy cattle[J].BMC Genet,2010,11,99. |
| 12 |
DE MESQUITAA Q,REZENDEC S M E,DE MESQUITAA J,et al.Association of TLR4 polymorphisms with subclinical mastitis in Brazilian holsteins[J].Braz J Microbiol,2012,43(2):692-697.
doi: 10.1590/S1517-83822012000200034 |
| 13 |
LIJ,WANGQ,CHENF H,et al.SNPs of CD14 change the mastitis morbidity of Chinese Holstein[J].Mol Med Rep,2017,16(6):9102-9110.
doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7727 |
| 14 |
KHANM Z,WANGJ J,MAY L,et al.Genetic polymorphisms in immune- and inflammation-associated genes and their association with bovine mastitis resistance/susceptibility[J].Front Immunol,2023,14,1082144.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1082144 |
| 15 |
KHANM Z,WANGD,LIUL,et al.Significant genetic effects of JAK2 and DGAT1 mutations on milk fat content and mastitis resistance in Holsteins[J].J Dairy Res,2019,86(4):388-393.
doi: 10.1017/S0022029919000682 |
| 16 |
KHANM Z,DARIG,KHANA,et al.Genetic polymorphisms of TRAPPC9 and CD4 genes and their association with milk production and mastitis resistance phenotypic traits in Chinese Holstein[J].Front Vet Sci,2022,9,1008497.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1008497 |
| 17 | GONZÁLEZJ R,ARMENGOLL,SOLÉX,et al.SNPassoc: an R package to perform whole genome association studies[J].Bioinformatics,2007,23(5):654-655. |
| 18 | 马裴裴,俞英,张沅,等.中国荷斯坦牛SCC变化规律及其与产奶性状之间的关系[J].畜牧兽医学报,2010,41(12):1529-1535. |
| MAP P,YUY,ZHANGY,et al.The distribution of SCC and its correlation with milk production traits in Chinese Holsteins[J].Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica,2010,41(12):1529-1535. | |
| 19 |
LINH Y,CHEND T,HUANGP Y,et al.SNP interaction pattern identifier (SIPI): an intensive search for SNP-SNP interaction patterns[J].Bioinformatics,2017,33(6):822-833.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw762 |
| 20 |
RUTERBUSCHM,PRUNERK B,SHEHATAL,et al.In vivo CD4+ T cell differentiation and function: revisiting the Th1/Th2 paradigm[J].Annu Rev Immunol,2020,38,705-725.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-103019-085803 |
| 21 | LUX B,ARBABA A I,ABDALLAI M,et al.Genetic parameter estimation and genome-wide association study-based loci identification of milk-related traits in Chinese Holstein[J].Front Genet,2021,12,799664. |
| 22 | LIUL Y,ZHOUJ H,CHENC J,et al.GWAS-based identification of new loci for milk yield, fat, and protein in Holstein cattle[J].Animals (Basel),2020,10(11):2048. |
| 23 |
PARVEENA,ASHRAFS,AKTASM,et al.Molecular epidemiology of Theileria annulata infection of cattle in Layyah District, Pakistan[J].Exp Appl Acarol,2021,83(3):461-473.
doi: 10.1007/s10493-021-00595-6 |
| 24 |
IQBALN,LIUX,YANGT,et al.Genomic variants identified from whole-genome resequencing of indicine cattle breeds from Pakistan[J].PLoS One,2019,14(4):e0215065.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215065 |
| 25 |
RAFIQA,ZAREENG,AKBARS,et al.Association of genotypes at rs438228855 in bovine SLC35A3 receptor gene of Pakistani cattle with the susceptibility to develop complex vertebral malformation[J].Reprod Domest Anim,2023,58(6):754-761.
doi: 10.1111/rda.14346 |
| 26 | 周月玲,达日格日乐,唐永杰,等.中国荷斯坦牛乳房炎抗性相关SNP效应扩群验证及分析[J].中国畜牧杂志,2022,58(12):92-98. |
| ZHOUY L,DARIGERILE,TANGY J,et al.Genetic effect of SNP loci associated with mastitis resistance in an extended validation cohort of Chinese Holstein cattle[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Science,2022,58(12):92-98. | |
| 27 | WORKUD,GOWANEG R,MUKHERJEEA,et al.Associations between polymorphisms of LAP3 and SIRT1 genes with clinical mastitis and milk production traits in Sahiwal and Karan Fries dairy cattle[J].Vet Med Sci,2022,8(6):2593-2604. |
| 28 | WORKUD,VERMAA.Genetic variation in bovine LAP3 and SIRT1 genes associated with fertility traits in dairy cattle[J].BMC Genom Data,2024,25(1):32. |
| 29 | BOYEC,NIRMALANS,RANJBARANA,et al.Genotype×environment interactions in gene regulation and complex traits[J].Nat Genet,2024,56(6):1057-1068. |
| 30 | FLETCHERO,DUDBRIDGEF.Candidate gene-environment interactions in breast cancer[J].BMC Med,2014,12,195. |
| 31 | HANJ H,LIANGJ,ZHOUW Q,et al.Association between NUDT17 polymorphisms and breast cancer risk[J].Expert Rev Mol Diagn,2024,24(5):459-466. |
| 32 | 冯文,董易春,王晓,等.TRAPPC9基因对奶牛金葡菌乳房炎抗性性状的遗传效应[J].畜牧兽医学报,2016,47(2):276-283. |
| FENGW,DONGY C,WANGX,et al.The genetic effect of TRAPPC9 on mastitis resistance to S.aureus in dairy cows[J].Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica,2016,47(2):276-283. | |
| 33 | MBIMBAT,HUSSEINN J,NAJEEDA,et al.TRAPPC9:Novel insights into its trafficking and signaling pathways in health and disease (Review)[J].Int J Mol Med,2018,42(6):2991-2997. |
| 34 | BODNARB,DEGRUTTOLAA,ZHUY J,et al.Emerging role of NIK/IKK2-binding protein (NIBP)/trafficking protein particle complex 9 (TRAPPC9) in nervous system diseases[J].Transl Res,2020,224,55-70. |
| 35 | YOSHIMURAS,BONDESONJ,BRENNANF M,et al.Role of NFκB in antigen presentation and development of regulatory T cells elucidated by treatment of dendritic cells with the proteasome inhibitor PSI[J].Eur J Immunol,2001,31(6):1883-1893. |
| 36 | SHARUNK,DHAMAK,TIWARIR,et al.Advances in therapeutic and managemental approaches of bovine mastitis: a comprehensive review[J].Vet Q,2021,41(1):107-136. |
| 37 | SALEEMA,SALEEMB S,OMONIJOF A,et al.Immunotherapy in mastitis: state of knowledge, research gaps and way forward[J].Vet Q,2024,44(1):1-23. |
| 38 | COSTAA,DE MARCHIM,NEGLIAG,et al.Milk somatic cell count-derived traits as new indicators to monitor udder health in dairy buffaloes[J].Ital J Anim Sci,2021,20(1):548-558. |
| 39 | HUMAZ I,SHARMAN,KOURS,et al.Phenotypic and molecular characterization of bovine mastitis milk origin bacteria and linkage of intramammary infection with milk quality[J].Front Vet Sci,2022,9,885134. |
| 40 |
杨晴,巩静,赵雪艳,等.芯片和重测序在猪遗传结构研究中的应用比较[J].畜牧兽医学报,2023,54(7):2772-2782.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.07.011 |
|
YANGQ,GONGJ,ZHAOX Y,et al.Comparison of array and resequencing in pig genetic structure studies[J].Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica,2023,54(7):2772-2782.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.07.011 |
|
| 41 | 黄金明, 王秀革, 姜强, 等. 一套同时检测93种牛遗传缺陷基因和致死单倍型的引物组合及试剂盒: 中国, 201710438948.9[P]. 2020-03-17. |
| HUANG J M, WANG X G, JIANG Q, et al. Primer combination and kit for simultaneous detection of 93 bovine genetic defect genes and lethal haplotypes: CN, 201710438948.9[P]. 2020-03-17. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | Guangxuan FAN, Tianjiao WANG, Yimeng DONG, Hongliang WANG, Ning DING, Xinhao WANG, Xiumei XING. Molecular Genealogy Construction and Population Genetic Structure Analysis of Jilin Sika Deer Based on SNP Loci [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3925-3935. |
| [2] | Ruiqi ZHANG, Yanqin PANG, Zaishan LI, Xiuguo SHANG, Ganqiu LAN, Jinbiao GUO, Yunxiang ZHAO. Research on Feeding Capacity Selection of Lactating Sows Based on Intelligent Precision Feeding [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2890-2900. |
| [3] | DUAN Yixin, ZHANG Linyun, ZHAO Yongju. The Evaluated Methods and Influencing Factors of SNP Heritability and Its Application in Farmer Animal Breeding [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 1854-1865. |
| [4] | CUI Shengdi, WANG Kai, ZHAO Zhenjian, CHEN Dong, SHEN Qi, YU Yang, WANG Junge, CHEN Ziyang, YU Shixin, CHEN Jiamiao, WANG Xiangfeng, TANG Guoqing. Identification of Candidate Genes for Pork Texture Traits Using GWAS Combined with Co-localisation of DNA Methylation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 1945-1957. |
| [5] | SUN Wenli, WANG Haoqi, ZE Licuo, GAO Yufan, ZHANG Feifan, ZHANG Jian, DUAN Mengqi, SHANG Peng, QIANG Bayangzong. Polymorphism of Pro-Inflammatory Factors (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α) in Tibetan Pigs and Its Association Analysis with Immune Traits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 1958-1969. |
| [6] | TU Yun, ZENG Yanan, ZHANG Zhenghao, HONG Rui, WANG Zhen, WU Ping, ZHOU Zeyang, YE Yiru, DU Yanan, ZUO Fuyuan, ZHANG Gongwei. Genetic Structure and Runs of Homozygosity Analysis of Fuling Buffalo and Southwest Buffalo Breeds [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 1989-1998. |
| [7] | LU Jinye, GAO Yabing, HAN Xinru, LIU Yuzhen, ZHAO Jiayu. The Effect of Streptococcus uberis Infection on Amino Acid Metabolism in Mammary Epithelial Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1766-1776. |
| [8] | SONG Kelin, YAN Zunqiang, WANG Pengfei, CHENG Wenhao, LI Jie, BAI Yaqin, SUN Guohu, GUN Shuangbao. Analysis on Genetic Diversity and Genetic Structure Based on SNP Chips of Huixian Qingni Black Pig [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 995-1006. |
| [9] | CAO Jinkang, ZHANG Chun, WANG Jiayao, LI Xiaotong, WANG Pengyu, FANG Yingyan, ZHANG Yu, DING Ning, JIANG Li. Proteomic Analysis of Sperm with Different Freezability in Chinese Holstein Bulls [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1052-1061. |
| [10] | LIU Yangguang, ZHANG Huibin, WEN Haoyu, XIE Fan, ZHAO Shiming, DING Yueyun, ZHENG Xianrui, YIN Zongjun, ZHANG Xiaodong. SNP/Indel Screening Analysis of Porcine Ovarian Granulosa Cells Treated with Follicular Fluid Exosomes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 576-586. |
| [11] | ZHUANG Cuicui, HAN Bo. Mechanism of Mitochondrial Damage in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells and Mouse Mammary Gland Infected with Escherichia coli Isolated from Bovine Mastitis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 822-833. |
| [12] | Qingzhen SHI, Hongyang XU, Yan ZHANG, Yi ZHANG, Yachun WANG, Jianyong HAN, Li JIANG. Detection and Comparative Analysis of Genomic Genetic Variations in Trace Cells Using Different Methods [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4311-4324. |
| [13] | Junfeng WU, Yiyuan YAN, Ning YANG, Congjiao SUN, Guangqi LI, Bin WANG, Guiqin WU, Ling LIAN. Accuracy Analysis of Genotype Imputation from 10K to 50K SNP Loci in Layers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4325-4333. |
| [14] | Longgang MA, Nan LIU, MA Qunzong NI, Xin WANG, Jian LU, Huaming MAO, Gong CHEN, ZENG Ouzhu DAN, BA Ciren LA, Nan ZHANG, Fuqing YU, Yachun WANG. Study on the Genetic Composition of Four Local Tibetan Cattle Breeds Based on SNP Chip Analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4377-4390. |
| [15] | MENG Lu, HU Haiyan, DONG Lei, ZHENG Nan, WANG Jiaqi. Influence of Dairy Farm Environment on Mastitis Milk Microbiota via SourceTracker [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(9): 3872-3883. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||