





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (11): 5817-5825.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.11.038
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Yaling( ), JING Wei(
), JING Wei( ), ZHAO Yan, HE Xiaobing, FANG Yongxiang, SU Yang, LI Xiaoming, ZHANG Hui, JING Zhizhong*(
), ZHAO Yan, HE Xiaobing, FANG Yongxiang, SU Yang, LI Xiaoming, ZHANG Hui, JING Zhizhong*( ), CHEN Guohua*(
), CHEN Guohua*( )
)
Received:2024-12-04
Online:2025-11-23
Published:2025-11-27
Contact:
JING Zhizhong, CHEN Guohua
E-mail:3200732270@qq.com;2635378262@qq.com;zhizhongj@163.com;chenguohua02@caas.cn
CLC Number:
ZHANG Yaling, JING Wei, ZHAO Yan, HE Xiaobing, FANG Yongxiang, SU Yang, LI Xiaoming, ZHANG Hui, JING Zhizhong, CHEN Guohua. Establishment of Prokaryotic Expression of the ORF002 Protein of Lumpy Skin Disease Virus and an Indirect ELISA Antibody Detection Method[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5817-5825.
Fig. 2
Construction and identification of recombinant plasmid pET-30a-LSDV ORF002 A. PCR-amplified ORF002 gene from LSDV(M. DNA marker; 1, 2. PCR product of the ORF002 gene); B. Identification of recombinant plasmid pET-30a-LSDV ORF002 by enzyme digestion(M. DNA marker; 3. pET-30a(+)-LSDV ORF002;4. The digestion of recombinant plasmid pET-30a(+)-LSDV ORF002 by NdeⅠ and XhoⅠ)"
Fig. 3
Expression, purification and identification of LSDV ORF002 protein A. Expression of recombinant protein(M. Protein marker; 1. pET-30a(+)-LSDV ORF002 uninduced whole bacteria; 2. Whole bacteria after induction by pET-30a(+)-LSDV ORF002;3. Centrifugation supernatant after IPTG induction; 4. Precipitation IPTG induction of pET-30a(+)-LSDV ORF002);B. Purification of recombinant protein(M. Protein marker; 5. unpurified; 6. Purified ORF002 recombinant protein); C. Western blot identification of recombinant protein(M. Protein marker; 7. LSDV positive serum identification)"
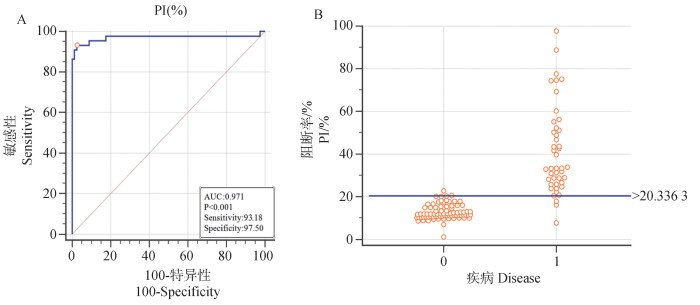
Table 2
Determination of optimal coating concentration of recombinant protein and serum dilution μg·mL-1"
| 血清稀释度 Serum dilution | 样品 Sample | 抗原包被浓度 Antigen concentration | |||||
| 20.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 2.5 | 1.25 | 0.625 | ||
| 1∶100 | P | 1.361 | 1.308 | 1.258 | 1.290 | 1.263 | 1.266 |
| N | 0.293 | 0.290 | 0.271 | 0.278 | 0.270 | 0.264 | |
| P/N | 4.578 | 4.641 | 4.736 | 5.088 | 4.663 | 3.981 | |
| 1∶200 | P | 1.000 | 0.949 | 0.926 | 0.937 | 0.94 | 0.925 |
| N | 0.231 | 0.219 | 0.203 | 0.195 | 0.202 | 0.193 | |
| P/N | 4.331 | 4.681 | 4.722 | 5.109 | 4.470 | 3.875 | |
| 1∶400 | P | 0.628 | 0.601 | 0.564 | 0.564 | 0.562 | 0.579 |
| N | 0.181 | 0.162 | 0.162 | 0.149 | 0.151 | 0.141 | |
| P/N | 3.583 | 3.627 | 3.908 | 3.930 | 2.694 | 2.586 | |
| 1∶800 | P | 0.396 | 0.384 | 0.370 | 0.365 | 0.357 | 0.303 |
| N | 0.145 | 0.127 | 0.122 | 0.114 | 0.122 | 0.115 | |
| P/N | 2.868 | 3.114 | 2.685 | 2.689 | 2.452 | 2.060 | |
| 1 | 聂福平. 牛结节性皮肤病检测新方法与ORF132基因表达及鉴定研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2020. |
| NIE F P. Research of molecular methods for the detection of lumpy skin disease and the expression of ORF132 gene in baculovirus system and identification[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 2 |
TUPPURAINEN E S M , OURA C A L . lumpy skin disease: an emerging threat to Europe, the Middle East and Asia[J]. Transbound Emerg Dis, 2012, 59 (1): 40- 48.
doi: 10.1111/j.1865-1682.2011.01242.x |
| 3 | 景志忠, 何小兵, 陈国华, 等. 牛结节性皮肤病防控技术研究现状及其策略[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2020, 50 (2): 205- 214. |
| JING Z Z , HE X B , CHEN G H , et al. Development status of prevention and control technology to lumpy skin disease and its strategy in China[J]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 2020, 50 (2): 205- 214. | |
| 4 | 周洪. 牛结节性皮肤病的流行现状与防控[J]. 吉林畜牧兽医, 2023, 44 (6): 117- 118. |
| ZHOU H . Current epidemiology and prevention and control of lumpy skin disease[J]. Jilin Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 44 (6): 117- 118. | |
| 5 | 景志忠. 牛结节性皮肤病[M]. 兰州: 兰州大学出版社, 2023. |
| JING Z Z . Lumpy skin disease[M]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University Press, 2023. | |
| 6 | 郑佳豪. 牛结节性皮肤病的时空分布及流行风险研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2021. |
| ZHENG J H. A study of the spatial and temporal distribution and epidemiologic risk of lumpy skin disease[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| 7 |
KITCHING R P , SMALE C . Comparison of the external dimensions of capripoxvirus isolates[J]. Res Vet Sci, 1986, 41 (3): 425- 427.
doi: 10.1016/S0034-5288(18)30646-5 |
| 8 |
TULMAN E R , AFONSO C L , LU Z , et al. The genomes of sheeppox and goatpox viruses[J]. J Virol, 2002, 76 (12): 6054- 6061.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.76.12.6054-6061.2002 |
| 9 |
TULMAN E R , AFONSO C L , LU Z , et al. Genome of lumpy skin disease virus[J]. J Virol, 2001, 75 (15): 7122- 7130.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.15.7122-7130.2001 |
| 10 | 袁向芬, 许晓琳, 孔玉方, 等. 牛结节性皮肤病病毒LAMP快检方法的建立与应用[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2023, 53 (11): 1355- 1362. |
| YUAN X F , XU X L , KONG Y F , et al. Establishment and application of a LAMP-based rapid diagnostic method for lumpy skin disease virus[J]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 2023, 53 (11): 1355- 1362. | |
| 11 |
周祉玉, 杜吉革, 莘若兰, 等. 中国三株牛结节性皮肤病病毒的分离鉴定及其GPCR基因分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (12): 5620- 5630.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.12.025 |
|
ZHOU Z Y , DU J G , XIN R L , et al. Isolation and identification of three lumpy skin disease viruses in China and their GPCR gene analysis[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (12): 5620- 5630.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.12.025 |
|
| 12 |
马春玲, 任善会, 杨雪, 等. 基于牛结节性皮肤病病毒ORF61基因荧光定量检测方法的建立[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (4): 1800- 1809.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.04.041 |
|
MA C L , REN S H , YANG X , et al. Establishment and application of fluorescence quantitative PCR detection method based on lumpy skin disease virus ORF61 gene[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (4): 1800- 1809.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.04.041 |
|
| 13 | 陈虎, 刘书怡, 蔺雅婷, 等. 非洲猪瘟病毒P54抗原表位分析及间接ELISA方法的建立[J/OL]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2024. [2024-08-22]. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZSJB20240716001.htm |
| CHENG H, LIU S Y, LIN Y T, et al. Analysis of epitope of African swine fever virus p54 and establishment of indirect ELISA method[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Animal Infectious Diseases, 2024. [2024-08-22]. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZSJB20240716001.htm(in Chinese) | |
| 14 | 王静, 陈柯源, 王胜华, 等. 牛病毒性腹泻病毒Erns-ELISA抗体检测试剂盒的制备[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2024, 60 (7): 65- 70. |
| WANG J , CHEN K Y , WANG S H , et al. Preparation of Erns-ELISA antibody test kit for bovine viral diarrhea virus[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 60 (7): 65- 70. | |
| 15 |
GARI G , BITEAU-COROLLER F , LEGOFF C , et al. Evaluation of indirect fluorescent antibody test (IFAT) for the diagnosis and screening of lumpy skin disease using Bayesian method[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2008, 129 (3-4): 269- 280.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2007.12.005 |
| 16 | TUPPURAINEN E . Diagnostic assays for the detection of lumpy skin disease virus and antibodies[J]. EMPRES, 2017, 47, 7- 9. |
| [1] | GUO Deyang, HU Hui, ZHENG Xueli, JIANG Yanfen. Prokaryotic Expression and Analysis of Bacteriostatic Effects of Porcine β-defensin-1 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2836-2846. |
| [2] | ZHAO Yunhai, ZHANG Yangyang, MA Haiyun, WANG Qing, HE Xiaoxiao, LIU Kai, ZHANG Yuting, LIU Yudong, YANG Yongning, WU Xiaochun, XING Xiaoyong, QUAN Guomei, ZHANG Zhixiong, BAO Shijun. Prokaryotic Expression and Adhesion Characteristics of Molecular Chaperone Dnak of Mycoplasma bovis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2868-2878. |
| [3] | WU Qiong, LI Lingdan, YUAN Hui, BIN Chen, DENG Ke, LI Wei, YE Shiyi, LI Guopan, SHEN Qingchun, XIONG Tao. Prokaryotic Expression of PoIFN-α 8s and Identification of Its Activity in vitro and in vivo [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(5): 2413-2423. |
| [4] | SHAO Yongheng, NI Minting, GAO Mengling, TANG Jiao, ZHANG Gengxin, LIN Shengyu, LIU Guangliang, CHEN Jianing, WANG Wenhui. Prokaryotic Expression of VP1 Protein to Porcine Teschovirus Type 5 and the Establishment of an Indirect ELISA Detection Method [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 883-889. |
| [5] | SONG Hongyan, CHEN Fuyou, JIA Chenyu, HUANG Yuzhou, LAI Yufang, ZHOU Qi, HUANG Lidong, CHEN Jilong, LI Xunliang. Expression of FtsZ Protein of Mycoplasma synoviae and Establishment of an Indirect ELISA Method for Antibody Detection [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5732-5742. |
| [6] | CAO Qiuxia, YAN Kexin, CHENG Zhenkong, BIAN Xianyu, WANG Chuanhong, LI Sufen, ZHANG Xuehan, FAN Baochao, GUO Rongli, YANG Shanshan, WANG Xiaodu, LI Bin. Expression and Biological Activity Analysis of Porcine CCL25 Recombinant Protein [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5864-5874. |
| [7] | ZENG Miaomiao, YANG Xiaoman, ZHANG Xin, LIU Dakai, SHI Hongyan, ZHANG Jiyu, ZHANG Liaoyuan, CHEN Jianfei, FENG Tingshuai, LI Xiuwen, SHI Da, FENG Li. Establishment and Preliminary Application of an Indirect ELISA for Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus N Protein [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 319-326. |
| [8] | Liguo GAO, Hanqin SHEN, Yiquan CHEN, Sheng CHEN, Wencheng LIN, Feng CHEN. Prokaryotic Expression of Recombinant VP6* Protein of Porcine Rotavirus and Establishment of Indirect ELISA Detection Method [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4021-4028. |
| [9] | Peng SHEN, Yi WANG, Weijie REN, Yongchun YANG, Houhui SONG, Zhiliang WANG. Meta Analysis of Immune Antibody Monitoring for Lumpy Skin Disease [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3649-3658. |
| [10] | Yanxin CHEN, Ruiqi HUA, Guoqing SHAO, Xiaowei ZHU, Wei HOU, Shengqiong LI, Aiguo YANG, Guangyou YANG. Prokaryotic Expression and Secretion Characterization of Annexin B5, B15, and B25 from Echinococcus granulosus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2607-2618. |
| [11] | HUANG Jin, LI Siyuan, MAO Li, CAI Xuhang, XIE Lingling, WANG Fu, ZHOU Hua, LI Jizong, LI Bin. Eukaryotic Expression of Bovine Coronavirus S1 Protein and Establishment and Application of Indirect ELISA [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2050-2060. |
| [12] | SONG Xiaoqing, DENG Ruide, LI Xin, LI Jiao, LI Runcheng, DU Lifei, DONG Wei, GE Meng. Establishment of ELISA for Detection of PCV4-Cap Antibody and Sero-epidemiological Survey [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2072-2079. |
| [13] | ZHAO Canqi, FENG Yu, LÜ Lang, LI Yanjun, WEI Yulei, DING Jiabo, CHEN Xiang, JIANG Hui. Study on Purification of Bovine Brucellosis by Competitive ELISA and Indirect ELISA [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2146-2153. |
| [14] | LUO Xiaofen, XIE Xiaodong, ZHAO Chao, HU Qian, WANG Yongxuan, RAN Fangfei, HU Pengfei, WEN Ming, ZHU Erpeng, CHENG Zhentao. Initial Identification of Adhesion-related Proteins of Mycoplasma bovis of Guizhou Strains [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1672-1683. |
| [15] | MA Chunling, REN Shanhui, YANG Xue, LIN Yugang, LI Jiyun, WANG Xiangwei, YIN Xiangping, SUN Yuefeng, WAN Xuerui, CHEN Haotai. Establishment and Application of Fluorescence Quantitative PCR Detection Method based on Lumpy Skin Disease Virus ORF61 Gene [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1800-1809. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||