





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (7): 3252-3264.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.07.019
• Animal Biotechnology and Reproduction • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHENG Hao1( ), LUO Fang1,2, SONG Chenglei1, TAO Jinzhong1,*(
), LUO Fang1,2, SONG Chenglei1, TAO Jinzhong1,*( )
)
Received:2024-12-02
Online:2025-07-23
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
TAO Jinzhong
E-mail:1571893591@qq.com;tao_jz@nxu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
ZHENG Hao, LUO Fang, SONG Chenglei, TAO Jinzhong. Screening Potential Plasma Biomarkers of Non-pregnant Dairy Cows after Artificial Insemination Based on Metabolomics Technology[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3252-3264.
Fig. 1
PCA scores of plasma metabolism in non-pregnant cows at different periods A, C, E, G, I, and K are PCA scores of A vs. B, A vs. C, A vs. D, B vs. C, B vs. D, and C vs. D groups in positive ion mode, respectively; B, D, F, H, J and L are the PCA scores of A vs. B, A vs. C, A vs. D, B vs. C, B vs. D and C vs. D groups in negative ion mode, respectively"
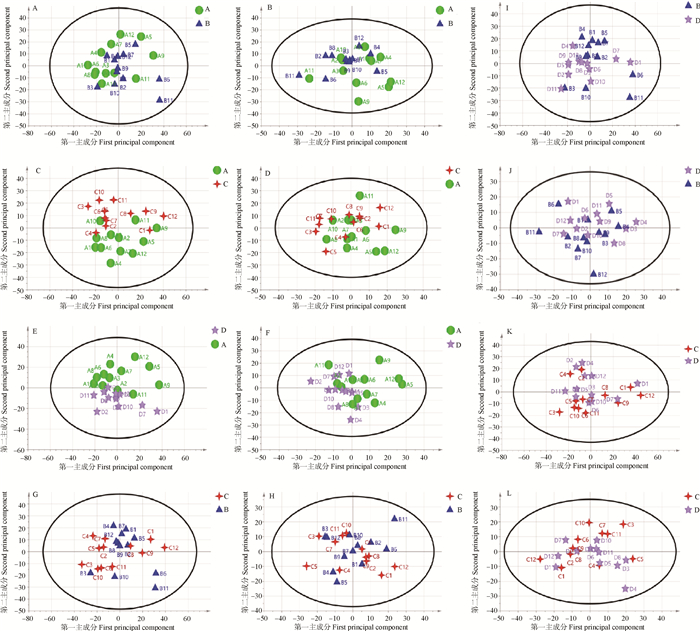

Fig. 2
OPLS-DA score map and replacement test map of plasma metabolism in non-pregnant cows at different periods Figure A, B, C, and D are OPLS-DA score charts and replacement test charts of group A vs. B in positive (left) and negative (right) ion modes; Figure E, F, G, and H are OPLS-DA score charts and replacement test charts of group A vs. C in positive (left) and negative (right) ion modes; Figure I, J, K and L are OPLS-DA score charts and displacement test charts of group A vs. D in positive (left) and negative (right) ion modes. Figure M, N, O, and P are OPLS-DA score charts and displacement test charts for group B vs. C in positive (left) and negative (right) ion modes; Figure Q, R, S, and T are OPLS-DA score charts and displacement test charts of group B vs. D in positive (left) and negative (right) ion modes. Figure U, V, W, and X are OPLS-DA score charts and displacement test charts for group C vs. D in positive (left) and negative (right) ion modes. R2 intercept and Q2 intercept represent the intercepts of R2 and Q2 regression lines with the Y-axis, Q2 intercept < 0 indicating that the OPLS-DA model is not overfitted"
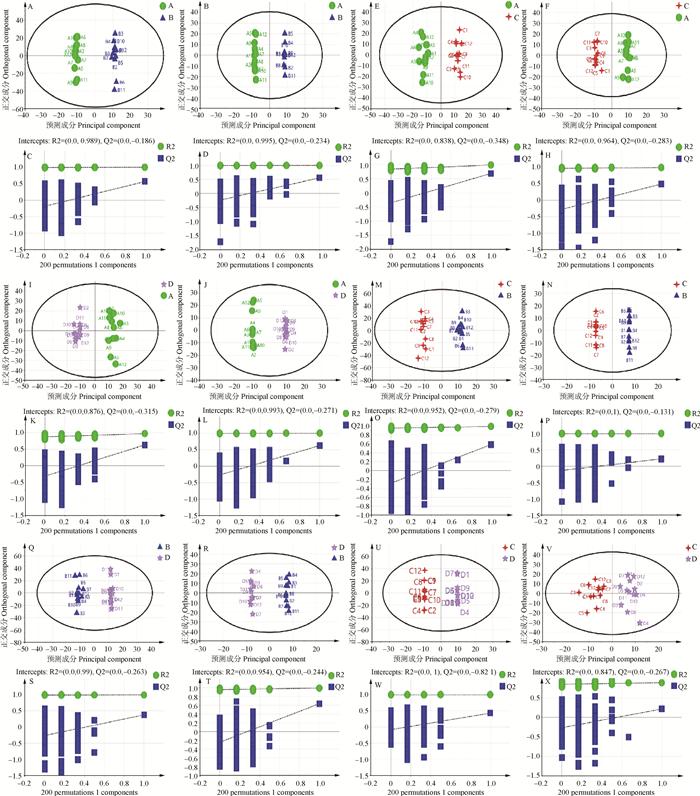
Table 2
The assessment parameters of PCA and OPLS-DA"
| 模式 Model | 组别 Group | PCA | OPLS-DA | OPLS-DA置换检验 OPLS-DA permutation test | |||
| R2X | R2Y | Q2 | Q2 intercept | ||||
| 正离子模式 POS | A vs. B | 0.502 | 0.997 | 0.563 | -0.186 | ||
| A vs. C | 0.510 | 0.980 | 0.683 | -0.348 | |||
| A vs. D | 0.474 | 0.974 | 0.631 | -0.315 | |||
| B vs. C | 0.449 | 0.988 | 0.584 | -0.279 | |||
| B vs. D | 0.432 | 0.990 | 0.635 | -0.244 | |||
| C vs. D | 0.491 | 1 | 0.428 | -0.082 1 | |||
| 负离子模式 NEG | A vs. B | 0.567 | 0.999 | 0.554 | -0.234 | ||
| A vs. C | 0.502 | 0.986 | 0.485 | -0.283 | |||
| A vs. D | 0.475 | 0.998 | 0.624 | -0.271 | |||
| B vs. C | 0.439 | 1 | 0.223 | -0.131 | |||
| B vs. D | 0.497 | 0.996 | 0.374 | -0.263 | |||
| C vs. D | 0.494 | 0.888 | 0.215 | -0.267 | |||
Table 3
The identified differential metabolites"
| 代谢物 Metabolite | 质荷比 m/z | 保留时间/s RT | AUC | A vs. B | A vs. C | A vs. D | ||||||||
| VIP | P | FC | VIP | P | FC | VIP | P | FC | ||||||
| 1. DL-香草扁桃酸 DL-vanillyl mandelic acid | 240.078 | 323.702 | 0.806 | 2.074 | 0.007 | 2.538 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 2. 光黄素 Lumichrome | 243.086 | 128.928 | 0.757 | 1.651 | 0.028 | 2.214 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 3. 组氨酸-苏氨酸 His-Thr | 257.125 | 334.948 | 0.167 | 1.923 | 0.015 | 0.328 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 4. 硬脂酰胺 Stearamide | 284.295 | 32.742 | 0.201 | 1.722 | 0.033 | 0.357 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 5. 二十碳五烯酸 Eicosapentaenoic acid | 303.232 | 39.786 | 0.264 | 1.665 | 0.035 | 0.417 | ||||||||
| 6. 苏氨酸-丝氨酸 Thr-Ser | 248.125 | 332.097 | 0.292 | 1.755 | 0.029 | 0.376 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 7. 缬氨酸-苏氨酸 Val-Thr | 201.125 | 198.098 | 0.174 | 2.088 | 0.008 | 0.458 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 8. 色氨酸-谷氨酸 Trp-Glu | 334.140 | 326.883 | 0.813 | - | - | - | 1.794 | 0.015 | 2.225 | - | - | - | ||
| 9. 异亮氨酸-精氨酸 Ile-Arg | 288.203 | 331.332 | 0.813 | - | - | - | 1.860 | 0.009 | 2.099 | - | - | - | ||
| 10. 甘氨脱氧胆酸 Glycodeoxycholic acid | 450.322 | 200.131 | 0.771 | - | - | - | 1.555 | 0.035 | 2.060 | - | - | - | ||
| 11.2-乙氧基乙醇 2-Ethoxyethanol | 151.097 | 63.058 | 1.000 | - | - | - | 2.591 | 0.000 | 2.049 | - | - | - | ||
| 12. 组氨酸-蛋氨酸 His-Met | 304.145 | 218.511 | 0.028 | - | - | - | 2.399 | 0.000 | 0.265 | |||||
| 13. 精氨酸琥珀酸 Argininosuccinic acid | 290.130 | 237.428 | 0.076 | - | - | - | 2.370 | 0.000 | 0.281 | |||||
| 14. 异胱氨酸 Allocystathionine | 187.058 | 276.689 | 0.215 | - | - | - | 1.796 | 0.007 | 0.469 | - | - | - | ||
| 15. 三乙醇胺 Triethanolamine | 150.113 | 154.899 | 0.014 | - | - | - | 2.770 | 0.000 | 0.204 | |||||
| 16.3-羟基异戊酸 3-Hydroxyisovaleric acid | 237.134 | 223.740 | 0.097 | - | - | - | 2.270 | 0.000 | 0.407 | - | - | - | ||
| 17.5′-O-甲基胸苷 5′-O-methylthymidine | 256.105 | 296.654 | 0.215 | 1.797 | 0.020 | 0.468 | - | - | - | |||||
| 18. (3-羧丙基)三甲基铵阳离子 (3-Carboxypropyl)trimethylammonium cation | 191.086 | 249.592 | 0.111 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.861 | 0.009 | 0.429 | ||
| 19. 丙氨酸-亮氨酸 Ala-Leu | 185.129 | 406.947 | 0.007 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.707 | 0.000 | 0.467 | ||
| 20. 丙戊酸 Valproic acid | 183.078 | 276.612 | 0.153 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.986 | 0.004 | 0.334 | ||
| 21. 柠檬酸 Citramalic acid | 207.052 | 298.551 | 0.174 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.910 | 0.006 | 0.333 | ||
| 代谢物 Metabolite | 质荷比 m/z | 保留时间/s RT | AUC | B vs. C | B vs. D | C vs. D | ||||||||
| VIP | P | FC | VIP | P | FC | VIP | P | FC | ||||||
| 1. 色氨酸-谷氨酸 Trp-Glu | 334.140 | 326.883 | 0.833 | 1.779 | 0.021 | 2.177 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 2.2-乙氧基乙醇 2-Ethoxyethanol | 151.097 | 63.058 | 1.000 | 2.734 | 0.000 | 2.037 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 3. 前列腺素 I2 Prostaglandin I2 | 416.249 | 240.224 | 0.188 | 1.784 | 0.026 | 0.213 | ||||||||
| 4. 中康酸 Mesaconic acid | 191.049 | 224.975 | 0.153 | 1.958 | 0.012 | 0.471 | ||||||||
| 5.1-甲基鸟苷 1-methylguanosine | 298.103 | 282.209 | 0.285 | 1.570 | 0.035 | 0.488 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 6. 异亮氨酸-丙氨酸-精氨酸 Ile-Ala-Arg | 358.245 | 49.318 | 0.118 | 2.222 | 0.004 | 0.340 | ||||||||
| 7.3-羟基异戊酸 3-Hydroxyisovaleric acid | 237.134 | 223.740 | 0.181 | 2.164 | 0.006 | 0.400 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 8. 己酸 Hexanoic acid | 158.118 | 45.819 | 0.181 | 1.700 | 0.041 | 0.179 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 9. 精氨酸-酪氨酸 Arg-Tyr | 337.173 | 460.582 | 0.813 | - | - | - | 1.457 | 0.048 | 2.075 | - | - | - | ||
| 13. 吡哆醇 Pyridoxine | 339.156 | 198.852 | 0.188 | - | - | - | 1.802 | 0.016 | 0.449 | |||||
| 11. 富马酸二羟基酯 Dihydroxyfumarate | 148.076 | 233.057 | 0.208 | - | - | - | 1.977 | 0.008 | 0.485 | |||||
| 10. 丙氨酸-亮氨酸 Ala-Leu | 185.129 | 406.947 | 0.000 | - | - | - | 3.190 | 0.000 | 0.492 | - | - | - | ||
| 12. S-甲基-5′-硫腺苷 S-Methyl-5′-thioadenosine | 298.098 | 71.609 | 0.208 | - | - | - | 1.620 | 0.017 | 0.466 | - | - | - | ||
| 14. 柠檬酸 Citramalic acid | 207.052 | 298.551 | 0.125 | - | - | - | 2.545 | 0.002 | 0.405 | - | - | - | ||
| 15. 硬脂酸 Pristanic acid | 297.280 | 38.254 | 0.910 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.037 | 0.025 | 2.227 | ||
| 1 | EALY A D , SEEKFORD Z K . Symposium review: predicting pregnancy loss in dairy cattle[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2019, 102 (12): 11798- 11804. |
| 2 | GUI L S , DAI T S , GUO X R , et al. Recent advances in early pregnancy loss diagnosis in dairy cows: New approaches[J]. Reprod Domest Anim, 2024, 59 (4): e14566. |
| 3 | LEUNG K Y . Applications of advanced ultrasound technology in obstetrics[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2021, 11 (7): 1217. |
| 4 | JIANG C , LI G F . Sensitive fluorescence analysis of pregnancy plasma associated protein A in amniotic fluid based on the plasma superstructure enhanced carbon polymer dots[J]. Sci Adv Mater, 2022, 14 (7): 1151- 1158. |
| 5 |
张馨蕊, 付予, 杨卓, 等. 奶牛早期妊娠诊断蛋白的研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (2): 451- 460.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.02.004 |
|
ZHANG X R , FU Y , YANG Z , et al. Study on early pregnancy diagnostic protein of dairy cows[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (2): 451- 460.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.02.004 |
|
| 6 | HAN A , QAMAR A Y , BANG S , et al. Effect of extracellular vesicles derived from oviductal and uterine fluid on the development of porcine preimplantation embryos[J]. Theriogenology, 2025, 234, 216- 224. |
| 7 | VASUDEVAN S , KAMAT M M , WALUSIMBI S S , et al. Effects of early pregnancy on uterine lymphocytes and endometrial expression of immune-regulatory molecules in dairy heifers†[J]. Biol Reprod, 2017, 97 (1): 104- 118. |
| 8 | DE OLIVEIRA E B , MONTEIRO H F , PEREIRA J M V , et al. Changes in uterine metabolome associated with metritis development and cure in lactating Holstein cows[J]. Metabolites, 2023, 13 (11): 1156. |
| 9 | JIANG H B , BAO J , XING Y N , et al. Metabolomic and metagenomic analyses of the Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis after challenge with Metschnikowia bicuspidata[J]. Front Microbiol, 2022, 13, 990737. |
| 10 | BOYLE J G , DAVIDSON D F , PERRY C G , et al. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of urinary free metanephrines, vanillyl mandelic Acid, and catecholamines and plasma catecholamines for diagnosis of pheochromocytoma[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2007, 92 (12): 4602- 4608. |
| 11 | YANG R H , LIU B J , YANG M Y , et al. Lumiflavin reduces cisplatin resistance in cancer stem-like cells of OVCAR-3 cell line by inducing differentiation[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12, 859275. |
| 12 | KALE H , HARIKUMAR P , KULKARNI S B , et al. Assessment of the genotoxic potential of riboflavin and lumiflavin. A. Effect of light[J]. Mutat Res, 1992, 298 (1): 17- 23. |
| 13 | MARTINEZ C A , RIZOS D , RODRIGUEZ-MARTINEZ H , et al. Oocyte-cumulus cells crosstalk: New comparative insights[J]. Theriogenology, 2023, 205, 87- 93. |
| 14 | GAO L , ZHANG C , ZHENG Y , et al. Glycine regulates lipid peroxidation promoting porcine oocyte maturation and early embryonic development[J]. J Anim Sci, 2023, 101, skac425. |
| 15 | WU G , BAZER F W , SATTERFIELD M C , et al. Impacts of arginine nutrition on embryonic and fetal development in mammals[J]. Amino Acids, 2013, 45 (2): 241- 256. |
| 16 | LI X , BAZER F W , GAO H , et al. Amino acids and gaseous signaling[J]. Amino Acids, 2009, 37 (1): 65- 78. |
| 17 | 黄祝. 小鼠围着床期子宫中精氨酸琥珀酸合成酶1的表达调节和功能[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2012. |
| HUANG Z. Expression regulation and function of argininosuccinate synthetase 1 in mouse uterus during peri implantation[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2012. (in Chinese) | |
| 18 | BALERCIA G , MORETTI S , VIGNINI A , et al. Role of nitric oxide concentrations on human sperm motility[J]. J Androl, 2004, 25 (2): 245- 249. |
| 19 | DUTTA S , SENGUPTA P . The role of nitric oxide on male and female reproduction[J]. Malays J Med Sci, 2022, 29 (2): 18- 30. |
| 20 | LEFÈVRE PAVINE L C , MARIE-FRANCE P , MURPHY B D . Polyamines on the reproductive landscape[J]. Endocr Rev, 2011 (5): 694- 712. |
| 21 | LI Z , YUE Z , AO Z , et al. Maternal dietary supplementation of arginine increases the ratio of total cloned piglets born to total transferred cloned embryos by improving the pregnancy rate of recipient sows[J]. Anim Reprod Sci, 2018, 196, 211- 218. |
| 22 | PETRUJKI B T , EFER D S , JOVANOVI I B , et al. Effects of commercial selenium products on glutathione peroxidase activity and semen quality in stud boars[J]. Anim Feed Sci Technol, 2014, 197, 194- 205. |
| 23 | LIU N , SUN S , WANG P , et al. The Mechanism of Secretion and Metabolism of Gut-Derived 5-Hydroxytryptamine[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22 (15): 7931. |
| 24 | WANG G , YAO S , LIANG X , et al. Detection of the metabolites of human plasma and follicular fluid in IVF-ET with microextraction and LC-TOF-MS[J]. Technol Health Care, 2015, 1 (s1): 29- 36. |
| 25 | DOE J E . Ethylene glycol monoethyl ether (2-ethoxyethanol)[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 1984, 57, 33- 41. |
| 26 | PEREZ M J , VELASCO E , MONTE M J , et al. Maternal ethanol consumption during pregnancy enhances bile acid-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in fetal rat liver[J]. Toxicology, 2006, 225 (2-3): 183- 194. |
| 27 | LEROY J L M R , VANHOLDER T , MATEUSEN B , et al. Non-esterified fatty acids in follicular fluid of dairy cows and their effect on developmental capacity of bovine oocytes in vitro[J]. Reproduction, 2005, 130 (4): 485- 495. |
| 28 | MIRABI P , CHAICHI M J , ESMAEILZADEH S , et al. The role of fatty acids on ICSI outcomes: a prospective cohort study[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2017, 16 (1): 18. |
| 29 | LIU S , SHARP A , VILLANUEVA E , et al. Breast Milk Iodine Concentration (BMIC) as a biomarker of iodine status in lactating women and children < 2 years of age: a systematic review[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14 (9): 1691. |
| 30 | PATEL A , PATEL S , PATEL P , et al. Salivary exosomal miRNA-1307-5p predicts disease aggressiveness and poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (18): 10639. |
| 31 | 王梦晓, 罗珂珂, 高文雅, 等. 基于非靶向尿液代谢组学技术的毛蕊花糖苷治疗嘌呤霉素氨基核苷肾病幼龄大鼠相关生物标志物研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2023, 48 (21): 5898- 5907. |
| WANG M X , LUO K K , GAO W Y , et al. Study on biomarkers of verbascoside in the treatment of puromycin aminonucleoside nephropathy in young rats based on non targeted urine metabolomics technology[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2023, 48 (21): 5898- 5907. | |
| 32 | 闫坤, 高黎明, 高正兴, 等. 唾液小细胞外囊泡novel-100作为母猪早期妊娠诊断候选生物标志物的研究[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2025, 61 (1): 299-304, 310. |
| YAN K , GAO L M , GAO Z X , et al. Study on salivary small extracellular vesicle novel-100 as a candidate biomarker for early pregnancy diagnosis in sows[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2025, 61 (1): 299-304, 310. | |
| 33 | VELEK K, MICHAUD S, BOUCHER K, 等. 爱德士牛怀孕检测[C]//中国奶业协会第26次繁殖学术年会暨国家肉牛牦牛/奶牛产业技术体系第3届全国牛病防治学术研讨会论文集. 兰州, 2011: 140-143. |
| VELEK K, MICHAUD S, BOUCHER K, et al. IDEXX cattle pregnancy test[C]//Proceedings of the26th Annual Conference of Breeding of China Dairy Association and the 3rd National Symposium on Cattle Disease Prevention and Control of National Beef Cattle, Yak/Dairy Cattle Industry Technology System. Lanzhou, 2011: 140-143. (in Chinese) | |
| 34 | KUMAR R , ALI S A , SINGH S K , et al. Peptide profiling in cow urine reveals molecular signature of physiology-driven pathways and in-silico predicted bioactive properties[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11 (1): 12427. |
| [1] | MENG Xiangxu, LI Jia, REN Deming, CHEN Kuirong, HE Yiyun, WANG Lixian, SHENG Xihui, WANG Ligang. Study on Serum Metabolomics of High and Low Resilience Group of Min Pigs with Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1689-1699. |
| [2] | WANG Xinxin, LIU Xiaoying, WANG Yi, WANG Fang, ZHAO Han, DU Zhiqiang, YANG Caixia. Acute Heat Stress Affects the Functions of Porcine Sertoli Cells via Decreasing Taurine Level [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1779-1790. |
| [3] | XIANG Hui, GUI Linsen, YANG Di, WEI Shihao, GONG Yanbin, SHI Yuangang, MA Yun, DAN Xingang. Research Progress on the Estrus Synchronization-fixed-timed Artificial Insemination Technology in Dairy Cows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1412-1422. |
| [4] | WANG Zhongbo, LIU Shuang, HE Lixia, FENG Xue, YANG Mengli, WANG Shuzhe, LIU Yuan, FENG Lan, DING Xiaoling, JI Guoshang, YANG Runjun, ZHANG Lupei, MA Yun. Metabolomics Analysis on Different Muscle Tissues of Guyuan Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1565-1578. |
| [5] | ZHANG Xinrui, FU Yu, YANG Zhuo, SHEN Wenjuan, TAO Jinzhong. Study of Early Pregnancy Diagnostic Proteins in Dairy Cows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 451-460. |
| [6] | ZHANG Zhaobo, HOU Liming, LI Pinghua, DU Taoran, WANG Zhongyu, WU Chengwu, HUANG Ruihua. Screening Candidate Metabolites of Dietary Fiber Affecting Meat Quality Traits of Erhualian Pigs Based on Plasma Metabolomics [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(9): 3758-3769. |
| [7] | WANG Ruijie, HONG Zhikai, DONG Yingjiao, CHEN Yao, WANG Jinyu, WANG Guanhua. Effect of Oxytetracycline and Andrographolide on the Metabolism of Chicken Intestinal Tracts Using UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS-based Metabolomic Approach [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(7): 3078-3090. |
| [8] | GUO Lingjun, ZHU Rui, LUO Yiqian, ZHANG Zhijin, ZHANG Yupeng, ZHANG Dezhi, LI Qianyong. Analysis of Blood Metabolites in Goat Chronic Distiller's Grain Poisoning and Expression Changes of Key Genes in Ethanol Poisoning Pathway [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(4): 1751-1765. |
| [9] | LIU Wangjing, TANG Defu, AO Changjin. Effect of Allium mongolicum Regel and Its Extract on the Metabolomic Characteristics of Perirenal Adipose Tissue Typical Odor and Flavor Substances in Captive Meat Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(9): 3029-3041. |
| [10] | SUN Na, CAO Zhigang, ZHANG Hua, WANG Hong, SUN Panpan, SUN Yaogui, FAN Kuohai, YIN Wei, LI Hongquan. Effects of Matrine on Feces and Plasma Metabolites of Kunming Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(7): 2364-2379. |
| [11] | WANG Ying, WEN Liang, MU Tong, FENG Xiaofang, LIU Jiamin, ZHANG Juan, WEN Wan, GU Yaling. Metabolomic Analysis of Milk from Holstein Cows with High and Low Milk Fat Percentage [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(5): 1396-1408. |
| [12] | WEI Ruiyuan, ZHAO Yiping, BAI Dongyi, HAN Haige, WANG Xisheng, Anaer, BOU Wuyingga, MANG Lai, LI Xudong. Plasma Metabolomics Features of Mongolian Horses with Different Endurance Exercise Levels [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(5): 1442-1454. |
| [13] | QI Mengfan, XIE Su, GAO Ruonan, SUN Yishan, SUN Xiaomei, HE Junfei, LU Huiwen, LU Shihao, CHEN Xin, LI Qingchun, HUANG Tao. Identification of Differentially Expressed Proteins in Blood of Sows at Early Pregnancy [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(4): 1109-1121. |
| [14] | LIU Shuibing, FANG Wenjie, LI Yankai, ZHANG Wentao, LIU Sanfeng, CHEN Biao. Effect of Acute Cage Stress on the Metabolism of Laying Ducks Studied by Plasma Nontargeted Metabolomics [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(12): 4271-4282. |
| [15] | REN Man, LIU Xin, TANG Yulin, ZHANG Ruixue, QIN Junjie, ZHU Hao, GUO Yansheng. Regulation of Guiqiyimu Compound Preparation on Rumen Microbes and Short-chain Fatty Acids in Postpartum Dairy Cows [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(12): 4461-4469. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||