





畜牧兽医学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (1): 46-57.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2026.01.005
孟云龙1,2( ), 邓远坤1,2, 谭碧娥1,2, 王婧1,2(
), 邓远坤1,2, 谭碧娥1,2, 王婧1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-24
出版日期:2026-01-23
发布日期:2026-01-26
通讯作者:
王婧
E-mail:15838295579@stu.hunau.edu.cn;jingwang023@hunau.edu.cn
作者简介:孟云龙,硕士生,主要从事动物营养与饲料科学研究,E-mail:15838295579@stu.hunau.edu.cn
基金资助:
MENG Yunlong1,2( ), DENG Yuankun1,2, TAN Bi’e1,2, WANG Jing1,2(
), DENG Yuankun1,2, TAN Bi’e1,2, WANG Jing1,2( )
)
Received:2024-12-24
Online:2026-01-23
Published:2026-01-26
Contact:
WANG Jing
E-mail:15838295579@stu.hunau.edu.cn;jingwang023@hunau.edu.cn
摘要:
胃肠道不仅是营养物质消化、吸收和代谢的主要场所,也是活性氧(ROS)产生的重要来源,同时也是ROS攻击的主要靶器官。肠道健康是动物生长的核心因素,是保证畜禽生产效率的重要条件。色氨酸作为一种必需氨基酸,经宿主-微生物协同代谢生成吲哚、犬尿氨酸及5-羟色胺等代谢产物,这些代谢产物通过与内源性配体结合,参与调节肠道中氧化应激反应和炎症损伤。本文综述了肠道中色氨酸的宿主和微生物代谢途径,并探讨了肠道色氨酸代谢产物调控氧化应激及损伤修复的生理功能以及益生菌、营养素补充等干预措施,以期对肠道氧化应激的营养调控研究提供参考。
中图分类号:
孟云龙, 邓远坤, 谭碧娥, 王婧. 色氨酸代谢产物调控肠道氧化应激研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2026, 57(1): 46-57.
MENG Yunlong, DENG Yuankun, TAN Bi’e, WANG Jing. Research Progress on Tryptophan Metabolites in Alleviating Intestinal Oxidative Stress[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2026, 57(1): 46-57.
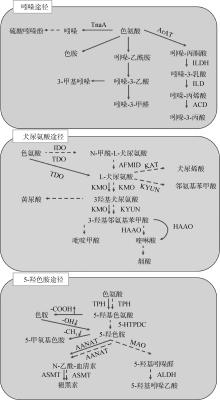
图1
色氨酸代谢途径[36]TnaA. 色氨酸酶;ArAT. 芳香族氨基酸转氨酶;ILDH. 吲哚乳酸脱氢酶;ILD. 吲哚乳酸脱水酶;ACD. 酰基辅酶A脱氢酶Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase;TDO. 色氨酸2,3-双加氧酶;IDO. 吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶;AFMID. 芳犬尿氨酸甲酰胺酶;KAT. 犬尿酸氨基转移酶;KYNU. 犬尿氨酸酶;KMO. 犬尿氨酸-3-单加氧酶;HAAO. 3-羟基氨苯甲酸双加氧酶;5-HTPDC. 5-羟色氨酸脱羧酶;MAO. 单胺氧化酶;ALDH. 醛脱氢酶;AANAT. 芳基烷基胺N-乙酰基转移酶;ASMT. 乙酰血清素O-甲基转移酶。虚线箭头代表宿主代谢途径;实线箭头代表微生物代谢途径"

表1
色氨酸代谢产物结合受体调控肠道氧化应激与损伤修复"
受体 Receptor | 代谢产物 Metabolites | 调节方式 Regulatory methods | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
芳香烃受体 Aryl hydrocarbon receptor | 犬尿氨酸 | 激活AhR下游Foxp3转录因子表达,诱导Treg细胞表达;缓解氧化应激造成的Treg细胞损失出现的免疫失衡,阻止肠道炎症发生 | [ |
| AA | 参与Nrf2信号转录途径,诱导HO-1表达,调控AhR抗氧化平衡 | [ | |
| IPA | 激活AhR调节肠道T细胞活性,减少炎症因子TNF-α、IL-1β以及IL-6表达,调控肠道免疫屏障 | [ | |
| 色胺 | 激活AhR之后,减少Th17细胞以及RORγT细胞的数量,增加Treg细胞水平,减少炎症发生 | [ | |
| IALD | 可以抑制肌动蛋白激活,维持顶部连接复合物表达,调控肠道上皮通透性;结合AhR之后,诱导下游IL-22的表达,IL-22激活STAT通路抑制肠道炎症 | [ | |
| IPyA | 抑制肌动蛋白激活,维持顶部连接复合物表达,调控肠道上皮通透性 | [ | |
| ILA | 与AhR结合抑制炎症细胞因子IL-8以及TNF-α表达,上调IL-22的表达,缓解肠道炎症 | [ | |
| IAA | 调控Foxp3信号通路,诱导Treg细胞的表达;结合AhR后,促进下游CYP1A1、CYP1B1和RegIIIγ表达,与Occludin和ZO-1的表达呈正相关;显著抑制炎症细胞因子IL-1β、TNF-α以及IL-6的表达,减轻炎症反应;激活AhR并通过NF-κB/MAPK信号通路减少Th17细胞水平,降低Th17细胞相关炎症因子IL-17、IL-6以及RORγt的表达;提高结肠IL-22分泌水平,并上调肠道紧密连接蛋白表达以缓解肠道损伤 | [ | |
5-羟色胺受体 6-5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor | 5-HT | 与5-HTR结合后,招募免疫细胞到肠道损伤或炎症部位,促进细胞因子、黏附因子释放;与5-HT4R结合,减少单核细胞TNF-α的释放 | [ |
孕烷X受体 Pregnane X receptor | IPA | 激活PXR之后,抑制TLR4/NF-κB信号通路,减少促炎细胞因子的释放,缓解炎症反应;激活PXR之后上调肠道紧密连接蛋白的表达、下调肠道中TNF-α表达,降低肠道通透性 | [ |
褪黑素受体 Melatonin receptor | 褪黑素 | 可直接进入线粒体内,清除线粒体中的ROS;提升抗氧化酶SOD、CAT等酶的活性,减少ROS水平;上调Nrf2信号通路,增加HO-1表达,增强肠道抗氧化能力;减少免疫细胞向炎症部位移动,降低IL-1β和TNF-β水平,抑制NLRP3表达,减轻炎症反应 | [ |
| [1] | 巩家慧,孔令斌,张 帆.肠道微生物介导的色氨酸代谢与肠粘膜屏障研究进展[J].中国病原生物学杂志,2023,18(9):1110-1113. |
| GONG J H,KONG L B,ZHANG F.Research progress on intestinal microbe-mediated tryptophan metabolism and intestinal mucosal barrier[J].Journal of Pathogen Biology,2023,18(9):1110-1113.(in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 黄 璇,邓 萍,李 闯,等.6~12周龄攸县麻鸭色氨酸需要量研究[J].动物营养学报,2023,35(11):7157-7164. |
| HUANG X,DENG P,LI C,et al.A study on tryptophan requirement of youxian partridge ducks during 6 to 12 weeks of age[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2023,35(11):7157-7164.(in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 林 俊,杜 蕾,齐仁立.色氨酸及其代谢物调控肌肉生长发育的研究进展[J].中国畜牧杂志,2022,58(6):21-25. |
| LIN J,DU L,QI R L.Research progress of tryptophan and its metabolites in regulating muscle growth and development[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Science,2022,58(6):21-25.(in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 朱艳芝,马文锋,陈晓晨,等.色氨酸分解代谢及其在猪饲粮中的应用进展[J].动物营养学报,2020,32(3):1019-1024. |
| ZHU Y Z,MA W F,CHEN X C,et al.Tryptophan catabolism and its application in pig diets[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2020,32(3):1019-1024.(in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 蔡怡旎,杨定平,朱 凯.NADPH氧化酶及其产物活性氧在急性肾损伤中的作用及研究进展[J].临床肾脏病杂志,2017,17(11):700-703. |
| CAI Y N,YANG D P,ZHU K.Role of NADPH oxidase and its product,reactive oxygen species,in acute kidney injury and progress of research thereon[J].Journal of Clinical Nephrology,2017,17(11):700-703.(in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 张轶凤,齐智利.热应激条件下机体发生氧化应激的机制[J].动物营养学报,2017,29(9):3051-3058. |
| ZHANG Y F,QI Z L.Mechanism of oxidative in body under heat stress[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2017,29(9):3051-3058.(in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 谌 龙.长期氨暴露仔猪肺组织氧化应激及表面活性蛋白表达规律研究[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2021. |
| SHEN L.Study on oxidative stress and surfacatant protein expression in lung tissue of piglets under long-term[D].Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University,2021.(in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 曾念宜.肠道细菌来源的超氧阴离子在损伤肠屏障功能以及加重脂肪肝表型中的作用[D].广州:南方医科大学,2023. |
| ZENG N Y.The role of intestinal bacteria derived extracellular superoxide in gut barrier disruption and fatty liver progression[D].Guangzhou:Southern Medical University,2023.(in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 杨 康,梅华迪,马现永,等.厚朴酚对动物肠道黏膜屏障功能的影响及其调控机制[J].动物营养学报,2024,36(1):74-85. |
| YANG K,MEI H D,MA X Y,et al.Effects of magnolol on animal intestinal mucosal barrier function and its regulatory mechanisms[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2024,36(1):74-85.(in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 张玉恒.旋毛虫及其丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂对肠道黏膜屏障功能的影响[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2023. |
| ZHANG Y H.Effects of trichinella spiralis and its serine protease inhibitors on intestinal mucosal barrier function[D]Harbin:Northeast Agricultural University,2023.(in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 邢 爽,冯京海.乳酸杆菌对肠道上皮紧密连接蛋白的调控[J].动物营养学报,2019,31(4):1540-1546. |
| XING S,FENG J H.Regulation of Lactobacillus on intestinal epithelial tight junctio protein[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2019,31(4):1540-1546.(in Chinese) | |
| [12] | LI X,WANG C,ZHU J,et al.Sodium butyrate ameliorates oxidative stress-induced intestinal epithelium barrier injury and mitochondrial damage through AMPK-Mitophagy pathway[J].Oxid Med Cell Longev,2022,2022:3745135. |
| [13] | 邵 丹,施寿荣,胡 艳,等.家禽热应激肠道黏膜屏障损伤及营养性修复研究进展[J].中国家禽,2019,41(13):47-51. |
| SHAO D,SHI S R,HU Y,et al.Research progress on damage effects of heat stress on poultry intestinal mucosal barrier function and its nutrional repair[J].China Poultry,2019,41(13):47-51.(in Chinese) | |
| [14] | WANG H C,CHOU H C,CHEN C M.Molecular mechanisms of hyperoxia-induced neonatal intestinal injury[J].Int J Mol Sci,2023,24(5):4366. |
| [15] | GUO H,GUO H,XIE Y,et al.Mo3Se4 nanoparticle with ros scavenging and multi-enzyme activity for the treatment of dss-induced colitis in mice[J].Redox Biol,2022,56:102441. |
| [16] | LI C,MA D,ZHOU H,et al.Effects of different doses lipopolysaccharides on the mucosal barrier in mouse intestine[J].Res Vet Sci,2020,133:75-84. |
| [17] | WANG T T,WANG Y L,HE K X,et al.Microbial sensing in the intestine[J].Protein Cell,14,11(2023):824-860. |
| [18] | 王宗伟,付建中,李洪涛,等.丁酸梭菌对肠道屏障的影响机制及其在畜禽养殖中应用的研究进展[J].动物营养学报,2022,34(06):3519-3528. |
| WANG Z W,FU J Z,LI H T,et al.Research progress on mechanism of Clostridium butyricum affecting intestinal barrier and its application in livestock and poultry breeding[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2022,34(06):3519-3528.(in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 李 维,孙开济,孙玉丽,等.乳酸菌缓解肠道氧化应激研究进展[J].动物营养学报,2016,28(1):9-14. |
| LI W,SUN K J,SUN Y L,et al.Research progress in relieve effect of Lactobacillus in intestinal oxidative stress[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2016,28(1):9-14.(in Chinese) | |
| [20] | LI L,PENG P,DING N,et al.Oxidative stress,inflammation,gut dysbiosis:What can polyphenols do in inflammatory bowel disease?[J].Antioxidants(Basel),2023,12(4):967. |
| [21] | 张雨婷,范 骏.免疫紊乱:与肠道相关的脓毒症病理机制[J].南昌大学学报(医学版),2023,63(4):85-89. |
| ZHANG Y T,FAN J.Immune disorders:Pathogenesis of gut-associated sepsis[J].Journal of Nanchang University(Medical Sciences),2023,63(4):85-89.(in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 孙忠鑫,柴露露,刘秋宏,等.慢性束缚应激对小鼠小肠屏障的损伤研究[J].西南大学学报(自然科学版),2024,46(2):52-61. |
| SUN Z X,CHAI L L,LIU Q H,et al.Studies on the damage of the small intestinal barrier in mice by chronic restraint stress[J].Journal of South west University(Natural Science Edition),2024,46(2):52-61.(in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 张萌萌,姜 宁,张爱忠.肠道微生物对肠道屏障功能完整性的维护机制研究概况[J].微生物学通报,2020,47(3):933-940. |
| ZHANG M M,JIANG N,ZHANG A Z.Maintenance mechanism of intestinal barrier function integrity by intestinal microbes[J].Microbiology China,2020,47(3):933-940.(in Chinese) | |
| [24] | WU B,LIU Y,ZHEN J,et al.Protective effect of methionine on the intestinal oxidative stress and microbiota change induced by nickel[J].Ecotoxicol Environ Saf,2022,244:114037. |
| [25] | 耿 雪.不同剂量氢气对大强度运动大鼠氧化应激与肠道菌群的影响[D].苏州:苏州大学,2019. |
| GENG X.Effects of different doses of hydrogen on oxidative dtress and intestinal flora in rats undergoing intensive exercise[D].Suzhou:Soochow University,2019.(in Chinese) | |
| [26] | SUN M,MA N,HE T,et al.Tryptophan(Trp) modulates gut homeostasis via aryl hydrocarbon receptor(AhR)[J].Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr,2020,60(10):1760-1768. |
| [27] | SU X,GAO Y,YANG R.Gut Microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites maintain gut and systemic homeostasis[J].Cells,2022,11(15):2296. |
| [28] | GAO K,MU C L,FARZI A,et al.Tryptophan metabolism:A link between the gut microbiota and brain[J].Adv Nutr,2020,11(3):709-723. |
| [29] | WLODARSKA M,LUO C,KOLDE R,et al.Indoleacrylic acid produced by commensal peptostreptococcus species suppresses inflammation[J].Cell Host Microbe,2017,22(1):25-37.e6. |
| [30] | ROAGER H M,TINE R L.Microbial tryptophan catabolites in health and disease[J].Nat Commun,2018,17;9(1):3294. |
| [31] | DODD D,SPITZER H M,TRERUREN W V,et al.A gut bacterial pathway metabolizes aromatic amino acids into nine circulating metabolites[J].Nature,2017,551(7682):648-652. |
| [32] | GAO J,XU K,LIU H,et al.Impact of the gut microbiota on intestinal immunity mediated by tryptophan metabolism[J].Front Cell Infect Microbiol,2018,8:13. |
| [33] | LEE J H,LEE J.Indole as an intercellular signal in microbial communities[J].FEMS Microbiol Rev,2010,34(4):426-444. |
| [34] | 何燕燕,王利华.硫酸吲哚酚在慢性肾脏病并发心血管疾病进展中的作用[J].临床肾脏病杂志,2024,24(2):136-142. |
| HE Y Y,WANG L H.Role of indoxyl sulfate in the progression of chronic kidney disease and associated cardiovascular diseases[J].Journal of Clinical Nephrology,2024,24(2):136-142.(in Chinese) | |
| [35] | KURNASOV O,GORAL V,COLABROY K,et al.NAD biosynthesis:identification of the tryptophan to quinolinate pathway in bacteria[J].Chem Biol,2003,10(12):1195-1204. |
| [36] | AGUS A,PLANCHAIS J,SOKOL H.Gut microbiota regulation of tryptophan metabolism in health and disease[J].Cell Host Microbe,2018,23(6):716-724. |
| [37] | F ORHAN,M BHAT,K SANDBERG,et al.Tryptophan metabolism along the kynurenine pathway downstream of Toll-like receptor stimulation in peripheral monocytes[J].Scand J Immunol,2016,84(5):262-271. |
| [38] | COMAI S,BERTAZZO A,BRUGHERA M,et al.Tryptophan in health and disease[J].Adv Clin Chem,2020,95:165-218. |
| [39] | 李苹苹.腹泻型肠易激综合征患者犬尿氨酸途径代谢的研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2019. |
| LI P P.Study of kynurenine pathway metabolism in patients with diarrhea-type irritable bowel syndrome[D].Shijiazhuang:Hebei Medical University,2019.(in Chinese) | |
| [40] | ZULPAITE R,MIKNEVICIUS P,LEBER B,et al.Tryptophan metabolism via kynurenine pathway:Role in solid organ transplantation[J].Int J Mol Sci,2021,22(4):1921. |
| [41] | MUÑIZ-CALVO S,BISQUERT R,FERNÁNDEZ-CRUZ E,et al.Deciphering the melatonin metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by the bioconversion of related metabolites[J].J Pineal Res,2019,66(3):e12554. |
| [42] | ANA MANDIĆ,ANNI W,TINA J,et al.Clostridium ramosum regulates enterochromaffin cell development and serotonin release[J].Sci Rep,2019,9(1):1177. |
| [43] | 和少英,郭太情,和世春,等.5-羟色胺对肠道疾病的影响[J].中国兽医学报,2022,42(4):818-823. |
| HE S Y,GUO T Q,HE S C,et al.The effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine on intestinal disorders[J].Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science,2022,42(4):818-823.(in Chinese) | |
| [44] | 常 鹏.核酸适配体修饰脂质体负载5-HTP高效穿越血脑屏障的抗抑郁生物学效应研究[D].西安:西安电子科技大学,2023. |
| CHANG P.Highly efficient ccrossing yhe blood-brain barrier by nucleic acid aptamer-modified liposome ioaded 5-HTP for antidepressive therapy[D].Xi'an:Xidian University,2023.(in Chinese) | |
| [45] | 肖状龙.肠道菌群色氨酸代谢/芳香烃受体通路调控慢性结肠炎的机制研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2023. |
| XIAO Z L.The mechanism of microbial tryptophan metabolism/aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway regulating chronic colitis[D].Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology,2023.(in Chinese) | |
| [46] | SCOTT S A,FU J,CHANG P V.Microbial tryptophan metabolites regulate gut barrier function via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2020,117(32):19376-19387. |
| [47] | ZELANTE T,IANNITTI R G,CUNHA C,et al.Tryptophan catabolites from microbiota engage aryl hydrocarbon receptor and balance mucosal reactivity via interleukin-22[J].Immunity,2013,39(2):372-385. |
| [48] | MENG D,SOMMELLA E,SALVIATI E,et al.Indole-3-lactic acid,a metabolite of tryptophan,secreted by Bifidobacterium longum subspecies infantis is anti-inflammatory in the immature intestine[J].Pediatr Res,2020,88(2):209-217. |
| [49] | DOPKINS N,BECKER W,MIRANDA K,et al.Tryptamine attenuates experimental multiple sclerosis through activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor[J].Front Pharmacol,2020,11:619265. |
| [50] | SHEN J,YANG L,YOU K,et al.Indole-3-acetic acid alters intestinal microbiota and alleviates ankylosing spondylitis in mice[J].Front Immunol,2022,13:762580. |
| [51] | RIVAS-ARANCIBIA S,HERNÁNDEZ-OROZCO E,RODRÍGUEZ-MARTÍNEZ E,et al.Ozone pollution,oxidative stress,regulatory T cells and antioxidants[J].Antioxidants(Basel),2022,11(8):1553. |
| [52] | XU K,LIU G,FU C.The tryptophan pathway targeting antioxidant capacity in the placenta[J].Oxid Med Cell Longev,2018,2018:1054797. |
| [53] | BANSKOTA S,GHIA J E,KHAN W I.Serotonin in the gut:Blessing or a curse[J].Biochimie,2019,161:56-64. |
| [54] | 胡天骄,薛 鑫,董秀山.肠道菌群对肠道运动调节的研究进展[J].中国微生态学杂志,2023,35(11):1350-1354. |
| HU T J,XUE X,DONG X S.Intestinal flora regulating intestinal motility:Research progress [J].Chinese Journal of Microecology,2023,35(11):1350-1354.(in Chinese) | |
| [55] | 罗易杨,吕 烨,李成杰,等.孕烷X受体介导的炎症反应在肠道和肝脏疾病中的作用[J].生命的化学,2022,42(12):2177-2184. |
| LUO Y Y,LV Y,LI C J,et al.Roles of PXR-mdiated iflammatory rsponses in itestinal and lver dseases[J].Chemistry of Life,2022,42(12):2177-2184.(in Chinese) | |
| [56] | VENKATESH M,MUKHERJEE S,WANG H,et al.Symbiotic bacterial metabolites regulate gastrointestinal barrier function via the xenobiotic sensor PXR and Toll-like receptor 4[J].Immunity,2014,41(2):296-310. |
| [57] | DVOŘÁK Z,SOKOL H,MANI S.Drug Mimicry:Promiscuous receptors PXR and AhR,and microbial metabolite interactions in the intestine[J].Trends Pharmacol Sci,2020,41(12):900-908. |
| [58] | LOH D,REITER R J.Melatonin:Regulation of biomolecular condensates in neurodegenerative disorders[J].Antioxidants(Basel),2021,10(9):1483. |
| [59] | JOSEPH T T,SCHUCH V,HOSSACK D J,et al.Melatonin:the placental antioxidant and anti-inflammatory[J].Front Immunol,2024,15:1339304. |
| [60] | 马梓毓.粪菌移植通过调节空肠Th17/Treg细胞平衡改善鸡生长性能的机理研究[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2023. |
| MA Z Y.Study on the mechanism of fecal microbiota transplantation iimproves chicken growth performance by balancing jejunal Th17/Treg cells[D].Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University,2023.(in Chinese) | |
| [61] | WANG J,ZHAO Y,CUI T,et al.AhR ligands from LGG metabolites promote piglet intestinal ILC3 activation and IL-22 secretion to inhibit PEDV infection[J].J Virol,2024,98(8):e0103924. |
| [62] | SINHA A K,LAURSEN M F,BRINCK J E,et al.Dietary fibre directs microbial tryptophan metabolism via metabolic interactions in the gut microbiota[J].Nat Microbiol,2024,98(8):1964-1978. |
| [63] | DANG G,WEN X,ZHONG R,et al.Pectin modulates intestinal immunity in a pig model via regulating the gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolite-AhR-IL22 pathway[J].J Anim Sci Biotechnol,2023,14(1):38. |
| [64] | WANG L,TU Y X,CHEN L,et al.Black rice diet alleviates colorectal cancer development through modulating tryptophan metabolism and activating AHR pathway[J].Imeta,2024,3(1):e165. |
| [65] | 郭晴君,杨惠蘩,杨蕴妍,等.槲皮素对高脂饮食诱导肥胖小鼠肝脏脂肪变性的改善作用及对色氨酸代谢物的影响[J].现代食品科技,2024,40(6):96-103. |
| GUO Q J,YANG H F,YANG Y Y,et al.Quercetin ameliorates hepatic steatosis and Influences tryptophan metabolites in obese mice induced by a high-fat diet[J].Modern Food Science and Technology,2024,40(6):96-103.(in Chinese) | |
| [66] | JIANG Z M,ZENG S L,HUANG T Q,et al.Sinomenine ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis by modulating tryptophan metabolism and activating aryl hydrocarbon receptor via gut microbiota regulation[J].Sci Bull(Beijing),2023,68(14):1540-1555. |
| [67] | 杨武奇.茯砖茶茶褐素及结合态多酚缓解结肠炎的生化机制研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2022. |
| YANG W Q.Biochemical mechanism of Fu brick tea theabrownin and bound polyphenols in alleviating colitis[D].Xi'an:Shaanxi Normal University,2022.(in Chinese) | |
| [68] | 欧阳经鑫,李秋粉,周 华,等.饲粮添加色氨酸对热应激肉鸡肝脏、肠道抗氧化能力和炎症反应的影响[J].中国兽医学报,2022,42(6):1256-1262,1269. |
| OUYANG J X,LI Q F,ZHOU H,et al.Effects of dietary tryptophan supplementation on antioxidant capacity and inflammatory response in liver and intestine of broilers subjected to heat stress[J].Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science,2022,42(6):1256-1262,1269.(in Chinese) | |
| [69] | 王 斌.L-色氨酸缓解动物肠道炎症的作用机制研究 [D]北京:中国农业大学,2018. |
| WANG B.Study of the mechanism for the regulatory role of L-Tryptophan in alleviating intestinal inflammation in animals[D].Beijign:China Agricultural University,2018.(in Chinese) | |
| [70] | LIU W,MI S,RUAN Z,et al.Dietary tryptophan enhanced the expression of tight junction protein ZO-1 in intestine[J].J Food Sci,2017,82(2):562-567. |
| [71] | 张若凡.日粮添加吲哚-3-醛对断奶仔猪生长性能、肠上皮功能及肠道微生物区系的影响[D].南京:南京农业大学,2022. |
| ZHANG R F.Effects of dietary indole-3-arboxaldehyde supplementation on growth performance,intestinal epithelial function,and intestinal microbial composition of weaned Piglets[D].Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University,2022.(in Chinese) | |
| [72] | XIE L W,CAI S,LU H Y,et al.Microbiota-derived I3A protects the intestine against radiation injury by activating AhR/IL-10/Wnt signaling and enhancing the abundance of probiotics [J].Gut Microbes,2024,16(1):2347722. |
| [73] | 谷 可.色氨酸对断奶仔猪生长性能和肠上皮屏障损伤修复的影响[D].雅安:四川农业大学,2022. |
| GU K.Effects of tryptophan on growth performance and intestinal epithelial barrier restoration in weaned piglets[D].Ya'an:Sichuan Agricultural University,2022.(in Chinese) |
| [1] | 郭震楠, 吕世政, 萧宗贤, 吴启吉, 包雨加, 李清, 李齐发, 李琦琦, 杜星. KLF5抑制氧化应激状态下猪卵泡颗粒细胞中miR-370与miR-219a的转录[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2026, 57(1): 234-245. |
| [2] | 王伏羲, 马翠, 黄康, 李蕊彤, 赵青余, 张军民, 闫益波, 司玮. 18β-甘草次酸可缓解D-半乳糖诱导断奶仔猪氧化应激肺损伤[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2026, 57(1): 305-316. |
| [3] | 郭志廷, 孙焕焕, 刘淑宁, 李建喜, 张少博, 刘圆, 罗晓琴, 魏小成, 李成义. 常山散对感染不同发育阶段球虫雏鸡盲肠机械屏障的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2026, 57(1): 526-539. |
| [4] | 赵琳, 邬昆富, 车思艳, 卢宇, 王梓, 吴苗苗. 三七茎叶提取物对脂多糖攻毒下仔猪生长性能、腹泻指数及肠道健康的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2026, 57(1): 540-552. |
| [5] | 李伟豪, 尚秀国, 朱晓萍, 郑春田. 岩藻多糖的生理功能及在畜禽生产中的应用研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2026, 57(1): 58-67. |
| [6] | 白广栋, 楼泽楷, 王瑞琪, 赵轩, 李家维, 夏耀耀, 庞家满. 畜禽m6A甲基化修饰及营养调控研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(9): 4215-4231. |
| [7] | 覃阳, 夏嗣廷, 何流琴, 王天丽, 刘宇炎, 姜肖翰, 刘智豪, 刘思危, 李铁军, 印遇龙. 慢性氧化应激对断奶仔猪器官组织微量元素含量的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(9): 4452-4460. |
| [8] | 茹敏, 蒋小丰, 罗国升, 武永厚. 饲粮添加枯草芽孢杆菌对大肠杆菌攻毒仔猪生长性能、血清免疫及抗氧化功能、肠道形态和微生物的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(9): 4461-4471. |
| [9] | 张晓宇, 刘进亿, 褚婷婷, 楚翼健, 牛晨, 武自宪, 张磊, 宋宇轩. 不同蛋白水平代乳粉对羔羊肠道健康的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(9): 4507-4518. |
| [10] | 王超慧, 刘筱影, 杨小军, 刘艳利. 甜菜碱缓解油酸诱导鸡胚原代肝细胞脂代谢紊乱及氧化应激的作用机制[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(9): 4741-4749. |
| [11] | 杨宇翔, 王朋朋, 李斌, 谢留威, 修福晓, 刘成武. 益生菌在犬肠道疾病中作用及机制的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(8): 3610-3620. |
| [12] | 孟亚轩, 刘彦, 王晶, 陈国顺, 冯涛. 氨基葡萄糖对断奶仔猪血清抗氧化、炎症指标以及肠道微生物的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(8): 3908-3921. |
| [13] | 王楠, 王城名, 王婧, 林星彤, 何凌云. 磷脂酰乙醇胺对出生后生长迟缓仔猪结肠黏膜屏障功能和肠道菌群的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(7): 3305-3315. |
| [14] | 彭文文, 张美婷, 徐灏铖, 徐保阳, 张玲玲, 杨彩梅. 地衣芽孢杆菌对大肠杆菌攻毒感染肉鸡免疫、抗氧化性能和肠道健康的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(7): 3344-3356. |
| [15] | 李志强, 陈雪清, 张源淑. 猪流行性腹泻病毒临床感染仔猪肠道组织中血管紧张素转化酶2的检测及其与肠道病理变化的关系分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(7): 3463-3473. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
