





畜牧兽医学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (11): 5912-5924.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.11.046
康欣1( ), 徐向杨1, 韩爱格1, 宋飞1, 芮慧媛1, 姜晓文1,3, 葛铭1,3, 于文会1,2,*(
), 徐向杨1, 韩爱格1, 宋飞1, 芮慧媛1, 姜晓文1,3, 葛铭1,3, 于文会1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-06
出版日期:2025-11-23
发布日期:2025-11-27
通讯作者:
于文会
E-mail:1120064738@qq.com;yuwenhui@neau.edu.cn
作者简介:康欣(1988-),女,山东招远人,硕士,主要从事临床兽医学研究,E-mail:1120064738@qq.com
基金资助:
KANG Xin1( ), XU Xiangyang1, HAN Aige1, SONG Fei1, RUI Huiyuan1, JIANG Xiaowen1,3, GE Ming1,3, YU Wenhui1,2,*(
), XU Xiangyang1, HAN Aige1, SONG Fei1, RUI Huiyuan1, JIANG Xiaowen1,3, GE Ming1,3, YU Wenhui1,2,*( )
)
Received:2025-02-06
Online:2025-11-23
Published:2025-11-27
Contact:
YU Wenhui
E-mail:1120064738@qq.com;yuwenhui@neau.edu.cn
摘要:
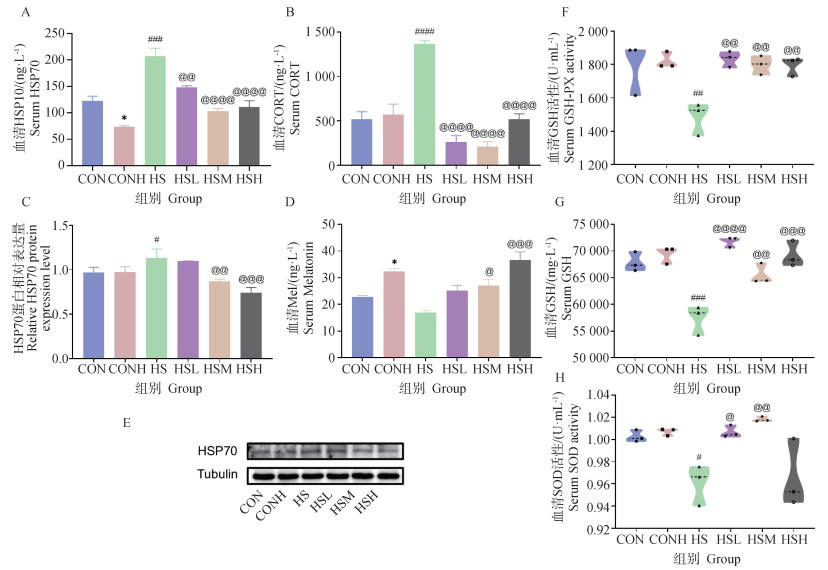
本研究旨在探讨外源性褪黑素(melatonin, Mel)对慢性热应激下肉鸡皮质酮合成分泌的机制,为褪黑素缓解慢性热应激提供理论依据。将90只2周龄的肉鸡随机分为6组:正常对照组(CON),慢性热应激(HS)组,褪黑素干预组:CONH(2.0 mg·kg-1)组、HSL(0.5 mg·kg-1)组、HSM(1.0 mg·kg-1)组、HSH(2.0 mg·kg-1)组。试验持续21 d。结果表明, 慢性热应激导致肉鸡生产性能下降和血清中皮质酮含量明显升高,而0.5 mg·kg-1 Mel处理的肉鸡生产性能显著改善(P<0.001),HSH组的肉鸡料重比显著下降(P<0.05)。日粮中补充0.5~2.0 mg·kg-1 Mel显著降低了慢性热应激下肉鸡血清中皮质酮含量(P<0.000 1)。此外,Mel能有效改善慢性热应激造成的还原型谷胱甘肽(GSH)含量下降,超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)活性下降。根据网络药理学分析,Mel干预慢性热应激,富集到cAMP信号通路,检测到Mel的作用机制与褪黑素受体MT1有关,并通过抑制cAMP/PKA/CREB信号通路,减弱肾上腺皮质酮的合成分泌,减轻应激反应。
中图分类号:
康欣, 徐向杨, 韩爱格, 宋飞, 芮慧媛, 姜晓文, 葛铭, 于文会. 在慢性热应激环境下外源性褪黑素干预对肉鸡皮质酮合成的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(11): 5912-5924.
KANG Xin, XU Xiangyang, HAN Aige, SONG Fei, RUI Huiyuan, JIANG Xiaowen, GE Ming, YU Wenhui. Effect of Exogenous Melatonin Intervention on Corticosterone Synthesis in Broilers under Chronic Heat Stress Conditions[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5912-5924.
表 1
本研究中使用的关键抗体"
| 抗体 Antibodys | 来源 Source | 货号 Identifier | 稀释比例 Dilution ratio |
| Anti-HSP70 antibody | Bioss | bs-0244R | 1∶1 000 |
| Anti-MT1 antibody | Bioss | bs-0027R | 1∶1 000 |
| Anti-MT2 antibody | Bioss | bs-0963R | 1∶1 000 |
| Anti-PKA antibody | Bioss | bs-0520R | 1∶1 000 |
| Anti-CYP11A1 antibody | Bioss | bs-3608R | 1∶1 000 |
| Anti-CREB antibody | Wanleibio | WL01848 | 1∶1 000 |
| Anti-CYP11B1 antibody | Wanleibio | WL05422 | 1∶1 000 |
| Anti-P-CREB antibody | Abways | CY5043 | 1∶1 000 |
| Anti-StAR antibody | Abclonal | A22166 | 1∶2 000 |
| Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L antibody | Bioss | bs-0295G-HRP | 1∶10 000 |
| Anti-Beta tubulin antibody | Bioss | bs-4511R | 1∶10 000 |
表 2
qRT-PCR寡核苷酸引物序列"
| 基因名称 Gene names | 序列(5′ → 3′) Sequence | 方向 Orientation | NCBI编号 NCBI No. |
| GAPDH | TATCTTCCAGGAGCGTGAC | Forward | NM_204305.2 |
| ATCTGCCCATTTGATGTTGC | Reverse | ||
| MT1 | TCCTGGTCATCCTCTCGGT | Forward | NM_205362.2 |
| CGTTCCGCAGTTTCTTGTTG | Reverse | ||
| MT2 | TGCTGATCTTCACCACCGT | Forward | NM_001293103.2 |
| AGGTTGCCCAAAATGTCCAC | Reverse | ||
| PKA | ATCACGTCTCTGAACTTGCT | Forward | XM_025152948.2 |
| ACTCTTCCGAATGATCCTGT | Reverse | ||
| CREB | CTAATAAGGCAGTAGATACCG | Forward | XM_040653773.2 |
| GAACACGTTTAACTTCCACT | Reverse | ||
| CYP11A1 | TGGCTCAACCTGTACCACT | Forward | NM_001001756.2 |
| ACGTTGTGGAAGCCTCCCTC | Reverse | ||
| HSD3B1 | CCCTCAATCATCCCCAGA | Forward Reverse | XM_046906757.1 |
| TTATTCAACATCTCCGTGCT | Reverse |
表 3
褪黑素对肉鸡生长性能的影响($\bar x \pm s$${\bar x}$)"
| 项目Item | 组别Group | |||||
| CON | CONH | HS | HSL | HSM | HSH | |
| 0-7 d ADG | 57.14±4.59 | 48.57±4.19 | 42.38±2.42 | 44.76±1.67 | 49.05±2.68 | 32.62±6.67 |
| 7-14 d ADG | 51.11±5.96 | 61.98±2.63 | 51.98±3.02 | 55.02±4.68 | 38.10±1.46 | 39.60±1.93 |
| 14-21 d ADG | 78.17±3.61 | 57.22±2.24* | 38.49±3.95#### | 63.17±3.79@@ | 53.25±4.40 | 46.35±2.01 |
| 0-21 d ADG | 62.14±1.17 | 55.93±1.20 | 44.29±1.55### | 54.32±2.91@ | 46.80±0.88 | 39.52±1.85 |
| 胸肌指数/% Breast muscle index | 0.182±0.001 | 0.165±0.005 | 0.161±0.006 | 0.143±0.002 | 0.165±0.008 | 0.192±0.006@ |
| F/G | 2.770±0.028 | 2.624±0.058 | 2.783±0.028 | 2.671±0.028 | 2.802±0.010 | 2.587±0.065@ |

图 1
褪黑素对热应激相关指标的影响(n=3) A. 血清HSP70水平;B. 血清CORT水平;C. HSP70蛋白相对表达水平;D. 血清褪黑素水平;E. 肾上腺HSP70蛋白水平;F. 血清GSH-Px活性;G. 血清GSH水平;H. 血清SOD活性。*代表CONH组与CON组之间的显著性差异,*.P<0.05,**.P<0.01,***.P<0.001,****.P<0.000 1;#表示HS组与CON组之间的显著性差异,#.P<0.05,##.P<0.01,###.P<0.001,####.P<0.000 1;@代表Mel干预组与HS组之间的显著性差异,@.P<0.05,@@.P<0.01,@@@.P<0.001,@@@@.P<0.000 1,下图同"
| 1 |
NICLOU M A , CHEN Y K , REDMAN M L . The juxtaposition between heat stress from global warming and human health[J]. J Appl Physiol, 2024, 136 (6): 1346- 1347.
doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00281.2024 |
| 2 | TAN X D , LIU R R , ZHAO D , et al. Large-scale genomic and transcriptomic analyses elucidate the genetic basis of high meat yield in chickens[J]. J Adv Res, 2023, 55, 1- 16. |
| 3 | VANDANA D G , SEJIAN V , LEES M A , et al. Heat stress and poultry production: impact and amelioration[J]. Int J Biometeorol, 2020, 65 (2): 1- 17. |
| 4 |
MCKECHNIE A E , WOLF B O . Climate change increases the likelihood of catastrophic avian mortality events during extreme heat waves[J]. Biol Lett, 2010, 6 (2): 253- 256.
doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2009.0702 |
| 5 |
CAO X H , GUO L Y , ZHOU C M , et al. Effects of N-acetyl-l-cysteine on chronic heat stress-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in the ovaries of growing pullets[J]. Poult Sci, 2023, 102 (1): 102274.
doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102274 |
| 6 |
ZHANG J F , BAI K W , SU W P , et al. Curcumin attenuates heat-stress-induced oxidant damage by simultaneous activation of GSH-related antioxidant enzymes and Nrf2-mediated phase Ⅱ detoxifying enzyme systems in broiler chickens[J]. Poult Sci, 2018, 97 (4): 1209- 1219.
doi: 10.3382/ps/pex408 |
| 7 |
ZABOLI G , HUANG X , FENG X , AHN D U . How can heat stress affect chicken meat quality?-a review[J]. Poult Sci, 2019, 98 (3): 1551- 1556.
doi: 10.3382/ps/pey399 |
| 8 |
PARDIS N , IDRUS Z , AMAT N J , et al. Environmental temperature and stocking density effects on acute phase proteins, heat shock protein 70, circulating corticosterone and performance in broiler chickens[J]. Int J Biometeorol, 2015, 59 (11): 1577- 1583.
doi: 10.1007/s00484-015-0964-3 |
| 9 |
ZAYTSOFF S J M , BORAS V F , UWIERA R R E , et al. A stress-induced model of acute necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens using dietary corticosterone administration[J]. Poult Sci, 2022, 101 (4): 101726.
doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101726 |
| 10 | YUN H , QINWEI S , JIE L , et al. In ovo injection of betaine alleviates corticosterone-induced fatty liver in chickens through epigenetic modifications[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7 (1-4): 40251. |
| 11 |
JOSEPH T T , SCHUCH V , HOSSACK J D , et al. Melatonin: the placental antioxidant and anti-inflammatory[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15, 1339304.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1339304 |
| 12 |
JANA T , DESISLAVA K , PETJ I , et al. The role of melatonin deficiency induced by pinealectomy on motor activity and anxiety responses in young adult, middle-aged and old rats[J]. Behav Brain Funct, 2024, 20 (1): 3.
doi: 10.1186/s12993-024-00229-y |
| 13 |
HARA T , OTSUKA F , TSUKAMOTO-YAMAUCHI N , et al. Mutual effects of melatonin and activin on induction of aldosterone production by human adrenocortical cells[J]. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, 2015, 152, 8- 15.
doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.04.012 |
| 14 |
CLARK W D , CLASSEN H L . The effects of continuously or diurnally fed melatonin on broiler performance and health[J]. Poult Sci, 1995, 74 (11): 1900- 1904.
doi: 10.3382/ps.0741900 |
| 15 |
HAO E Y , LIU X L , CHANG L Y , et al. Melatonin alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress to improve ovarian function by regulating the mTOR pathway in aged laying hens[J]. Poult Sci, 2024, 103 (6): 103703.
doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103703 |
| 16 |
ZHOU G , ZHANG J , LIU S , et al. Potential of exogenous melatonin administration to mitigate heat stress induce pathophysiology of chicken[J]. J Therm Biol, 2024, 122, 103883.
doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2024.103883 |
| 17 |
BAI M , LIU H , XU K , et al. A review of the immunomodulatory role of dietary tryptophan in livestock and poultry[J]. Amino Acids, 2017, 49 (1): 67- 74.
doi: 10.1007/s00726-016-2351-8 |
| 18 |
WU Q , YANG F , TANG H . Based on network pharmacology method to discovered the targets and therapeutic mechanism of Paederia scandens against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in chicken[J]. Poult Sci, 2021, 100 (4): 101042.
doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101042 |
| 19 |
ZHANG H Y , KONG Q B , WANG J , et al. Complex roles of cAMP-PKA-CREB signaling in cancer[J]. Exp Hematol Oncol, 2020, 9 (1): 32.
doi: 10.1186/s40164-020-00191-1 |
| 20 |
OKAMOTO H H , CECON E , NUREKI O , et al. Melatonin receptor structure and signaling[J]. J Pineal Res, 2024, 76 (3): e12952.
doi: 10.1111/jpi.12952 |
| 21 | JIN W , MA R , ZHAI L , et al. Ginsenoside Rd attenuates ACTH-induced corticosterone secretion by blocking the MC2R-cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway in Y1 mouse adrenocortical cells[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 245 (C): 117337. |
| 22 | MANGAN M , SIWEK M . Strategies to combat heat stress in poultry production-A review[J]. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl), 2023, 108 (3): 576- 595. |
| 23 |
NAWAB A , IBTISHAM F , LI G , et al. Heat stress in poultry production: Mitigation strategies to overcome the future challenges facing the global poultry industry[J]. J Therm Biol, 2018, 78, 131- 139.
doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2018.08.010 |
| 24 |
MAJID S , HUU H L . Deleterious effects of heat stress on poultry production: unveiling the benefits of betaine and polyphenols[J]. Poultry, 2022, 1 (3): 147- 156.
doi: 10.3390/poultry1030013 |
| 25 |
ROUSHDY M E , ZAGLOOL W A , EL-TARABANY S M . Effects of chronic thermal stress on growth performance, carcass traits, antioxidant indices and the expression of HSP70, growth hormone and superoxide dismutase genes in two broiler strains[J]. J Therm Biol, 2018, 74, 337- 343.
doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2018.04.009 |
| 26 |
SHAN X , XU X , WANG L , et al. Dietary curcumin supplementation attenuates hepatic damage and function abnormality in a chronic corticosterone-induced stress model in broilers[J]. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, 2024, 243, 106579.
doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2024.106579 |
| 27 | ZHANG R , SUN J , WANG Y , et al. Ameliorative effect of phenolic compound-pterostilbene on corticosterone-induced hepatic lipid metabolic disorder in broilers[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2024, 137, 109822. |
| 28 |
BALLUR A F H , ALTINOZ E , YIGITTURK G , et al. Influence of pinealectomy and long-term melatonin administration on inflammation and oxidative stress in experimental gouty arthritis[J]. Inflammation, 2022, 45 (3): 1332- 1347.
doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01623-2 |
| 29 |
ZIAEI S , HASANI M , MALEKAHMADI M , et al. Effect of melatonin supplementation on cardiometabolic risk factors, oxidative stress and hormonal profile in PCOS patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials[J]. J Ovarian Res, 2024, 17 (1): 138.
doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01450-z |
| 30 |
ANDERSEN L P , GÖGENUR I , ROSENBERG J , et al. The safety of melatonin in humans[J]. Clin Drug Investig, 2016, 36 (3): 169- 175.
doi: 10.1007/s40261-015-0368-5 |
| 31 |
FISCHER T W , KLESZCZYN'SKI K , HARDKOP L H , et al. Melatonin enhances antioxidative enzyme gene expression (CAT, GPx, SOD), prevents their UVR-induced depletion, and protects against the formation of DNA damage (8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine) in ex vivo human skin[J]. J Pineal Res, 2013, 54 (3): 303- 312.
doi: 10.1111/jpi.12018 |
| 32 |
BOCHEVA G , BAKALOV D , ILIEV P , et al. The vital role of melatonin and its metabolites in the neuroprotection and retardation of brain aging[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25 (10): 5122.
doi: 10.3390/ijms25105122 |
| 33 |
CHIN K V , YANG W L , RAVATN R , et al. Reinventing the wheel of cyclic AMP: novel mechanisms of cAMP signaling[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2002, 968 (1): 49- 64.
doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04326.x |
| 34 |
TSE H L , CHEUNG T S , LEE S , et al. Real-time determination of intracellular cAMP reveals functional coupling of Gs protein to the melatonin MT1 receptor[J]. I Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25 (5): 2919.
doi: 10.3390/ijms25052919 |
| 35 | LEWIS A E , AESOY R , BAKKE M . Role of EPAC in cAMP-mediated actions in adrenocortical cells[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2016, 7, 63. |
| 36 |
CHEN D , WANG J , CAO J , et al. cAMP-PKA signaling pathway and anxiety: Where do we go next?[J]. Cell Sign, 2024, 122, 111311.
doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111311 |
| 37 |
KHANNPNAVAR B , MEHTA V , QI C , et al. Structure and function of adenylyl cyclases, key enzymes in cellular signaling[J]. Curr Opin Str Biol, 2020, 63, 34- 41.
doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2020.03.003 |
| 38 |
STWORA K K , KOZLOWSKA A , JASTRZABEK D , et al. Impact of endocrine-active compounds on adrenal androgen production in pigs during neonatal period[J]. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol, 2024, 107, 104435- 104435.
doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2024.104435 |
| 39 | PIHLAJOKI M , DÖRNER J , COCHRAN R S , et al. Adrenocortical zonation, renewal, and remodeling[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2015, 6, 27. |
| 40 |
LIM H S , LEE S H , SEO H , et al. Early stage ultraviolet irradiation damage to skin collagen can be suppressed by HPA axis control via controlled CYP11B[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2022, 155, 113716.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113716 |
| 41 |
IRENE M , ALFONSO B G , JULIA C , et al. Pharmacokinetics of exogenous melatonin in relation to formulation, and effects on sleep: a systematic review[J]. Sleep Med Rev, 2021, 57, 101431- 101431.
doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2021.101431 |
| 42 |
ANDERSEN L P , WERNER M U , ROSENKILDE M M , et al. Pharmacokinetics of oral and intravenous melatonin in healthy volunteers[J]. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol, 2016, 17 (1): 8.
doi: 10.1186/s40360-016-0052-2 |
| 43 |
SÉBASTIEN L , CLAIRE F , M G A , et al. Melatonin: From pharmacokinetics to clinical use in autism spectrum disorder[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22 (3): 1490.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22031490 |
| 44 | 荆瀛黎, 武清斌, 苑晓晨, 等. 褪黑素对人体睡眠和血压的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2013, 13 (11): 2165- 2167. |
| JING Y L , WU Q B , YUAN X C , et al. The effect of melalonin on human sleep and blood pressure[J]. Progress in Modern Biomedicine, 2013, 13 (11): 2165- 2167. | |
| 45 |
ZISAPEL N . New perspectives on the role of melatonin in human sleep, circadian rhythms and their regulation[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2018, 175 (16): 3190- 3199.
doi: 10.1111/bph.14116 |
| [1] | 孙淑佳, 郑嘉祺, 卢姝婉, 刘金松, 姚春雷, 杨彩梅, 许英蕾, 张瑞强. 乳酸菌对黄羽肉鸡生长性能、消化功能和养分利用率的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(7): 3335-3343. |
| [2] | 彭文文, 张美婷, 徐灏铖, 徐保阳, 张玲玲, 杨彩梅. 地衣芽孢杆菌对大肠杆菌攻毒感染肉鸡免疫、抗氧化性能和肠道健康的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(7): 3344-3356. |
| [3] | 陈艳茹, 马小春, 王明慧, 唐瑶瑶, 白露, 赵桂苹, 文杰, 刘冉冉. 白羽肉鸡胸肌意大利面肉和木质肉发生率及其对肉品质影响研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(6): 2672-2684. |
| [4] | 张岩岩, 葛红帆, 周振雷. 红景天苷对甲泼尼龙诱导的肉鸡股骨头坏死的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(5): 2496-2506. |
| [5] | 朱云, 王钰明, 孙晓晓, 陈辉, 赵峰, 解竞静, 陈一凡, 萨仁娜. 低蛋白多元化饲粮添加玉米蛋白粉对白羽肉鸡生长性能和消化特性的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(4): 1802-1812. |
| [6] | 赵少猛, 董瑞玲, 刘大伟, 营凡, 李森, 赵桂苹, 张敏红, 文杰, 冯京海. 广明2号肉鸡蛋白质需要量预测模型的研究及验证[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(3): 1313-1323. |
| [7] | 苏蒙, 刘莎, 宋丹丽, 高倩梅, 郑麦青, 文杰, 赵桂苹, 李庆贺. 基于转录组测序筛选肉鸡腹水综合征相关候选基因[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(2): 559-570. |
| [8] | 杭振宇, 汪子怡, 张林, 邢通, 赵良, 高峰. 不同来源玉米28日龄白羽肉鸡标准回肠氨基酸消化率评定和预测方程的建立[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(2): 722-736. |
| [9] | 成浩彤, 张林, 赵良, 高峰, 邢通. 肉鸡胴体外观和肉质性状候选基因研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(11): 5352-5366. |
| [10] | 胡文悦, 梁慧情, 赵鹏宇, 冯思嘉, 姚子豪, 韩帅娟, 陈宝江. 槲皮万寿菊素对过氧化氢攻毒肉鸡屠宰性能、肉品质、抗氧化、免疫功能及肠道菌群的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(11): 5600-5611. |
| [11] | 李薇羽, 呙于明, 付蹇洋, 刘爱巧, 李文斌, 李冬立, 董晓丽, 吕增鹏, 李建慧. 低蛋白日粮条件下1~14日龄沃德188肉鸡精氨酸需要量研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(11): 5612-5622. |
| [12] | 杨佳, 赵丽媛, 马可涵, DieudonnéM. Dansou, 韩昊洋, 汤超华, 秦玉昌, 张凯, 余雅男, 张军民. 牛磺酸的生理功能及在家禽生产中应用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(10): 4821-4838. |
| [13] | 刘馨蔓, 周鸿缘, 桑锐, 葛冰洁, 闫可心, 王巍, 于明弘, 刘晓童, 邱谦, 张雪梅. 蒲公英甾醇对AFB1性肝损伤肉鸡肝组织氧化应激的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(9): 4141-4152. |
| [14] | 王一诺, 徐丹, 杨建华, 刘洋, 田尧夫, 赵小玲. 基于超声波测量胸肌厚预测肉鸡产肉性能的选育方法研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(7): 2901-2912. |
| [15] | 李明, 崔洪伟, 高婕, 安乐乐, 李松励, 饶正华. 白羽肉鸡小肠内容物中致病性大肠杆菌的鉴定及基因组分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(6): 2692-2700. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
