





畜牧兽医学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (12): 5692-5705.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.12.032
杨荣荣1( ), 张婷1, 唐萍萍2, 何爽方3, 赵苗苗1, 雷连成1,4, 张付贤1,*(
), 张婷1, 唐萍萍2, 何爽方3, 赵苗苗1, 雷连成1,4, 张付贤1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-26
出版日期:2024-12-23
发布日期:2024-12-27
通讯作者:
张付贤
E-mail:yangrr0702@163.com;zhangfuxian99@163.com
作者简介:杨荣荣(2001-),女,陕西宝鸡人,硕士生,主要从事多杀性巴氏杆菌相关研究, E-mail: yangrr0702@163.com
基金资助:
YANG Rongrong1( ), ZHANG Ting1, TANG Pingping2, HE Shuangfang3, ZHAO Miaomiao1, LEI Liancheng1,4, ZHANG Fuxian1,*(
), ZHANG Ting1, TANG Pingping2, HE Shuangfang3, ZHAO Miaomiao1, LEI Liancheng1,4, ZHANG Fuxian1,*( )
)
Received:2024-01-26
Online:2024-12-23
Published:2024-12-27
Contact:
ZHANG Fuxian
E-mail:yangrr0702@163.com;zhangfuxian99@163.com
摘要:
为探究湖北荆州某生猪养殖企业育肥猪呼吸道疾病的致病原,采集病猪肺组织进行病原的筛查和分离鉴定。本研究对分离菌株进行形态学观察、生理生化、16S rDNA基因序列测定、血清型分型、多位点序列分析、药物敏感性试验、耐药基因测序分析以及动物致病性试验。结果显示,分离菌株Pm0525为革兰阴性短杆菌;生化试验、PCR和16S rDNA测序鉴定为多杀性巴氏杆菌。该菌为荚膜血清型A型,分子分型为ST201型,与ST1615型聚为一支;分离菌株对庆大霉素、卡那霉素、麦迪霉素等13种抗生素敏感,对氯霉素、克林霉素、头孢呋辛、头孢他啶和四环素耐药;分离菌株具有中等生物被膜形成能力,携带SulⅠ、SulⅡ、tetA和bla-TEM四种耐药基因,可通过产金属β-内酰胺酶(MBL)方式发挥抗β-内酰胺类抗生素的作用。中药药敏试验结果显示,该分离菌株对中药黄连呈现明显的敏感性。该分离株携带18种毒力基因,并对小鼠具有较强的致病性。本研究系统性分析了猪源多杀性巴氏杆菌的血清型、分子分型、药物敏感性和致病性,为进一步研究多杀性巴氏杆菌感染的致病机制、防控和精准施治提供科学依据和数据参考。
中图分类号:
杨荣荣, 张婷, 唐萍萍, 何爽方, 赵苗苗, 雷连成, 张付贤. 产金属β-内酰胺酶猪源ST201型多杀性巴氏杆菌的耐药性和致病性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(12): 5692-5705.
YANG Rongrong, ZHANG Ting, TANG Pingping, HE Shuangfang, ZHAO Miaomiao, LEI Liancheng, ZHANG Fuxian. Analysis of Drug Resistance and Pathogenicity of Metallo-β-Lactamase-producing Porcine ST201 Pasteurella multocida[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5692-5705.
表 1
多杀性巴氏杆菌荚膜分型引物"
| 血清型 Serotype | 基因 Gene | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequences | 片段大小/bp Fragment size |
| A | hyaD-hyaC | F: TGCCAAAATCGCAGTCAG | 1 044 |
| R: TTGCCATCATTGTCAGTG | |||
| B | bcbD | F: CATTTATCCAAGCTCCACC | 760 |
| R: GCCCGAGAGTTTCAATCC | |||
| D | dcbF | F: TTACAAAAGAAAGACTAGGAGCCC | 657 |
| R: CATCTACCCACTCAACCATATCAG | |||
| E | ecbJ | F: TCCGCAGAAAATTATTGACTC | 511 |
| R: GCTTGCTGCTTGATTTTGTC | |||
| F | fcbD | F: AATCGGAGAACGCAGAAATCAG | 851 |
| R: TTCCGCCGTCAATTACTCTG |

图 4
药敏敏感性和生物被膜形成能力分析 A. 分离株耐药基因筛查结果(M. DL2000 DNA相对分子质量标准;1~18. SulⅠ、SulⅡ、sul3、lunA、ermA、ermC、bla-IMP、bla-TEM、tetA、tetG、tetH、tetR、bla-OXA、dfrA5、dfrA7、dfrA13、bla-DHA、bla-SHV);B. 生物被膜形成能力检测;C. 双纸片协同扩散试验(1. 头孢他啶;2. 头孢他啶/克拉维酸;-. 空白纸片;3. 头孢噻肟;4. 头孢噻肟/克拉维酸;-. 空白纸片;EDTA-纸片协同扩散试验,5. 亚胺培南;6. 亚胺培南/EDTA;-. 空白纸片);D. TEM-1耐药基因的进化树分析"
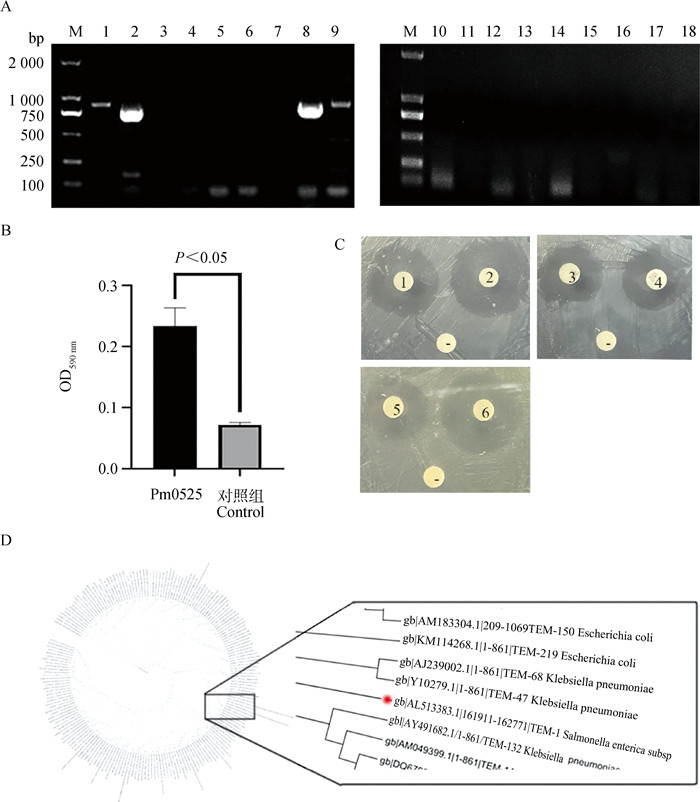
表 3
分离菌株的药敏试验结果"
| 耐药类型 Types of drug resistance | 耐药谱 Antibiotic resistance |
| 耐药 | 氯霉素Chloramphenicol,克林霉素Clindamycin,头孢呋辛Cefuroxime,头孢他啶Ceftazidime,四环素Tetracycline |
| 中介 | 红霉素Erythromycin,羧苄西林Carbenicillin,氨苄西林Ampicillin,呋喃唑酮Furazolidone |
| 敏感 | 庆大霉素Gentamicin,卡那霉素Kanamycin,环丙沙星Ciprofloxacin,麦迪霉素Midecamycin,新霉素Neomycin,氧氟沙星Ofloxacin,诺氟沙星Norfloxacin,哌拉西林Piperacillin,丁胺卡那Amikacin,头孢氨苄Cephalexin,头孢咪唑Cefpimizole,头孢拉定Cefradine,头孢哌酮Cefoperazone |
表 4
中药抑制试验结果"
| 中药 Traditional Chinese medicine | 抑菌圈直径/mm IZD/mm | 敏感性 Sensitivity | 中药 Traditional Chinese medicine | 抑菌圈直径/mm IZD/mm | 敏感性 Sensitivity | |
| 连翘 Forsythia suspensa | 7 | + | 乌梅 Dark plum | 8 | + | |
| 黄连 Coptis chinensis | 19 | ++ | 秦皮 Ash bark | 7 | + | |
| 五倍子 Gallnut | 12 | ++ | 荆芥 Schizonepeta | 10 | ++ | |
| 肉桂 Cinnamomum cassia | 7 | + | 五味子 Schisandra chinensis | 0 | - | |
| 款冬花 Coltsfoot flower | 2 | - | 蒲公英 Dandelion | 2 | - | |
| 金银花 Honeysuckle | 0 | - | 枳壳 Fructus Aurantii | 0 | - | |
| 炒僵蚕 Fried Silkworm | 0 | - | 板蓝根 Radix isatidis | 0 | - | |
| 金蝎 Golden Scorpion | 3 | - | 羌活 Notopterygium root | 0 | - | |
| 桑皮 Mulberry bark | 0 | - | 炙白附子 Roasted White Aconite | 4 | - | |
| 薄荷 Mint | 0 | - | 鱼腥草 Houttuynia cordata | 0 | - | |
| 苏子 Perillaseed | 0 | - | 贝川母 Beichuan mother | 0 | - | |
| 桑白皮 Morus alba | 0 | - | 胖大海 scaphium scaphigerum | 0 | - | |
| 黄芩 Scutellaria baicalensis | 0 | - | 首乌 Polygonum multiflorum | 1 | - | |
| 茯苓 Poria cocos | 0 | - | 罗汉果 Siraitia grosvenorii | 0 | - |
| 1 | WILKIE I W, HARPER M, BOYCE J D, et al. Pasteurella multocida: diseases and pathogenesis[M]//AKTORIES K, ORTH J, ADLER B. Pasteurella multocida: Molecular Biology, Toxins and Infection. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 1-22. |
| 2 | 李贵琴. 牛巴氏杆菌的分离鉴定及黄芩苷对巴氏杆菌肺炎的治疗作用[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2022. |
| LI G Q. Isolation and identification of Pasteurella bovis and the therapeutic effect of baicalin on Pasteurella pneumonia[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 3 |
SARANGI L N , THOMAS P , GUPTA S K , et al. Virulence gene profiling and antibiotic resistance pattern of Indian isolates of Pasteurella multocida of small ruminant origin[J]. Comparat Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis, 2015, 38, 33- 39.
doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2014.11.003 |
| 4 | CARTER G R . The type specific capsular antigen of Pasteurella multocida[J]. Canad J Med Sci, 1952, 30 (1): 48- 53. |
| 5 |
TOWNSEND K M , BOYCE J D , CHUNG J Y , et al. Genetic organization of Pasteurella multocida cap Loci and development of a multiplex capsular PCR typing system[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2001, 39 (3): 924- 929.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.3.924-929.2001 |
| 6 |
HARPER M , JOHN M , TURNI C , et al. Development of a rapid multiplex PCR assay to genotype Pasteurella multocida strains by use of the Lipopolysaccharide outer core biosynthesis Locus[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2015, 53 (2): 477- 485.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.02824-14 |
| 7 | BROGDEN K A , RHOADES K R , HEDDLESTON K L . A new serotype of Pasteurella multocida associated with fowl cholera[J]. Avian Dis, 1978, 229 (1): 185- 190. |
| 8 |
彭忠, 梁婉, 艾伟诚, 等. 我国猪群中多杀性巴氏杆菌的基因型分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2019, 50 (5): 1064- 1072.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2019.05.017 |
|
PENG Z , LIANG W , AI W C , et al. Genotypical characteristics of swine Pasteurella multocida in China[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2019, 50 (5): 1064- 1072.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2019.05.017 |
|
| 9 | 王豪男. 我国部分省区猪源多杀性巴氏杆菌的分子流行病学调查[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2017. |
| WANG H N. Molecular epidemiology of Pasteurella multocida from swine in some provinces of China[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese) | |
| 10 |
许文博, 吴丽梅, 刘鑫, 等. 1株多杀性巴氏杆菌的全基因组序列及致病相关基因分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53 (6): 1858- 1869.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.06.019 |
|
XU W B , WU L M , LIU X , et al. Analysis on complete genome sequence and pathogenic genes of a Pasteurella multocida strain[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53 (6): 1858- 1869.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.06.019 |
|
| 11 |
WANG Y H , ZHU J , LU C P , et al. Evidence of circulation of an epidemic strain of Pasteurella multocida in Jiangsu, China by multi-locus sequence typing (MLST)[J]. Infect Genet Evolut, 2013, 20, 34- 38.
doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2013.07.027 |
| 12 |
张亚楠, 李亚菲, 陈汝佳, 等. A: L1 ST128型鸭源多杀性巴氏杆菌的耐药性及毒力分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2021, 52 (10): 2852- 2863.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.010.016 |
|
ZHANG Y N , LI Y F , CHEN R J , et al. Resistance and virulence analysis of type A: L1 ST128 Pasteurella multocida from Ducks[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52 (10): 2852- 2863.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.010.016 |
|
| 13 |
MAY B J , ZHANG Q , LI L L , et al. Complete genomic sequence of Pasteurella multocida, Pm70[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2001, 98 (6): 3460- 3465.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.051634598 |
| 14 |
CHRISTENSEN H , SAJID S M , BISGAARD M , et al. Prediction of Pasteurella multocida serotypes based on whole genomic sequences[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2022, 271, 109492.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2022.109492 |
| 15 | 邬琴, 张星星, 顾晓晓, 等. 牛源多杀性巴氏杆菌血清分型及毒力相关基因的检测研究[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2020, 47 (6): 1910- 1920. |
| WU Q , ZHANG X X , GU X X , et al. Study on serotyping and detection of virulence-associated genes of Pasteurella multocida isolated from bovine[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 47 (6): 1910- 1920. | |
| 16 |
王斐, 杨洁, 吕庆杰, 等. 致脑膜炎多杀性巴氏杆菌的分离鉴定及全基因组重测序[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53 (12): 4346- 4355.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.12.020 |
|
WANG F , YANG J , LV Q J , et al. Isolation and genomic characterization of a meningitis causing Pasteurella multocida[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53 (12): 4346- 4355.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.12.020 |
|
| 17 | 阮紫涵, 黄安雄, 王秀娟, 等. CLSI、EUCAST和中国耐药判定标准概述[J]. 生物技术通报, 2022, 38 (9): 47- 58. |
| RUAN Z H , HUANG A X , WANG X J , et al. Overview of CLSI, EUCAST, and susceptibility breakpoints in China[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2022, 38 (9): 47- 58. | |
| 18 |
林祥宏. 金属β-内酰胺酶检测方法学研究进展[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2007, 28 (3): 255- 258.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2007.03.023 |
|
LIN X H . Research progress in the detection methodology of Metallo-β-lactamases[J]. International Journal of Laboratory Medicine, 2007, 28 (3): 255- 258.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2007.03.023 |
|
| 19 |
YONG D , LEE K , YUM J H , et al. Imipenem-EDTA disk method for differentiation of metallo-β-lactamase-producing clinical isolates of Pseudomonas spp[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2002, 40 (10): 3798- 3801.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.10.3798-3801.2002 |
| 20 |
ARUHOMUKAMA D . Review of phenotypic assays for detection of extended-spectrum β-lactamases and carbapenemases: a microbiology laboratory bench guide[J]. Afr Health Sci, 2020, 20 (3): 1090- 1108.
doi: 10.4314/ahs.v20i3.11 |
| 21 | 徐州, 周德端, 段国勋, 等. 中药对幽门螺杆菌抑杀作用的实验研究[J]. 中国医药学报, 1993, 8 (5): 25- 26. |
| XU Z , ZHOU D D , DUAN G X , et al. Experimental study on the inhibitory and killing effects of traditional Chinese medicine on Helicobacter pylori[J]. Chinese Medical Journal, 1993, 8 (5): 25- 26. | |
| 22 |
WILSON B A , HO M . Pasteurella multocida: from zoonosis to cellular microbiology[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2013, 26 (3): 631- 655.
doi: 10.1128/CMR.00024-13 |
| 23 | 王立程, 朱雄, 陈海, 等. 四株临床分离多杀性巴氏杆菌分子特征分析[J]. 疾病监测, 2023, 38 (8): 983- 988. |
| WANG L C , ZHU X , CHEN H , et al. Molecular characterization of four strains of Pasteurella multocida isolated from clinical sources[J]. Disease Surveilliance, 2023, 38 (8): 983- 988. | |
| 24 | 张哲玮, 曹维维, 代小童, 等. 猪多杀性巴氏杆菌的分离鉴定、血清分型及耐药性分析[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2023, 43 (5): 930- 936. |
| ZHANG Z W , CAO W W , DAI X T , et al. Isolation, identification, serotyping and drug resistance analysis of Pasteurella multocida suis[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2023, 43 (5): 930- 936. | |
| 25 | 王羽, 董文龙, 王巍, 等. 猪源荚膜血清F型多杀性巴氏杆菌分离鉴定[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2017, 53 (6): 31-33, 36. |
| WANG Y , DONG W L , WANG W , et al. Isolation and identification of a Pasteurella multocida strain belonged to capsular type F from swine[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2017, 53 (6): 31-33, 36. | |
| 26 |
林星宇, 胡凌, 王印, 等. 猪源多杀性巴氏杆菌的分离鉴定及荚膜血清分型[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2016, 28 (4): 558- 562.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2016.04.03 |
|
LIN X Y , HU L , WANG Y , et al. Isolation, identification and capsule serotyping of Pasteurella multocida originated from swine[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2016, 28 (4): 558- 562.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2016.04.03 |
|
| 27 |
PENG Z , WANG H N , LIANG W , et al. A capsule/lipopolysaccharide/MLST genotype D/L6/ST11 of Pasteurella multocida is likely to be strongly associated with swine respiratory disease in China[J]. Arch Microbiol, 2018, 200 (1): 107- 118.
doi: 10.1007/s00203-017-1421-y |
| 28 | 胡璇, 蔡平, 李红婷, 等. 一株猪源A型多杀性巴氏杆菌的分离鉴定[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2021, 51 (12): 1568- 1578. |
| HU X , CAI P , LI H T , et al. Isolation and identification of a strain of Pasteurella multocida type A from swine[J]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 2021, 51 (12): 1568- 1578. | |
| 29 | TANG X B , ZHAO Z Q , HU J Y , et al. Isolation, antimicrobial resistance, and virulence genes of Pasteurella multocida strains from swine in China[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2009, 47 (4): 951- 958. |
| 30 | 张晓兵, 府伟灵, 廖扬, 等. 临床产ESBLs细菌的耐药特征和基因分型的研究[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2005, 15 (4): 386- 389. |
| ZHANG X B , FU W L , LIAO Y , et al. Identification, antibacterial susceptibility and gene typing of clinical ESBLs-producing Bacteria[J]. Chinese Journal of Nosocomiology, 2005, 15 (4): 386- 389. | |
| 31 | 司红彬, 宋剑武, 王鹏霞, 等. 救必应中药血清与抗菌药联合对产ESBLs细菌抑菌效果的研究[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2015, 42 (4): 1009- 1014. |
| SI H B , SONG J W , WANG P X , et al. Study on the antibacterial effect of Chinese material medica serum of holly bark combined with antimicrobials on ESBLs-producing bacteria[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2015, 42 (4): 1009- 1014. | |
| 32 | JU L C , CHENG Z S , FAST W , et al. The continuing challenge of metallo-β-lactamase inhibition: mechanism matters[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 39 (7): 635- 647. |
| 33 | 李娟, 邓秋连, 龙燕, 等. 肠杆菌科产ESBLs细菌的临床耐药研究[J]. 中国当代医药, 2017, 24 (15): 126- 128. |
| LI J , DENG Q L , LONG Y , et al. Clinical drug resistance of Enterobacteriaceae producing ESBLs bacteria[J]. China Modern Medicine, 2017, 24 (15): 126- 128. | |
| 34 | 李达怡, 佘琳曼, 黄妙容, 等. 中药联合对巴氏杆菌的体外抑菌作用研究[J]. 中兽医医药杂志, 2020, 39 (3): 82- 85. |
| LI D Y , SHE L M , HUANG M R , et al. Bacteriostasis of traditional Chinese medicine on Pasteurella in vitro[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 39 (3): 82- 85. | |
| 35 | 姚姗姗, 刘静茹, 陈静, 等. 基于网络药理学探究中药黄连抗菌作用机制[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2020, 47 (5): 1593- 1601. |
| YAO S S , LIU J R , CHEN J , et al. Study on anti-bacterial mechanism of Coptidis rhizoma based on network pharmacology[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 47 (5): 1593- 1601. | |
| 36 | MENG F C , WU Z F , YIN Z Q , et al. Coptidis rhizoma and its main bioactive components: recent advances in chemical investigation, quality evaluation and pharmacological activity[J]. Chin Med, 2018, 13, 13. |
| 37 | 张睿. 黄连碱含量的测定及其对禽多杀性巴氏杆菌抑菌机制的研究[D]. 荆州: 长江大学, 2023. |
| ZHANG R. Determination of the content of coptisine and its inhibition mechanism against Pasteurella multocida[D]. Jingzhou: Yangtze University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 38 | 刘冬梅, 郭梦雨, 费冰, 等. 黄连素抑制肺炎克雷伯菌生物膜形成作用机制研究[J]. 中国现代医药杂志, 2024, 26 (1): 6- 10. |
| LIU D M , GUO M Y , FEI B , et al. Research on the mechanism of Berberine inhibiting the formation of Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilm[J]. Modern Medicine Journal of China, 2024, 26 (1): 6- 10. | |
| 39 | 干铁儿, 林少华, 李文杰, 等. 黄连素联合亚胺培南西司他丁对耐碳青霉烯类肺炎克雷伯菌的体外抑菌作用[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2021, 31 (21): 3211- 3215. |
| GAN T E , LIN S H , LI W J , et al. In vitro antibacterial effect of berberine combined with imipenem-cilastatin on carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae[J]. Chinese Journal of Nosocomiology, 2021, 31 (21): 3211- 3215. |
| [1] | 张姗, 刘大虎, 刘宝京, 梁琳, 梁瑞英, 汤新明, 仇旭升, 丁铲, 丁家波, 侯绍华. 一株鸽副黏病毒Ⅰ型分离鉴定及致病性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(9): 4051-4060. |
| [2] | 谢碧林, 林志敏, 林彬彬, 徐以娟, 林锋强, 闫露, 伍慧妮, 李翠婷, 周海欧, 李兆龙. 鸭疫里氏杆菌LC1和CX1株的分离鉴定及致病性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(9): 4196-4203. |
| [3] | 王佳宁, 张自强, 王帅帅, 刘玉梅. 兔源大肠杆菌、奇异变形杆菌和球虫混合感染及药物敏感性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(9): 4204-4212. |
| [4] | 王艳, 高亚东, 蒋成辉, 曾巧英. 一株鹅源禽腺病毒4型的分离及致病性[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(9): 4232-4240. |
| [5] | 张帆帆, 李杰茂, 谭佳, 黄江南, 吴玲, 韦启鹏, 康昭风. 禽偏肺病毒的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(8): 3344-3353. |
| [6] | 孙雨点, 宋紫玥, 张洪亮, 秦志华, 单虎, 杨瑞梅. 鸭短喙与侏儒综合征病毒分离与鉴定[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(8): 3623-3630. |
| [7] | 刘维哲, 罗成刚, 袁蓉, 廖艺杰, 文艺悯, 孙莹, 俞恩波, 曹三杰, 黄小波. 一株猪流行性腹泻病毒强毒株的分离与鉴定[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(7): 3049-3063. |
| [8] | 班玛王清, 陈曦, 岳怡, 苏玉蓉, 岳华, 汤承. 一株牛呼吸道冠状病毒的分离鉴定及部分生物学特征[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(7): 3094-3104. |
| [9] | 刘博华, 符汉宇, 王玉恒, 索朗斯珠, 牛家强, 包玉花, 李家奎, 徐业芬. 西藏那曲市牦牛源B型多杀性巴氏杆菌的分离鉴定及基因组分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(7): 3105-3118. |
| [10] | 田思瑾, 赵佳琪, 王晓明, 王丽平, 黄金虎. 我国猪链球菌对常用抗菌药物耐药性的Meta分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(7): 3163-3176. |
| [11] | 杨坤, 马静文, 周新瑞, 罗烈柱, 刘喆, 胡自强, 武星辰, 梁立滨, 高诗敏. 三株传染性法氏囊病病毒重组毒株的致病性研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(6): 2550-2559. |
| [12] | 周宁, 汤承, 许佳, 岳华, 陈曦. 猫泛白细胞减少症病毒A91S变异株对猫的致病性及基因组特征研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(6): 2560-2568. |
| [13] | 邹紫莹, 黄安雄, 阮紫涵, 郝海红. 鸡滑液囊支原体对常用抗菌药流行病学临界值的建立[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(6): 2701-2715. |
| [14] | 熊挺, 何献铭, 赵希雅, 庄婷婷, 黄美珍, 梁世金, 余传照, 梁雪静, 陈瑞爱. 三株鸡传染性支气管炎病毒优势流行毒株全基因组分析及其致病性[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(5): 2109-2122. |
| [15] | 高洁, 李晓成, 穆杨, 张慧, 魏荣, 李劼. 荚膜B型多杀性巴氏杆菌外膜囊泡生物学特性分析与免疫效果评价[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(5): 2168-2175. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
