





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 2893-2905.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.06.032
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Enhao1( ), SHI Hongmei2, GESANG Zhuoma3, SUOLANG Sizhu1,*(
), SHI Hongmei2, GESANG Zhuoma3, SUOLANG Sizhu1,*( ), GONG Ga1,*(
), GONG Ga1,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-08
Online:2025-06-23
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
SUOLANG Sizhu, GONG Ga
E-mail:3425171673@qq.com;xzslsz@163.com;xzlzgg@163.com
CLC Number:
ZHAO Enhao, SHI Hongmei, GESANG Zhuoma, SUOLANG Sizhu, GONG Ga. Genetic Evolution, Virulence Genes, and Drug Resistance Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae from Yak in Gansu Province[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(6): 2893-2905.
Table 2
K serotype primer parameters"
| 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′→3′) Sequence (5′→3′) | 退火温度/℃ Tm | 长度/bp Length |
| K1 | GGTGCTCTTTACATCATTGC | 53 | 1 383 |
| GCAATGGCCATTGCGTTAG | |||
| K2 | GACCCGATATTCATACTTGACAGAG | 54 | 641 |
| CCTGAAGTAAAATCGTTAAATAGATGGC | |||
| K3 | AGGCAATTGACTTTAGGTG | 50 | 547 |
| AGTGAATCAGCCTTCACCT | |||
| K5 | TGGTAGTGATGCTCGCGA | 56 | 280 |
| CCTGAACCCACCCCAATC | |||
| K16 | GTGCTTAACGGAGAACTGAAC | 53 | 922 |
| CCTCACCTGGAAGAAGTGTA | |||
| K20 | CGGTGCTACAGTGCATCATT | 54 | 741 |
| GTTATACGATGCTCAGTCGC | |||
| K54 | CATTAGCTCAGTGGTTGGC | 55 | 881 |
| GCTTGACAAACACCATAGCAG | |||
| K57 | CTCAGGGCTAGAAGTGTCAT | 53 | 547 |
| CACTAACCCAGAAAGTCGAG |
Table 3
Primer parameters of virulence genes"
| 类别 Category | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′→3′) Sequence (5′→3′) | 退火温度/℃ Tm | 长度/bp Length |
| 荚膜多糖合成调控基因 Genes regulating capsular polysaccharide synthesis | rmpA | ACTGGGCTACCTCTGCTTCA | 52 | 535 |
| CTTGCATGAGCCATCTTTCA | ||||
| magA | GGTGCTCTTTACATCATTGC | 55 | 1 283 | |
| GCAATGGCCATTTGCGTTAG | ||||
| 菌毛合成相关基因 Genes involved in pilus biosynthesis | fimH | GCTCTGGCCGATACCACCACGG | 55 | 423 |
| GCGAAGTAACGTGCCTGGAACGG | ||||
| mrkD | ATGAAAAAACTGACGCTTTTTATTG | 58 | 963 | |
| TTAATCGTACGTCAGGTTAAAGACC | ||||
| 脲酶相关基因 Urease-related genes | ureA | GCTGACTTAAGAGAACGTTATG | 55 | 337 |
| GATCATGGCGCTACCTCA | ||||
| 脂多糖相关基因 Lipopolysaccharide-related genes | uge | GATCATCCGGTCTCCCTGTA | 55 | 534 |
| TCTTCACGCCTTCCTTCACT | ||||
| wabG | CGGACTGGCAGATCCATATC | 55 | 683 | |
| ACCATCGGCCATTTGATAGA | ||||
| 铁摄取系统 Iron ingestion system | ybtA | ATGACGGAGTCACCGCAAAC | 53 | 960 |
| TTACATCACGCGTTTAAAGG |
Table 4
Primer parameters of drug resistance genes"
| 类别 Category | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′→3′) Sequence (5′→3′) | 退火温度/℃ Tm | 长度/bp Length |
| 超广谱β-内酰胺酶 Extended spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) | blaSHV | GCCTTTATCGGCCTTCACTCAAG | 55 | 898 |
| TTAGCGTTGCCAGTGCTCGATCA | ||||
| blaTEM | CAGCGGTAAGATCCTTGAGA | 52 | 643 | |
| ACTCCCCGTCGTGTAGATAA | ||||
| blaCTX | AACCGTCACGCTGTTGTTAG | 52 | 766 | |
| TTGAGGCGTGGTGAAGTAAG | ||||
| 碳青霉烯类 Carbopenems | blaOXA | GCGTGGTTAAGGATGAACAC | 52 | 438 |
| CATCAAGTTCAACCCAACCG | ||||
| VIM | GATGGTGTTTGGTCGCATA | 52 | 390 | |
| CGAATGCGCAGCACCAG | ||||
| NDM | GGTTTGGCGATCTGGTTTTC | 55 | 621 | |
| CGGAATGGCTCATCACGATC | ||||
| 喹诺酮类 Quinolones | qnr | ATTTCTCACGCCAGGATTTG | 53 | 516 |
| GATCGGCAAAGGTTAGGTCA | ||||
| gyrA | CGCGTACTATACGCCATGAACGTA | 55 | 420 | |
| ACCGTTGATCACTTCGGTCAGG | ||||
| 氨基糖苷类 Aminoglycoside | acc(3’)-IIa | CGGAAGGCAATAACGGAG | 53 | 740 |
| TCGAACAGGTAGCACTGAG | ||||
| acc(6’)-Ib | ATGACCTTGCGATGCTCTATGA | 54 | 486 | |
| CGAATGCCTGGCGTGTTT | ||||
| 磺胺类 Sulfonamides | Sul 1 | GTGACGGTGTTCGGCATTCT | 58 | 779 |
| TCCGAGAAGGTGATTGCGCT | ||||
| 四环素类 Tetracyclines | tetB | CCTCAGCTTCTCAACGCGTG | 57 | 634 |
| GCACCTTGCTGATGACTCTT | ||||
| 酰胺醇类 Acetamine alcohols | flor | CACGTTGAGCCTCTATAT | 52 | 868 |
| ATGCAGAAGTAGAACGCG | ||||
| 头孢菌素类 Cephalosporins | blaDHA | GCCTGTTTGGTGCTCTGA | 55 | 460 |
| GCACGGTTATACGGCTGA | ||||
| 多黏菌素类 Polymyxins | mcr-1 | AGTCCGTTTGTTCTTGTGGC | 56 | 320 |
| AGATCCTTGGTCTCGGCTTG | ||||
| 大环内酯类 Macrolides | ereA | GCCGGTGCTCATGAACTTGAG | 57 | 419 |
| CGACTCTATTCGATCAGAGGC |
Table 5
Information on drug susceptibility tablets"
| 药物种类 Drug types | 药物名称 Drug name | 药品规格/(μg·片-1) Specifications | 抑菌圈直径判断标准/mm Criteria for determining the inhibitory diameter | ||
| 耐药Resistent | 中介Intermedia | 敏感Senstive | |||
| β-内酰胺类β-lactamase | 氨苄西林 | 10 | < 13 | 13~17 | >17 |
| 羧苄西林 | 100 | < 19 | 19~23 | >23 | |
| 哌拉西林 | 100 | < 17 | 17~21 | >21 | |
| 头孢氨苄 | 30 | < 14 | 14~18 | >18 | |
| 头孢唑林 | 30 | < 14 | 14~18 | >18 | |
| 头孢拉定 | 30 | < 14 | 14~18 | >18 | |
| 头孢呋辛 | 30 | < 14 | 14~18 | >18 | |
| 头孢他啶 | 30 | < 14 | 14~18 | >18 | |
| 头孢曲松 | 30 | < 14 | 14~23 | >23 | |
| 头孢哌酮 | 30 | < 15 | 15~21 | >21 | |
| 氨基糖苷类Aminoglycoside | 丁胺卡那 | 30 | < 14 | 14~17 | >17 |
| 庆大霉素 | 30 | < 12 | 12~15 | >15 | |
| 卡那霉素 | 10 | < 13 | 13~18 | >18 | |
| 新霉素 | 30 | < 12 | 12~17 | >17 | |
| 四环素类Tetracyclines | 四环素 | 30 | < 14 | 14~19 | >19 |
| 多西环素 | 30 | < 12 | 12~16 | >16 | |
| 米诺环素 | 30 | < 12 | 12~16 | >16 | |
| 大环内酯类Macrolides | 红霉素 | 15 | < 13 | 13~23 | >23 |
| 麦迪霉素 | 30 | < 13 | 13~18 | >18 | |
| 喹诺酮类Quinolones | 诺氟沙星 | 10 | < 12 | 12~17 | >17 |
| 氧氟沙星 | 5 | < 12 | 12~16 | >16 | |
| 环丙沙星 | 5 | < 15 | 15~21 | >21 | |
| 糖肽类Glycopeptides | 万古霉素 | 30 | < 14 | 14~17 | >17 |
| 多黏菌素b | 7.5 | < 8 | 8~12 | >12 | |
| 磺胺类Sulfonamides | 复方新诺明 | 23.75 | < 23 | 23~32 | >32 |
| 硝基咪唑类Nitroimidazole class | 呋喃唑酮 | 300 | < 14 | 14~17 | >17 |
| 酰胺醇类Acetamine alcohols | 氯霉素 | 30 | < 12 | 12~18 | >18 |
| 林可胺类Linkomide | 克林霉素 | 2 | < 14 | 14~21 | >21 |
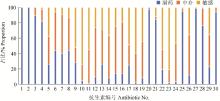
Fig. 4
Drug susceptibility results of Klebsiella pneumoniae 1. Ampicillin; 2. Benzillin; 3. Piperacillin; 4. Cephalexin; 5. Cefazolin; 6. Cefarradine; 7. Cefuroxime; 8. Ceftazidime; 9. Ceftriaxone; 10. Cefoperazone; 11. Butanana; 12. Gentamicin; 13. Kanamycin; 14. Neomycin; 15. Tetracycline; 16. Doxycycline; 17. Minocycline; 18. Erythromycin; 19. Medimamycin; 20. Norfloxacin; 21. Oloxacin; 22. Ciprofloxacin; 23. Vancomycin; 24. Polymyxin B; 25. Cotrimoxazole; 26. Furanazolidone; 27. Chloramphenicol; 28. Clindamycin"
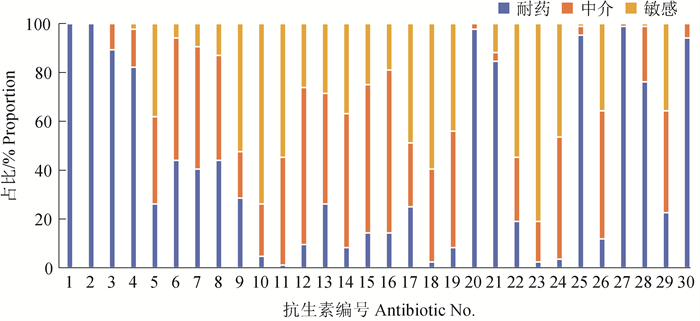

Fig. 7
The ERIC-PCR cluster analysis plot of K. pneumoniae Ⅰ. Ultra spectrum β-lactamase; Ⅱ. Carbopenems(ESBLs); Ⅲ. Quinolones; Ⅳ. Aminoglycosides; V. Sulfonamides; Ⅵ. TCs; Ⅶ. Amide alcohol; Ⅷ. Cephalosporins; Ⅸ. Polymyxins; X. Macrolides; XI. Regulation of capsular polysaccharide synthesis genes; XII. Fucoil synthesis-related genes; XIII. Ulrease-related genes; XIV. Lolipopolysaccharide-related genes; XV. Iron uptake system; 1. blaSHV; 2. blaTEM; 3. blaOXA; 4. blaCTX; 5. VIM; 6. NDM; 7. qnr; 8. acc(6')-Ib; 9. gyrA; 10. acc(3)-IIa; 11. Sul 1; 12. tetB; 13. flor; 14. blaDHA; 15. mcr-1; 16. ereA; 17. rmpA; 18. magA; 19. fimH; 20. mrkD; 21. uerA; 22. uge; 23. wabG; 24. ybtA"
| 1 | 王蔚莎, 叶龙, 张妮, 等. 2012—2023年某医院耐碳青霉烯类肺炎克雷伯菌感染流行特征分析[J]. 中国消毒学杂志, 2024, 41 (6): 436-439, 443. |
| WANG W S , YE L , ZHANG N , et al. Analysis of the epidemic characteristics of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in a hospital from 2012 to 2023[J]. Chinese Journal of Disinfection, 2024, 41 (6): 436-439, 443. | |
| 2 | 李学英. 大熊猫源肺炎克雷伯菌的分离鉴定及其部分生物学特性研究[D]. 成都: 西南民族大学, 2022. |
| LI X Y. Isolation and identification of Giant panda source Klebsiella pneumoniae and some biological characteristics[D]. Chengdu: Southwest University for Nationalities, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 3 | 陈悦, 陈景燕, 马春霞, 等. 高毒力肺炎克雷伯菌感染的研究进展[J]. 宁夏医学杂志, 2024, 46 (6): 546- 550. |
| CHEN Y , CHEN J Y , MA C X , et al. Progress in highly virulent K. pneumoniae infection[J]. Ningxia Medical Journal, 2024, 46 (6): 546- 550. | |
| 4 |
NJEUNA A , FOUNOU L L , FOUNOU R C , et al. High prevalence and genetic diversity of multidrug resistant and extended spectrum ß-lactamase producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in mothers and neonates in a Cameroonian labour ward[J]. Am J Infect Control, 2024, 52 (11): 1273- 1282.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2024.06.002 |
| 5 | MANIKANDAN P , ALOYUNI S , OTHAIM A A , et al. Prevalence and antimicrobial mechanism of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and its molecular properties[J]. Journal of King Saud University-Science, 2024, 36 (8): 10328. |
| 6 | 田李均. 肺炎克雷伯菌的临床特征及高毒力菌株的耐药机制研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2017. |
| TIAN L J. Clinical characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae and drug resistance mechanisms of highly virulent strains[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2017. (in Chinese) | |
| 7 | 丘江, 张洁, 孙杨, 等. 多重耐药肺炎克雷伯菌62种耐药基因元件的检测与gyrA基因突变的发现[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2019, 35 (6): 539- 544. |
| QIU J , ZHANG J , SUN Y , et al. Detection of 62 drug-resistant gene elements in multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and discovery of gyrA gene mutations[J]. Chinese Journal of Zoonosis, 2019, 35 (6): 539- 544. | |
| 8 |
张凯川, 王晋宇, 李守军, 等. 广东省羊源肺炎克雷伯菌遗传进化与毒力基因及耐药性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (1): 328- 337.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.01.030 |
|
ZHANG K C , WANG J Y , LI S J , et al. Genetic evolution and virulence genes and drug resistance analysis of sheep source Klebsiella pneumoniae in Guangdong Province[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (1): 328- 337.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.01.030 |
|
| 9 | 徐睿, 赖华敏, 欧正阳, 等. 福建省莆田地区猪源肺炎克雷伯菌的分离鉴定及耐药情况检测[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2023 (15): 72-77, 136. |
| XU R , LAI H M , OU Z Y , et al. Isolation, identification and resistance detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Putian, Fujian Province[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2023 (15): 72-77, 136. | |
| 10 |
赵菲菲, 李杰, 韩宁, 等. 分离自屠宰场的肺炎克雷伯菌的耐药性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (7): 3044- 3053.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.07.035 |
|
ZHAO F F , LI J , HAN N , et al. Analysis of drug resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from slaughterhouses[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (7): 3044- 3053.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.07.035 |
|
| 11 | 李花. 肝脓肿肺炎克雷伯菌血清分型及毒力基因的研究[D]. 沈阳: 中国医科大学, 2018. |
| LI H. Serotyping and virulence genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae in liver abscess[D]. Shenyang: China Medical University, 2018. (in Chinese) | |
| 12 |
王佳宁, 张自强, 孔德婧, 等. 家兔肺炎克雷伯菌的分离鉴定[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54 (12): 5198- 5206.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.12.029 |
|
WANG J N , ZHANG Z Q , KONG D J , et al. Isolation and identification of K. pneumoniae in rabbits[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54 (12): 5198- 5206.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2023.12.029 |
|
| 13 | 贡嘎, 格桑卓玛, 左伟, 等. 西藏部分地区牦牛源肺炎克雷伯菌的分离、鉴定、毒力及耐药基因分析[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2021, 41 (1): 102- 109. |
| GONG G , GESANG Z M , ZUO W , et al. Isolation, identification, virulence and drug resistance gene analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae in some parts of Tibet[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 41 (1): 102- 109. | |
| 14 | 吴香云. 湖北地区奶牛乳房炎源肺炎克雷伯菌毒力和耐药分子特征研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2022. |
| WU X Y. Study on virulence and drug resistance of dairy cow mastitis source Klebsiella pneumoniae in Hubei province[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 15 | 崔琦. 奶牛乳房炎源性肺炎克雷伯菌MrkD基因原核表达以及对乳腺上皮细胞黏附的研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2021. |
| CUI Q. Prokaryotic expression of MrkD gene in Kbsiella pneumoniae and adhesion to mammary epithelial cells[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| 16 | 买尔哈巴·吾斯曼. 国内部分地区奶牛乳腺炎源肺炎克雷伯菌生物学特性研究[D]. 塔里木: 塔里木大学, 2022. |
| MAIERHABA W S M. Research on the biological characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae in some areas of China[D]. Tarim: Tarim University, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| 17 |
张自强, 王佳佳, 任玉莹, 等. 兔源支气管败血波氏杆菌和肺炎克雷伯菌的分离鉴定及其对抗菌药物的敏感性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2021, 52 (8): 2254- 2264.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.08.018 |
|
ZHANG Z Q , WANG J J , REN Y Y , et al. Isolation and identification of B. septicus and K. pneumoniae and its sensitivity to antimicrobial agents[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52 (8): 2254- 2264.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.08.018 |
|
| 18 | 隋明, 王静霞, 唐贤华, 等. 四川地区牦牛源肺炎克雷伯氏菌的分离鉴定及其耐药性分析[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2019, 46 (6): 1816- 1824. |
| SUI M , WANG J X , TANG X H , et al. Isolation and resistance analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Sichuan[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 46 (6): 1816- 1824. | |
| 19 |
王奇林, 曹润来, 王威阳, 等. 狐狸流产胎儿体内肺炎克雷伯菌的分离鉴定及耐药性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (8): 3640- 3648.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.08.035 |
|
WANG Q L , CAO R L , WANG W Y , et al. Isolation, identification and resistance analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae in fox ted fetuses[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (8): 3640- 3648.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.08.035 |
|
| 20 | 陈瑞格, 李赟辉, 项维, 等. 鸽源ST443肺炎克雷伯菌的分离鉴定和生物学特性分析[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2024, 60 (5): 46- 55. |
| CHEN R G , LI Y H , XIANG W , et al. Isolation, identification and biological characterization of pigeon-derived ST443 K. pneumoniae[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 60 (5): 46- 55. | |
| 21 |
DEEKSHA S , SHILPEE P , SRIKRISHNA S , et al. Comparative genomics of an extensively drug resistant strain Klebsiella pneumoniae ⅡTR008 with international high-risk clonal lineage ST147 isolated from river water[J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 2024, 117 (1): 57.
doi: 10.1007/s10482-024-01955-z |
| 22 | 安舒琦. 吉林省肺炎克雷伯菌临床分离株耐药性及耐药基因研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2023. |
| AN S Q. Study on drug resistance and resistance genes of K. pneumoniae clinical isolates in Jilin province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 23 | 周新新, 刘瑞杰, 孙桂芹. 肺炎克雷伯菌临床分布及耐药性分析[J]. 浙江临床医学, 2023, 25 (12): 1844- 1846. |
| ZHOU X X , LIU R J , SUN G Q . Clinical distribution and drug resistance analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae[J]. Zhejiang Clinical Medicine Journal, 2023, 25 (12): 1844- 1846. | |
| 24 |
DIMAITINO V , VENDITTI C , MESSINA F , et al. Screening of Klebsiella pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae strains with multi-drug resistance and virulence profiles isolated from an Italian hospital between 2020 and 2023[J]. Antibiotics (Basel), 2024, 13 (6): 561.
doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13060561 |
| 25 |
QIAN J , JIN P , YANG Y , et al. Protein function annotation and virulence factor identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae genome by multiple machine learning models[J]. Microbial pathogenesis, 2024, 193, 106727.
doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106727 |
| 26 |
李华明, 项维, 卢文兵, 等. 1株猪源ST-35型肺炎克雷伯菌的致病性和药物敏感性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53 (12): 4356- 4366.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.12.021 |
|
LI H M , XIANG W , LU W B , et al. Pathogenicity and drug susceptibility analysis of one pig-derived ST-35 K. pneumoniae strain[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53 (12): 4356- 4366.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.12.021 |
|
| 27 | 林楠, 岳广欣, 兰小琴, 等. 中药成分对多药耐药肺炎克雷伯菌的抑菌及耐药逆转作用的体外研究[J]. 中国研究型医院, 2023, 10 (3): 23- 27. |
| LIN N , YUE G X , LAN X Q , et al. In vitro study of antibacterial and resistance reversal of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae[J]. Chinese Research Hospitals, 2023, 10 (3): 23- 27. | |
| 28 | 唐金蓉, 张碟, 李盛. 四种中药单体联合亚胺培南对耐碳青霉烯肺炎克雷伯菌体外抑菌作用研究[J]. 现代检验医学杂志, 2022, 37 (6): 162-165, 197. |
| TANG J R , ZHANG D , LI S . Study on the bacteriostatic effect of four single Chinese medicines combined with imipenem on carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in vitro[J]. Journal of Modern Laboratory Medicine, 2022, 37 (6): 162-165, 197. |
| [1] | LIAO Yiwen, YE Jingfen, WU Shaobi, CHEN Shixiong, YANG Wan, LUO Xue, YANG Qi. Development of Ring-mediated Isothermal Amplification Technology and Its Application to the Detection of Drug Resistance Genes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1621-1631. |
| [2] | DU Qingjie, WU Liping, ZHANG Fan, DAI Pengxiu, FENG Xiancheng, ZHANG Xinke. Difference Analysis of Oral Flora in Dogs with Periodontitis and Drug Resistance of Oral Porphyromonas [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 934-942. |
| [3] | FAN Wei, LIU Xinxin, ZHAI Yilu, ZHANG Xinyu, WANG Wei, FU Jiaqi, SUN Fuliang. Isolation and Identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae of Sheep Origin and Establishment of a Method for the Extraction of Its Outer Membrane Vesicles [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 353-364. |
| [4] | Qilin WANG, Runlai CAO, Weiyang WANG, Bo ZHANG, Zhijie LIU, Xiaoxu WANG. Isolation, Identification and Drug Resistance Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Aborted Fetuses of Fox [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3640-3648. |
| [5] | SONG Yan, YUAN Yongfeng, QIAN Hongyu, LI Xincan, LUO Hongyan, WANG Zhiying, ZHOU Zuoyong. Identification and Partial Biological Characteristics Analysis of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Isolated from Goats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 680-687. |
| [6] | WU Sujuan, LIN Changcheng, WAN Peng, LI Jie, LU Yixing, HU Jianxin, PENG Xianfeng, ZENG Zhenling. Synergistic Antimicrobial Effect of Isopropoxy Benzene Guanidine Combined with Colistin on Klebsiella pneumoniae in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5792-5801. |
| [7] | LIU Xinhuan, YUN Jialei, MAO Li, LI Jizong, HAO Fei, HE Miaofeng, YANG Leilei, ZHANG Wenwen, CHENG Zilong, SUN Min, LIU Maojun, WANG Shaohui, BAI Juan, LI Wenliang. Isolation, Identification, Virulence Genes and Drug Resistance Analysis of Escherichia coli Isolated from Diarrheal Goat and Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(8): 3445-3454. |
| [8] | ZHAO Feifei, LI Jie, HAN Ning, XIE Shiting, ZENG Zhenling. Antibacterial Drug Resistance Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Slaughterhouse [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(7): 3044-3053. |
| [9] | JIANG Zenghai, TENG Lin, HE Anwen, LIU Yanyan, YUE Min, HE Qigai. Genomic Analysis of Salmonella Typhimurium Isolates and Salmonella Serotype 4, [5], 12: i:- Isolates from Pig-borne Food Chain [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(3): 1199-1209. |
| [10] | WANG Jianing, ZHANG Ziqiang, KONG Dejing, FENG Caicai, ZHANG Feike, LIU Yumei. Isolation and Identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 5198-5206. |
| [11] | YANG Menglin, ZHENG Shiqi, PENG Kai, WANG Wei, HUANG Yanhua, PENG Jie. Isolation and Identification of Pigeon-derived Salmonella Typhimurium and Pathogenic Analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(11): 4880-4888. |
| [12] | ZHANG Kaichuan, WANG Jinyu, LI Shoujun, JIA Kun. Isolation, Identification and Biological Characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae from Sheep in Guangdong Province [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(1): 328-337. |
| [13] | WANG Xi, LI Ke, LI Tingcui, YAN Hongya, ZHAO Rong, CHANG Zhishun, LIAO Ming, SUN Minhua, XIN Aiguo. MLST Typing and Drug Resistance Analysis of 75 Salmonella Strains Isolated from Laying Hens [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(5): 1626-1631. |
| [14] | ZHAO Xueliang, WANG Bin, MIAO Yongqiang, ZHAO Haoyu, XIE Qingfang, WANG Juan, YANG Zengqi. Detection of Virulence Genes and Antimicrobial Resistance Analysis of Escherichia coli Isolated from Diarrhea Sheep in Shaanxi Province [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(5): 1644-1648. |
| [15] | LI Huaming, XIANG Wei, LU Wenbing, LIU Feng, LEI Liancheng, ZHANG Fuxian. Pathogenicity and Drug Sensitivity Analysis of a Porcine Klebsiella pneumoniae Type ST-35 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(12): 4356-4366. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||