





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (9): 4051-4060.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.09.029
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Shan ZHANG1,2( ), Dahu LIU1,2,3, Baojing LIU4, Lin LIANG1,2, Ruiying LIANG1,2, Xinming TANG1,2, Xusheng QIU5, Chan DING5, Jiabo DING1,2,*(
), Dahu LIU1,2,3, Baojing LIU4, Lin LIANG1,2, Ruiying LIANG1,2, Xinming TANG1,2, Xusheng QIU5, Chan DING5, Jiabo DING1,2,*( ), Shaohua HOU1,*(
), Shaohua HOU1,*( )
)
Received:2023-11-16
Online:2024-09-23
Published:2024-09-27
Contact:
Jiabo DING, Shaohua HOU
E-mail:zhangshan0276@163.com;dingjiabo@caas.cn;houshaohua@caas.cn
CLC Number:
Shan ZHANG, Dahu LIU, Baojing LIU, Lin LIANG, Ruiying LIANG, Xinming TANG, Xusheng QIU, Chan DING, Jiabo DING, Shaohua HOU. Isolation, Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of a Pigeon Paramyxovirus-1 Strain[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4051-4060.

Fig. 3
Phylogentic tree based on the F nucleotide sequences of NDV strains A. Complete phylogentic tree, △Strains from China before 2000, ○ Strains from China 2001-2010, □ Strains from China after 2010; B. Detailed information on sub-genotypes Ⅵ.2.1.1.2.2 (Ⅵk) in the dashed part of Figure A. ●. TJ20"
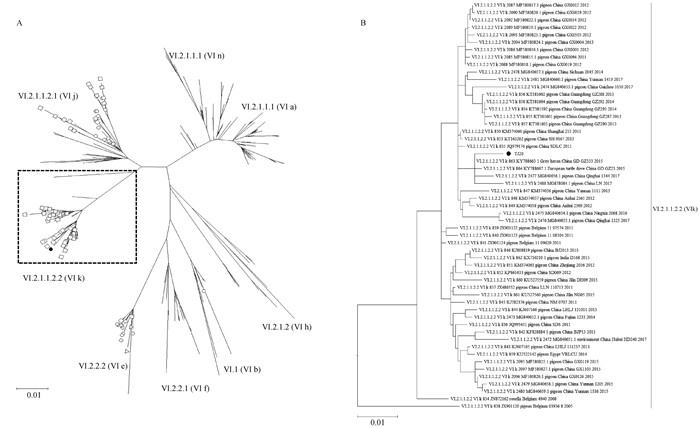
Table 2
Virus shedding after infection with TJ20 strain"
| 组别Group | 毒株Strain | 数量/只Number | 口咽Oropharyngeal | 泄殖腔Cloacal | ||||||
| 第3天3 dpc | 第5天5 dpc | 第7天7 dpc | 第10天10 dpc | 第3天3 dpc | 第5天5 dpc | 第7天7 dpc | 第10天10 dpc | |||
| 感染组Infection group | TJ20 | 10 | 0/10 | 3/10 | 3/9 | 2/3 | 1/10 | 10/10 | 9/9 | 3/3 |
| 对照组Control group | / | 10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 |
| 1 |
MAYO M A . A summary of taxonomic changes recently approved by ICTV[J]. Arch Virol, 2002, 147 (8): 1655- 1656.
doi: 10.1007/s007050200039 |
| 2 | MILLAR N S , CHAMBERS P , EMMERSON P T . Nucleotide sequence of the fusion and haemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein genes of Newcastle disease virus, strain Ulster: molecular basis for variations in pathogenicity between strains[J]. J Gen Virol, 1988, 69 (Pt 3): 613- 620. |
| 3 |
SELIM K M , SELIM A , ARAFA A , et al. Molecular characterization of full fusion protein (F) of Newcastle disease virus genotype VⅡd isolated from Egypt during 2012-2016[J]. Vet World, 2018, 11 (7): 930- 938.
doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2018.930-938 |
| 4 |
CZEGLÉDI A , UJVÁRI D , SOMOGYI E , et al. Third genome size category of avian paramyxovirus serotype 1(Newcastle disease virus) and evolutionary implications[J]. Virus Res, 2006, 120 (1-2): 36- 48.
doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2005.11.009 |
| 5 |
GOULD A R , HANSSON E , SELLECK K , et al. Newcastle disease virus fusion and haemagglutinin-neuraminidase gene motifs as markers for viral lineage[J]. Avian Pathol, 2003, 32 (4): 361- 373.
doi: 10.1080/0307945031000121112 |
| 6 |
WEI T C , DENG Q M , LI H Q , et al. Molecular characterization of two novel sub-sublineages of pigeon paramyxovirus type 1 in China[J]. Arch Virol, 2018, 163 (11): 2971- 2984.
doi: 10.1007/s00705-018-3950-3 |
| 7 |
QIU X S , MENG C C , ZHAN Y , et al. Phylogenetic, antigenic and biological characterization of pigeon paramyxovirus type 1 circulating in China[J]. Virol J, 2017, 14 (1): 186.
doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0857-7 |
| 8 |
LIU X F , WAN H Q , NI X X , et al. Pathotypical and genotypical characterization of strains of Newcastle disease virus isolated from outbreaks in chicken and goose flocks in some regions of China during 1985-2001[J]. Arch Virol, 2003, 148 (7): 1387- 1403.
doi: 10.1007/s00705-003-0014-z |
| 9 |
DIMITROV K M , ABOLNIK C , AFONSO C L , et al. Updated unified phylogenetic classification system and revised nomenclature for Newcastle disease virus[J]. Infect Genet Evol, 2019, 74, 103917.
doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2019.103917 |
| 10 |
ABD EL-HAMID H S , SHAFI M E , ALBAQAMI N M , et al. Sequence analysis and pathogenicity of Avian Orthoavulavirus 1 strains isolated from poultry flocks during 2015-2019[J]. BMC Vet Res, 2020, 16 (1): 253.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02470-9 |
| 11 |
HE Y , LU B X , DIMITROV K M , et al. Complete genome sequencing, molecular epidemiological, and pathogenicity analysis of pigeon paramyxoviruses type 1 isolated in Guangxi, China during 2012-2018[J]. Viruses, 2020, 12 (4): 366.
doi: 10.3390/v12040366 |
| 12 |
WANG J J , LIU H L , LIU W , et al. Genomic characterizations of six pigeon paramyxovirus type 1 viruses isolated from live bird markets in China during 2011 to 2013[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10 (4): e0124261.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124261 |
| 13 |
LIU M D , QU Y J , WANG F K , et al. Genotypic and pathotypic characterization of Newcastle disease virus isolated from racing pigeons in China[J]. Poult Sci, 2015, 94 (7): 1476- 1482.
doi: 10.3382/ps/pev106 |
| 14 | 韩坤, 梁琳, 李复煌, 等. 鸽新城疫病毒BJ-C分离株基因组测序及系统发育分析[J]. 微生物学通报, 2022, 49 (12): 5034- 5044. |
| HAN K , LIANG L , LI F H , et al. Genome sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of Newcastle disease virus BJ-C strain in pigeons[J]. Microbiology China, 2022, 49 (12): 5034- 5044. | |
| 15 | 袁万哲, 邹云婧, 孙继国, 等. 禽流感病毒与新城疫病毒二重RT-PCR检测方法的建立[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2015, 38 (6): 88- 91. |
| YUAN W Z , ZOU Y J , SUN J G , et al. Development of a duplex RT-PCR assay for detection of avian influenza virus and Newcastle disease virus[J]. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 2015, 38 (6): 88- 91. | |
| 16 |
ARCHETTI I , HORSFALL F L Jr . Persistent antigenic variation of influenza A viruses after incomplete neutralization in OVO with heterologous immune serum[J]. J Exp Med, 1950, 92 (5): 441- 462.
doi: 10.1084/jem.92.5.441 |
| 17 |
LI Z J , LI Y , CHANG S , et al. Antigenic variation between Newcastle disease viruses of goose and chicken origin[J]. Arch Virol, 2010, 155 (4): 499- 505.
doi: 10.1007/s00705-010-0610-7 |
| 18 |
LEI C F , YANG J , HU J , et al. On the calculation of TCID50 for quantitation of virus infectivity[J]. Virol Sin, 2021, 36 (1): 141- 144.
doi: 10.1007/s12250-020-00230-5 |
| 19 |
PALDURAI A , KIM S H , NAYAK B , et al. Evaluation of the contributions of individual viral genes to Newcastle disease virus virulence and pathogenesis[J]. J Virol, 2014, 88 (15): 8579- 8596.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.00666-14 |
| 20 |
CHEN X , CHEN S Q , CHEN H T , et al. Comparative biology of two genetically closely related Newcastle disease virus strains with strongly contrasting pathogenicity[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2021, 253, 108977.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2020.108977 |
| 21 |
XUE C , XU X H , YIN R F , et al. Identification and pathotypical analysis of a novel Ⅵk sub-genotype Newcastle disease virus obtained from pigeon in China[J]. Virus Res, 2017, 238, 1- 7.
doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2017.05.011 |
| 22 |
LIU H L , WANG Z L , SONG C P , et al. Characterization of pigeon-origin Newcastle disease virus isolated in China[J]. Avian Dis, 2006, 50 (4): 636- 640.
doi: 10.1637/7618-042606R1.1 |
| 23 | 杨少华, 崔宁, 张琳, 等. 3株鸽源新城疫病毒的分子特征及对鸽的致病性[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2021, 41 (1): 20- 25. |
| YANG S H , CUI N , ZHANG L , et al. Molecular characteristics of three strains of pigeon Newcastle disease virus and its pathogenicity to pigeon[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2021, 41 (1): 20- 25. | |
| 24 | 罗瑶瑶, 王静静, 王云平, 等. 2014—2017年我国部分地区10株鸽副黏病毒的分布及其分子特征[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2018, 38 (10): 1883-1886, 1931. |
| LUO Y Y , WANG J J , WANG Y P , et al. Distribution and molecular characteristics of 10 pigeon paramyxovirus type Ⅰ isolates in some regions of China during 2014 to 2017[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2018, 38 (10): 1883-1886, 1931. | |
| 25 |
ALEXANDER D J , RUSSELL P H , PARSONS G , et al. Antigenic and biological characterisation of avian paramyxovirus type Ⅰ isolates from pigeons-an international collaborative study[J]. Avian Pathol, 1985, 14 (3): 365- 376.
doi: 10.1080/03079458508436238 |
| 26 | HUTCHISON D C . Paramyxovirus infection in pigeons[J]. Vet Rec, 1984, 115 (13): 335. |
| 27 |
GANAR K , DAS M , SINHA S , et al. Newcastle disease virus: current status and our understanding[J]. Virus Res, 2014, 184, 71- 81.
doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.02.016 |
| 28 | ALEXANDER D J . Newcastle disease and other avian paramyxoviruses[J]. Rev Sci Tech, 2000, 19 (2): 443- 462. |
| 29 | ALDOUS E W , FULLER C M , MYNN J K , et al. A molecular epidemiological investigation of isolates of the variant avian paramyxovirus type 1 virus (PPMV-1) responsible for the 1978 to present panzootic in pigeons[J]. Avian Pathol, 2004, 33 (2): 258- 269. |
| 30 | COLLINS M S , STRONG I , ALEXANDER D J . Evaluation of the molecular basis of pathogenicity of the variant Newcastle disease viruses termed "pigeon PMV-1 viruses"[J]. Arch Virol, 1994, 134 (3-4): 403- 411. |
| 31 | 李仕超, 仇旭升, 刘开春, 等. 六株鸽源新城疫病毒的分离、鉴定及生物信息学分析[J]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2014, 22 (5): 1- 9. |
| LI S C , QIU X S , LIU K C , et al. Isolation, identification and bioinformatics analysis of six Newcastle disease virus of pigeon origin[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Infectious Diseases, 2014, 22 (5): 1- 9. | |
| 32 | DORTMANS J C F M , KOCH G , ROTTIER P J M , et al. Virulence of pigeon paramyxovirus type 1 does not always correlate with the cleavability of its fusion protein[J]. J Gen Virol, 2009, 90 (Pt 11): 2746- 2750. |
| 33 | HEIDEN S , GRUND C , HÖPER D , et al. Pigeon paramyxovirus type 1 variants with polybasic F protein cleavage site but strikingly different pathogenicity[J]. Virus Genes, 2014, 49 (3): 502- 506. |
| 34 | 钱晶, 刘雪, 王玮, 等. 鸽新城疫病毒Ⅵ-HZ株的分离鉴定及其遗传进化分析[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2022, 42 (4): 651- 656. |
| QIAN J , LIU X , WANG W , et al. Isolation, identification and genetic evolution analysis of pigeon Newcastle disease virus Ⅵ-HZ strain[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2022, 42 (4): 651- 656. | |
| 35 | 裴育, 孙雅丽, 赵烨, 等. 4株鸽新城疫病毒的基因组序列与致病性分析[J]. 病毒学报, 2022, 38 (2): 402- 414. |
| PEI Y , SUN Y L , ZHAO Y , et al. Genome sequencing and pathogenicity analyses of four isolates of the Newcastle disease virus in pigeons[J]. Chinese Journal of Virology, 2022, 38 (2): 402- 414. |
| [1] | XIE Bilin, LIN Zhimin, LIN Binbin, XU Yijuan, LIN Fengqiang, YAN Lu, WU Huini, LI Cuiting, ZHOU Haiou, LI Zhaolong. Isolation, Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of Riemerella anatipestifer Strain LC1 and CX1 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4196-4203. |
| [2] | Yan WANG, Yadong GAO, Chenghui JIANG, Qiaoying ZENG. Isolation and Pathogenicity of a Goose Derived Fowl Adenovirus Type 4 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4232-4240. |
| [3] | Fanfan ZHANG, Jiemao LI, Jia TAN, Jiangnan HUANG, Ling WU, Qipeng WEI, Zhaofeng KANG. Research Progress on Avian Metapneumovirus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3344-3353. |
| [4] | Cheng YANG, Ye LIU, Ning CHENG, Kaiyue WANG, Xinlei LI, Jiuying SUN, Junping HAN, Wenjun LI, Huanhuan WANG, Xiao SHAO, Xuejiao CHENG, Yingfeng SUN. Genomic Characterization of a Recombinant Strain of PRRSV-2 between Lineages 1.8 and 1.5 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3570-3578. |
| [5] | Yudian SUN, Ziyue SONG, Hongliang ZHANG, Zhihua QIN, Hu SHAN, Ruimei YANG. Isolation and ldentification of Duckling Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3623-3630. |
| [6] | Huanqin ZHENG, Xiaomin JIANG, Hong YUE, Baoyan WANG, Yang LIU, Xingxiao ZHANG, Jianlong ZHANG, Hongwei ZHU. Isolation, Identification and Partial Biological Characteristics Analysis of Feline Herpesvirus-1 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3040-3048. |
| [7] | Weizhe LIU, Chenggang LUO, Rong YUAN, Yijie LIAO, Yimin WEN, Ying SUN, Enbo YU, Sanjie CAO, Xiaobo HUANG. Isolation and Identification of a Highly Pathogenic Strain of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3049-3063. |
| [8] | Jitong LI, Tong ZHU, Junfeng LÜ, Yuehua GAO, Feng HU, Kexiang YU, Minxun SONG, Jianlin WANG, Yufeng LI. Isolation and Identification of Novel Picornavirus from Ducks and Whole Genome Sequence Analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3075-3084. |
| [9] | Wangqing BAN MA, Xi CHEN, Yi YUE, Yurong SU, Hua YUE, Cheng TANG. Isolation, Identification and Partial Biological Characteristics of a Bovine Respiratory Coronavirus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3094-3104. |
| [10] | Bohua LIU, Hanyu FU, Yuheng WANG, Suolangsizhu, Jiaqiang NIU, Yuhua BAO, Jiakui LI, Yefen XU. Isolation, Identification and Genome Analysis of Type B Pasteurella multocida Isolated from Yak in Tibetan Nakchu City [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3105-3118. |
| [11] | Kun YANG, Jingwen MA, Xinrui ZHOU, Liezhu LUO, Zhe LIU, Ziqiang HU, Xingchen WU, Libin LIANG, Shimin GAO. Pathogenicity of Three Recombinant Strains of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2550-2559. |
| [12] | Ning ZHOU, Cheng TANG, Jia XU, Hua YUE, Xi CHEN. Pathogenicity and Genomic Characteristics of Feline Panleukopenia Virus A91S Variant in Cats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2560-2568. |
| [13] | XIONG Ting, HE Xianming, ZHAO Xiya, ZHUANG Tingting, HUANG Meizhen, LIANG Shijin, YU Chuanzhao, LIANG Xuejing, CHEN Ruiai. Whole Genome Analysis of Three Predominant Epidemic Strains of Chicken Infectious Bronchitis Virus and Their Pathogenicity [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2109-2122. |
| [14] | ZHENG Rui, LIU Zishi, ZHANG Kangyou, YAN Yong, WEI Ling, ZEREN Wengmu, DINGZE Demi, HUANG Jianjun, WANG Li, WEI Yong. Isolation, Identification and Biological Characterization of Colletotrichum jasminigenum in Stems of Peanuts [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2206-2213. |
| [15] | TIAN Rui, XU Sixiang, XIE Feng, LIU Guangjin, WANG Gang, LI Qingxia, DAI Lei, XIE Guoxin, ZHANG Qiongwen, LU Yajing, WANG Guangwen, WANG Jinxiu, ZHANG Wei. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Genome of Clostridium perfringens Isolated from Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1707-1715. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||