





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (9): 3824-3832.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.09.008
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xu GUO, Xiaoxiao CHEN, Yiming CHI, Wenyu MA, Mengze DU, Jian AN, Qiuming LI*( ), Deqi YIN*(
), Deqi YIN*( )
)
Received:2023-12-07
Online:2024-09-23
Published:2024-09-27
Contact:
Qiuming LI, Deqi YIN
E-mail:liqiuming007@126.com;yindeqi1992@163.com
CLC Number:
Xu GUO, Xiaoxiao CHEN, Yiming CHI, Wenyu MA, Mengze DU, Jian AN, Qiuming LI, Deqi YIN. Research Progress of Toxoplasma gondii AP2 Family[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3824-3832.
Table 1
Overview of Toxoplasma gondii AP2 transcription factors"
| 基因号 Gene ID | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 基因描述 Gene description | 功能 Function | 参考文献 Reference |
| TGME49_306620 | 1 388 aa | 转录因子AP2IX-9 AP2 domain transcription factor AP2IX-9 | 缓殖子发育的抑制因子 Inhibitory factors of bradyzoite development | [ |
| TGME49_318610 | 1 369 aa | 转录因子AP2IV-3 AP2 domain transcription factor AP2IV-3 | 缓殖子基因表达的激活剂 Activator of bradyzoite gene expression | [ |
| TGME49_288950 | 951 aa | 转录因子AP2IX-4 AP2 domain transcription factor AP2IX-4 | 促进组织包囊的形成 Promote the formation of tissue cyst | [ |
| TGME49_315760 | 3 236 aa | 转录因子AP2XI-4 AP2 domain transcription factor AP2XI-4 | 寄生虫分化和包囊形成过程中调节缓殖子基因表达 Regulation of bradyzoite gene expression during parasite differentiation and cyst formation | [ |
| TGME49_289710 | 2 282 aa | 转录因子AP2IX-5 AP2 domain transcription factor AP2IX-5 | 调控细胞周期和速殖子增殖 Regulation of cell cycle and tachyzoite proliferation | [ |
| TGME49_217700 | 1 737 aa | 转录因子AP2XII-2 AP2 domain transcription factor AP2XII-2 | 调控细胞周期S期和缓殖子分化 Regulation of cell cycle S-phase and bradyzoite differentiation | [ |
| TGME49_318470 | 2 406 aa | 转录因子AP2IV-4 AP2 domain transcription factor AP2IV-4 | 调节组织包囊的形成 Regulating the formation of tissue cysts | [ |
| TGME49_216220 | 868 aa | 转录因子AP2XI-5 AP2 domain transcription factor AP2XI-5 | 调节关键毒力因子的基因转录 Regulation of gene transcription of key virulence factors | [ |
| TGME49_247730 | 1 502 aa | 转录因子AP2XII-5 AP2 domain transcription factor AP2XII-5 | 调控弓形虫生活史各阶段基因的有序表达而影响毒株毒力 Regulating the orderly expression of genes at all stages of Toxoplasma gondii life cycle and affecting the virulence of the strain | [ |
| TGME49_224050 | 868 aa | 转录因子AP2X-4 AP2 domain transcription factor AP2X-4 | 调控基因转录;调节棒状体蛋白质的表达 Regulate gene transcription and the expression of rhoptry proteins | [ |
| TGME49_218960 | 2 282 aa | 转录因子AP2XII-1 AP2 domain transcription factor AP2XII-1 | 调控急性感染性速殖子阶段向有性裂殖子阶段的转变 Regulation of the transition from the acute infectious tachyzoite stage to the sexual cleavage stage | [ |
| TGME49_310900 | 2 243 aa | 转录因子AP2XI-2 AP2 domain transcription factor AP2XI-2 | 调控速殖子阶段向有性裂殖子阶段的转变 Regulation of the tachyzoite stage to the sexual cleavage stage | [ |
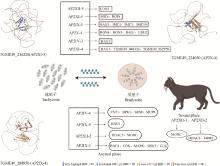
Fig. 1
The relationship map of some AP2 transcription factors with different developmental stages of Toxoplasma gondii In AlphaFold, the per-residue Local Distance Difference Test (LDDT), abbreviated as "pLDDT", is represented by a color scheme indicating confidence levels ranging from 1 to 100. It assesses the confidence of each residue in the predicted structure when the native structure is not available. For more details, please refer to https://toxodb.org/toxo/app/"

| 1 |
KOCHANOWSKY J A , KOSHY A A . Toxoplasma gondii [J]. Curr Biol, 2018, 28 (14): R770- R771.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.05.035 |
| 2 |
VALLEAU D , SIDIK S M , GODOY L C , et al. A conserved complex of microneme proteins mediates rhoptry discharge in Toxoplasma[J]. EMBO J, 2023, 42 (23): e113155.
doi: 10.15252/embj.2022113155 |
| 3 |
ATTIAS M , TEIXEIRA D E , BENCHIMOL M , et al. The life-cycle of Toxoplasma gondii reviewed using animations[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2020, 13 (1): 588.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04445-z |
| 4 |
GEORGE B P , SCHNEIDER E B , VENKATESAN A . Encephalitis hospitalization rates and inpatient mortality in the United States, 2000-2010[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9 (9): e104169.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104169 |
| 5 |
ZHOU J , LI C X , LUO Y Q , et al. Antigenic epitope analysis and efficacy evaluation of GRA41 DNA vaccine against T. gondii infection[J]. Acta Parasitol, 2019, 64 (3): 471- 478.
doi: 10.2478/s11686-019-00091-3 |
| 6 |
PIAO L X , CHENG J H , AOSAI F , et al. Cellular immunopathogenesis in primary Toxoplasma gondii infection during pregnancy[J]. Parasite Immunol, 2018, 40 (9): e12570.
doi: 10.1111/pim.12570 |
| 7 |
ZHOU D H , ZHAO F R , HUANG S Y , et al. Changes in the proteomic profiles of mouse brain after infection with cyst-forming Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2013, 6, 96.
doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-96 |
| 8 |
SMITH N C , GOULART C , HAYWARD J A , et al. Control of human toxoplasmosis[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2021, 51 (2-3): 95- 121.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2020.11.001 |
| 9 |
MVLLER J , HEMPHILL A . Toxoplasma gondii infection: novel emerging therapeutic targets[J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2023, 27 (4-5): 293- 304.
doi: 10.1080/14728222.2023.2217353 |
| 10 |
AUGUSTO L , WEK R C , SULLIVAN W J . Host sensing and signal transduction during Toxoplasma stage conversion[J]. Mol Microbiol, 2021, 115 (5): 839- 848.
doi: 10.1111/mmi.14634 |
| 11 |
WALDMAN B S , SCHWARZ D , WADSWORTH II M H , et al. Identification of a master regulator of differentiation in Toxoplasma[J]. Cell, 2020, 180 (2): 359- 372. e16.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.12.013 |
| 12 |
ROSENBERG A , SIBLEY L D . Epigenetic modifiers alter host cell transcription to promote Toxoplasma infection[J]. ACS Infect Dis, 2022, 8 (3): 411- 413.
doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.2c00054 |
| 13 |
SOKOL-BORRELLI S L , REILLY S M , HOLMES M J , et al. A transcriptional network required for bradyzoite development in Toxoplasma gondii is dispensable for recrudescent disease[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14 (1): 6078.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40948-w |
| 14 |
MARKUS B M , WALDMAN B S , LORENZI H A , et al. High-resolution mapping of transcription initiation in the asexual stages of Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2021, 10, 617998.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.617998 |
| 15 |
DU K G , LU F , XIE C Z , et al. Toxoplasma gondii infection induces cell apoptosis via multiple pathways revealed by transcriptome analysis[J]. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B, 2022, 23 (4): 315- 327.
doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2100877 |
| 16 |
BEHNKE M S , WOOTTON J C , LEHMANN M M , et al. Coordinated progression through two subtranscriptomes underlies the tachyzoite cycle of Toxoplasma gondii[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5 (8): e12354.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012354 |
| 17 |
IWANAGA S , KANEKO I , KATO T , et al. Identification of an AP2-family protein that is critical for malaria liver stage development[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7 (11): e47557.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047557 |
| 18 |
RIECHMANN J L , MEYEROWITZ E M . The AP2/EREBP family of plant transcription factors[J]. Biol Chem, 1998, 379 (6): 633- 646.
doi: 10.1515/bchm.1998.379.6.633 |
| 19 |
BALAJI S , BABU M M , IYER L M , et al. Discovery of the principal specific transcription factors of Apicomplexa and their implication for the evolution of the AP2-integrase DNA binding domains[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2005, 33 (13): 3994- 4006.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gki709 |
| 20 |
RADKE J B , LUCAS O , DE SILVA E K , et al. ApiAP2 transcription factor restricts development of the Toxoplasma tissue cyst[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2013, 110 (17): 6871- 6876.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1300059110 |
| 21 |
JENINGA M D , QUINN J E , PETTER M . ApiAP2 transcription factors in apicomplexan parasites[J]. Pathogens, 2019, 8 (2): 47.
doi: 10.3390/pathogens8020047 |
| 22 |
CAMPBELL T L , DE SILVA E K , OLSZEWSKI K L , et al. Identification and genome-wide prediction of DNA binding specificities for the ApiAP2 family of regulators from the malaria parasite[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2010, 6 (10): e1001165.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001165 |
| 23 |
RADKE J B , WORTH D , HONG D , et al. Transcriptional repression by ApiAP2 factors is central to chronic toxoplasmosis[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2018, 14 (5): e1007035.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007035 |
| 24 |
KIM S K , BOOTHROYD J C . Stage-specific expression of surface antigens by Toxoplasma gondii as a mechanism to facilitate parasite persistence[J]. J Immunol, 2005, 174 (12): 8038- 8048.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.12.8038 |
| 25 | HUANG S , HOLMES M J , RADKE J B , et al. Toxoplasma gondii AP2IX-4 regulates gene expression during bradyzoite development[J]. mSphere, 2017, 2 (2): e00054- 17. |
| 26 |
WANG J C , DIXON S E , TING L M , et al. Lysine acetyltransferase GCN5b interacts with AP2 factors and is required for Toxoplasma gondii proliferation[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2014, 10 (1): e1003830.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003830 |
| 27 |
KHELIFA A S , SANCHEZ C G , LESAGE K M , et al. TgAP2IX-5 is a key transcriptional regulator of the asexual cell cycle division in Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12 (1): 116.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20216-x |
| 28 | WANG C Y , HU D D , TANG X M , et al. Internal daughter formation of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites is coordinated by transcription factor TgAP2IX-5[J]. Cell Microbiol, 2021, 23 (3): e13291. |
| 29 |
BECK J R , RODRIGUEZ-FERNANDEZ I A , DE LEON J C , et al. A novel family of Toxoplasma IMC proteins displays a hierarchical organization and functions in coordinating parasite division[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2010, 6 (9): e1001094.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001094 |
| 30 | HONG D P , RADKE J B , WHITE M W . Opposing transcriptional mechanisms regulate Toxoplasma development[J]. mSphere, 2017, 2 (1): e00347- 16. |
| 31 |
WALKER R , GISSOT M , CROKEN M M , et al. The Toxoplasma nuclear factor TgAP2XI-4 controls bradyzoite gene expression and cyst formation[J]. Mol Microbiol, 2013, 87 (3): 641- 655.
doi: 10.1111/mmi.12121 |
| 32 |
WALKER R , GISSOT M , HUOT L , et al. Toxoplasma transcription factor TgAP2XI-5 regulates the expression of genes involved in parasite virulence and host invasion[J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288 (43): 31127- 31138.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.486589 |
| 33 | ANTUNES A V , SHAHINAS M , SWALE C , et al. In vitro production of cat-restricted Toxoplasma pre-sexual stages[J]. Nature, 2023, 625 (7994): 366- 376. |
| 34 | FAN F Q , XUE L L , YIN X Y , et al. AP2XII-1 is a negative regulator of merogony and presexual commitment in Toxoplasma gondii[J]. mBio, 2023, 14 (5): e01785- 23. |
| 35 |
ANDERSON-WHITE B R , IVEY F D , CHENG K , et al. A family of intermediate filament-like proteins is sequentially assembled into the cytoskeleton of Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Cell Microbiol, 2011, 13 (1): 18- 31.
doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01514.x |
| 36 | SRIVASTAVA S , WHITE M W , SULLIVAN JR W J . Toxoplasma gondii AP2XII-2 contributes to proper progression through S-phase of the cell cycle[J]. mSphere, 2020, 5 (5): e00542- 20. |
| 37 | SRIVASTAVA S , HOLMES M J , WHITE M W , et al. Toxoplasma gondii AP2XII-2 contributes to transcriptional repression for sexual commitment[J]. mSphere, 2023, 8 (2): e00606- 22. |
| 38 | 张晶雯. AP2X-4和AP2XⅡ-5对弓形虫生长发育的调节作用[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2020. |
| ZHANG J W. Regulation of Toxoplasma gondii growth and development by AP2X-4 and AP2XII-5[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 39 | ZHANG J W , FAN F Q , ZHANG L H , et al. Nuclear factor AP2X-4 governs the expression of cell cycle- and life stage-regulated genes and is critical for Toxoplasma growth[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2022, 10 (4): e00120- 22. |
| 40 |
DE MONERRI N C S , YAKUBU R R , CHEN A L , et al. The ubiquitin proteome of Toxoplasma gondii reveals roles for protein ubiquitination in cell-cycle transitions[J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2015, 18 (5): 621- 633.
doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.10.014 |
| 41 |
VANAGAS L , MUÑOZ D , CRISTALDI C , et al. Histone variant H2B. Z acetylation is necessary for maintenance of Toxoplasma gondii biological fitness[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech, 2023, 1866 (3): 194943.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2023.194943 |
| 42 |
FLECK K , NITZ M , JEFFERS V . "Reading" a new chapter in protozoan parasite transcriptional regulation[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2021, 17 (12): e1010056.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010056 |
| 43 |
JEFFERS V , SULLIVAN JR W J . Lysine acetylation is widespread on proteins of diverse function and localization in the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Eukaryot Cell, 2012, 11 (6): 735- 742.
doi: 10.1128/EC.00088-12 |
| 44 |
MIAO J , LAWRENCE M , JEFFERS V , et al. Extensive lysine acetylation occurs in evolutionarily conserved metabolic pathways and parasite-specific functions during Plasmodium falciparum intraerythrocytic development[J]. Mol Microbiol, 2013, 89 (4): 660- 675.
doi: 10.1111/mmi.12303 |
| 45 |
GAJI R Y , SHARP A K , BROWN A M . Protein kinases in Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2021, 51 (6): 415- 429.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2020.11.006 |
| 46 |
BLUME M , MAUS D . Converting and hoarding driven by protein phosphorylation in Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Trends Parasitol, 2023, 39 (4): 232- 234.
doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2023.02.002 |
| 47 |
SEDDON A R , DAS A B , HAMPTON M B , et al. Site-specific decreases in DNA methylation in replicating cells following exposure to oxidative stress[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2023, 32 (4): 632- 648.
doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddac232 |
| 48 |
CHEN C , WANG Z H , DING Y , et al. DNA methylation: from cancer biology to clinical perspectives[J]. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2022, 27 (12): 326.
doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2712326 |
| 49 |
SAKSOUK N , BHATTI M M , KIEFFER S , et al. Histone-modifying complexes regulate gene expression pertinent to the differentiation of the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2005, 25 (23): 10301- 10314.
doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.23.10301-10314.2005 |
| 50 |
AFONSO C F , MARQUES M C , ANTÓNIO J P M , et al. Cysteine-assisted click-chemistry for proximity-driven, site-specific acetylation of histones[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2022, 61 (46): e202208543.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202208543 |
| 51 |
HARRIS M T , JEFFERS V , MARTYNOWICZ J , et al. A novel GCN5b lysine acetyltransferase complex associates with distinct transcription factors in the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Mol Biochem Parasitol, 2019, 232, 111203.
doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2019.111203 |
| 52 |
NDOJA A , COHEN R E , YAO T T . Ubiquitin signals proteolysis-independent stripping of transcription factors[J]. Mol Cell, 2014, 53 (6): 893- 903.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.02.002 |
| 53 |
YIN D Q , JIANG N , ZHANG Y , et al. Global lysine crotonylation and 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation in phenotypically different Toxoplasma gondii parasites[J]. Mol Cell Proteomics, 2019, 18 (11): 2207- 2224.
doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA119.001611 |
| 54 |
YIN D Q , JIANG N , CHENG C , et al. Protein lactylation and metabolic regulation of the zoonotic parasite Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics, 2023, 21 (6): 1163- 1181.
doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2022.09.010 |
| 55 |
NARDELLI S C , DE MONERRI N C S , VANAGAS L , et al. Genome-wide localization of histone variants in Toxoplasma gondii implicates variant exchange in stage-specific gene expression[J]. BMC Genomics, 2022, 23 (1): 128.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08338-6 |
| 56 |
ULAHANNAN N , CUTLER R , DOÑA-TERMINE R , et al. Genomic insights into host and parasite interactions during intracellular infection by Toxoplasma gondii[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17 (9): e0275226.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275226 |
| 57 |
BRAUN L , CANNELLA D , ORTET P , et al. A complex small RNA repertoire is generated by a plant/fungal-like machinery and effected by a metazoan-like Argonaute in the single-cell human parasite Toxoplasma gondii[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2010, 6 (5): e1000920.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000920 |
| 58 |
郑雨昕, 张义伟, 姜宁. 恶性疟原虫ApiAP2蛋白质家族研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53 (5): 1354- 1363.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.05.004 |
|
ZHENG Y X , ZHANG Y W , JIANG N . Research advance on ApiAP2 family of Plasmodium falciparum[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53 (5): 1354- 1363.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.05.004 |
|
| 59 |
SANTOS J M , JOSLING G , ROSS P , et al. Red blood cell invasion by the malaria parasite is coordinated by the PfAP2-I transcription factor[J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2017, 21 (6): 731- 741. e10.
doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.05.006 |
| 60 |
JOSLING G A , PETTER M , OEHRING S C , et al. A Plasmodium falciparum bromodomain protein regulates invasion gene expression[J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2015, 17 (6): 741- 751.
doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.05.009 |
| [1] | Fangzhou WANG, Lingyun TAN, Yan LI, Hongjing GU, Hui WANG. Progress on the Characteristics of Virus-encoded Proteins and Pathogenic Mechanism of Henipavirus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3802-3811. |
| [2] | LIU Siyu, ZHANG Man, ZHANG Yan, WEI Zhitong, QI Xinglei, GAO Tengyun, LIU Xian, LIANG Dong, FU Tong. Evaluation of the Conservation Effect in Nanyang Cattle Based on Resequencing Data [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3876-3886. |
| [3] | HUANG Hongyan, ZHANG Liyun, HUANG Zhirong, WU Zhongping, ZHANG Xumeng, OUYANG Hongjia, CHEN Junpeng, LIN Zhenping, TIAN Yunbo, LI Xiujin, HUANG Yunmao. The Study on Population Genetic Diversity and Genome-wide Association Study of Body Weight and Size Traits for Lion-head Geese [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3914-3924. |
| [4] | FAN Guangxuan, WANG Tianjiao, DONG Yimeng, WANG Hongliang, DING Ning, WANG Xinhao, XING Xiumei. Molecular Genealogy Construction and Population Genetic Structure Analysis of Jilin Sika Deer Based on SNP Loci [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3925-3935. |
| [5] | Baigao YANG, Xi LONG, Liang ZHANG, Jiehuan XU, Jianjun DAI, Xueming ZHAO, Hongmei PAN. Exploring the Effect of Vitrification on Gene Expression in Porcine Parthenogenetic Blastocysts by Smart-seq2 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3936-3946. |
| [6] | SHI Rui, LI Shanshan, ZHANG Hailiang, LU Haibo, YAN Qingxia, ZHANG Yi, CHEN Shaohu, WANG Yachun. Genotype by Environment Interaction of Fertility Traits for the Holstein Cattle in China [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3968-3977. |
| [7] | ZHAO Kangning, YANG Zhonglong, CHEN Yi, ZHU Chuncheng, GUO Yunfei, YIN Yuncong, QIN Tao, CHEN Sujuan, PENG Daxin. Genetic Variation Analysis of Sixteen Novel H3N3 Subtype Avian Influenza Viruses [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4029-4040. |
| [8] | MA Jinrui, SHI Wenjing, TIAN Changqing, DONG Zhijie, ZHAO Xuehui, ZHI Ji, CAO Qing, WEI Yanquan, SONG Weili, XUE Huiwen, GOU Huitian. Preparation of Monoclonal Antibodies against Internalin G of Listeria monocytogenes and Their Preliminary Application [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4069-4076. |
| [9] | XIE Bilin, LIN Zhimin, LIN Binbin, XU Yijuan, LIN Fengqiang, YAN Lu, WU Huini, LI Cuiting, ZHOU Haiou, LI Zhaolong. Isolation, Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of Riemerella anatipestifer Strain LC1 and CX1 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4196-4203. |
| [10] | Wenwen LIU, Faming DONG, Yanzhen BI. The Development of Multi-Gene Editing Technology and Its Application in Agricultural Biological Germplasm Innovation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3267-3275. |
| [11] | Tana AN, Haige HAN, Togtokh MONGKE, Baoyindeligeer MONGKEJARGAL, Wenbo LI, Manglai DUGARJAVIIN. A Review of the Genetic Characteristics of Different Coat Colors in Domestic Horses [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3297-3308. |
| [12] | Ruiying LIANG, Jingxia SUO, Lin LIANG, Xianyong LIU, Jiabo DING, Xun SUO, Xinming TANG. Genetic Manipulation of Eimeria: Platform Development, Application, and Perspective [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3362-3373. |
| [13] | Zhangrong PENG, Haoran SUN, Qiaoru ZHANG, Ying YANG, Hongying GUO, Tong CHANG, Hui ZHAO, Tietao ZHANG. Study on the Pattern of Intramuscular Fat Deposition and Its Influence in Flavor Quality of Sika Deer at Different Ages [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3541-3551. |
| [14] | Yue LI, Changchun ZHANG, Guangyu LIU, Mengyuan GAO, Chaojun FU, Jiabao XING, Sijia XU, Qiyuan KUANG, Jing LIU, Xiaopeng GAO, Heng WANG, Lang GONG, Guihong ZHANG, Yankuo SUN. Application and Analysis of Meta-transcriptomics Sequencing Technology in the Diagnosis of Viral Diarrhea Diseases in Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3579-3589. |
| [15] | Qilin WANG, Runlai CAO, Weiyang WANG, Bo ZHANG, Zhijie LIU, Xiaoxu WANG. Isolation, Identification and Drug Resistance Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Aborted Fetuses of Fox [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3640-3648. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||