





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (11): 5124-5134.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.11.028
• Animal Nutrition and Feeds • Previous Articles Next Articles
Kexin WANG1( ), Xian WU1, Haizhou GONG3, Qiaoyu FANG1, Xiangchen LI1, Yanan ZHANG1,2,*(
), Xian WU1, Haizhou GONG3, Qiaoyu FANG1, Xiangchen LI1, Yanan ZHANG1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-01-03
Online:2024-11-23
Published:2024-11-30
Contact:
Yanan ZHANG
E-mail:2661895207@qq.com;ynzhang1515@163.com
CLC Number:
Kexin WANG, Xian WU, Haizhou GONG, Qiaoyu FANG, Xiangchen LI, Yanan ZHANG. Effects of Co-Treatment of Sodium Butyrate and Indole-3-Propionic Acid on Tight Junctions and Inflammatory Cytokines in Caco-2 Cells[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 5124-5134.
Table 1
Real-time quantitative PCR primer"
| 基因名称 Gene name | 引物序列(5'→3') Primer sequence(5'→3') | 参考文献 Reference |
| Occludin | F: GGGCATTGCTCATCCTGAAG R: GCCTGTAAGGAGGTGGACTT | [ |
| ZO-1 | F: TTCACGCAGTTACGAGCAAG R: TTGGTGTTTGAAGGCAGAGC | [ |
| Claudin-1 | F: CCAGGTACGAATTTGGTCAGG R: TGGTGTTGGGTAAGAGGTTGT | [ |
| Claudin-2 | F: CCTAAACCACAAGGCTAAGGGCTA R: GGTGTCTTCCTCAGTACCCCACA | [ |
| IL-6 | F: TGGCAGCCTTCCTGATTTCT R: AATTTCTGTGTTGGCGCAGT | [ |
| IL-1β | F: GAATGACGCCCTCAATCAAAGT R: TCATCTTGGGCAGTCACATACA | [ |
| IL-8 | F: CCTGAACCTTCCAAAGATGGC R: TTCACCAGGCAAGTCTCCTCA | [ |
| TNF-α | F: CTGCCTGCTGCACTTTGGAG R: ACATGGGCTACAGGCTTGTCACT | [ |
| β-Actin | F: TGCAGAAAGAGATCACCGC R: CCGATCCACACCGAGTATTTG | [ |

Fig. 1
Effects of sodium butyrate and indole-3-propionic acid on cell viability and co-treatment of sodium butyrate and indole-3-propionic acid on cell transmembrane electrical resistance (TEER) in Caco-2 cells A. Effect of different concentrations of NaB on cell viability; B. Effect of different concentrations of IPA on cell viability; C. Effect of NaB and IPA co-treatment on cell transmembrane electrical resistance (TEER). * is expressed comparison with the control group and between the two groups, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001. The same as below"


Fig. 3
Effect of co-treatment of sodium butyrate and indole-3-propionic acid on the expression of tight junction-related genes in Caco-2 cells A. Relative mRNA expression of ZO-1; B. Relative mRNA expression of Occludin; C. Relative mRNA expression of Claudin-1; D. Relative mRNA expression of Claudin-2"


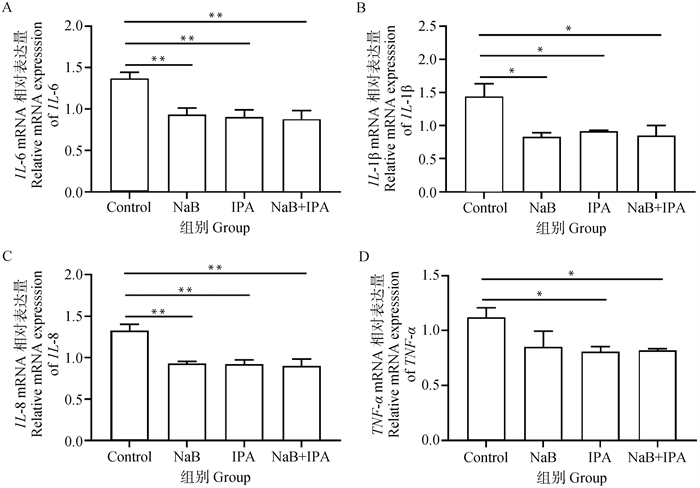
Fig. 5
Effect of co-treatment of sodium butyrate and indole-3-propionic acid on the relative expression of genes related inflammation in Caco-2 cells A. Relative mRNA expression of IL-6; B. Relative mRNA expression of IL-1β; C. Relative mRNA expression of IL-8; D. Relative mRNA expression of TNF-α"
| 1 |
PETERSON L W , ARTIS D . Intestinal epithelial cells: regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2014, 14 (3): 141- 153.
doi: 10.1038/nri3608 |
| 2 |
SLIFER Z M , BLIKSLAGER A T . The integral role of tight junction proteins in the repair of injured intestinal epithelium[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21 (3): 972.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21030972 |
| 3 |
GASALY N , DE VOS P , HERMOSO M A . Impact of bacterial metabolites on gut barrier function and host immunity: a focus on bacterial metabolism and its relevance for intestinal inflammation[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12, 658354.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.658354 |
| 4 |
KAŹMIERCZAK-SIEDLECKA K , MARANO L , MEROLA E , et al. Sodium butyrate in both prevention and supportive treatment of colorectal cancer[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12, 1023806.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1023806 |
| 5 |
HUANG C , SONG P X , FAN P X , et al. Dietary sodium butyrate decreases postweaning diarrhea by modulating intestinal permeability and changing the bacterial communities in weaned piglets[J]. J Nutr, 2015, 145 (12): 2774- 2780.
doi: 10.3945/jn.115.217406 |
| 6 |
ZHAO H B , JIA L , YAN Q Q , et al. Effect of Clostridium butyricum and butyrate on intestinal barrier functions: study of a rat model of severe acute pancreatitis with intra-abdominal hypertension[J]. Front Physiol, 2020, 11, 561061.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.561061 |
| 7 |
WANG H B , WANG P Y , WANG X , et al. Butyrate enhances intestinal epithelial barrier function via up-regulation of tight junction protein Claudin-1 transcription[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2012, 57 (12): 3126- 3135.
doi: 10.1007/s10620-012-2259-4 |
| 8 | HUANG X Y , OSHIMA T , TOMITA T , et al. Butyrate alleviates cytokine-induced barrier dysfunction by modifying Claudin-2 levels[J]. Biology (Basel), 2021, 10 (3): 205. |
| 9 |
MA N , MA X . Dietary amino acids and the gut-microbiome-immune axis: physiological metabolism and therapeutic prospects[J]. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf, 2019, 18 (1): 221- 242.
doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12401 |
| 10 |
JIANG H , CHEN C Y , GAO J . Extensive summary of the important roles of indole propionic acid, a gut microbial metabolite in host health and disease[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 15 (1): 151.
doi: 10.3390/nu15010151 |
| 11 |
JENNIS M , CAVANAUGH C R , LEO G C , et al. Microbiota-derived tryptophan indoles increase after gastric bypass surgery and reduce intestinal permeability in vitro and in vivo[J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2018, 30 (2): e13178.
doi: 10.1111/nmo.13178 |
| 12 |
LI J J , ZHANG L , WU T , et al. Indole-3-propionic acid improved the intestinal barrier by enhancing epithelial barrier and mucus barrier[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2021, 69 (5): 1487- 1495.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c05205 |
| 13 |
QIU Y Q , MA X Y , YANG X F , et al. Effect of sodium butyrate on cell proliferation and cell cycle in porcine intestinal epithelial (IPEC-J2) cells[J]. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim, 2017, 53 (4): 304- 311.
doi: 10.1007/s11626-016-0119-9 |
| 14 | LAN H , ZHANG L Y , HE W , et al. Sinapic acid alleviated inflammation-induced intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in lipopolysaccharide-(LPS-) treated Caco-2 cells[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2021, 2021, 5514075. |
| 15 |
MA Y H , WANG Q M , YU K , et al. 6-Formylindolo(3, 2-b)carbazole induced aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation prevents intestinal barrier dysfunction through regulation of Claudin-2 expression[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2018, 288, 83- 90.
doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.04.020 |
| 16 |
HE S S , GUO Y H , ZHAO J X , et al. Ferulic acid ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced barrier dysfunction via MicroRNA-200c-3p-mediated activation of PI3K/AKT pathway in caco-2 cells[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11, 376.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00376 |
| 17 |
KUO W T , ODENWALD M A , TURNER J R , et al. Tight junction proteins occludin and ZO-1 as regulators of epithelial proliferation and survival[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2022, 1514 (1): 21- 33.
doi: 10.1111/nyas.14798 |
| 18 |
RUSSO E , GIUDICI F , FIORINDI C , et al. Immunomodulating activity and therapeutic effects of short chain fatty acids and tryptophan post-biotics in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10, 2754.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02754 |
| 19 |
FU Y F , LYU J , WANG S S . The role of intestinal microbes on intestinal barrier function and host immunity from a metabolite perspective[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14, 1277102.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1277102 |
| 20 |
PARADA VENEGAS D , DE LA FUENTE M K , LANDSKRON G , et al. Short chain fatty acids (SCFAs)-mediated gut epithelial and immune regulation and its relevance for inflammatory bowel diseases[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10, 277.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00277 |
| 21 | 张秋玉, 卞中博, 孙小蝶, 等. 丁酸钠通过自噬途径降解HIF-1α抑制结直肠癌细胞生长[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2022, 30 (5): 762- 767. |
| ZHANG Q Y , BIAN Z B , SUN X D , et al. Sodium butyrate inhibits the growth of colorectal cancer cells by promoting autophagic degradation of HIF-1α[J]. Journal of Modern Oncology, 2022, 30 (5): 762- 767. | |
| 22 |
MARTIN-GALLAUSIAUX C , MARINELLI L , BLOTTIōRE H M , et al. SCFA: mechanisms and functional importance in the gut[J]. Proc Nutr Soc, 2021, 80 (1): 37- 49.
doi: 10.1017/S0029665120006916 |
| 23 | 张笑添, 车昌燕, 姚步月, 等. miR-92a/Dickkopf相关蛋白1介导丁酸钠调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制结肠癌细胞增殖[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2023, 39 (12): 1743- 1752. |
| ZHANG X T , CHE C Y , YAO B Y , et al. Sodium butyrate inhibits colon cancer proliferation through miR-92a/DKK1-mediated inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2023, 39 (12): 1743- 1752. | |
| 24 |
PARADIS T , BōGUE H , BASMACIYAN L , et al. Tight junctions as a key for pathogens invasion in intestinal epithelial cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22 (5): 2506.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22052506 |
| 25 | CHELAKKOT C , GHIM J , RYU S H . Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2018, 50 (8): 1- 9. |
| 26 |
GANAPATHY A S , SAHA K , SUCHANEC E , et al. AP2M1 mediates autophagy-induced CLDN2 (Claudin 2) degradation through endocytosis and interaction with LC3 and reduces intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability[J]. Autophagy, 2022, 18 (9): 2086- 2103.
doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.2016233 |
| 27 | 冯燕海. 紧密连接蛋白Claudin-2研究进展[J]. 重庆医学, 2018, 47 (5): 697- 699. |
| FENG Y H . Research progress of tight junction protein Claudin-2[J]. Chongqing Medicine Journal, 2018, 47 (5): 697- 699. | |
| 28 |
MIAO W , WU X J , WANG K , et al. Sodium butyrate promotes reassembly of tight junctions in Caco-2 monolayers involving inhibition of MLCK/MLC2 pathway and phosphorylation of PKCβ2[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2016, 17 (10): 1696.
doi: 10.3390/ijms17101696 |
| 29 |
SEGAIN J P , RAINGEARD DE LA BLETIERE D , BOURREILLE A , et al. Butyrate inhibits inflammatory responses through NFκB inhibition: implications for Crohn's disease[J]. Gut, 2000, 47 (3): 397- 403.
doi: 10.1136/gut.47.3.397 |
| 30 |
GAO J , XU K , LIU H N , et al. Impact of the gut microbiota on intestinal immunity mediated by tryptophan metabolism[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2018, 8, 13.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00013 |
| 31 |
VENKATESH M , MUKHERJEE S , WANG H W , et al. Symbiotic bacterial metabolites regulate gastrointestinal barrier function via the xenobiotic sensor PXR and Toll-like receptor 4[J]. Immunity, 2014, 41 (2): 296- 310.
doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.014 |
| 32 |
CAPALDO C T , NUSRAT A . Cytokine regulation of tight junctions[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2009, 1788 (4): 864- 871.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.08.027 |
| 33 |
KORSTEN S G P J , VROMANS H , GARSSEN J , et al. Butyrate protects barrier integrity and suppresses immune activation in a Caco-2/PBMC Co-culture model while HDAC inhibition mimics butyrate in restoring cytokine-induced barrier disruption[J]. Nutrients, 2023, 15 (12): 2760.
doi: 10.3390/nu15122760 |
| [1] | Yiqian FU, Dongge LIANG, Mingyang WANG, Jiajia PAN, Yanbin YANG, Lei ZENG, Xiangtao KANG. Construction of Interferon Regulatory Factor Knockdown Cell Line and Its Effect on Pseudorabies Virus Proliferation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4100-4109. |
| [2] | Xiangchen LI, Linnan WANG, Zhengqing YU, Li ZHANG, Chenchen YANG, Liangli SONG. Quercetin Inhibits Autophagy to Restore LTA-induced Tight Junction Function in Mammary Alveolar Cells-large T Antigen [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 3887-3896. |
| [3] | DU Haidong, NA Renhua. Study on Gastrointestinal Epithelial Barrier Function and Interaction with Microorganisms in Ruminants [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 1804-1814. |
| [4] | LIU Yankun, LUO Runbo, LIN Yan, ZHU Weiyun. Effects of Phage Cocktail on Growth Performance, Blood Parameters and Fecal Microbiota of Weaned Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(4): 1555-1567. |
| [5] | LI Lin, CAO Meng, GONG Binbin, ZHAO Mei, WANG Jie, ZHANG Xiaohui. The Mechanism of Sodium Butyrate through AMPK Pathway to Regulate Lipid Metabolism Disorder Caused by LPS in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(9): 3221-3230. |
| [6] | CHEN Danian, MA Xusheng, DAI Junfei, WANG Yang, LI Qian, BAI Heng, MAO Tiantian, LIU Yongsheng, DING Long, CHEN Haohan, CHEN Siyan, RAO Yufei, JIA Ning, ZHANG Jie, ZHENG Haixue, LIU Xiangtao. Preliminary Study on the Function of MGF360-13L Gene of African Swine Fever Virus Multigene Family [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(12): 4419-4428. |
| [7] | YU Yingmei, SHI Xuan, OUYANG Jingxin, LIU Sanfeng, LI Guanhong. Effects of Puerarin on Intestinal Barrier Function and Antioxidant Capacity of Broilers Fed with Oxidized Soybean Oil [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(12): 3512-3523. |
| [8] | OU Aiqun, WANG Kai, WU Liming, LI Jianghong, PENG Wenjun. Effects of Propolis on Transcript Levels of Inflammation-related Genes and Tight Junction Proteins of Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells Stimulated by Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(5): 1149-1157. |
| [9] | XU Zhaokun, WANG Jianhong, LI Wu, WANG Yujiong. The effects of the Recombinant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis CFP10 Protein on the TLR Signal-mediated Inflammatory Responses in A549 Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(10): 2509-2517. |
| [10] | ZHANG Jian-long, QIU Fu-an, DONG Xing, QIN Tao, MA Yu-fang, HUANG Yi-fan, LI Jian. Effects of Hericium Erinaceus Polysaccharide on Ileal Morphology and Permeability of Piglets under Oxidative Stress [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2018, 49(1): 203-210. |
| [11] | HE Huan,CHEN Xin-nuo,ZENG Ze,REN Yu-peng,TANG Cheng,ZHANG Bin,YUE Hua. The Initial Research of OmpP2 in Haemophilus parasuis Induces Pro-inflammatory Cytokine mRNA Transcription and Inflammatory Mechanism in Porcine Alveolar Macrophages [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2016, 47(7): 1428-1434. |
| [12] | LIU Dan-dan,ZHAO Yuan,HAN Rui,ZHANG Shi-yao. Effects of β-conglycinin Hydrolyzed Peptide on the Permeability and Expression of Tight Junction Protein in Piglet Intestinal Epithelial Cells [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2015, 46(5): 768-773. |
| [13] | YU Chang-song,JIA Gang,DENG Qiu-hong,CHEN Xiao-ling,ZHAO Hua,LIU Guang-mang,WANG Kang-ning. The Effects of GLP-2 on Cell Morphology and the Gene Expression of Tight Junction in LPS Stressed IPEC-J2 Cells [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2015, 46(4): 592-599. |
| [14] | ZHAO Hui-li, GAO Yan-xia, LI Jian-guo, LI Qiu-feng, CAO Yu-feng. Effect of Sodium Butyrate on Growth, Serum Biochemical Parameters and Gastrointestinal Development of Weaning Calves [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2013, 44(10): 1600-1608. |
| [15] | HU Caihong;QIAN Zhongcang;LIU Haiping;XU Yong. Effect of High Level of Zinc Oxide on Tight Junction Protein Expression in Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Intestinal Mucosal Barrier in Early Weaning Piglets [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2009, 40(11): 0-1644. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||