





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (11): 5475-5488.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.11.011
• Animal Genetics and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Bingzhi1,2,4( ), GUO Juntao2,3, WANG Jianfang2,3, YU Shengchen2,3, PAN Yueting2,3, YU Hengwei2,3, LIU Haibing2,3, ZHANG Ke2,3, CHENG Gong2,3, TIAN Wanqiang1,4,*(
), GUO Juntao2,3, WANG Jianfang2,3, YU Shengchen2,3, PAN Yueting2,3, YU Hengwei2,3, LIU Haibing2,3, ZHANG Ke2,3, CHENG Gong2,3, TIAN Wanqiang1,4,*( ), ZAN Linsen2,3,*(
), ZAN Linsen2,3,*( )
)
Received:2025-03-25
Online:2025-11-23
Published:2025-11-27
Contact:
TIAN Wanqiang, ZAN Linsen
E-mail:3640910@qq.com;twqiang2003@163.com;zanlinsen@163.com
CLC Number:
LI Bingzhi, GUO Juntao, WANG Jianfang, YU Shengchen, PAN Yueting, YU Hengwei, LIU Haibing, ZHANG Ke, CHENG Gong, TIAN Wanqiang, ZAN Linsen. Study on the Effect of Interfering with MAPK6 Gene on the Differentiation of Qinchuan Cattle Myoblast Cells[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5475-5488.
Table 1
Real time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) primers sequence"
| 基因 Gene | GenBank号 GenBank number | 引物 Primer | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequence | 产物长度/bp Product length |
| GAPDH | NM_001034034.2 | GAPDH-F | AGTTCAACGGCACAGTCAAGG | 124 |
| GAPDH-R | ACCACATACTCAGCACCAGCA | |||
| MAPK6 | XM_059890855.1 | MAPK6-F | ACTTGGTGCTGAAGATAGGTGA | 206 |
| MAPK6-R | AAAGAGGGTTTTACCAGTCAGC | |||
| MEF2C | XM_059888100.1 | MEF2C-F | GCACCAACAAGCTGTTCCAG | 117 |
| MEF2C-R | GAACAGCCTCCACGATGTCT | |||
| MYH7 | XM_024997290.2 | MYH7-F | TCCAGTCTTCTCTCCTTGCTG | 187 |
| MYH7-R | AGGTCGAAAGGCCTGGTCTG | |||
| MYL2 | NM_001035025.2 | MYL2-F | CTTTCCACCATGTCACCTAAGA | 114 |
| MYL2-R | GATGGTGAAGGCCTCCTTAAA | |||
| CEND1 | NM_001080222.1 | CEND1-F | GAGCAGCAGCGCCCATA | 125 |
| CEND1-R | CTTCCCTCTGGACTCCATGC | |||
| SORD | NM_001037320.1 | SORD-F | CTGGCAGCATGGTCGAATTG | 102 |
| SORD-R | TGCCTGACCAATGATCCCAC | |||
| WASF3 | XM_005213794.5 | WASF3-F | CCAGGTTATCACAGAGCGCA | 102 |
| WASF3-R | CCGGGTACGAGTAATCCGTG | |||
| VPS50 | NM_001105413.2 | VPS50-F | ATGAGGGTCGTGCCTTGATG | 162 |
| VPS50-R | TGTGCTCTTTGATCCAGCGT | |||
| ZFP90 | XM_059877474.1 | ZFP90-F | CGAGTGAAGACGGCACAGAA | 85 |
| ZFP90-R | CCAGGGACAGGGTTGACTTC | |||
| CCNG1 | NM_001013364.1 | CCNG1-F | GCTGTGAAGCCTCAAAACATC | 170 |
| CCNG1-R | TCCAGGCTTGTCATTTGCATT | |||
| NR1D2 | XM_059882241.1 | NR1D2-F | GTCTAATTACCTGGTTTCCCCC | 127 |
| NR1D2-R | GACGCGGACTGGAAGCTATT | |||
| GCSH | NM_174844.1 | GCSH-F | TATTGAGGAGTGAAACTGGAACCC | 188 |
| GCSH-R | AGATGCAGTGTTTATCTGAAGTCAT | |||
| ABCB10 | XM_024986813.2 | ABCB10-F | CTCATGCAGACGTCAGGTCA | 107 |
| ABCB10-R | TCTCCTGTGCGTGTCTTGTC |
Fig. 1
Tissue expression profile and interference efficiency of MAPK6 A. Expression analysis of MAPK6 in various tissues of Qinchuan cattle; B. Interference efficiency of MAPK6; C. The protein expression level of MAPK6; D. Protein grayscale value analysis. Different small letters indicate significant differences, "*" indicates significant difference (P < 0.05), " **" indicates extremely significant difference (P < 0.01), the same as below"
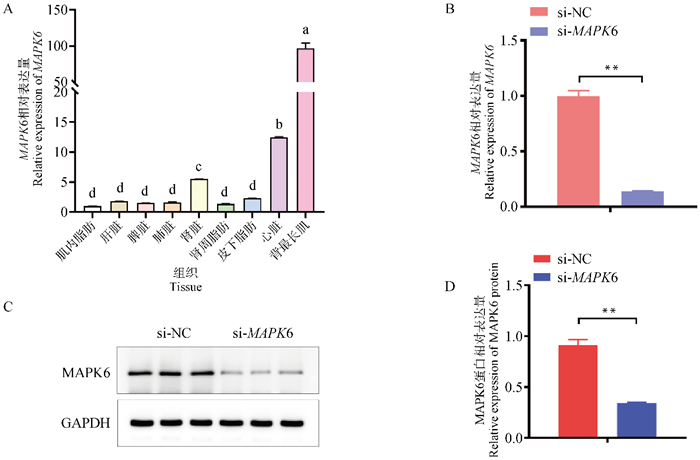
Table 2
Quality control analysis of sequencing data"
| 样品 Sample | 原始数据Raw data | 过滤数据Clean data | 有效比对率/% Valid ratio (reads) | Q20% | Q30% | GC含量/% GC content | |||
| 读数 Read | 碱基/G Base | 读数 Read | 碱基/G Base | ||||||
| MAPK6S1 | 40 273 634 | 6.04 | 38 754 750 | 5.81 | 96.23 | 99.93 | 98.04 | 50.50 | |
| MAPK6S2 | 40 890 852 | 6.13 | 39 414 348 | 5.91 | 96.39 | 99.94 | 97.97 | 50.50 | |
| MAPK6S3 | 40 659 854 | 6.10 | 39 237 220 | 5.89 | 96.50 | 99.94 | 98.04 | 49.50 | |
| SINC1 | 39 899 744 | 5.98 | 38 249 602 | 5.74 | 95.86 | 99.93 | 97.97 | 50.50 | |
| SINC2 | 38 885 912 | 5.83 | 37 072 804 | 5.56 | 95.34 | 99.92 | 97.89 | 51.50 | |
| SINC3 | 39 628 850 | 5.94 | 38 159 344 | 5.70 | 96.29 | 99.93 | 97.97 | 51.50 | |
Table 3
Reference genome alignment results"
| 样品 Sample | 过滤数据 Clean reads | 比对读数 Mapped reads | 唯一比对读数 Unique mapped reads | 多比对读数 Multi mapped reads |
| MAPK6S1 | 38 754 750 | 36 246 759(93.53%) | 35 413 870(91.38%) | 832 889(2.15%) |
| MAPK6S2 | 39 414 348 | 36 937 794(93.72%) | 36 105 382(91.60%) | 832 412(2.11%) |
| MAPK6S3 | 39 237 220 | 36 907 942(94.06%) | 36 079 312(91.95%) | 828 630(2.11%) |
| SINC1 | 38 249 602 | 35 839 948(93.70%) | 34 934 213(91.33%) | 905 735(2.37%) |
| SINC2 | 37 072 804 | 34 373 945(92.72%) | 33 513 528(90.40%) | 860 417(2.32%) |
| SINC3 | 38 159 344 | 35 644 691(93.41%) | 34 805 597(91.21%) | 839 094(2.20%) |
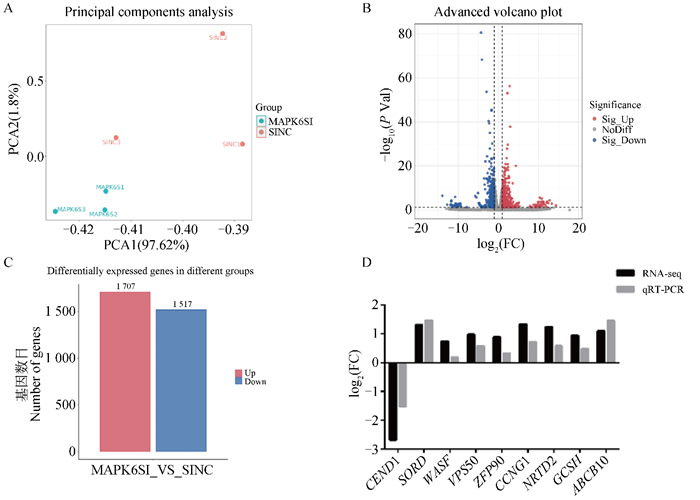
Fig. 4
RNA-seq analysis of bovine myoblast differentiation after interfering with the MAPK6 gene A. Principal component analysis of samples; B. Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes; C. Statistics of differentially expressed genes; D. Quantitative validation of differentially expressed genes expression"
| 1 | 付玉, 张博, 凌遥, 等. 骨骼肌生长发育过程及调控研究现状[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2021, 48 (10): 3565- 3574. |
| FU Y , ZHANG B , LING Y , et al. Reviews on process and regulation of skeletal muscle growth and development[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 48 (10): 3565- 3574. | |
| 2 |
WANG Y P , ZHANG Z J , ZHANG Y Q , et al. Regulatory role of TEX10 gene in proliferation differentiation and apoptosis of bovine myoblasts[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biology, 2025, 182-183, 106771.
doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2025.106771 |
| 3 | 凌笑笑, 唐朋, 梁春年, 等. miRNAs对骨骼肌调控的研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2018, 45 (6): 1486- 1492. |
| LING X X , TANG P , LIANG C N , et al. Research progress on miRNAs in skeletal muscle regulation[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 45 (6): 1486- 1492. | |
| 4 |
LI L , ZHANG Z H , XU H D , et al. Chicken CircZNF609 encodes a protein induced by IRES-like region that inhibits the proliferation and promotes the differentiation of myoblasts[J]. Poul Sci, 2025, 104 (8): 105339.
doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105339 |
| 5 |
WEN X M , JIAO L D , TAN H . MAPK/ERK pathway as a central regulator in vertebrate organ regeneration[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (3): 1464.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23031464 |
| 6 | TURGEON B , SABA-EL-LEIL M K , MELOCHE S . Cloning and characterization of mouse extracellular-signal-regulated protein kinase 3 as a unique gene product of 100 kDa[J]. Biochem J, 2000, 346 (Pt 1): 169- 175. |
| 7 | SOULEZ M , SABA-EL-LEIL M K , TURGEON B , et al. Reevaluation of the role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 3 in perinatal survival and postnatal growth using new genetically engineered mouse models[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2019, 39 (6): e00527- 18. |
| 8 |
SOULEZ M , TANGUAY PL , DO F , et al. ERK3-MK5 signaling regulates myogenic differentiation and muscle regeneration by promoting FoxO3 degradation[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2022, 237 (4): 2271- 2287.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.30695 |
| 9 |
COULOMBE P , RODIER G , PELLETIER S , et al. Rapid turnover of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 3 by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway defines a novel paradigm of mitogen-activated protein kinase regulation during cellular differentiation[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2003, 23 (13): 4542- 4558.
doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.13.4542-4558.2003 |
| 10 |
LI B Z , WANG J F , RAZA S H A , et al. MAPK family genes' influences on myogenesis in cattle: genome-wide analysis and identification[J]. Res Vet Sci, 2023, 159, 198- 212.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2023.04.024 |
| 11 |
龚宇轩, 黑伟, 鲍武, 等. TMEM182基因调控猪骨骼肌卫星细胞成肌分化的研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56 (4): 1676- 1688.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.04.017 |
|
GONG Y X , HEI W , BAO W , et al. Study on the regulation of myogenie differentiation of porcine skeletal muscle satellite cells by gene TMEM182[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56 (4): 1676- 1688.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.04.017 |
|
| 12 | 赵晓, 莫德林, 张悦, 等. 猪的骨骼肌生长发育研究进展[J]. 生命科学, 2011, 23 (1): 37- 44. |
| ZHAO X , MO D L , ZHANG Y , et al. Progress in research on skeletal muscle growth and development in swine[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2011, 23 (1): 37- 44. | |
| 13 |
JEONG S Y , CHOI J H , ALLEN P D , et al. Immature skeletal myotubes are an effective source for improving the terminal differentiation of skeletal muscle[J]. Cells, 2024, 13 (24): 2136.
doi: 10.3390/cells13242136 |
| 14 |
PIASECKA A , SEKRECKI M , SZCZES'NIAK M W , et al. MEF2C shapes the microtranscriptome during differentiation of skeletal muscles[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11 (1): 3476.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82706-2 |
| 15 |
DONG C , YANG X Z , ZHANG C Y , et al. Myocyte enhancer factor 2C and its directly-interacting proteins: A review[J]. Progress Biophys MolBiol, 2017, 126, 22- 30.
doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2017.02.002 |
| 16 | BHARATHY N , LING B M , TANEJA R . Epigenetic regulation of skeletal muscle development and differentiation[J]. Subcell Biochem, 2013, 61, 139- 150. |
| 17 |
YANG X R , NING Y , ABBAS RAZA S H , et al. MEF2C expression is regulated by the post-transcriptional activation of the METTL3-m(6)A-YTHDF1 axis in myoblast differentiation[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2022, 9, 900924.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.900924 |
| 18 | 刘瑞莉, 吴磊, 袁玮, 等. MYL2基因在肌肉生长过程中的研究[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2018 (3): 10-14+252. |
| LIU R L , WU L , YUAN W , et al. The study on the function of MYL2 gene in muscle growth[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2018 (3): 10-14+252. | |
| 19 |
CIECIERSKA A , MOTYL T , SADKOWSKI T . Transcriptomic profile of primary culture of skeletal muscle cells isolated from semitendinosus muscle of beef and dairy bulls[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21 (13): 4794.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21134794 |
| 20 |
WANG H J , DOU M M , LI J , et al. Expression patterns and correlation analyses of muscle-specific genes in the process of sheep myoblast differentiation[J]. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim, 2022, 58 (9): 798- 809.
doi: 10.1007/s11626-022-00721-7 |
| 21 |
TAO L J , HUANG W X , LI Z Y , et al. Transcriptome analysis of differentially expressed genes and molecular pathways involved in C2C12 cells myogenic differentiation[J]. Mol Biotechnol, 2025, 67 (9): 3640- 3655.
doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01259-7 |
| 22 |
ENDO T . Postnatal skeletal muscle myogenesis governed by signal transduction networks: MAPKs and PI3K-Akt control multiple steps[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2023, 682, 223- 243.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.09.048 |
| 23 | 陈博, 邓强, 李中锋, 等. Hippo信号通路成骨、成肌分化功能研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2023, 29 (10): 1538- 1543. |
| CHEN B , DENG Q , LI Z F , et al. Research progress of Hippo signaling pathway in osteogenic and myogenic differentiation[J]. Chinese Journal of Osteoporosis, 2023, 29 (10): 1538- 1543. | |
| 24 | 程春芳, 万娟, 丁恺志, 等. 成肌细胞增殖与分化及其调控机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27 (14): 2200- 2206. |
| CHENG C F , WAN J , DING K Z , et al. Regulatory mechanism of myoblast proliferation and differentiation[J]. Chinese Journal ofTissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27 (14): 2200- 2206. | |
| 25 | SEGALÉS J , PERDIGUERO E , MUÑOZ-CÁNOVES P . Regulation of muscle stem cell functions: a focus on the p38 MAPK signaling pathway[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2016, 4, 91. |
| 26 | 党彩霞, 朱袁婕, 包雅婷, 等. p38-MAPK信号通路对骨骼肌再生的影响研究进展[J]. 江西科技师范大学学报, 2023 (6): 109- 113. |
| DANG C X , ZHU Y J , BAO Y T , et al. Research progress on the effect of p38 MAPK signaling pathway on skeletal muscle regeneration[J]. Journal of Jiangxi Science & Technology Normal University, 2023 (6): 109- 113. | |
| 27 | 郑丽蓉, 许艳华, 曾卫卫, 等. 细胞膜去极化通过激活MAPK信号通路促进原代肌母细胞增殖[J]. 南京师大学报(自然科学版), 2020, 43 (1): 100- 106. |
| ZHENG L R , XU Y H , ZENG W W , et al. Plasma membrane depolarization promotes primary myoblast proliferation through activation of MAPK signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Nanjing Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 43 (1): 100- 106. | |
| 28 |
HU Y , FU J H , LIU X Y , et al. ERK1/2 signaling pathway activated by EGF eromotes proliferation, transdifferentiation, and migration of cultured primary newborn rat lung fibroblasts[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020, 7176169.
doi: 10.1155/2020/7176169 |
| 29 |
MARTIN-VEGA A , COBB M H . ERK1/2-MAPK signaling: metabolic, organellar, and cytoskeletal interactions[J]. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2025, 95, 102526.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2025.102526 |
| 30 |
EIGLER T , ZARFATI G , AMZALLAG E , et al. ERK1/2 inhibition promotes robust myotube growth via CaMKII activation resulting in myoblast-tomyotube fusion[J]. Dev Cell, 2021, 56 (24): 3349- 3363.
doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.11.022 |
| 31 |
FU X J , MATSUI T , FUNABA M . Enhancement of vitamin C-induced myogenesis by inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 pathway[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2022, 612, 57- 62.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.04.103 |
| 32 |
LIU H , LEE S M , JOUNG H . 2-D08 treatment regulates C2C12 myoblast proliferation and differentiation via the Erk1/2 and proteasome signaling pathways[J]. J Muscle Res Cell Motil, 2021, 42 (2): 193- 202.
doi: 10.1007/s10974-021-09605-x |
| 33 |
BENNETT A M , TONKS N K . Regulation of distinct stages of skeletal muscle differentiation by mitogen-activated protein kinases[J]. Science, 1997, 278 (5341): 1288- 1291.
doi: 10.1126/science.278.5341.1288 |
| 34 |
CHEN S J , YUE J , ZHANG J X , et al. Continuous exposure of isoprenaline inhibits myoblast differentiation and fusion through PKA/ERK1/2-FOXO1 signaling pathway[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2019, 10 (1): 70.
doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1160-x |
| 35 |
LIU S F , GAO F , WEN L , et al. Osteocalcin induces proliferation via positive activation of the PI3K/Akt, P38 MAPK pathways and promotes differentiation through activation of the GPRC6A-ERK1/2 pathway in C2C12 myoblast cells[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2017, 43 (3): 1100- 1112.
doi: 10.1159/000481752 |
| 36 |
KUPPUSAMY P , SOUNDHARRAJAN I , KIM D H , et al. 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy cinnamic acid accelerate myoblasts differentiation on C2C12 mouse skeletal muscle cells via AKT and ERK 1/2 activation[J]. Phytomedicine, 2019, 60, 152873.
doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152873 |
| [1] | WU Silin, YANG Benshun, YE Miaomiao, LIANG Entang, LI Fuqiang, MA Weidong, ZAN Linsen, ZHAO Chunping, YANG Wucai. Effect of Luteolin on Semen Cryopreservation of Qinchuan Bull [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3244-3251. |
| [2] | GONG Yuxuan, HEI Wei, BAO Wu, CHEN Jiayi, LI Meng, GUO Xiaohong, LI Bugao. Study on the Regulation of Myogenic Differentiation of Porcine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells by Gene TMEM182 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1676-1688. |
| [3] | ZHAO Gangkui, GAO Haixu, YIN Siqi, SUN Honghong, XIN Yiran, ZAN Linsen, ZHAO Chunping. The Effects of the SFRP4 Gene on Bovine Preadipocyte Differentiation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 611-620. |
| [4] | ZHANG Le, NING Yue, LI Pei-wei, WANG Hong-bao, ZAN Lin-sen. The Overexpression and Interference of Smad3 Gene in Qinchuan Cattle Preadipocytes Mediated by Adenovirus Vector [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2018, 49(9): 1840-1850. |
| [5] | XING Yi-shen, HU Xin, REN Ling, WANG Ya-hui, XU Ling-yang, LI Jun-ya, ZHANG Lu-pei. Identification of microRNAs Involved in Myogenic Differentiation of Bovine Fetal Skeletal Muscle Derived Myoblasts [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2018, 49(6): 1134-1144. |
| [6] | GUI Lin-sheng,ZAN Lin-sen,WANG Hong-bao,WANG Hong-cheng. Effects of Single and Combined Genotypes of SIRT1 and SIRT2 Genes on Meat Quality Traits in Qinchuan Cattle [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2015, 46(10): 1741-1749. |
| [7] | ZHANG Song,ZAN Lin-sen,WANG Hong-bao,WANG Guo-qing,FU Chang-zhen,ZHANG Ya-ran,MEI Chu-gang,DENG Guan-qun. Association of CD36 Gene Polymorphism with Meat Traits in Qinchuan Cattle [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2014, 45(7): 1060-1067. |
| [8] | FU Chang-zhen, ZAN Lin-sen, WANG Hong, JIANG Bi-jie, CHENG Gong,WANG Hong-bao, ZHU Guang-xing, LI Yao-kun, WANG Hong-cheng. Construction of Recombinant Adenovirus Vector Specific to SREBP1 Gene of Qinchuan Cattle and the Packaging and Amplifying of the Corresponding Adenovirus [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2013, 44(8): 1323-1329. |
| [9] | GAO Jian-bin, ZAN Lin-sen,YANG Ning, LI Yao-kun, HUANGFU Yi-fan, HAO Rui-jie, MA Xiang-hui, FU Chang-zhen, JIANG Bi-jie, CHENG Gong. Polymorphisms of DKK1 Gene and Its Association with Body Measurement and Meat Quality Traits in Qinchuan Cattle [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2013, 44(3): 376-386. |
| [10] | MA Xianghui;ZAN Linsen;;GAO Jianbin;YANG Ning;ZHU Guangxing;CHENG Gong;WANG Hongbao;HAO Ruijie;FU Changzhen;JIANG Bijie; ZHAN Xiaoli;BAI Yinping. Association of IRS-1 Gene Polymorphism with Body Measurement and Meat Quality Traits in Qinchuan Cattle [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2012, 43(8): 1200-1209. |
| [11] | HUANG Lei;ZAN Lin-sen;WANG Hong-bao;LIU Hong-yu. Study on SNP of LXRα Gene Exon2 and Its Association with Some Meat Traits in Qinchuan Cattle [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2010, 41(5): 531-535. |
| [12] | FAN Yueyuan;ZAN Linsen;WANG Hongbao;YANG Yanjie . Study on the Relationship between Polymorphism of PLIN Gene and Carcass and Meat Quality Traits in Qinchuan Cattle [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2010, 41(3): 268-273. |
| [13] | ZHAO Xianlin;ZAN Linsen;HU Jianhong;GUI Linsheng;HAO Ruijie . The Antioxidation Protective Effects of Vitamin E on Frozenthawed Semen in Qinchuan Cattle [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2010, 41(1): 117-122. |
| [14] | HAN Ruihua;ZAN Linsen. SNPs Detection of UCP3 Gene and Its Relationship with Carcass and Meat Quality Traits in Qinchuan Cattle and Its Hybrid Cattle [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2009, 40(6): 806-812. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||