





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (12): 5725-5737.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.12.035
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Xiuqin1( ), QIU Yangyuan2, LÜ Qingbo2, HUANG Meiqing1,*(
), QIU Yangyuan2, LÜ Qingbo2, HUANG Meiqing1,*( )
)
Received:2024-02-02
Online:2024-12-23
Published:2024-12-27
Contact:
HUANG Meiqing
E-mail:lyunxqchen@163.com;meiqingmail@126.com
CLC Number:
CHEN Xiuqin, QIU Yangyuan, LÜ Qingbo, HUANG Meiqing. Characteristics and Phylogenetic Analysis of Mitochondrial Genome in the Ligula intestinalis[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5725-5737.
Table 1
Detailed information of Ligula_intestinalis studied in this study"
| 编号 No. | mtDNA GenBank登录号 GenBank accession No. of mtDNA | 国家 Country | 宿主 Host | mtDNA长度/bp Length of mtDNA |
| 1 | NC_039445.1 | 中国 | 青海湖裸鲤 | 13 621 |
| 2 | MW602519.1 | 俄罗斯 | 拉多加环斑海豹 | 13 623 |
| 3 | MW602520.1 | 俄罗斯 | 拉多加环斑海豹 | 13 589 |
| 4 | OR756289.1 | 秘鲁 | 阿氏山鳉 | 13 657 |
| 5 | PP109086.1 | 中国 | 麦穗鱼 | 13 655 |
Table 2
Mitochondrial genome information of cestode used for phylogenetic analyses"
| 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | mtDNA GenBank登录号 GenBank accession No. of mtDNA | mtDNA长度/bp Length of mtDNA |
| 带科 Taeniidae | 泡尾带属 Hydatigera | 克氏泡尾带绦虫 H. krepkogorski | NC_021142.1 | 13 792 |
| H. parva | NC_021141.1 | 13 482 | ||
| 带属 Taenia | 豆状带绦虫 T. pisiformis | NC_013844.1 | 13 387 | |
| T. crocutae | NC_024591.1 | 13 711 | ||
| 泡状带绦虫 T. hydatigena | NC_012896.1 | 13 492 | ||
| 棘球属 Echinococcus | 细粒棘球绦虫 E. granulosus | NC_044548.1 | 17 675 | |
| 马棘球绦虫 E. equinus | NC_020374.1 | 13 605 | ||
| 多房棘球绦虫 E. multilocularis | NC_000928.2 | 13 738 | ||
| 沃氏棘球绦虫 E. vogeli | NC_009462.1 | 13 750 | ||
| 裂头科 Diphyllobothriidae | 双槽头属 Dibothriocephalus | 阔节裂头绦虫 D. latum | NC_008945.1 | 13 608 |
| D. nihonkaiensis | NC_009463.1 | 13 747 | ||
| 舌状属 Ligula | 肠舌状绦虫 L. intestinalis | NC_039445.1 | 13 621 | |
| 复殖孔属 Diplogonoporus | D. balaenopterae 巨大殖孔绦虫 | NC_017613.1 NC_017615.1 | 13 724 13 725 | |
| D. grandis | ||||
| 双线属 Digramma | 双线绦虫 D. interrupta | NC_039446.1 | 13 685 | |
| 迭宫属 Spirometra | S. decipiens 刺猬绦虫 | NC_026852.1 NC_011037.1 | 13 641 13 643 | |
| S. erinaceieuropaei | ||||
| 膜壳科 Hymenolepididae | 腔带属 Cloacotaenia | 大腔带绦虫 C. megalops | NC_032295.1 | 13 887 |
| 剑带属 Drepanidotaenia | 矛形剑带绦虫 D. lanceolata | NC_028164.1 | 13 573 | |
| 膜壳属 Hymenolepis | H. diminuta 微小膜壳绦虫 | NC_002767.1 NC_029245.1 | 1 3900 137 64 | |
| H. nana | ||||
| 假裸头属 Pseudanoplocephala | 克氏假裸头绦虫 P. crawfordi | NC_028334.1 | 14 192 | |
| 头槽科 Bothriocephalidae | Schyzocotyle | 头槽绦虫 S. acheilognathi IHB0601 | KX589243.1 | 14 046 |
| S. nayarensis | NC_030317.1 | 13 852 | ||
| S. ophiocephalina | NC_034715.1 | 13 816 | ||
| 头颊绦虫科 Capingentidae | Breviscolex | 东方短结绦虫 B. orientalis | NC_035634.1 | 14 011 |
| 纽带绦虫科 Lytocestidae | Atractolytocestus Khawia | A. huronensis K. sinensis | NC_035635.1 NC_034800.1 | 15 130 13 759 |
| 裸头科 Anoplocephalidae | 裸头属 Anoplocephala | 大裸头绦虫 A. magna | NC_031801.1 | 13 759 |
| 叶状大裸头绦虫 A. perfoliata | NC_028425.1 | 14 459 | ||
| 莫尼茨属 Moniezia | 扩展莫尼茨绦虫 M. expansa | NC_036219.1 | 13 934 | |
| 贝氏莫尼茨绦虫 M. benedeni | NC_036218.1 | 13 958 | ||
| 双壳科 Dipylidiida | 复孔属 Dipylidium | 犬复孔绦虫 D. caninum | NC_021145.1 | 14 296 |
| 双腔科 Dicrocoeliidae | 窄体属 Lyperosomum | 长尾窄体吸虫* L. longicauda | NC_048467.1 | 14 567 |
Table 3
Gene distribution and annotation of the Ligula intestinalis mtDNA"
| 基因或区域 Gene or region | 位置/nt Position | 长度/bp Size | 反密码子 Anticodon | 起始密码子 Start codon | 终止密码子 Stop codon | 基因间隔/bp Intergenic length |
| cox3 | 1~642 | 642 | - | GTG | - | |
| trn-His(H) | 644~710 | 67 | GTG | - | - | 1 |
| cytb | 714~1820 | 1 107 | - | ATG | TAA | 3 |
| nad4L | 1 822~2 082 | 261 | - | ATG | TAA | 1 |
| nad4 | 2 043~3 293 | 1 251 | - | ATG | TAG | -40 |
| trn-Gln(Q) | 3 297~3 352 | 56 | TTG | - | - | 3 |
| trn-Phe(F) | 3 353~3 419 | 67 | GAA | - | - | 0 |
| trn-Met(M) | 3 416~3 482 | 67 | CAT | - | - | -4 |
| atp6 | 3 486~3 995 | 510 | - | ATG | TAA | 3 |
| nad2 | 3 998~4 876 | 879 | - | ATG | TAG | 2 |
| trn-Val(V) | 4 878~4 941 | 64 | TAC | - | - | 1 |
| trn-Ala(A) | 4 950~5 010 | 61 | TGC | - | - | 8 |
| trn-Asp(D) | 5 014~5 077 | 64 | GTC | - | - | 3 |
| nad1 | 5 078~5 968 | 891 | - | ATG | TAG | 0 |
| trn-Asn(N) | 5 968~6 033 | 66 | GTT | - | - | -1 |
| trn-Pro(P) | 6 041~6 105 | 65 | TGG | - | - | 7 |
| trn-Ile(I) | 6 114~6 178 | 65 | GAT | - | - | 8 |
| trn-Lys(K) | 6 195~6 258 | 64 | CTT | - | - | 16 |
| nad3 | 6 260~6 613 | 354 | - | ATG | - | 1 |
| trn-Ser(S1) | 6 606~6 664 | 59 | GCT | - | - | -8 |
| trn-Trp(W) | 6 667~6 729 | 63 | TCA | - | - | 2 |
| cox1 | 6 738~8 303 | 1 566 | - | ATG | TAG | 8 |
| trn-Thr(T) | 8 294~8 355 | 62 | TGT | - | - | -10 |
| rrnL | 8 356~9 321 | 966 | - | - | - | 0 |
| trn-Cys(C) | 9 322~9 385 | 64 | GCA | - | - | 0 |
| rrnS | 9 386~10 101 | 716 | - | - | - | 0 |
| cox2 | 10 129~10 698 | 570 | - | ATG | TAA | 27 |
| trn-Glu(E) | 10 700~10 763 | 64 | TTC | - | - | 1 |
| nad6 | 10 769~11 227 | 459 | - | ATG | TAG | 5 |
| trn-Tyr(Y) | 11 231~11 296 | 66 | GTA | - | - | 3 |
| NCR1 | 11 297~11 521 | 225 | - | - | - | - |
| trn-Leu(L1) | 11 522~11 588 | 67 | TAG | - | - | 225 |
| trn-Ser(S2) | 11 599~11 664 | 66 | TGA | - | - | 10 |
| trn-Leu(L2) | 11 676~11 739 | 64 | TAA | - | - | 11 |
| trn-Arg(R) | 11 740~11 794 | 55 | ACG | - | - | 0 |
| nad5 | 11 798~13 366 | 1 569 | - | ATG | TAA | 3 |
| NCR2 | 13 367~13 586 | 220 | - | - | - | - |
| trn-Gly(G) | 13 587~13 652 | 66 | TCC | 220 |
Table 4
Nucleotide composition and skew of the mitochondrial genome of Ligula intestinalis"
| 区域 Regions | 大小/bp Size (bp) | T (U)含量/% T (U)% | C含量/% C% | A含量/% A% | G含量/% G% | AT含量/% AT% | AT偏斜度 AT skew | GC偏斜度 GC skew |
| PCGs | 10 059 | 45.7 | 12.4 | 21.4 | 20.5 | 67.1 | -0.362 | 0.245 |
| 1st condon | 3 353 | 41.1 | 11.4 | 23.3 | 24.2 | 64.4 | -0.277 | 0.360 |
| 2nd condon | 3 353 | 47.2 | 15.4 | 17.6 | 19.8 | 64.8 | -0.458 | 0.124 |
| 3rd condon | 3 353 | 48.6 | 10.5 | 23.4 | 17.5 | 72.0 | -0.351 | 0.252 |
| atp6 | 510 | 47.3 | 13.3 | 19.6 | 19.8 | 66.9 | -0.413 | 0.195 |
| cox1 | 1 566 | 44.8 | 13.0 | 21.6 | 20.5 | 66.4 | -0.349 | 0.223 |
| cox2 | 570 | 39.8 | 13.0 | 24.6 | 22.6 | 64.4 | -0.237 | 0.271 |
| cox3 | 642 | 47.2 | 12.1 | 19.5 | 21.2 | 66.7 | -0.416 | 0.271 |
| cytb | 1 107 | 43.7 | 13.9 | 22 | 20.3 | 65.7 | -0.33 | 0.187 |
| nad1 | 891 | 45.9 | 10.7 | 20.5 | 22.9 | 66.4 | -0.382 | 0.365 |
| nad2 | 879 | 50.5 | 9.4 | 20.6 | 19.5 | 71.1 | -0.421 | 0.346 |
| nad3 | 354 | 48.9 | 11.0 | 21.5 | 18.6 | 70.4 | -0.39 | 0.257 |
| nad4 | 1 251 | 46.6 | 14.3 | 18.9 | 20.1 | 65.5 | -0.422 | 0.169 |
| nad4L | 261 | 50.2 | 8.8 | 25.7 | 15.3 | 75.9 | -0.323 | 0.27 |
| nad5 | 1 569 | 43.3 | 13.1 | 23.2 | 20.5 | 66.5 | -0.302 | 0.221 |
| nad6 | 459 | 47.5 | 10.5 | 21.1 | 20.9 | 68.6 | -0.384 | 0.333 |
| rrnL | 966 | 39.8 | 12.0 | 28.9 | 19.4 | 68.7 | -0.158 | 0.234 |
| rrnS | 716 | 37.6 | 13.1 | 29.7 | 19.6 | 67.3 | -0.116 | 0.197 |
| rRNAs | 1 682 | 38.8 | 12.5 | 29.3 | 19.4 | 68.1 | -0.141 | 0.218 |
| tRNAs | 1 272 | 37.7 | 12.7 | 28.8 | 20.8 | 66.5 | -0.135 | 0.239 |
| NCR | 445 | 46.97 | 7.19 | 29.89 | 15.96 | 76.85 | -0.222 | 0.379 |
| Full genome | 13 655 | 44.1 | 12.3 | 23.5 | 20.2 | 67.6 | -0.305 | 0.245 |
Table 5
Analysis of gene variation sites in the mitogenome Ligula intestinalis"
| 参数 Parameter | 基因名称Gene name | |||||||||||||
| cox3 | cytb | nad4L | nad4 | atp6 | nad2 | nad1 | nad3 | cox1 | cox2 | nad6 | nad5 | rrnS | rrnL | |
| 总位点数* Total number of sites | 642 | 1107 | 261 | 1251 | 510 | 879 | 891 | 346 | 1 566 | 570 | 459 | 1 569 | 711 | 966 |
| 保守位点数 Invariable sites | 522 | 926 | 226 | 997 | 425 | 717 | 740 | 278 | 1 325 | 487 | 363 | 1 239 | 664 | 885 |
| 变异位点数 Variable sites | 120 | 181 | 35 | 254 | 85 | 162 | 151 | 68 | 241 | 83 | 96 | 330 | 47 | 81 |
| 简约突变数 Parsimony informative sites | 42 | 79 | 17 | 107 | 27 | 60 | 62 | 22 | 85 | 30 | 31 | 137 | 17 | 32 |
| 单现突变数 Singleton variable sites | 74 | 102 | 18 | 135 | 58 | 102 | 89 | 46 | 156 | 53 | 65 | 193 | 28 | 49 |
| 变异位点比例% Ratio of variable sites/% | 18.69 | 16.35 | 0.44 | 20.30 | 16.67 | 22.59 | 16.94 | 19.65 | 15.39 | 14.56 | 20.92 | 21.03 | 6.61 | 8.39 |

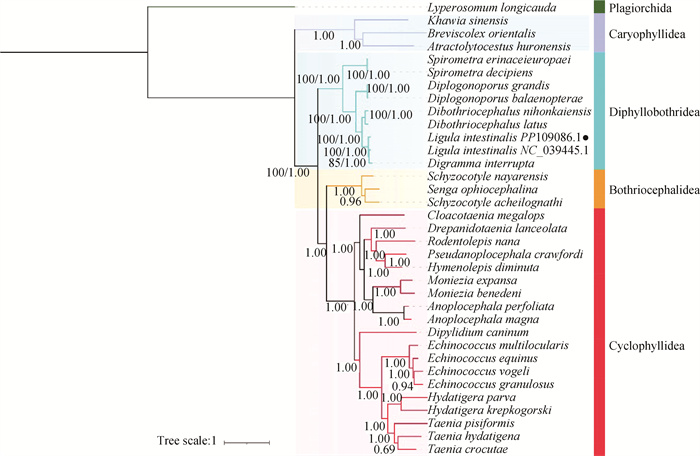
Fig. 4
Phylogeny of five cestode orders using maximum likelihood and bayesian inference analysis inferred from concatenated nucleotide sequences of 12 PCGs in the mitogenome The values on the branches are the bootstrap probability and posterior probability (BP/PP). ●. The worm strain isolated in this study"
| 1 |
LAGRUE C , PRESSWELL B , DUNCKLEY N , et al. The invasive cestode parasite ligula from salmonids and bullies on the South Island, New Zealand[J]. Parasitol Res, 2018, 117 (1): 151- 156.
doi: 10.1007/s00436-017-5684-7 |
| 2 | KAPUSTA A , BOGACKA-KAPUSTA E , CZARNECKI B . The significance of stone moroko, Pseudorasbora Parva (temminck and schlegel), in the small-sized fish assemblages in the littoral zone of the heated Lake Licheńskie[J]. Arch Pol Fish, 2008, 16 (1): 49- 62. |
| 3 |
GUTIÉRREZ J S , HOOLE D . Ligula intestinalis[J]. Trends Parasitol, 2022, 38 (4): 344- 345.
doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2021.09.005 |
| 4 | 申夕, 饶天宇, 许薇, 等. 芜湖间断双线绦虫裂头蚴的形态和分子特征及系统发育研究[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报, 2020, 41 (11): 1321- 1325. |
| SHEN X , RAO T Y , XU W , et al. Characteristics of morphology and molecular and phylogenetic analysis of the Digramma interrupta plerocercoid in Wuhu[J]. Journal of Qiqihar Medical University, 2020, 41 (11): 1321- 1325. | |
| 5 | 张学勇, 简莹娜, 李秀萍, 等. 青海湖裸鲤舌状绦虫裂头蚴的分子鉴定及系统发育研究[J]. 水生生物学报, 2018, 42 (1): 33- 38. |
| ZHANG X Y , JIAN Y N , LI X P , et al. Molecular identification and phylogenetic study of Ligula intestinalis pleroceroid in Gymnocypris przewalskii from the Qinghai Lake, China[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2018, 42 (1): 33- 38. | |
| 6 |
LI J , LIAO X . The taxonomic status of Digramma (Pseudophyllidea: Ligulidae) inferred from DNA sequences[J]. J Parasitol, 2003, 89 (4): 792- 799.
doi: 10.1645/GE-3078 |
| 7 |
LOGAN F J , HORÁK A , ŠTEFKA J , et al. The phylogeny of diphyllobothriid tapeworms (Cestoda: Pseudophyllidea) based on ITS-2 rDNA sequences[J]. Parasitol Res, 2004, 94 (1): 10- 15.
doi: 10.1007/s00436-004-1164-y |
| 8 |
JIMÉNEZ-AVALOS G , SOTO-OBANDO A , SOLIS M , et al. Assembly and phylogeographical analysis of novel Taenia solium mitochondrial genomes suggest stratification within the African-American genotype[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2023, 16 (1): 349.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-05958-z |
| 9 |
ZHOU X , WANG Z , ZHU P C , et al. Eimeria zuernii (Eimeriidae: Coccidia): mitochondrial genome and genetic diversity in the Chinese yak[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2023, 16 (1): 312.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-05925-8 |
| 10 | 伊平昌, 李国平, 顾冬花, 等. 青海大通北川河源区鱼类舌状绦虫和双线绦虫的分子鉴定及系统发育关系研究[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2019, 55 (11): 17- 21. |
| YI P C , LI G P , GU D H , et al. Molecular identification and phylogenetic research of Ligula intestinalis and Digramma interuota in fish from the Qinghai Datongbeiheyuanqu Nature Reserve, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 55 (11): 17- 21. | |
| 11 |
LI W X , FU P P , ZHANG D , et al. Comparative mitogenomics supports synonymy of the genera Ligula and Digramma (Cestoda: Diphyllobothriidae)[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2018, 11 (1): 324.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-2910-9 |
| 12 |
CAO Z Y , XI B W , LI S W , et al. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Nippotaenia mogurndae Yamaguti and Miyata, 1940 (Cestoda: Nippotaeniidae)[J]. J Helminthol, 2022, 96, e65.
doi: 10.1017/S0022149X22000530 |
| 13 |
BOHARD L , LALLEMAND S , BORNE R , et al. Complete mitochondrial exploration of Echinococcus multilocularis from French alveolar echinococcosis patients[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2023, 53 (10): 555- 564.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2023.03.006 |
| 14 | 叶玉龙. 6种肉孢子虫线粒体基因组组成和结构分析[D]. 昆明: 云南大学, 2020. |
| YE Y L. Analysis of the composition and structure of mitochondrial genomes of 6 species of Sarcocystis[D]. Kunming: Yunnan University, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 15 |
XIANG C Y , GAO F L , JAKOVLIC ' I , et al. Using PhyloSuite for molecular phylogeny and tree-based analyses[J]. iMeta, 2023, 2 (1): e87.
doi: 10.1002/imt2.87 |
| 16 |
TALAVERA G , CASTRESANA J . Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments[J]. Syst Biol, 2007, 56 (4): 564- 577.
doi: 10.1080/10635150701472164 |
| 17 |
KALYAANAMOORTHY S , MINH B Q , WONG T K F , et al. ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates[J]. Nat Methods, 2017, 14 (6): 587- 589.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4285 |
| 18 |
TRIFINOPOULOS J , NGUYEN L T , VON HAESELER A , et al. W-IQ-TREE: a fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2016, 44 (W1): W232- W235.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw256 |
| 19 | RONQUIST F , TESLENKO M , VAN DER MARK P , et al. MrBayes 3. 2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space[J]. Syst Biol, 201, 61 (3): 539- 542. |
| 20 |
LETUNIC I , BORK P . Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v5: an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021, 49 (W1): W293- W296.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab301 |
| 21 |
KAARNIRANTA K , PAWLOWSKA E , SZCZEPANSKA J , et al. Role of mitochondrial DNA damage in ROS-mediated pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration (AMD)[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20 (10): 2374.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20102374 |
| 22 |
LE T H , BLAIR D , MCMANUS D P . Mitochondrial genomes of parasitic flatworms[J]. Trends Parasitol, 2002, 18 (5): 206- 213.
doi: 10.1016/S1471-4922(02)02252-3 |
| 23 |
YU T H , LI J S , YANG Y , et al. Codon usage patterns and adaptive evolution of marine unicellular cyanobacteria Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus[J]. Mol Phylogenet Evol, 2012, 62 (1): 206- 213.
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2011.09.013 |
| 24 |
FRAIJA-FERNÁNDEZ N , WAESCHENBACH A , BRISCOE A G , et al. Evolutionary transitions in broad tapeworms (Cestoda: Diphyllobothriidea) revealed by mitogenome and nuclear ribosomal operon phylogenetics[J]. Mol Phylogenet Evol, 2021, 163, 107262.
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2021.107262 |
| 25 |
LI W X , ZHANG D , BOYCE K , et al. The complete mitochondrial DNA of three monozoic tapeworms in the Caryophyllidea: a mitogenomic perspective on the phylogeny of eucestodes[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2017, 10 (1): 314.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2245-y |
| 26 |
WAESCHENBACH A , BRABEC J , SCHOLZ T , et al. The catholic taste of broad tapeworms-multiple routes to human infection[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2017, 47 (13): 831- 843.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2017.06.004 |
| 27 |
HOOLE D , CARTER V , DUFOUR S . Ligula intestinalis (Cestoda: Pseudophyllidea): an ideal fish-metazoan parasite model?[J]. Parasitology, 2010, 137 (3): 425- 438.
doi: 10.1017/S0031182010000107 |
| [1] | MA Shujuan, XU Yijie, HE Ke, MA Ruifeng, ZHU Ying. Molecular Evolution and Expression Patterns of a Multigene Family of Toll-like Receptors in Ruminants [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(9): 3722-3734. |
| [2] | LI Guangzhen, MA Zhijie, CHEN Shengmei, LEI Chuzhao, LI Ruizhe, XIE Yinlu, CHAO Shengyu. Maternal Genetic Diversity, Differentiation and Phylogeny of Mitogenome Sequence Variations of Wild Yak and Local Yak Breeds in Qinghai [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(5): 1420-1430. |
| [3] | SHAN Wenjuan, DAI Huiying, ZHANG Yucong. Classification and Genetic Diversity of Three Hare Species in Xinjiang Based on Mitochondrial DNA [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(10): 2403-2412. |
| [4] | DENG Juan, ZHANG Hong-ping, BA Gui, CIREN De-ji, SONG Tian-zeng, LI Li. Genetic Structure and Maternal Origins of 8 Tibetan Goat Populations in Tibet Inferred from Cytb Gene Diversity [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2018, 49(1): 65-74. |
| [5] | REN Xiu-juan, ZHAO Yi-ping, Sarula, BAO Hong-mei, WANG Xi-sheng, DAO Leng, LI Anaer, WEI Rui-yuan, Suriga, CAI Li-gan, BAI Dong-yi, LI Bei, YANG Li-hua, SHIRAIGOL Wunierfu,DUGARJAVIIN Manglai. The Review for the Characteristics of the Equus Evolution [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2017, 48(3): 385-392. |
| [6] | KUANG Xue-qian, YUE Hua, CHEN Xiao-fei, TANG Cheng. The Research of Campylobacter jejuni cmp Gene Structure and ST Type in Livestock and Poultry [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2013, 44(4): 657-664. |
| [7] | LI Qi-fa;LI Yin-xia;ZHAO Xing-bo;PAN Zeng-xiang;LIU Zhen-shan;ZHANG Qing-bo;QU Xu-Guang;SONG Da-wei;DONG Li-yan;LI Ning;XIE Zhuang. Sequencing D-loop Region of Mitochondrial DNA in Yak and Study on Its Taxonomic Status in Bovinae [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2008, 39(1): 1-6. |
| [8] | . Study on mtDNA Genetic Diversity and Phylogeny Evolution of 5 Indigenous Sheep Populations in Southwest China [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2007, 38(3): 219-224. |
| [9] | . Comparative Analysis on Partial Sequence of Follicle- Stimulating Hormone Beta Gene between 20 Goat Breeds and 8 Other Species [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2007, 38(3): 225-231. |
| [10] | ZHANG Chuan-sheng;GENG Li-ying;WAN Hai-wei;LI Ji-tao;DU Li-xin. Study on Sequence Variation of Mitochondrial Cytochromeb Gene and Phylogenetic Relationships of Four Native Sheep Breeds [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2005, 36(4): 313-317. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||