





畜牧兽医学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (7): 3252-3264.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.07.019
收稿日期:2024-12-02
出版日期:2025-07-23
发布日期:2025-07-25
通讯作者:
陶金忠
E-mail:1571893591@qq.com;tao_jz@nxu.edu.cn
作者简介:郑浩(2001-),男,河南济源人,硕士,主要从事动物遗传育种与繁殖研究,E-mail:1571893591@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHENG Hao1( ), LUO Fang1,2, SONG Chenglei1, TAO Jinzhong1,*(
), LUO Fang1,2, SONG Chenglei1, TAO Jinzhong1,*( )
)
Received:2024-12-02
Online:2025-07-23
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
TAO Jinzhong
E-mail:1571893591@qq.com;tao_jz@nxu.edu.cn
摘要:
旨在揭示未妊娠荷斯坦奶牛在人工授精当天到第28天的血浆代谢变化规律,并筛选指示奶牛未妊娠结局的生物标志物,为减少奶牛空怀时间、缩短产犊间隔及早期妊娠诊断提供新思路。本研究以宁夏某奶牛场健康荷斯坦奶牛(体重550±50 kg、3~4岁、2~3胎次)为试验对象。经同期发情处理后人工授精(AI)。分别于AI后第0天(A组)、第5天(B组)、第17天(C组)和第28天(D组)采集尾静脉血(晨饲前),分离血浆并冻存于-80℃。在第32天经B超筛选出未妊娠且未返情的12头奶牛,对其4个时期(n=12)血浆样品进行单样本超高效液相色谱串联四级杆飞行时间质谱(UHPLC-QTOF-MS)非靶向代谢组学技术检测与分析。结果显示:1)人工授精后不同时期,未妊娠奶牛血浆代谢特征存在差异;2)在筛选出的32种差异代谢物中,8种差异代谢物具备较高灵敏度(AUC>0.7),相比于人工授精当天,DL-香草扁桃酸和光黄素在授精第5天高表达,色氨酸-谷氨酸、异亮氨酸-精氨酸、甘氨脱氧胆酸和2-乙氧基乙醇在授精第17天高表达,而精氨酸-酪氨酸和硬脂酸在授精第28天高表达,且授精后第0天和第17天之间未妊娠奶牛血浆差异代谢物主要富集在精氨酸生物合成通路上。结果表明,精氨酸生物合成提示为影响奶牛妊娠发生的关键通路,DL-香草扁桃酸、光黄素等AUC值较高的8种关键代谢物提示为人工授精后早期指示奶牛未妊娠的生物标志物,结果可为提高奶牛繁殖效率提供新的思路。
中图分类号:
郑浩, 罗芳, 宋承磊, 陶金忠. 基于代谢组学技术筛选人工授精后未妊娠奶牛血浆潜在生物标志物的研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(7): 3252-3264.
ZHENG Hao, LUO Fang, SONG Chenglei, TAO Jinzhong. Screening Potential Plasma Biomarkers of Non-pregnant Dairy Cows after Artificial Insemination Based on Metabolomics Technology[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3252-3264.

图 2
不同时期未妊娠奶牛血浆代谢OPLS-DA得分图和置换检验图 图A、B、C、D分别展示A vs. B组在正(左)、负(右)离子模式下的OPLS-DA得分图及置换检验图;图E、F、G、H为A vs. C组在正(左)、负(右)离子模式下的OPLS-DA得分图及置换检验图;图I、J、K、L为A vs. D组在正(左)、负(右)离子模式下OPLS-DA得分图及置换检验图;图M、N、O、P为B vs. C组在正(左)、负(右)离子模式下OPLS-DA得分图及置换检验图;图Q、R、S、T为B vs. D组在正(左)、负(右)离子模式下OPLS-DA得分图及置换检验图;图U、V、W、X为C vs. D组在正(左)、负(右)离子模式下OPLS-DA得分图及置换检验图。R2 intercept和Q2 intercept分别表示R2和Q2回归直线与Y轴的交点,当Q2 intercept < 0表明OPLS-DA模型未出现过度拟合现象"
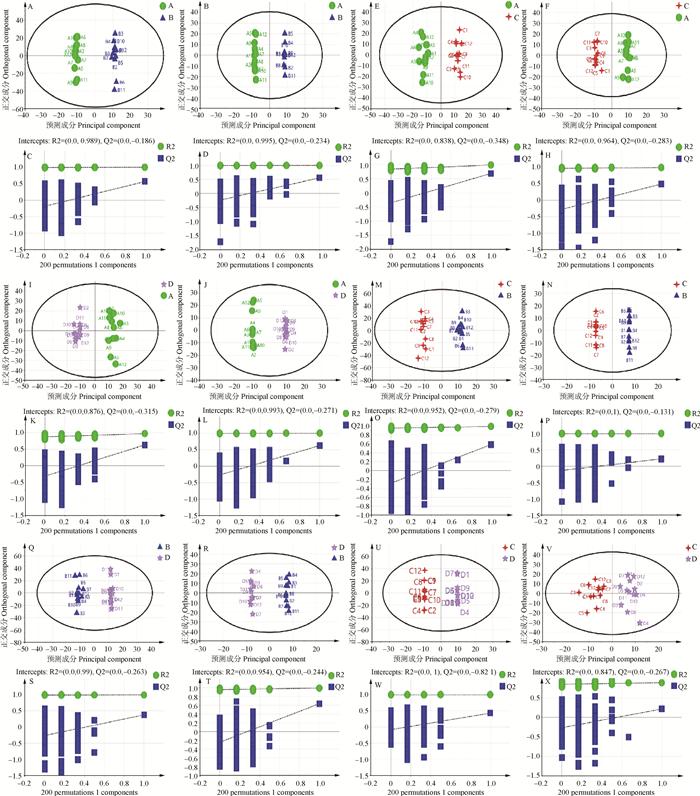
表 2
PCA和OPLS-DA模型的评价参数"
| 模式 Model | 组别 Group | PCA | OPLS-DA | OPLS-DA置换检验 OPLS-DA permutation test | |||
| R2X | R2Y | Q2 | Q2 intercept | ||||
| 正离子模式 POS | A vs. B | 0.502 | 0.997 | 0.563 | -0.186 | ||
| A vs. C | 0.510 | 0.980 | 0.683 | -0.348 | |||
| A vs. D | 0.474 | 0.974 | 0.631 | -0.315 | |||
| B vs. C | 0.449 | 0.988 | 0.584 | -0.279 | |||
| B vs. D | 0.432 | 0.990 | 0.635 | -0.244 | |||
| C vs. D | 0.491 | 1 | 0.428 | -0.082 1 | |||
| 负离子模式 NEG | A vs. B | 0.567 | 0.999 | 0.554 | -0.234 | ||
| A vs. C | 0.502 | 0.986 | 0.485 | -0.283 | |||
| A vs. D | 0.475 | 0.998 | 0.624 | -0.271 | |||
| B vs. C | 0.439 | 1 | 0.223 | -0.131 | |||
| B vs. D | 0.497 | 0.996 | 0.374 | -0.263 | |||
| C vs. D | 0.494 | 0.888 | 0.215 | -0.267 | |||
表 3
已鉴定差异代谢物"
| 代谢物 Metabolite | 质荷比 m/z | 保留时间/s RT | AUC | A vs. B | A vs. C | A vs. D | ||||||||
| VIP | P | FC | VIP | P | FC | VIP | P | FC | ||||||
| 1. DL-香草扁桃酸 DL-vanillyl mandelic acid | 240.078 | 323.702 | 0.806 | 2.074 | 0.007 | 2.538 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 2. 光黄素 Lumichrome | 243.086 | 128.928 | 0.757 | 1.651 | 0.028 | 2.214 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 3. 组氨酸-苏氨酸 His-Thr | 257.125 | 334.948 | 0.167 | 1.923 | 0.015 | 0.328 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 4. 硬脂酰胺 Stearamide | 284.295 | 32.742 | 0.201 | 1.722 | 0.033 | 0.357 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 5. 二十碳五烯酸 Eicosapentaenoic acid | 303.232 | 39.786 | 0.264 | 1.665 | 0.035 | 0.417 | ||||||||
| 6. 苏氨酸-丝氨酸 Thr-Ser | 248.125 | 332.097 | 0.292 | 1.755 | 0.029 | 0.376 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 7. 缬氨酸-苏氨酸 Val-Thr | 201.125 | 198.098 | 0.174 | 2.088 | 0.008 | 0.458 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 8. 色氨酸-谷氨酸 Trp-Glu | 334.140 | 326.883 | 0.813 | - | - | - | 1.794 | 0.015 | 2.225 | - | - | - | ||
| 9. 异亮氨酸-精氨酸 Ile-Arg | 288.203 | 331.332 | 0.813 | - | - | - | 1.860 | 0.009 | 2.099 | - | - | - | ||
| 10. 甘氨脱氧胆酸 Glycodeoxycholic acid | 450.322 | 200.131 | 0.771 | - | - | - | 1.555 | 0.035 | 2.060 | - | - | - | ||
| 11.2-乙氧基乙醇 2-Ethoxyethanol | 151.097 | 63.058 | 1.000 | - | - | - | 2.591 | 0.000 | 2.049 | - | - | - | ||
| 12. 组氨酸-蛋氨酸 His-Met | 304.145 | 218.511 | 0.028 | - | - | - | 2.399 | 0.000 | 0.265 | |||||
| 13. 精氨酸琥珀酸 Argininosuccinic acid | 290.130 | 237.428 | 0.076 | - | - | - | 2.370 | 0.000 | 0.281 | |||||
| 14. 异胱氨酸 Allocystathionine | 187.058 | 276.689 | 0.215 | - | - | - | 1.796 | 0.007 | 0.469 | - | - | - | ||
| 15. 三乙醇胺 Triethanolamine | 150.113 | 154.899 | 0.014 | - | - | - | 2.770 | 0.000 | 0.204 | |||||
| 16.3-羟基异戊酸 3-Hydroxyisovaleric acid | 237.134 | 223.740 | 0.097 | - | - | - | 2.270 | 0.000 | 0.407 | - | - | - | ||
| 17.5′-O-甲基胸苷 5′-O-methylthymidine | 256.105 | 296.654 | 0.215 | 1.797 | 0.020 | 0.468 | - | - | - | |||||
| 18. (3-羧丙基)三甲基铵阳离子 (3-Carboxypropyl)trimethylammonium cation | 191.086 | 249.592 | 0.111 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.861 | 0.009 | 0.429 | ||
| 19. 丙氨酸-亮氨酸 Ala-Leu | 185.129 | 406.947 | 0.007 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.707 | 0.000 | 0.467 | ||
| 20. 丙戊酸 Valproic acid | 183.078 | 276.612 | 0.153 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.986 | 0.004 | 0.334 | ||
| 21. 柠檬酸 Citramalic acid | 207.052 | 298.551 | 0.174 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.910 | 0.006 | 0.333 | ||
| 代谢物 Metabolite | 质荷比 m/z | 保留时间/s RT | AUC | B vs. C | B vs. D | C vs. D | ||||||||
| VIP | P | FC | VIP | P | FC | VIP | P | FC | ||||||
| 1. 色氨酸-谷氨酸 Trp-Glu | 334.140 | 326.883 | 0.833 | 1.779 | 0.021 | 2.177 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 2.2-乙氧基乙醇 2-Ethoxyethanol | 151.097 | 63.058 | 1.000 | 2.734 | 0.000 | 2.037 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 3. 前列腺素 I2 Prostaglandin I2 | 416.249 | 240.224 | 0.188 | 1.784 | 0.026 | 0.213 | ||||||||
| 4. 中康酸 Mesaconic acid | 191.049 | 224.975 | 0.153 | 1.958 | 0.012 | 0.471 | ||||||||
| 5.1-甲基鸟苷 1-methylguanosine | 298.103 | 282.209 | 0.285 | 1.570 | 0.035 | 0.488 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 6. 异亮氨酸-丙氨酸-精氨酸 Ile-Ala-Arg | 358.245 | 49.318 | 0.118 | 2.222 | 0.004 | 0.340 | ||||||||
| 7.3-羟基异戊酸 3-Hydroxyisovaleric acid | 237.134 | 223.740 | 0.181 | 2.164 | 0.006 | 0.400 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 8. 己酸 Hexanoic acid | 158.118 | 45.819 | 0.181 | 1.700 | 0.041 | 0.179 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 9. 精氨酸-酪氨酸 Arg-Tyr | 337.173 | 460.582 | 0.813 | - | - | - | 1.457 | 0.048 | 2.075 | - | - | - | ||
| 13. 吡哆醇 Pyridoxine | 339.156 | 198.852 | 0.188 | - | - | - | 1.802 | 0.016 | 0.449 | |||||
| 11. 富马酸二羟基酯 Dihydroxyfumarate | 148.076 | 233.057 | 0.208 | - | - | - | 1.977 | 0.008 | 0.485 | |||||
| 10. 丙氨酸-亮氨酸 Ala-Leu | 185.129 | 406.947 | 0.000 | - | - | - | 3.190 | 0.000 | 0.492 | - | - | - | ||
| 12. S-甲基-5′-硫腺苷 S-Methyl-5′-thioadenosine | 298.098 | 71.609 | 0.208 | - | - | - | 1.620 | 0.017 | 0.466 | - | - | - | ||
| 14. 柠檬酸 Citramalic acid | 207.052 | 298.551 | 0.125 | - | - | - | 2.545 | 0.002 | 0.405 | - | - | - | ||
| 15. 硬脂酸 Pristanic acid | 297.280 | 38.254 | 0.910 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.037 | 0.025 | 2.227 | ||
| 1 | EALY A D , SEEKFORD Z K . Symposium review: predicting pregnancy loss in dairy cattle[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2019, 102 (12): 11798- 11804. |
| 2 | GUI L S , DAI T S , GUO X R , et al. Recent advances in early pregnancy loss diagnosis in dairy cows: New approaches[J]. Reprod Domest Anim, 2024, 59 (4): e14566. |
| 3 | LEUNG K Y . Applications of advanced ultrasound technology in obstetrics[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2021, 11 (7): 1217. |
| 4 | JIANG C , LI G F . Sensitive fluorescence analysis of pregnancy plasma associated protein A in amniotic fluid based on the plasma superstructure enhanced carbon polymer dots[J]. Sci Adv Mater, 2022, 14 (7): 1151- 1158. |
| 5 |
张馨蕊, 付予, 杨卓, 等. 奶牛早期妊娠诊断蛋白的研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55 (2): 451- 460.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.02.004 |
|
ZHANG X R , FU Y , YANG Z , et al. Study on early pregnancy diagnostic protein of dairy cows[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55 (2): 451- 460.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.02.004 |
|
| 6 | HAN A , QAMAR A Y , BANG S , et al. Effect of extracellular vesicles derived from oviductal and uterine fluid on the development of porcine preimplantation embryos[J]. Theriogenology, 2025, 234, 216- 224. |
| 7 | VASUDEVAN S , KAMAT M M , WALUSIMBI S S , et al. Effects of early pregnancy on uterine lymphocytes and endometrial expression of immune-regulatory molecules in dairy heifers†[J]. Biol Reprod, 2017, 97 (1): 104- 118. |
| 8 | DE OLIVEIRA E B , MONTEIRO H F , PEREIRA J M V , et al. Changes in uterine metabolome associated with metritis development and cure in lactating Holstein cows[J]. Metabolites, 2023, 13 (11): 1156. |
| 9 | JIANG H B , BAO J , XING Y N , et al. Metabolomic and metagenomic analyses of the Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis after challenge with Metschnikowia bicuspidata[J]. Front Microbiol, 2022, 13, 990737. |
| 10 | BOYLE J G , DAVIDSON D F , PERRY C G , et al. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of urinary free metanephrines, vanillyl mandelic Acid, and catecholamines and plasma catecholamines for diagnosis of pheochromocytoma[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2007, 92 (12): 4602- 4608. |
| 11 | YANG R H , LIU B J , YANG M Y , et al. Lumiflavin reduces cisplatin resistance in cancer stem-like cells of OVCAR-3 cell line by inducing differentiation[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12, 859275. |
| 12 | KALE H , HARIKUMAR P , KULKARNI S B , et al. Assessment of the genotoxic potential of riboflavin and lumiflavin. A. Effect of light[J]. Mutat Res, 1992, 298 (1): 17- 23. |
| 13 | MARTINEZ C A , RIZOS D , RODRIGUEZ-MARTINEZ H , et al. Oocyte-cumulus cells crosstalk: New comparative insights[J]. Theriogenology, 2023, 205, 87- 93. |
| 14 | GAO L , ZHANG C , ZHENG Y , et al. Glycine regulates lipid peroxidation promoting porcine oocyte maturation and early embryonic development[J]. J Anim Sci, 2023, 101, skac425. |
| 15 | WU G , BAZER F W , SATTERFIELD M C , et al. Impacts of arginine nutrition on embryonic and fetal development in mammals[J]. Amino Acids, 2013, 45 (2): 241- 256. |
| 16 | LI X , BAZER F W , GAO H , et al. Amino acids and gaseous signaling[J]. Amino Acids, 2009, 37 (1): 65- 78. |
| 17 | 黄祝. 小鼠围着床期子宫中精氨酸琥珀酸合成酶1的表达调节和功能[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2012. |
| HUANG Z. Expression regulation and function of argininosuccinate synthetase 1 in mouse uterus during peri implantation[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2012. (in Chinese) | |
| 18 | BALERCIA G , MORETTI S , VIGNINI A , et al. Role of nitric oxide concentrations on human sperm motility[J]. J Androl, 2004, 25 (2): 245- 249. |
| 19 | DUTTA S , SENGUPTA P . The role of nitric oxide on male and female reproduction[J]. Malays J Med Sci, 2022, 29 (2): 18- 30. |
| 20 | LEFÈVRE PAVINE L C , MARIE-FRANCE P , MURPHY B D . Polyamines on the reproductive landscape[J]. Endocr Rev, 2011 (5): 694- 712. |
| 21 | LI Z , YUE Z , AO Z , et al. Maternal dietary supplementation of arginine increases the ratio of total cloned piglets born to total transferred cloned embryos by improving the pregnancy rate of recipient sows[J]. Anim Reprod Sci, 2018, 196, 211- 218. |
| 22 | PETRUJKI B T , EFER D S , JOVANOVI I B , et al. Effects of commercial selenium products on glutathione peroxidase activity and semen quality in stud boars[J]. Anim Feed Sci Technol, 2014, 197, 194- 205. |
| 23 | LIU N , SUN S , WANG P , et al. The Mechanism of Secretion and Metabolism of Gut-Derived 5-Hydroxytryptamine[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22 (15): 7931. |
| 24 | WANG G , YAO S , LIANG X , et al. Detection of the metabolites of human plasma and follicular fluid in IVF-ET with microextraction and LC-TOF-MS[J]. Technol Health Care, 2015, 1 (s1): 29- 36. |
| 25 | DOE J E . Ethylene glycol monoethyl ether (2-ethoxyethanol)[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 1984, 57, 33- 41. |
| 26 | PEREZ M J , VELASCO E , MONTE M J , et al. Maternal ethanol consumption during pregnancy enhances bile acid-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in fetal rat liver[J]. Toxicology, 2006, 225 (2-3): 183- 194. |
| 27 | LEROY J L M R , VANHOLDER T , MATEUSEN B , et al. Non-esterified fatty acids in follicular fluid of dairy cows and their effect on developmental capacity of bovine oocytes in vitro[J]. Reproduction, 2005, 130 (4): 485- 495. |
| 28 | MIRABI P , CHAICHI M J , ESMAEILZADEH S , et al. The role of fatty acids on ICSI outcomes: a prospective cohort study[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2017, 16 (1): 18. |
| 29 | LIU S , SHARP A , VILLANUEVA E , et al. Breast Milk Iodine Concentration (BMIC) as a biomarker of iodine status in lactating women and children < 2 years of age: a systematic review[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14 (9): 1691. |
| 30 | PATEL A , PATEL S , PATEL P , et al. Salivary exosomal miRNA-1307-5p predicts disease aggressiveness and poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (18): 10639. |
| 31 | 王梦晓, 罗珂珂, 高文雅, 等. 基于非靶向尿液代谢组学技术的毛蕊花糖苷治疗嘌呤霉素氨基核苷肾病幼龄大鼠相关生物标志物研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2023, 48 (21): 5898- 5907. |
| WANG M X , LUO K K , GAO W Y , et al. Study on biomarkers of verbascoside in the treatment of puromycin aminonucleoside nephropathy in young rats based on non targeted urine metabolomics technology[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2023, 48 (21): 5898- 5907. | |
| 32 | 闫坤, 高黎明, 高正兴, 等. 唾液小细胞外囊泡novel-100作为母猪早期妊娠诊断候选生物标志物的研究[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2025, 61 (1): 299-304, 310. |
| YAN K , GAO L M , GAO Z X , et al. Study on salivary small extracellular vesicle novel-100 as a candidate biomarker for early pregnancy diagnosis in sows[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2025, 61 (1): 299-304, 310. | |
| 33 | VELEK K, MICHAUD S, BOUCHER K, 等. 爱德士牛怀孕检测[C]//中国奶业协会第26次繁殖学术年会暨国家肉牛牦牛/奶牛产业技术体系第3届全国牛病防治学术研讨会论文集. 兰州, 2011: 140-143. |
| VELEK K, MICHAUD S, BOUCHER K, et al. IDEXX cattle pregnancy test[C]//Proceedings of the26th Annual Conference of Breeding of China Dairy Association and the 3rd National Symposium on Cattle Disease Prevention and Control of National Beef Cattle, Yak/Dairy Cattle Industry Technology System. Lanzhou, 2011: 140-143. (in Chinese) | |
| 34 | KUMAR R , ALI S A , SINGH S K , et al. Peptide profiling in cow urine reveals molecular signature of physiology-driven pathways and in-silico predicted bioactive properties[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11 (1): 12427. |
| [1] | 孟祥旭, 李佳, 任德明, 陈奎蓉, 和艺云, 王立贤, 盛熙晖, 王立刚. 民猪猪繁殖与呼吸综合征恢复力高低组血清代谢组学研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(4): 1689-1699. |
| [2] | 王昕昕, 刘小英, 王宜, 王芳, 赵晗, 杜志强, 杨彩侠. 急性热应激通过降低牛磺酸水平影响猪睾丸支持细胞的功能[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2025, 56(4): 1779-1790. |
| [3] | 郭子骄, 郑伟杰, 孙伟, 吴宝江, 包向男, 张琪, 贺巾锋, 包斯琴, 赵高平, 王子馨, 韩博, 李喜和, 孙东晓. 荷斯坦奶牛胚胎基因组遗传评估研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(7): 2940-2950. |
| [4] | 王中波, 刘爽, 贺丽霞, 冯雪, 杨梦丽, 汪书哲, 刘源, 冯兰, 丁晓玲, 冀国尚, 杨润军, 张路培, 马云. 固原黄牛不同部位肌肉组织代谢组学分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(4): 1565-1578. |
| [5] | 张馨蕊, 付予, 杨卓, 沈文娟, 陶金忠. 奶牛早期妊娠诊断蛋白的研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(2): 451-460. |
| [6] | 张志飞, 唐雪颖, 闵力, 童雄, 陈卫东, 巨向红, 李大刚. 荷斯坦奶牛肝脏组织中与泌乳时期及繁殖力相关的基因共表达网络构建[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2024, 55(2): 528-539. |
| [7] | 张兆博, 侯黎明, 李平华, 杜陶然, 王中宇, 吴承武, 黄瑞华. 基于血浆代谢组学筛选日粮纤维影响二花脸猪肉质性状的候选代谢物[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(9): 3758-3769. |
| [8] | 王芮杰, 洪志楷, 董英娇, 陈瑶, 王晋宇, 王冠华. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS代谢组学研究土霉素和穿心莲内酯对鸡代谢的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(7): 3078-3090. |
| [9] | 张琰, 刘佳悦, 吴梅金, 周家豪, 刁洪秀. 非编码RNA作为犬肿瘤潜在生物标志物的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(6): 2264-2271. |
| [10] | 曾成容, 王娜, 毕文文, 梅世慧, 何广霞, 张峻杰, 陈泽, 文明, 周碧君. A型产气荚膜梭菌感染鸭回肠代谢组学分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(6): 2555-2569. |
| [11] | 郭灵君, 朱瑞, 罗怡茜, 张芝金, 张余蓬, 张德志, 李前勇. 山羊慢性酒糟中毒血液代谢物分析及乙醇中毒通路关键基因mRNA转录水平变化[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(4): 1751-1765. |
| [12] | 杨洋, 周子薇, 张京一, 杨硕, 王博宇, 葛楠, 林叶, 侯晓明. 奶牛SP1基因结构及对乳脂合成功能的初步分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53(9): 2970-2981. |
| [13] | 刘旺景, 唐德富, 敖长金. 沙葱及其提取物对舍饲肉羊肾周脂肪膻味物质代谢组特征的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53(9): 3029-3041. |
| [14] | 孙娜, 曹志刚, 张华, 王弘, 孙盼盼, 孙耀贵, 范阔海, 尹伟, 李宏全. 苦参碱对昆明小鼠粪便及血浆代谢物的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53(7): 2364-2379. |
| [15] | 王影, 文亮, 母童, 冯小芳, 刘佳敏, 张娟, 温万, 顾亚玲. 荷斯坦牛高、低乳脂率牛乳代谢组分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53(5): 1396-1408. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
