





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (11): 5770-5777.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.11.034
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
XIONG Yaoyu1,2( ), LIU Dan1(
), LIU Dan1( ), GAO Jianshuai1, LI Huitong1, ZHANG Boyuan1, DING Jiabo1, JIANG Hui1, FAN Xuezheng1, SHEN Qingchun1,*(
), GAO Jianshuai1, LI Huitong1, ZHANG Boyuan1, DING Jiabo1, JIANG Hui1, FAN Xuezheng1, SHEN Qingchun1,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-06
Online:2025-11-23
Published:2025-11-27
Contact:
SHEN Qingchun
E-mail:616203596@qq.com;1465512558@qq.com;shenqingchun@caas.cn
CLC Number:
XIONG Yaoyu, LIU Dan, GAO Jianshuai, LI Huitong, ZHANG Boyuan, DING Jiabo, JIANG Hui, FAN Xuezheng, SHEN Qingchun. Preparation of N-protein Gene Armor RNA Control for Infectious Bronchitis Virus Nucleic Acid Detection[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5770-5777.
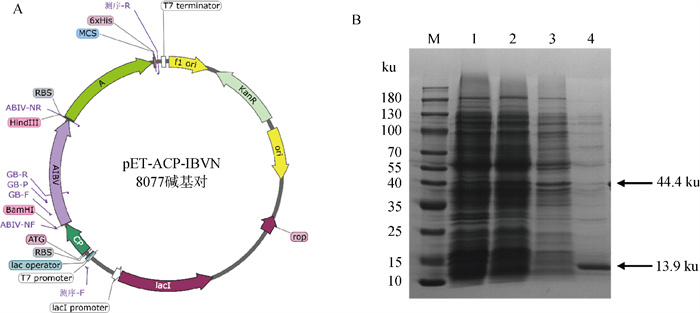
Fig. 1
Vector construction model and SDS-PAGE purification diagram A. Vector construction model; B. SDS-PAGE purification diagram: M. Protein ladder; 1. Empty vector after induction; 2. Ultrasonic crushing supernatant; 3. Ammonium sulfate precipitate supernatant; 4. Molecular sieve purification supernatant"
| 1 |
NIIT,ISOBEN,YOSHIMURAY.Effects of Avian infectious bronchitis virus antigen on eggshell formation and immunoreaction in hen oviduct[J].Theriogenology,2014,81(8):1129-1138.
doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2014.02.002 |
| 2 |
BOLTZD A,ZIMMERMANC R,NAKAIM,et al.Epididymal stone formation and decreased sperm production in roosters vaccinated with a killed strain of Avian infectious bronchitis virus[J].Avian Dis,2006,50(4):594-598.
doi: 10.1637/7654-052506R.1 |
| 3 | BANDEF,ARSHADS S,OMARA R,et al.Pathogenesis and diagnostic approaches of Avian infectious bronchitis[J].Adv Virol,2016,2016,4621659. |
| 4 | 刘胜旺.我国鸡传染性支气管炎流行现状及原因分析[J].中国家禽,2010,32(16):5-9. |
| LIUS W.Epidemic status and causes of infectious bronchitis in chickens in China[J].China Poultry,2010,32(16):5-9. | |
| 5 |
WILLEM,HOLMESE C.Wild birds as reservoirs for diverse and abundant gamma-and deltacoronaviruses[J].FEMS Microbiol Rev,2020,44(5):631-644.
doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuaa026 |
| 6 |
RAFIQUES,JABEENZ,PERVAIZT,et al.Avian infectious bronchitis virus (AIBV) review by continent[J].Front Cell Infect Microbiol,2024,14,1325346.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1325346 |
| 7 | 周蛟.近年世界禽病流行现状[J].中国畜牧杂志,2007(16):2-7. |
| ZHOUJ.World epidemiological status of avian diseases in recent years[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Science,2007(16):2-7. | |
| 8 |
KHATABYK,FELLAHIS,LOUTFIC,et al.Avian infectious bronchitis virus in Africa: a review[J].Vet Q,2016,36(2):71-75.
doi: 10.1080/01652176.2015.1126869 |
| 9 | KONGX Q,WANGY J,FANGZ X,et al.False-positive results of SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR in oropharyngeal swabs from vaccinators[J].Front Med (Lausanne),2022,9,847407. |
| 10 | 李金明,宋如俊,王露楠,等.耐核糖核酸酶病毒样颗粒的构建和表达[J].中华检验医学杂志,2003(2):21-23, 64. |
| LIJ M,SONGR J,WANGL N,et al.Construction and expression of RNase-resistant virus-like particles[J].Chinese Journal of Laboratory Medicine,2003(2):21-23, 64. | |
| 11 |
PASLOSKEB L,WALKERPEACHC R,OBERMOELLERR D,et al.Armored RNA technology for production of ribonuclease-resistant viral RNA controls and standards[J].J Clin Microbiol,1998,36(12):3590-3594.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.36.12.3590-3594.1998 |
| 12 | 李朋霏,宋晓明,周保琨,等.用于非洲猪瘟病毒核酸检测的假病毒阳性对照品的制备和标定[J].中国畜牧兽医,2023,50(2):647-655. |
| LIP F,SONGX M,ZHOUB K,et al.Preparation and calibration of pseudovirus positive controls for nucleic acid detection of African swine fever virus[J].China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine,2023,50(2):647-655. | |
| 13 | 乔彩霞. H1和H3亚型流感病毒荧光RT-PCR及装甲RNA标准物质的研究和应用[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2014. |
| QIAO C X. Research and application of H1 and H3 subtype influenza viruses by fluorescence RT-PCR and armored RNA reference materials[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese) | |
| 14 |
WALKERPEACHC R,WINKLERM,DUBOISD B,et al.Ribonuclease-resistant RNA controls (armored RNA) for reverse transcription-PCR, branched DNA, and genotyping assays for hepatitis C virus[J].Clin Chem,1999,45(12):2079-2085.
doi: 10.1093/clinchem/45.12.2079 |
| 15 |
GONCHAROVAE A,DEDKOVV G,DOLGOVAA S,et al.One-step quantitative RT-PCR assay with armored RNA controls for detection of SARS-CoV-2[J].J Med Virol,2021,93(3):1694-1701.
doi: 10.1002/jmv.26540 |
| 16 | 刘帆,任广彩,闫圆圆,等.鸡传染性支气管炎病毒的分离鉴定及其致病性的研究[J].中国兽医科学,2019,49(7):861-870. |
| LIUF,RENG C,YANY Y,et al.Isolation, identification and pathogenicity of infectious bronchitis virus in chickens[J].Chinese Veterinary Science,2019,49(7):861-870. | |
| 17 |
TANL,WENG,YUANY,et al.Development of a recombinant thermostable Newcastle disease virus (NDV) vaccine express infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) multiple epitopes for protecting against IBV and NDV challenges[J].Vaccines (Basel),2020,8(4):564.
doi: 10.3390/vaccines8040564 |
| 18 | 赵史宇辰,汤思淇,冯亚莉,等.病毒检测方法研究进展[J].中国畜牧兽医,2023,50(11):4536-4544. |
| ZHAOS Y C,TANGS Q,FENGY L,et al.Research progress on virus detection methods[J].China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine,2023,50(11):4536-4544. | |
| 19 |
STORCHG A.Diagnostic virology[J].Clin Infect Dis,2000,31(3):739-751.
doi: 10.1086/314015 |
| 20 | 夏立业.鸡传染性支气管炎诊断方法的研究进展[J].家禽科学,2023,45(8):70-73. |
| XIAL Y.Research progress on diagnostic methods for infectious bronchitis in chickens[J].China Poultry Science,2023,45(8):70-73. | |
| 21 | 温和心,龙英全,蒋荣华,等.RNA病毒质控物研究进展[J].动物医学进展,2013,34(1):97-101. |
| WENH X,LONGY Y,JIANGR H,et al.Research progress on RNA virus quality controls[J].Progress in Veterinary Medicine,2013,34(1):97-101. | |
| 22 |
XIAY,LIUK,WANGF,et al.Self-assembled virus-like particle vaccines via fluorophilic interactions enable infection mimicry and immune protection[J].Adv Healthc Mater,2023,12(32):e2301647.
doi: 10.1002/adhm.202301647 |
| 23 |
ARGETSINGERJ E,GUSSING N.Intact ribonucleic acid from defective particles of bacteriophage R17[J].J Mol Biol,1966,21(3):421-434.
doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90016-7 |
| 24 |
ZHANS,LIJ,XUR,et al.Armored long RNA controls or standards for branched DNA assay for detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1[J].J Clin Microbiol,2009,47(8):2571-2576.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.00232-09 |
| 25 |
WEIY,YANGC,WEIB,et al.RNase-resistant virus-like particles containing long chimeric RNA sequences produced by two-plasmid coexpression system[J].J Clin Microbiol,2008,46(5):1734-1740.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.02248-07 |
| 26 |
WEIB,WEIY,ZHANGK,et al.Construction of armored RNA containing long-size chimeric RNA by increasing the number and affinity of the pac site in exogenous RNA and sequence coding coat protein of the MS2 bacteriophage[J].Intervirology,2008,51(2):144-150.
doi: 10.1159/000141707 |
| 27 |
NASKALSKAA,HEDDLEJ G.Virus-like particles derived from bacteriophage MS2 as antigen scaffolds and RNA protective shells[J].Nanomedicine (Lond),2024,19(12):1103-1115.
doi: 10.2217/nnm-2023-0362 |
| [1] | ZHAO Jingyu, LI Dan, ZHANG Bing, ZHANG Qianyi, ZHANG Jinhua, SONG Yafen, YANG Chenghuai. Genome Sequencing and Pathogenicity Analysis of Infectious Bronchitis Virus M41 Strain [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3967-3975. |
| [2] | CHI Shunshun, WU Dan, WANG Nan, WANG Wanjie, NIE Yuxin, MU Yulian, LIU Zhiguo, ZHU Zhendong, LI Kui. Establishment and Application of A Detection Method for MSTN Gene-Edited Pigs Based on RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3734-3748. |
| [3] | GUO Sen, LI Huixin, HAN Zongxi, SUN Junfeng, XIA Changyou. Expression and Immunogenicity Analysis of the Fusion Protein Composed of IBV S1 Protein Neutralizing Epitope and Avian IgY Fc Fragment [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5758-5769. |
| [4] | Lu FENG, Hong TIAN, Haixue ZHENG, Zhengwang SHI, Juncong LUO, Xiaoyang ZHANG, Juanjuan WEI, Jing ZHOU, Huancheng LIAO, Wanying WANG. A Detection Method of African Swine Fever Virus based on Enzymatic Recombinase Amplification [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4226-4231. |
| [5] | XIONG Ting, HE Xianming, ZHAO Xiya, ZHUANG Tingting, HUANG Meizhen, LIANG Shijin, YU Chuanzhao, LIANG Xuejing, CHEN Ruiai. Whole Genome Analysis of Three Predominant Epidemic Strains of Chicken Infectious Bronchitis Virus and Their Pathogenicity [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2109-2122. |
| [6] | HUANG Jian, LIU Yunjia, YANG Xiaonong, LI Yan. RPA-Cas12a-LFD Based Nucleic Acid Detection for Feline Herpesvirus-1 and Preliminary Application [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(5): 1638-1643. |
| [7] | FAN Wensheng, ZHU Dan, ZHANG Yu, LIAO Jianqi, WANG Lu, YONG Lu, WEI Ping, MO Meilan. Prediction, Identification and Preliminary Study on Immune Efficacy of S1 Protein Epitope-polypeptides of Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(9): 2257-2264. |
| [8] | XU Lu, ZHANG Qianyi, XIA Yingju, WANG Zhen, LI Cui, ZOU Xingqi, WANG Qin, ZHAO Qizu. Result Analysis of National Proficiency Testing Program for the Detection of Classical Swine Fever Virus Nucleic Acid [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(8): 1949-1955. |
| [9] | DING Xue,ZHANG Xing-yi,HAO Xiao-yan,WANG Xiao-fan,XUE Shi-chong,WANG Ming-jun,LI Zhong-yu,ZHANG Yong-gen,XIN Hang-shu. Protein Molecular Structure in Relation to Protein Nutritive Values at Different Sections of Corn Stover [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2016, 47(8): 1592-1600. |
| [10] | ZHU Feng-zhu,LU Mei,HUANG Qing-hua,YANG Shao-hua1,HUANG Yan-yan,WU Jia-qiang,TAN Liu-gang,ZHANG Xiu-mei,CUI Yan-shun,XU Chuan-tian . Identification of the MHC Class Ⅰ-restricted Cytotoxic T Cell Epitope in Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus S1 Protein [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2016, 47(3): 559-565. |
| [11] | WEN Gui-lan ZHANG Han-song, HU Hong-xia, ZHANG Xian, ZHANG Yi, WANG Xiao-du, LI Xiao-liang, FANG Wei-huan. Analysis of Nsp2 Expression in Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Infected Cells [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2013, 44(7): 1109-1116. |
| [12] | MO Mei-lan;LI Meng;WEI Ping;FAN Wen-sheng;HUANG Bai-cheng;LANG Ya-hui;CHEN Qiu-ying;HOU Jin-lian;WEI Tian-chao. Genetic Variations of Main Structural Genes of Infectious Bronchitis Virus Strains Isolated in Guangxi Province of China [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2010, 41(9): 1138-1146. |
| [13] | LIU Xing-you;HE Hong-xuan;YAO Si-xin;CHEN De-sheng;GAN Meng-hou;CHEN Pu-yan. Studies on the Character of Infectious Bronchitis Virus of TJ9602 Strain,HN9604 Strain and BJ9601 Strain Isolated from China [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2005, 36(12): 1323-1328. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||