





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 1791-1801.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.04.027
• Animal Nutrition and Feeds • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Suchen1( ), LU Tingting1, CHEN Junguang4, MIAO Hui1,2, MAO Haiguang3, HAN Xinyan1,2,*(
), LU Tingting1, CHEN Junguang4, MIAO Hui1,2, MAO Haiguang3, HAN Xinyan1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-06-03
Online:2025-04-23
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
HAN Xinyan
E-mail:lsc1207520@163.com;xyhan@zju.edu.cn
CLC Number:
LI Suchen, LU Tingting, CHEN Junguang, MIAO Hui, MAO Haiguang, HAN Xinyan. Changes of Rectum Microbiota and Virome before and after Weaning and Their Interactions of Chalu Black Pigs[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1791-1801.
Table 1
Composition and nutrient level of creep feed and nursery feed (dry matter) %"
| 饲粮组成 Diet composition | 教槽料 Creep feed | 保育料 Nursery feed | 营养水平2) Nutrient level2) | 教槽料 Creep feed | 保育料Nursery feed | |
| 玉米Corn | 16.5 | 35.4 | 消化能/(MJ·kg-1) DE | 14.18 | 14.23 | |
| 膨化玉米Extruded corn | - | 12.0 | 粗蛋白CP | 19.20 | 18.30 | |
| 豆粕Soybean meal | - | 8.0 | 粗灰分Ash | 4.60 | 4.90 | |
| 膨化大豆Expanded soybean | 8.0 | 11.5 | 钙Ca | 0.70 | 0.71 | |
| 大豆浓缩蛋白Soy protein concentrate | 6.5 | - | 总磷P | 0.62 | 0.61 | |
| 发酵豆粕Fermented soybean meal | 7.0 | 2.0 | 赖氨酸Lys | 1.75 | 1.75 | |
| 碎米Broken rice | 6.0 | 5.0 | 蛋氨酸Met | 1.35 | 1.35 | |
| 米皮糠Rice husk | 5.0 | 6.0 | ||||
| 面粉Flour | 17.0 | 0.0 | ||||
| 乳清粉Dried whey | 14.0 | 7.0 | ||||
| 糖Sugar | 4.0 | 0.0 | ||||
| 鱼粉Fish meal | 3.0 | 3.0 | ||||
| 大豆油Soybean oil | 4.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| 麸皮Bran | 4.0 | 4.0 | ||||
| 石粉Limestone | 0.5 | 0.6 | ||||
| 磷酸氢钙CaHPO3 | 0.5 | 0.5 | ||||
| 赖氨酸Lys | 1.6 | 1.6 | ||||
| 蛋氨酸Met | 1.2 | 1.2 | ||||
| 复合预混料1)Compound premix1) | 7.00 | 4.00 | ||||
| 复合酶制剂Complex enzyme preparation | 0.2 | 0.2 | ||||
| 总量Total | 100.0 | 100.0 |
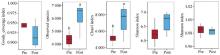
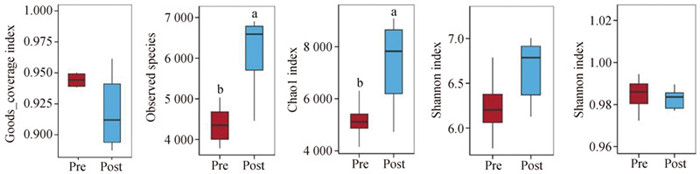
Fig. 2
α diversity of rectum microbiota Goods_coverage is the microbial coverage, Observed species is the species richness, Chao1 index is the Chao1 index, Shannon index is the Shannon index, and Simpson index is the Simpson index, and different lower case letters indicate significant differences, the same as below"
| 1 |
GUEVARRA R B , LEE J H , LEE S H , et al. Piglet gut microbial shifts early in life: causes and effects[J]. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 2019, 10, 1.
doi: 10.1186/s40104-018-0308-3 |
| 2 |
DING S J , CHENG Y T , AZAD M A K , et al. Developmental changes of immunity and different responses to weaning stress of Chinese indigenous piglets and Duroc piglets during suckling and weaning periods[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (24): 15781.
doi: 10.3390/ijms232415781 |
| 3 | 吕玉华, 何孟纤, 徐皆欢, 等. 冷冻精液在岔路黑猪资源保护中的应用[J]. 上海畜牧兽医通讯, 2023 (6): 10-12, 17. |
| LÜ Y H , HE M X , XU J H , et al. Application of frozen semen in resource conservation of Chalu black pig[J]. Shanghai Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2023 (6): 10-12, 17. | |
| 4 |
NEURATH M F , ÜBERLA K , NG S C . Gut as viral reservoir: lessons from gut viromes, HIV and COVID-19[J]. Gut, 2021, 70 (9): 1605- 1608.
doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-324622 |
| 5 |
TIAMANI K , LUO S Q , SCHULZ S , et al. The role of virome in the gastrointestinal tract and beyond[J]. FEMS Microbiol Rev, 2022, 46 (6): fuac027.
doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuac027 |
| 6 |
CAO Z R , SUGIMURA N , BURGERMEISTER E , et al. The gut virome: a new microbiome component in health and disease[J]. eBioMedicine, 2022, 81, 104113.
doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104113 |
| 7 |
ROURA E , KOOPMANS S J , LALLÈS J P , et al. Critical review evaluating the pig as a model for human nutritional physiology[J]. Nutr Res Rev, 2016, 29 (1): 60- 90.
doi: 10.1017/S0954422416000020 |
| 8 |
WANG W L , HU H F , ZIJLSTRA R T , et al. Metagenomic reconstructions of gut microbial metabolism in weanling pigs[J]. Microbiome, 2019, 7 (1): 48.
doi: 10.1186/s40168-019-0662-1 |
| 9 | HU J , NIE Y F , CHEN J W , et al. Gradual changes of gut microbiota in weaned miniature piglets[J]. Front Microbiol, 2016, 7, 1727. |
| 10 |
LI Y , GUO Y , WEN Z S , et al. Weaning stress perturbs gut microbiome and its metabolic profile in piglets[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8 (1): 18068.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33649-8 |
| 11 |
HAN G G , LEE J Y , JIN G D , et al. Tracing of the fecal microbiota of commercial pigs at five growth stages from birth to shipment[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8 (1): 6012.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24508-7 |
| 12 |
WANG C , BAI J Y , CHEN X Y , et al. Gut microbiome-based strategies for host health and disease[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2024, 64 (19): 6834- 6849.
doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2176464 |
| 13 |
PAJARILLO E A B , CHAE J P , BALOLONG M P , et al. Assessment of fecal bacterial diversity among healthy piglets during the weaning transition[J]. J Gen Appl Microbiol, 2014, 60 (4): 140- 146.
doi: 10.2323/jgam.60.140 |
| 14 |
TURNBAUGH P J , LEY R E , MAHOWALD M A , et al. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest[J]. Nature, 2006, 444 (7122): 1027- 1031.
doi: 10.1038/nature05414 |
| 15 |
STOJANOV S , BERLEC A , ŠTRUKELJ B . The Influence of probiotics on the firmicutes/bacteroidetes ratio in the treatment of obesity and inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Microorganisms, 2020, 8 (11): 1715.
doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8111715 |
| 16 |
WEI X Y , BOTTOMS K A , STEIN H H , et al. Dietary organic acids modulate gut microbiota and improve growth performance of nursery pigs[J]. Microorganisms, 2021, 9 (1): 110.
doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9010110 |
| 17 |
GUEVARRA R B , HONG S H , CHO J H , et al. The dynamics of the piglet gut microbiome during the weaning transition in association with health and nutrition[J]. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 2018, 9, 54.
doi: 10.1186/s40104-018-0269-6 |
| 18 |
FENG T , WANG J . Oxidative stress tolerance and antioxidant capacity of lactic acid bacteria as probiotic: a systematic review[J]. Gut Microbes, 2020, 12 (1): 1801944.
doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1801944 |
| 19 |
CHEN L M , XU Y S , CHEN X Y , et al. The maturing development of gut microbiota in commercial piglets during the weaning transition[J]. Front Microbiol, 2017, 8, 1688.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01688 |
| 20 |
SALADRIGAS-GARCÍA M , D'ANGELO M , KO H L , et al. Understanding host-microbiota interactions in the commercial piglet around weaning[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11 (1): 23488.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02754-6 |
| 21 |
GRESSE R , CHAUCHEYRAS-DURAND F , FLEURY M A , et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in postweaning piglets: understanding the keys to health[J]. Trends Microbiol, 2017, 25 (10): 851- 873.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.05.004 |
| 22 |
TAO S Y , ZOU H C , LI J J , et al. Landscapes of enteric virome signatures in early-weaned piglets[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2022, 10 (4): e0169822.
doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01698-22 |
| 23 |
CHEN Q , ZHANG X J , SHI W L , et al. Longitudinal investigation of enteric virome signatures from parental-generation to offspring pigs[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2023, 11 (3): e0002323.
doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00023-23 |
| 24 |
JANSEN D , MATTHIJNSSENS J . The emerging role of the gut virome in health and inflammatory bowel disease: challenges, covariates and a viral imbalance[J]. Viruses, 2023, 15 (1): 173.
doi: 10.3390/v15010173 |
| 25 |
BAO S W , WANG H , LI W , et al. Viral metagenomics of the gut virome of diarrheal children with Rotavirus A infection[J]. Gut Microbes, 2023, 15 (1): 2234653.
doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2234653 |
| 26 |
TUN H M , PENG Y , MASSIMINO L , et al. Gut virome in inflammatory bowel disease and beyond[J]. Gut, 2024, 73 (2): 350- 360.
doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330001 |
| 27 |
NORMAN J M , HANDLEY S A , BALDRIDGE M T , et al. Disease-specific alterations in the enteric virome in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Cell, 2015, 160 (3): 447- 460.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.002 |
| 28 |
ZUO T , LU X J , ZHANG Y , et al. Gut mucosal virome alterations in ulcerative colitis[J]. Gut, 2019, 68 (7): 1169- 1179.
doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-318131 |
| 29 |
GOGOKHIA L , BUHRKE K , BELL R , et al. Expansion of bacteriophages is linked to aggravated intestinal inflammation and colitis[J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2019, 25 (2): 285- 299.
doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.01.008 |
| 30 |
SPINDELBOECK W , SCHULZ E , UHL B , et al. Repeated fecal microbiota transplantations attenuate diarrhea and lead to sustained changes in the fecal microbiota in acute, refractory gastrointestinal graft-versus-host-disease[J]. Haematologica, 2017, 102 (5): e210- e213.
doi: 10.3324/haematol.2016.154351 |
| 31 |
ZHANG F , ZUO T , YEOH Y K , et al. Longitudinal dynamics of gut bacteriome, mycobiome and virome after fecal microbiota transplantation in graft-versus-host disease[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12 (1): 65.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20240-x |
| 32 | ZUO T , WONG S H , LAM K , et al. Bacteriophage transfer during faecal microbiota transplantation in Clostridium difficile infection is associated with treatment outcome[J]. Gut, 2018, 67 (4): 634- 643. |
| 33 |
LAM S , BAI X W , SHKOPOROV A N , et al. Roles of the gut virome and mycobiome in faecal microbiota transplantation[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 7 (5): 472- 484.
doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00303-4 |
| 34 |
MIRZAEI M K , MAURICE C F . Ménage à trois in the human gut: interactions between host, bacteria and phages[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2017, 15 (7): 397- 408.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2017.30 |
| 35 | 冀亚路. 腹泻断奶仔猪肠道噬菌体组特征及其相关耐药和裂解酶基因研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2023. |
| JI Y L. Study on the characteristics of intestinal phageome and its related drug resistance and lysin genes in weaned piglets with diarrhea[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 36 |
CANI P D , DEPOMMIER C , DERRIEN M , et al. Akkermansia muciniphila: paradigm for next-generation beneficial microorganisms[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 19 (10): 625- 637.
doi: 10.1038/s41575-022-00631-9 |
| [1] | Ting QING, Hehao OUYANG, Qicong PAN, Bibo ZHU, Jing YE, Shengbo CAO, Xiuyu WANG, Youhui SI. Application Progress in Flow Virometry [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 4840-4851. |
| [2] | Xiaoxiu ZHAN, Pengyu LIU, Xiao'e XIANG, Shengyong MAO, Wei JIN. Effects of Methanomassiliicoccus DZ1 on Serum Trimethylamine-N-oxide and Inflammatory Factors, Liver Antioxidant Capacity and Cecum Microbiota in Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4679-4689. |
| [3] | ZHAO Wei, Mahmoud M. Abdelsattar, CHAI Jianmin, WANG Xin, DIAO Qiyu, ZHANG Naifeng. Research Progress of Rumen Microbiota Transplantation and Its Application [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 1792-1803. |
| [4] | ZHANG Wenchang, WANG Zhihua, LIAN Jiale, QU Qian, LÜ Weijie, CHEN Shu'ai, GUO Shining. Supplement of Shenling Baizhu Powder to Offspring Rats during Sucking Improved Intestinal Dyshomeostasis Induced by Antibiotics [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(2): 825-836. |
| [5] | LIU Pan, LI Ruiqi, TAN Zhankun, WANG Yifei, CHEN Xiaochen, HE Weixian, DU Renrang, MA Jian, CHU Guiyan, CAI Chuanjiang. Effects of High Fiber Diet on Growth Performance, Meat Quality and Intestinal Microbiome of Growing-finishing Pigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(10): 4247-4259. |
| [6] | SUN Na, CAO Zhigang, ZHANG Hua, WANG Hong, SUN Panpan, SUN Yaogui, FAN Kuohai, YIN Wei, LI Hongquan. Effects of Matrine on Feces and Plasma Metabolites of Kunming Mice [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(7): 2364-2379. |
| [7] | NING Xinnuan, LI Jie, FANG Hui, YU Siyuan, LIANG Jiaxi, ZHANG Lu, JIN Yaping, ZHOU Dong. Effect of Assisted Calving on Postpartum Uterine Flora of Dairy Cow [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(12): 4501-4506. |
| [8] | DENG Wenwen, LI Caiwu, JIN Lei, LI Guo, WU Honglin, ZHANG Guiquan, WEI Rongping, CHEN Rui, WANG Minglei, HE Yongguo, LI Ti, LI Desheng, ZHANG Hemin, HUANG Yan, ZOU Likou. Transcriptome Analysis of Microbiome and Parasites in Feces of Giant Pandas [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(11): 2812-2824. |
| [9] | NIU Huaxin, CHANG Jie, HU Zongfu, WANG Yuxi. Research Progress on Rumen Microbiomes and Their Metabolic Functions in Ruminants Based on Omics Technology [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2019, 50(6): 1113-1122. |
| [10] | XIAO Hai-xia,TUOHUTI?Aji-de,SHI Guo-qing,ZHANG Li,LI Hai. Effects of Weaning Stress on Blood Serum Indices and Body Growth at Different Ages Foals [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2015, 46(11): 2010-2019. |
| [11] | HAN Ya-nan,YANG Chen-yu,WANG Zi-xu,CHEN Yao-xing,SUN Jia-yi,QIN Zhuo-ming,CAO Jing,DONG Yu-lan . Effects of Serotonin on Intestinal Antioxidative Function in the Stress-diarrheal Weaning ICR Mice [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2014, 45(12): 2067-2073. |
| [12] | ZHAO Hui-li, GAO Yan-xia, LI Jian-guo, LI Qiu-feng, CAO Yu-feng. Effect of Sodium Butyrate on Growth, Serum Biochemical Parameters and Gastrointestinal Development of Weaning Calves [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2013, 44(10): 1600-1608. |
| [13] | HE Biao, TU Chang-chun. The Advances and Applications of Viral Metagenomics [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2012, 43(12): 1865-1870. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||