





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 1366-1375.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.03.035
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
YU Xinya1( ), HE Haijian2, WANG Lei1, NI Yuchen1, DU Jing1, ZHOU Yingshan1, DONG Wanyu1,*(
), HE Haijian2, WANG Lei1, NI Yuchen1, DU Jing1, ZHOU Yingshan1, DONG Wanyu1,*( ), WANG Xiaodu1,*(
), WANG Xiaodu1,*( )
)
Received:2024-04-17
Online:2025-03-23
Published:2025-04-02
Contact:
DONG Wanyu, WANG Xiaodu
E-mail:1131440070@qq.com;wanyudong@zafu.edu.cn;xdwang@zafu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
YU Xinya, HE Haijian, WANG Lei, NI Yuchen, DU Jing, ZHOU Yingshan, DONG Wanyu, WANG Xiaodu. Effect of lncRNA 18850 on Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1366-1375.
Table 1
Sequences of lncRNA real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR primers"
| 基因 Gene | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequences(5′→3′) | 长度/bp Length(bp) |
| lncRNA 18850 | GTCCTGCCTCTTCTTTCCATAAG | 137 |
| GAGTTCCAAGTGGCTATCTACAA | ||
| CCN2 | TGGAAGAGAACATTAAGAAGGGCA | 190 |
| TCAGGGCACTTGAACTCCAC | ||
| TFPI2 | TGCCAACGTGACTCGCTATT | 141 |
| ATTGGCCTCAACCCTTTTGC | ||
| NOTCH3 | GGTGGAAGAGCTTATCGCCA | 166 |
| CAGAGGGGTTTCTTCCTTGCT | ||
| CXCL8 | AAACCACCGGAAGGAACCAT | 113 |
| GGCAAAACTGCACCTTCACA | ||
| PTN | TGTTCACCTAACTGCCGTAGCA | 101 |
| TGGTACTGTTGAGCCTGCAT | ||
| RRAD | GTATGGTGGGAGACGGATGG | 134 |
| GTCTGTCCACGACCATGAGG | ||
| ITGA7 | CAAGTATGAAGTCACGGTC | 133 |
| GTCCACATCCAGGTAGAG | ||
| GAPDH | GGATGCAGGGATGATGTTC | 374 |
| TGCACCACCAACTGCTTAG |

Fig. 1
Changes in lncRNA in Vero-E6 cells infected with PEDV A. lncRNA expression profiles at 24 hours post-PEDV infection; B. Number of differentially expressed lncRNAs at various time points; C. Top ten lncRNAs with significant differential expression; D. Venn plots of significantly changed lncRNAs at different time points; E. qPCR detection of lncRNA 18850 expression at different time points of PEDV infection. **. P < 0.01"


Fig. 2
Effect of lncRNA 18850 overexpression on PEDV replication in Vero-E6 cells A. Expression levels of lncRNA 18850 overexpression at different time points of; B. Effect of lncRNA 18850 overexpression on PEDV-induced CPE; C. indirect immunofluorescence detection of the effect of lncRNA 18850 overexpression on PEDV N protein expression; D. Western blot detection of PEDV N protein expression in cells overexpressing lncRNA 18850; E. Gray scale analysis of PEDV N protein expression in D plot; F. TCID50 determination of viral titers in PEDV-infected cells overexpressing lncRNA 18850; G. qPCR determination of viral RNA copy number in PEDV-infected cells overexpressing lncRNA 18850. *. P < 0.05; ***. P < 0.001"


Fig. 3
lncRNA 18850 regulates multiple signaling pathways and genes A. Differential gene expression profiles in Vero-E6 cells overexpressing lncRNA 18850; B. Heatmap analysis of the number of up-and down-regulated genes in lncRNA 18850 overexpressing Vero-E6 cells (P < 0.05); C. Volcano plot of differentially genes. Red indicates up-regulated significantly differentially expressed genes, blue indicates down-regulated significantly differentially expressed genes, and grey indicates non-significant genes; D. Changes in differentially expressed gene from transcriptome sequencing results; E. qPCR detection of changes in gene shown in D plot after overexpression of lncRNA 18850. NC represents the control group. *. P < 0.05; **. P < 0.01; ***. P < 0.001; ns. No significant difference."

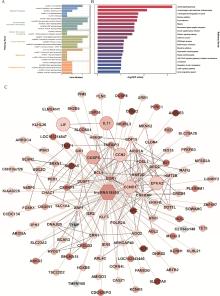
Fig. 4
Signaling pathways and genes regulated by lncRNA 18850 A. KEGG hierarchical bar chart. The horizontal coordinates represents the number of differential genes in each pathway, and the color indicates the KEGG level 1 classification; B. KEGG enrichment bar chart. The vertical coordinate is the pathway name and the horizontal coordinate is the-lg P from GO term enrichment analysis; C. Co-expression and trans relationships plot. Target genes were screened using Pearson correlation test and RIsearch-2.0. Red indicates up-regulated genes, blue indicates down-regulated genes, with darker colors indicating higher significance of differential expression, Grey solid lines indicate co-expression and trans relationship between the gene and lncRNA 18850, while black solid lines indicate protein interaction relationships between genes"

| 1 |
ZHANG H , ZOU C C , PENG O Y , et al. Global dynamics of porcine enteric coronavirus PEDV epidemiology, evolution, and transmission[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2023, 40 (3): msad052.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msad052 |
| 2 | 张志, 董雅琴, 刘爽, 等. 我国部分省份猪流行性腹泻的流行病学监测[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2014, 31 (10): 47- 51. |
| ZHANG Z , DONG Y Q , LIU S , et al. Survey and surveillance of porcine epidemic diarrhea in some provinces in China[J]. China Animal Health Inspection, 2014, 31 (10): 47- 51. | |
| 3 |
CESANA M , CACCHIARELLI D , LEGNINI I , et al. A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA[J]. Cell, 2011, 147 (2): 358- 369.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.028 |
| 4 |
HUSSEN B M , AZIMI T , HIDAYAT H J , et al. NF-KappaB interacting lncRNA: review of its roles in neoplastic and non-neoplastic conditions[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 139, 111604.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111604 |
| 5 | LI X D , GUO G J , LU M , et al. Long noncoding RNA lnc-Mxa inhibits beta interferon transcription by forming RNA-DNA triplexes at its promoter[J]. J Virol, 2019, 93 (21): e00786- 19. |
| 6 |
WANG J , WANG Y J , ZHOU R , et al. Host long noncoding RNA lncRNA-PAAN regulates the replication of influenza a virus[J]. Viruses, 2018, 10 (6): 330.
doi: 10.3390/v10060330 |
| 7 |
WANG J , CEN S . Roles of lncRNAs in influenza virus infection[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect, 2020, 9 (1): 1407- 1414.
doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1778429 |
| 8 |
QIN W J , QI X Y , XIE Y X , et al. LncRNA446 regulates tight junctions by inhibiting the ubiquitinated degradation of Alix after porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection[J]. J Virol, 2023, 97 (3): e0188422.
doi: 10.1128/jvi.01884-22 |
| 9 |
YIN Y F , YAN P X , LU J L , et al. Opposing roles for the lncRNA haunt and its genomic locus in regulating HOXA gene activation during embryonic stem cell differentiation[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2015, 16 (5): 504- 516.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.03.007 |
| 10 |
ALI T , GROTE P . Beyond the RNA-dependent function of LncRNA genes[J]. eLife, 2020, 9, e60583.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.60583 |
| 11 | GUITO J , LUKAC D M . KSHV Rta promoter specification and viral reactivation[J]. Front Microbiol, 2012, 3, 30. |
| 12 |
CHEN L L , ZHOU Y , LI H J . LncRNA, miRNA and lncRNA-miRNA interaction in viral infection[J]. Virus Res, 2018, 257, 25- 32.
doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2018.08.018 |
| 13 |
HU B X , HUO Y X , YANG L P , et al. ZIKV infection effects changes in gene splicing, isoform composition and lncRNA expression in human neural progenitor cells[J]. Virol J, 2017, 14 (1): 217.
doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0882-6 |
| 14 |
PARK J , PARK M Y , KIM Y , et al. Apelin as a new therapeutic target for COVID-19 treatment[J]. QJM, 2023, 116 (3): 197- 204.
doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcac229 |
| 15 |
ZAYKOV V , CHAQOUR B . The CCN2/CTGF interactome: an approach to understanding the versatility of CCN2/CTGF molecular activities[J]. J Cell Commun Signal, 2021, 15 (4): 567- 580.
doi: 10.1007/s12079-021-00650-2 |
| 16 |
KUBOTA S , TAKIGAWA M . Cellular and molecular actions of CCN2/CTGF and its role under physiological and pathological conditions[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2015, 128 (3): 181- 196.
doi: 10.1042/CS20140264 |
| 17 |
PARK I B , CHUN T . Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) non-structural protein (NSP)1 transcriptionally inhibits CCN1 and CCN2 expression by blocking ERK-AP-1 axis in pig macrophages in vitro[J]. Res Vet Sci, 2020, 132, 462- 465.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2020.07.029 |
| 18 |
ABDEL WAHAB N , WESTON B S , MASON R M . Modulation of the TGFβ/Smad signaling pathway in mesangial cells by CTGF/CCN2[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2005, 307 (2): 305- 314.
doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.03.022 |
| 19 |
WANG W B , CHEN J Z , HU D W , et al. SARS-CoV-2 N protein induces acute kidney injury via Smad3-dependent g1 cell cycle arrest mechanism[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2022, 9 (3): 2103248.
doi: 10.1002/advs.202103248 |
| 20 |
HE D , WANG D , LU P , et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals heterogeneous tumor and immune cell populations in early-stage lung adenocarcinomas harboring EGFR mutations[J]. Oncogene, 2021, 40 (2): 355- 368.
doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01528-0 |
| 21 |
NICOLA N A , BABON J J . Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF)[J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2015, 26 (5): 533- 544.
doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.07.001 |
| 22 |
XIONG W J , CHEN Y H , ZHANG C T , et al. Pharmacologic inhibition of IL11/STAT3 signaling increases MHC-I expression and T cell infiltration[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21 (1): 416.
doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04079-6 |
| 23 | WU Z P , XU L H , HE Y Z , et al. DUSP5 suppresses interleukin-1β-induced chondrocyte inflammation and ameliorates osteoarthritis in rats[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2020, 12 (24): 26029- 26046. |
| 24 | 黄国平, 袁青, 叶迎春, 等. 屋尘螨提取物激活气道上皮细胞EphA2-STAT3/p38 MAPK信号通路介导气道炎症[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2021, 37 (1): 31- 38. |
| HUANG G P , YUAN Q , YE Y C , et al. House dust mite extract activates EphA2-STAT3/p38 MAPK signaling pathway in airway epithelial cells to mediate airway inflammation[J]. Chinese Journal of Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 2021, 37 (1): 31- 38. | |
| 25 |
MA X W , ZHANG Y Z , GOU D Y , et al. Metabolic reprogramming of microglia enhances proinflammatory cytokine release through EphA2/p38 MAPK pathway in alzheimer's disease[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2022, 88 (2): 771- 785.
doi: 10.3233/JAD-220227 |
| 26 |
YANG R C , DUAN C H , ZHANG S , et al. Prolactin regulates ovine ovarian granulosa cell apoptosis by affecting the expression of MAPK12 gene[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (12): 10269.
doi: 10.3390/ijms241210269 |
| 27 |
XUE M , ZHAO J , YING L , et al. IL-22 suppresses the infection of porcine enteric coronaviruses and rotavirus by activating STAT3 signal pathway[J]. Antiviral Res, 2017, 142, 68- 75.
doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.03.006 |
| 28 |
ZHENG H Q , XU L , LIU Y Z , et al. MicroRNA-221-5p inhibits porcine epidemic diarrhea virus replication by targeting genomic viral RNA and activating the NF-κB pathway[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19 (11): 3381.
doi: 10.3390/ijms19113381 |
| 29 |
DING L , XU X G , HUANG Y , et al. Transmissible gastroenteritis virus infection induces apoptosis through FasL- and mitochondria-mediated pathways[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2012, 158 (1-2): 12- 22.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.01.017 |
| 30 | 陈昭. 猪流行性腹泻病毒诱导IPEC-J2细胞凋亡发生的分子机制[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2023. |
| CHEN Z. Molecular mechanisms underlying porcine epidemic diarrhea virus-induced apoptosis in IPEC-J2 cells[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese) | |
| 31 | CHU H , HOU Y X , YANG D , et al. Coronaviruses exploit a host cysteine-aspartic protease for replication[J]. Nature, 2022, 609 (7928): 785- 792. |
| [1] | WU Peiling, LI Yixuan, WANG Haojie, LI Yafei, LIU Shaomeng, LIU Qingyun, WANG Xiangru. Research Progress of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Vaccine for Pigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1042-1058. |
| [2] | CHEN Qiong, MAO Shuaixiang, WU Longfei, YANG Chuang, SUN Baoli. lncRNA Expression Characteristics in Semitendinosus Muscle of Leiqiong Cattle and Lufeng Cattle and Its ceRNA Network Analysis in Skeletal Muscle Development and Fat Deposition [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1203-1215. |
| [3] | YANG Yang, LI Liangyuan, WAN Pengcheng, LU Shouliang, LIU Changbin, YANG Hua, WANG Limin, DAI Rong, ZHOU Ping. Screening and Analysis of Core Genes and Key lncRNAs for Seasonal Estrus Traits in Sheep [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(3): 1264-1277. |
| [4] | LU Jian, MA Meng, GUO Jun, WANG Xingguo, DOU Taocun, HU Yuping, WANG Qiang, LI Yongfeng, SHAO Dan, TONG Haibing, GUO Jie, QU Liang. Studies on Key Genes and Signaling Pathways of Regulation of Energy Restriction during Rearing and Conversion to Ad libitum on the Reproductive Organ Development of Hens at the Initiation of Laying Period [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 737-754. |
| [5] | ZHANG Dongxuan, WANG Zhihao, QIAO Yan, ZHAO Xiaoxiao, FAN Songjie, ZHANG Chao. Prokaryotic Expression of S1 Protein in Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and Screening of Its Aptamers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 839-850. |
| [6] | Weizhe LIU, Chenggang LUO, Rong YUAN, Yijie LIAO, Yimin WEN, Ying SUN, Enbo YU, Sanjie CAO, Xiaobo HUANG. Isolation and Identification of a Highly Pathogenic Strain of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3049-3063. |
| [7] | Dongliang LI, Guanmin ZHENG, Shuai LI, Hongsen ZHU, Chao WU. Differential Expression of Transcriptome in Jejunal of Piglets Infected with Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2652-2661. |
| [8] | Yan ZHANG, Meijin WU, Jiahao ZHOU, Hongxiu DIAO. The Effect of Doxorubicin Treatment on the Differential Expression of lncRNAs in Canine Mammary Tumor CHMp Cell Line [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2716-2726. |
| [9] | WANG Jing, ZHANG Shujuan, HU Xia, LIU Xiangyang, ZHANG Xingcui, SONG Zhenhui. CD44 Regulates Na+/H+ Exchanger 3 Activity by Influencing Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2176-2185. |
| [10] | HU Zeqi, LI Runcheng, TAN Zuming, XIE Xiuyan, WANG Jiangping, QIN Lejuan, LI Rong, GE Meng. Establishment and Preliminary Application of PEDV, PoRVA and PDCoV TaqMan Triple RT-qPCR Assay [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2267-2272. |
| [11] | LIN Lili, ZHANG Mengdi, ZHU Linlin, MA Hailong, SUN Qi, HE Qigai, ZHANG Mengjia, LI Wentao. Establishment of Neutralizing Antibody Detection Method based on Recombinant Fluorescent Virus of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus GⅡb Strain [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1649-1660. |
| [12] | REN Lixin, ZHANG Jingyi, XU Shasha, YANG Liu, ZHANG Xingcui, SONG Zhenhui. Effect of ACE2 on Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells Infected with Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1238-1248. |
| [13] | LIU Yangguang, ZHANG Huibin, WEN Haoyu, XIE Fan, ZHAO Shiming, DING Yueyun, ZHENG Xianrui, YIN Zongjun, ZHANG Xiaodong. SNP/Indel Screening Analysis of Porcine Ovarian Granulosa Cells Treated with Follicular Fluid Exosomes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 576-586. |
| [14] | Shuang XU, Juan DU, Kaiyi ZHANG, Jiakun MIAO, Yu YANG, Yanfang WANG, Shulin YANG. Molecular Pathological Mechanisms of Subcutaneous Fat Dysfunction in Metabolic Disease Susceptible Pigs [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 4938-4949. |
| [15] | Weiyu ZHANG, Jing CHENG, Jiabao XU, Jing WANG, Xinyan TAO, Bo LI, Yawei ZHANG, Dandan ZHANG, Ning ZHANG, Zhenkai HAO, Chenbo ZHOU, Yuanqing ZHANG. Regulation of Preadipocyte Differentiation by SREBP1 Gene in Jinnan Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 5003-5017. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||