





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 392-403.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.01.036
• Basic Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Hao1, WANG Shiyu2, XIAO Jinlong2, SHEN Jue2, PAN Tianling2, ZHANG Jingsong2, XIAO Peng2,*( ), GAO Hong2,*(
), GAO Hong2,*( )
)
Received:2024-03-01
Online:2025-01-23
Published:2025-01-18
Contact:
XIAO Peng, GAO Hong
E-mail:aipengpengpiao@163.com;gaohongping@163.com
CLC Number:
WANG Hao, WANG Shiyu, XIAO Jinlong, SHEN Jue, PAN Tianling, ZHANG Jingsong, XIAO Peng, GAO Hong. Evolutionary Analysis of High Pathogenicity Virulence Island Structure Gene of Escherichia coli from Pigs and Its Effect on TNF/NF-κB Pathway[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 392-403.
Table 1
The primer information"
| 基因 Genes | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequences | 基因 Genes | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequences | |
| PTGS2 | TTCCAATCCATGTCAAAACCGT | TNF-α | CAGGCGGTGCCTATGTCTC | |
| NM_011198 | AGTCCGGGTACAGTCACACTT | NM_013693 | CGATCACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAG | |
| NF-κB | ATGGCAGACGATGATCCCTAC | ATF4 | CCTGAACAGCGAAGTGTTGG | |
| NM_008689 | CGGAATCGAAATCCCCTCTGTT | NM_009716 | TGGAGAACCCATGAGGTTTCAA | |
| TRAF6 | TACGATGTGGAGTTTGACCCA | cxcl2 | CCAACCACCAGGCTACAGG | |
| NM_009424 | CACTGCTTCCCGTAAAGCCAT | NP_033166 | GCGTCACACTCAAGCTCTG | |
| TRIF | CGATCAAGACGGCCATGAGTC | IL-6 | CTGCAAGAGACTTCCATCCAG | |
| NM_173394 | CTCGTCGGTGTCATCTTCTGC | NM_031168 | AGTGGTATAGACAGGTCTGTTGG |

Fig. 2
Re-analysis of GEO data for E. coli infection A. Boxplot of E.coli infection GEO data after standardization; B. PCA diagram after batch data removal; C. Differentially expressed genes were enriched in Top15 KEGG pathways; D. Intersection of genes shared by TNF pathway and NF-κB pathway; E. Volcano map of differentially expressed genes, annotated with common genes of TNF pathway and NF-κB pathway; F. Network interaction of genes shared by TNF pathway and NF-κB pathway"
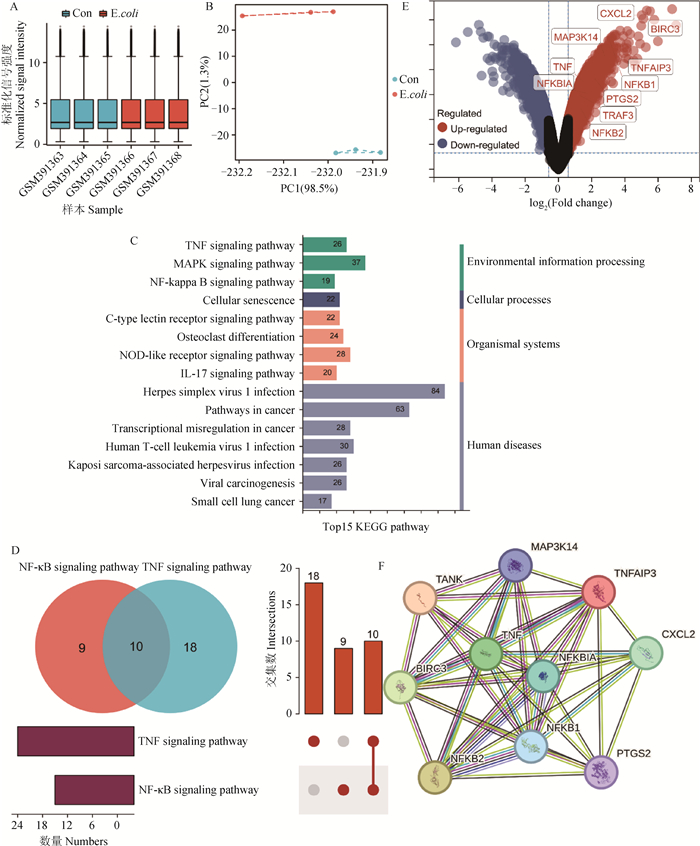

Fig. 3
Involvement of the TNF/NF-κB pathway in E. coli infection A. KEGG interaction of common genes of TNF pathway and NF-κB pathway; B. Heat map of differentially expressed genes in TNF pathway and NF-κB pathway in GEO database of E.coli infection; C. Expression correlation analysis of genes shared by TNF pathway and NF-κB pathway"
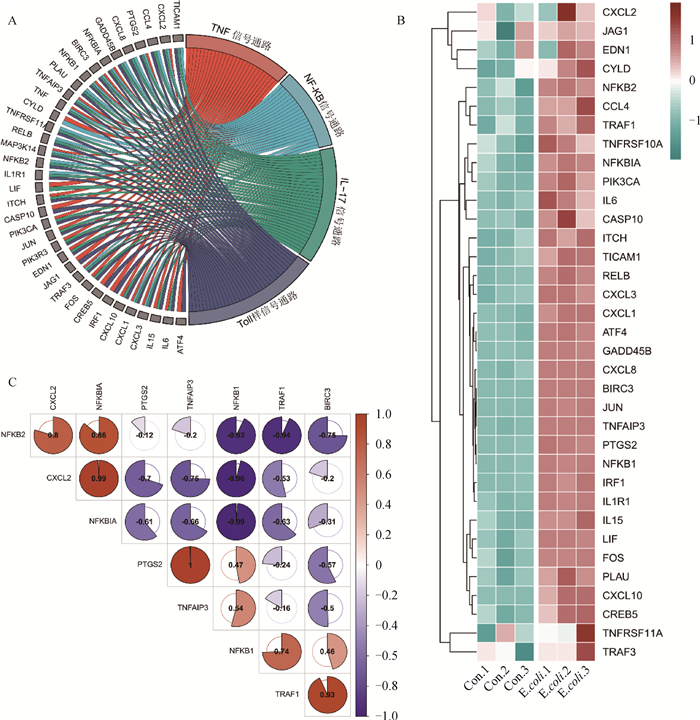

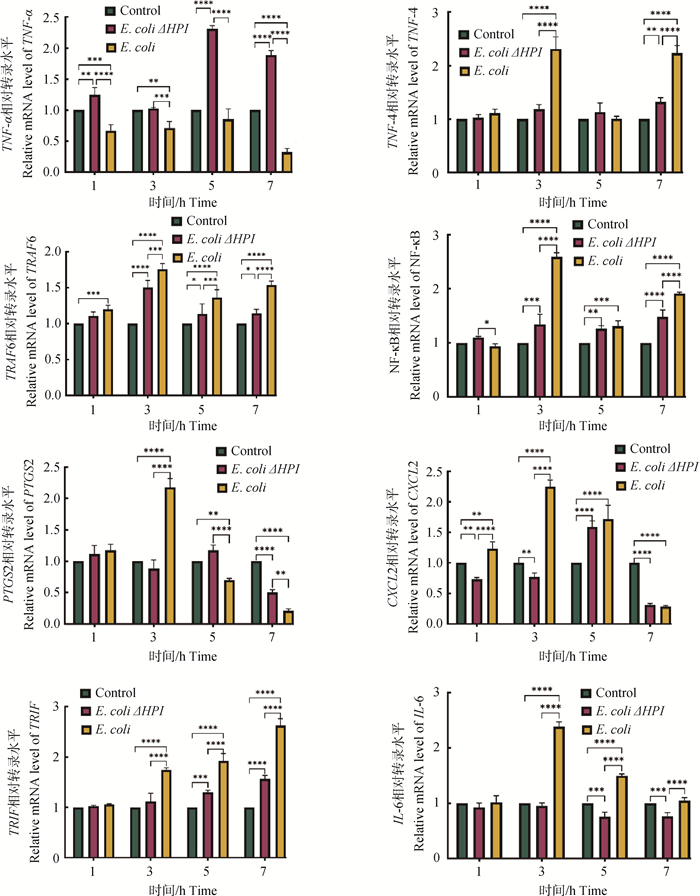
Fig. 5
Effects of E.coli HPI infection on TNF/NF-κB pathway-related genes "*" means significant difference compared with the control group, "*" means significant difference (P < 0.05), " **" means extremely significant difference (P < 0.01), " ***" means extremely significant difference (P < 0.001), " ****" means extremely significant difference (P < 0.000 1). The following are the same"
| 1 |
LEEH,YOONY.Etiological agents implicated in foodborne illness world wide[J].Food Sci Anim Resour,2021,41(1):1-7.
doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2020.e75 |
| 2 |
COIPANC E,FRIESEMAI H,VAN DEN BELDM J C,et al.Sporadic occurrence of enteroaggregative shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O104:H4 similar to 2011 outbreak strain[J].Emerg Infect Dis,2022,28(9):1890-1894.
doi: 10.3201/eid2809.220037 |
| 3 |
PAKBINB,ALLAHYARIS,AMANIZ,et al.Prevalence, phylogroups and antimicrobial susceptibility of Escherichia coli isolates from food products[J].Antibiotics (Basel),2021,10(11):1291.
doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10111291 |
| 4 |
HACKERJ,BLUM-OEHLERG,MVHLDORFERI,et al.Pathogenicity islands of virulent bacteria: structure, function and impact on microbial evolution[J].Mol Microbiol,1997,23(6):1089-1097.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.3101672.x |
| 5 |
CARNIELE,GUILVOUTI,PRENTICEM.Characterization of a large chromosomal "high-pathogenicity island" in biotype 1B Yersinia enterocolitica[J].J Bacteriol,1996,178(23):6743-6751.
doi: 10.1128/jb.178.23.6743-6751.1996 |
| 6 |
SCHUBERTS,RAKINA,KARCHH,et al.Prevalence of the "high-pathogenicity island" of Yersinia species among Escherichia coli strains that are pathogenic to humans[J].Infect Immun,1998,66(2):480-485.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.2.480-485.1998 |
| 7 |
SHANC L,MIAOS S,LIUC Y,et al.Induction of macrophage pyroptosis-related factors by pathogenic E. coli high pathogenicity island (HPI) in Yunnan Saba pigs[J].BMC Vet Res,2021,17(1):114.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-02824-x |
| 8 |
MARTINP,TRONNETS,GARCIEC,et al.Interplay between siderophores and colibactin genotoxin in Escherichia coli[J].IUBMB Life,2017,69(6):435-441.
doi: 10.1002/iub.1612 |
| 9 |
WANGH,SHANC L,GAOB,et al.Yersiniabactin-Producing E. coli induces the pyroptosis of intestinal epithelial cells via the NLRP3 pathway and promotes gut inflammation[J].Int J Mol Sci,2023,24(14):11451.
doi: 10.3390/ijms241411451 |
| 10 |
ZHAOW W,GAOB,LIUC,et al.High pathogenicity island is associated with enhanced autophagy in pathogenic Escherichia coli HPI-infected macrophages[J].Res Vet Sci,2021,135,113-120.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2021.01.006 |
| 11 |
LIUC Y,SHANC L,DONGQ,et al.Pathogenic E. coli HPI upregulate the expression of inflammatory factors in porcine small intestinal epithelial cells by ubiquitin proteasome pathway[J].Res Vet Sci,2018,120,41-46.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2018.08.009 |
| 12 |
ZHANGB,ZHAOW W,GAOB,et al.Whole genome sequencing and biological characteristics of two strains of porcine Escherichia coli isolated from Saba pigs[J].Curr Microbiol,2022,79(6):182.
doi: 10.1007/s00284-022-02873-x |
| 13 |
ZHANGB,WANGH D,ZHAOW W,et al.New insights into the construction of wild-type Saba pig-derived Escherichia coli irp2 gene deletion strains[J].3 Biotech,2021,11(9):408.
doi: 10.1007/s13205-021-02951-0 |
| 14 |
PUTAALAH,BARRANGOUR,LEYERG J,et al.Analysis of the human intestinal epithelial cell transcriptional response to Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus salivarius, Bifidobacterium lactis and Escherichia coli[J].Benef Microbes,2010,1(3):283-295.
doi: 10.3920/BM2010.0003 |
| 15 |
YUG C,WANGLG,HANY Y,et al.ClusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters[J].OMICS,2012,16(5):284-287.
doi: 10.1089/omi.2011.0118 |
| 16 |
PDBe-KB Consortium.PDBe-KB: collaboratively defining the biological context of structural data[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2022,50(D1):D534-D542.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab988 |
| 17 |
GEE J,BUSHA I,CASINIA,et al.Connecting copper and cancer: from transition metal signalling to metalloplasia[J].Nat Rev Cancer,2022,22(2):102-113.
doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00417-2 |
| 18 | 刘淑娟, 李亚, 范正媛, 等. 泊马度胺通过抑制TNF-α/NF-κB信号通路改善COPD大鼠气道炎症及黏液高分泌[J/OL]. 解放军医学杂志, 2023. (2024-05-20). http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1056.R.20230619.1056.002.html. |
| LIU S J, LI Y, FAN Z Y, et al. Pomalidomide improves airway inflammation and mucus hypersecretion in COPD rats by inhibiting TNF-α/NF-κB signaling pathway[J/OL]. Medical Journal of Chinese People 's Liberation Army, 2023. (2024-05-20). http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1056.R.20230619.1056.002.html. (in Chinese) | |
| 19 |
WANGJ,YANGJ J,XIAW H,et al.Escherichia coli enhances Th17/Treg imbalance via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in oral lichen planus[J].Int Immunopharmacol,2023,119,110175.
doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110175 |
| 20 |
DALMASSOG,NGUYENH T T,FAÏST,et al.Yersiniabactin siderophore of crohn 's disease-associated adherent-invasive Escherichia coli is involved in autophagy activation in host cells[J].Int J Mol Sci,2021,22(7):3512.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22073512 |
| 21 |
GERNERR R,HOSSAINS,SARGUNA,et al.Siderophore immunization restricted colonization of adherent-invasive Escherichia coli and ameliorated experimental colitis[J].mBio,2022,13(5):e0218422.
doi: 10.1128/mbio.02184-22 |
| 22 |
SUNS C.The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation[J].Nat Rev Immunol,2017,17(9):545-558.
doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.52 |
| 23 |
FUSELLAF,SECLÌL,CANNATAC,et al.The one thousand and one chaperones of the NF-κB pathway[J].Cell Mol Life Sci,2020,77(12):2275-2288.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03402-z |
| [1] | Jianing WANG, Ziqiang ZHANG, Shuaishuai WANG, Yumei LIU. Mixed Infection and Drug Sensitivity Analysis of Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis and Coccidia from Rabbits [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4204-4212. |
| [2] | Wei WANG, Jingsong WANG, Ya'nan GUO, Le GAO, Lingling WANG, Can CHEN, Jianlin WANG, Jiandong WANG, Ke MA, Jidong LI. Toxicity Factor Detection and Analysis of Escherichia coli Isolated Strains from Calf Diarrhea Samples in Some Areas of Ningxia [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3261-3266. |
| [3] | JIN Ruiyan, ZHANG Yang, HUANG Zhongshun, RAN Wei, DING Honglei. Phenotype Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance and β-lactamase, PMQR Genes Detection of Escherichia coli Isolated from Mawang Ducks [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1738-1746. |
| [4] | XIAO Le, LIU Junyuan, ZENG Wenyu, WANG Qin, HAN Wenjue, LIU Yanling, FAN Yu, XU Yuting, YANG Beini, XIAO Xiong, WANG Zili. Microbiome and Transcriptome Analyses Revealed the Regulatory Mechanism of Xiangsha Liujunzi Decoction on Ileal Injury Induced by ETEC in Weaned Piglets with Diarrhea [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 797-808. |
| [5] | ZHUANG Cuicui, HAN Bo. Mechanism of Mitochondrial Damage in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells and Mouse Mammary Gland Infected with Escherichia coli Isolated from Bovine Mastitis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 822-833. |
| [6] | GAO Jiaojiao, ZHENG Nan, SHAO Wei, CHEN He, MA Xianlan, ZHAO Yankun. Characterization of Heterogeneous Drug-resistant Escherichia coli and Its Drug-resistant Subpopulations from Milk Sources [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5813-5824. |
| [7] | Kangwei HUANG, Pengcheng ZHOU, Chenyu TIAN, Yi LAN, Zhiliang SUN. First Report of Colistin-Resistant Escherichia coli Carrying mcr-1 IncI2(Delta) Plasmids from Pigs in Hunan Province, China [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 5278-5286. |
| [8] | XIAO Jinlong, WANG Hao, WAN Quan, SHEN Jue, ZHANG Bo, ZHAO Weiwei, DENG Jing, WANG Xi, ZHAO Ru, XIAO Peng, GAO Hong. Induction of IPEC-J2 Pyroptosis by E.coli HPI from Saba Pig via NLRP3/ASC/Caspase-1 Pathway [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(12): 5218-5227. |
| [9] | TONG Panpan, HUANG Shunmin, WANG Yudan, SHI Xuhui, CHEN Wenxia, SONG Xinlong, ZHANG Yi, SU Zhanqiang, XIE Jinxin. Phylogenetic Clustering, Serotype and Drug Resistance Analysis of Escherichia coli from Diarrhea with Piglets in Xinjiang [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(1): 414-420. |
| [10] | SUN Dong, QU Sha, LI Xuan, TANG Shanhu, LI Sining, HAO Gang. Comparative Study on the Membrane Action Mechanism of Tachyplesin Ⅰ and Its Analogue on Escherichia coli [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(9): 3180-3189. |
| [11] | WANG Huajian, ZHANG Ning, YANG Wei, ZHAO Zhiqiang, LI Qian, LU An, TIAN Yong, HE Xin, ZHAO Xinghua, LI Jiefeng. Establishment of a Multiplex TaqMan Fluorescence Quantitative PCR Method for Detection of Three Foodborne Pathogens [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(4): 1201-1209. |
| [12] | LIU Chang, LIU Jiao, CHEN Jin, WANG Mianzhi, XIONG Wenguang, ZENG Zhenling. Isolation and Biological Characteristics of a Bacteriophage Capable of Lysing blaNDM-5 and mcr-1 Positive Escherichia coli [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(3): 857-866. |
| [13] | MEN Kaikai, LIU Jialong, GUO Yage, HE Lei, JIA Yanyan, YU Zuhua. Effects of Chicken TGF-β1 on the Adhesion of Escherichia coli and Salmonella pullorum to DF1 Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(11): 4000-4007. |
| [14] | SHAO Ying, FU Dandan, WU Xiaoyan, GU Yi, SONG Xiangjun, TU Jian, QI Kezong. Effect of the ETT2 Structural Gene epaPQR on the Biological Properties and Pathogenicity of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(10): 3631-3641. |
| [15] | WANG Haidi, CAI Qinling, MA Rui, YU Minhuan, LIU Weimin, WEI Yuxi. Protective Effect of Yeast Mannatide on Mice Infected with Pathogenic Escherichia coli [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(10): 3642-3653. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||