





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (9): 4196-4203.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.09.043
• Clinical Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Bilin XIE1( ), Zhimin LIN1, Binbin LIN1, Yijuan XU1, Fengqiang LIN2, Lu YAN2, Huini WU2, Cuiting LI2, Haiou ZHOU2, Zhaolong LI2,*(
), Zhimin LIN1, Binbin LIN1, Yijuan XU1, Fengqiang LIN2, Lu YAN2, Huini WU2, Cuiting LI2, Haiou ZHOU2, Zhaolong LI2,*( )
)
Received:2023-10-31
Online:2024-09-23
Published:2024-09-27
Contact:
Zhaolong LI
E-mail:xiebilin@njau.edu.cn;lizhaolong522@163.com
CLC Number:
Bilin XIE, Zhimin LIN, Binbin LIN, Yijuan XU, Fengqiang LIN, Lu YAN, Huini WU, Cuiting LI, Haiou ZHOU, Zhaolong LI. Isolation, Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of Riemerella anatipestifer Strain LC1 and CX1[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4196-4203.
Table 1
Primer sequences for MLST typing"
| 名称Name | 序列Sequence | 长度/bp Length |
| RAdnaB-F | GAATGATTTCTTCCGAGACAGG | 570 |
| RAdnaB-R | AAAGCCTTACTTCGCCCGT | |
| RAgroE-F | TCAAGAGACGCACTTAAAAGAGGTG | 519 |
| RAgroE-R | TGTACCTTTAGCCTCTTCCACAGTA | |
| RAgyrA-F | GCCTCATAACTTATCGGAATC | 797 |
| RAgyrA-R | AATAGCTTTGTACTCATCACGG | |
| RAmdh-F | ACAGCAGGGTCTCAAGTGG | 532 |
| RAmdh-R | TCTGGTCGCAAGCAATAGC | |
| RAgluD-F | TTGTTTCCGCTCGCTCTAAG | 769 |
| RAgluD-R | TAATCCCGTTCATCGCCAC | |
| RAgpi-F | GCGATAGATAGTATGTTTTCTGGAG | 575 |
| RAgpi-R | TCTACCACCAACCCAGTCC | |
| RArpoB-F | TTAGATCCCATCAAGGCACG | 686 |
| RArpoB-R | GAGCAGTTGGCAGGTCAGTT |
Table 2
Results of partial drug susceptibility testing for the isolates"
| 抗菌素Antibiotic | 判定标准/mm Criterion | 分离株Isolates | ||||
| R | I | S | LC1 | CX1 | ||
| 青霉素G Penicillin G | ≤17 | 18~20 | ≥21 | 24 | 25 | |
| 氨苄西林Ampicillin | ≤13 | 14~16 | ≥17 | 17 | 20 | |
| 阿莫西林Amoxicillin | ≤13 | 14~17 | ≥18 | 30 | 32 | |
| 头孢曲松Ceftriaxone | ≤14 | 15~17 | ≥18 | 31 | 33 | |
| 头孢吡肟Cefepime | ≤14 | 15~17 | ≥18 | 33 | 31 | |
| 庆大霉素Gentamicin | ≤12 | 13~14 | ≥15 | 0 | 0 | |
| 阿米卡星Amikacin | ≤14 | 15~16 | ≥17 | 0 | 0 | |
| 新霉素Neomycin | ≤12 | 13~16 | ≥17 | 0 | 0 | |
| 四环素Tetracycline | ≤14 | 15~18 | ≥19 | 30 | 35 | |
| 强力霉素Doxycycline | ≤12 | 13~15 | ≥16 | 31 | 32 | |
| 红霉素Erythromycin | ≤13 | 14~22 | ≥23 | 0 | 0 | |
| 恩诺沙星Enrofloxacin | ≤15 | 16~20 | ≥21 | 0 | 13 | |
| 环丙沙星Ciprofloxacin | ≤15 | 16~20 | ≥21 | 0 | 15 | |
| 复方新诺明Compound sulfamethoxazole | ≤9 | 10~16 | ≥17 | 0 | 0 | |
| 多黏菌素B Polymyxin B | ≤7 | 8~11 | ≥12 | 0 | 0 | |
| 氟苯尼考Florfenicol | ≤12 | 13~17 | ≥18 | 34 | 30 | |
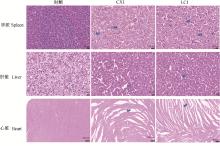
Fig. 4
Pathological results of LC 1 and CX1 isolates on visceral injury in Muscovy ducks Arrow indicating the direction of the lesion outcome(infiltrating basophile granulocyte at the blue arrows of CX1 and LC1 in the spleen; enlarged hepatocyte interstitium at the arrowheads in the liver; and tear-like lesions of cardiac fibres at the arrowheads in the heart)"

| 1 |
SEGERS P , MANNHEIM W , VANCANNEYT M , et al. Riemerella anatipestifer gen. nov., comb. nov., the causative agent of septicemia anserum exsudativa, and its phylogenetic affiliation within the flavobacterium-cytophaga rRNA homology group[J]. Int J Syst Bacteriol, 1993, 43 (4): 768- 776.
doi: 10.1099/00207713-43-4-768 |
| 2 |
HELFER D H , HELMBOLDT C F . Pasteurella anatipestifer infection in turkeys[J]. Avian Dis, 1977, 21 (4): 712- 715.
doi: 10.2307/1589432 |
| 3 |
GLüNDER G , HINZ K H . Isolation of Moraxella anatipestifer from embryonated goose eggs[J]. Avian Pathol, 1989, 18 (2): 351- 355.
doi: 10.1080/03079458908418608 |
| 4 | 郭玉璞, 陈德威, 范国雄, 等. 北京鸭小鸭传染性浆膜炎的调查研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 1982, 13 (2): 35- 41. |
| GUO Y P , CHEN D W , FAN G X , et al. Studies on infections serositis in white Beijing ducklings[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 1982, 13 (2): 35- 41. | |
| 5 | 冯雅婷, 朱敏, 刘丹, 等. 鸭疫里默氏杆菌流行菌株的分离鉴定及生物学特性[J]. 微生物学通报, 2022, 49 (11): 4778- 4785. |
| FENG Y T , ZHU M , LIU D , et al. Isolation, identification, and biological characterization of Riemerella anatipestifer epidemic strains[J]. Microbiology China, 2022, 49 (11): 4778- 4785. | |
| 6 | 吕泽昊, 韩姗姗, 秦立廷, 等. 3株鸭疫里默氏杆菌的分离鉴定和耐药性分析[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2023, 59 (6): 87- 92. |
| LYU Z H , HAN S S , QIN L T , et al. Isolation, identification and drug sensitivity test of three strains of riemeria anatipestipestis[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 59 (6): 87- 92. | |
| 7 | 刘传辉, 韩楠. 鸭疫里默氏杆菌商丘流行株的分离鉴定及耐药性分析[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2022, 58 (8): 64- 68. |
| LIU C H , HAN N . Isolation, identification and drug resistance test of Riemerella anatipestifer epidemic strains in Shangqiu[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 58 (8): 64- 68. | |
| 8 |
郭晶莹, 李亚菲, 蒋红霞, 等. 广东省Ⅰ型鸭疫里氏杆菌分离鉴定及PFGE分型研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2018, 49 (9): 1969- 1978.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2018.09.018 |
|
GUO J Y , LI Y F , JIANG H X , et al. Analysis and PFGE Genotyping of Serotype I Riemerella anatipestifer in Guangdong province[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2018, 49 (9): 1969- 1978.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2018.09.018 |
|
| 9 |
程安春, 汪铭书, 陈孝跃, 等. 我国鸭疫里默氏杆菌血清型调查及新血清型的发现和病原特性[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2003, 23 (4): 320- 323.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4545.2003.04.004 |
|
CHENG A C , WANG M S , CHEN X Y , et al. Epidemiology and new serotypes of Riemerella anatipestifer isolated from ducks in China and studies on their pathogenic characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2003, 23 (4): 320- 323.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4545.2003.04.004 |
|
| 10 | 陈栋, 张言浩, 张阳, 等. 3株鸭疫里氏杆菌的分离鉴定与药敏试验[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2023, 50 (3): 1250- 1258. |
| CHEN D , ZHANG Y H , ZHANG Y , et al. Isolation, identification and drug sensitivity of 3 strains of Riemerella anatipestifer[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 50 (3): 1250- 1258. | |
| 11 | 宋晓恒. 鸭疫里默氏菌的分离鉴定及RCAD0122株多重耐药基因簇的解析[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2016. |
| SONG X H. Isolation and identification of Riemerella anatipestifer and analysis of multidrug-resistant gene clusters in strain RCADO122[D]. Ya'an: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese) | |
| 12 | 林彬彬, 谢碧林, 王秀祯, 等. 番鸭源鸭疫里默氏杆菌的耐药性及rpoB基因突变分析[J]. 福建农业学报, 2021, 36 (11): 1337- 1343. |
| LIN B B , XIE B L , WANG X Z , et al. Drug resistance and rpoB gene mutation of Riemerella anatipestifer isolated from diseased muscovy ducks[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 36 (11): 1337- 1343. | |
| 13 | 林彬彬, 谢碧林, 王秀祯, 等. 鸭疫里默氏菌的分离鉴定及药物敏感性分析[J]. 养禽与禽病防治, 2021, (11): 11- 16. |
| LIN B B , XIE B L , WANG X Z , et al. Isolation, identification and drug susceptibility analysis of R.marae[J]. Poultry Husbandry and Disease Control, 2021, (11): 11- 16. | |
| 14 |
ZHU B F , CHAO M K , YANG X F , et al. Multilocus sequence typing of the Guangdong isolates of Riemerella anatipestifer from ducks in China[J]. Open J Anim Sci, 2015, 5 (3): 332- 342.
doi: 10.4236/ojas.2015.53037 |
| 15 |
JOLLEY K A , BRAY J E , MAIDEN M C J . Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications[J]. Wellcome Open Res, 2018, 3, 124.
doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.14826.1 |
| 16 | 雷云, 嵇辛勤, 段志强, 等. 鸭疫里默氏杆菌贵州分离株的耐药性及致病性分析[J]. 中国家禽, 2016, 38 (16): 58- 61. |
| LEI Y , JI X Q , DUAN Z Q , et al. Analysis of drug resistance and pathogenicity of Guizhou isolates of A. duck[J]. China Poultry, 2016, 38 (16): 58- 61. | |
| 17 | 祝希辉, 李艳兰, 王志伟, 等. 1株鸭疫里默氏杆菌的全基因组测序及耐药性与遗传进化分析[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2023, 50 (3): 1140- 1149. |
| ZHU X H , LI Y L , WANG Z W , et al. Whole genome sequencing of a resistant Riemerella anatipestifer strain and analysis of antibiotic resistance and genetic evolution[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 50 (3): 1140- 1149. | |
| 18 | 张少敏, 徐建国. 多位点序列分型及其应用[J]. 疾病监测, 2008, 23 (10): 648- 650. |
| ZHANG S M , XU J G . Multilocus sequence typing and its application[J]. Disease Surveillance, 2008, 23 (10): 648- 650. | |
| 19 | 苏敬良, 黄瑜, 胡薛英. 鸭病学[M]. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2016. |
| SU J L , HUANG Y , HU X Y . Duck diseases[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2016. | |
| 20 | 陈国权, 吴征卓, 姚碧琼, 等. 两株鸭疫里默氏杆菌的分离鉴定及生物学特性分析[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2020, 42 (12): 1226- 1232. |
| CHEN G Q , WU Z Z , YAO B Q , et al. Isolation, identification and biological characteristics analysis of Riemerella anatipestifer serotype 11[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 42 (12): 1226- 1232. |
| [1] | Shan ZHANG, Dahu LIU, Baojing LIU, Lin LIANG, Ruiying LIANG, Xinming TANG, Xusheng QIU, Chan DING, Jiabo DING, Shaohua HOU. Isolation, Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of a Pigeon Paramyxovirus-1 Strain [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4051-4060. |
| [2] | Yan WANG, Yadong GAO, Chenghui JIANG, Qiaoying ZENG. Isolation and Pathogenicity of a Goose Derived Fowl Adenovirus Type 4 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4232-4240. |
| [3] | Fanfan ZHANG, Jiemao LI, Jia TAN, Jiangnan HUANG, Ling WU, Qipeng WEI, Zhaofeng KANG. Research Progress on Avian Metapneumovirus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3344-3353. |
| [4] | Yue LI, Changchun ZHANG, Guangyu LIU, Mengyuan GAO, Chaojun FU, Jiabao XING, Sijia XU, Qiyuan KUANG, Jing LIU, Xiaopeng GAO, Heng WANG, Lang GONG, Guihong ZHANG, Yankuo SUN. Application and Analysis of Meta-transcriptomics Sequencing Technology in the Diagnosis of Viral Diarrhea Diseases in Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3579-3589. |
| [5] | Yudian SUN, Ziyue SONG, Hongliang ZHANG, Zhihua QIN, Hu SHAN, Ruimei YANG. Isolation and ldentification of Duckling Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3623-3630. |
| [6] | Weizhe LIU, Chenggang LUO, Rong YUAN, Yijie LIAO, Yimin WEN, Ying SUN, Enbo YU, Sanjie CAO, Xiaobo HUANG. Isolation and Identification of a Highly Pathogenic Strain of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3049-3063. |
| [7] | Wangqing BAN MA, Xi CHEN, Yi YUE, Yurong SU, Hua YUE, Cheng TANG. Isolation, Identification and Partial Biological Characteristics of a Bovine Respiratory Coronavirus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3094-3104. |
| [8] | Bohua LIU, Hanyu FU, Yuheng WANG, Suolangsizhu, Jiaqiang NIU, Yuhua BAO, Jiakui LI, Yefen XU. Isolation, Identification and Genome Analysis of Type B Pasteurella multocida Isolated from Yak in Tibetan Nakchu City [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3105-3118. |
| [9] | Kun YANG, Jingwen MA, Xinrui ZHOU, Liezhu LUO, Zhe LIU, Ziqiang HU, Xingchen WU, Libin LIANG, Shimin GAO. Pathogenicity of Three Recombinant Strains of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2550-2559. |
| [10] | Ning ZHOU, Cheng TANG, Jia XU, Hua YUE, Xi CHEN. Pathogenicity and Genomic Characteristics of Feline Panleukopenia Virus A91S Variant in Cats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2560-2568. |
| [11] | XIONG Ting, HE Xianming, ZHAO Xiya, ZHUANG Tingting, HUANG Meizhen, LIANG Shijin, YU Chuanzhao, LIANG Xuejing, CHEN Ruiai. Whole Genome Analysis of Three Predominant Epidemic Strains of Chicken Infectious Bronchitis Virus and Their Pathogenicity [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2109-2122. |
| [12] | ZHENG Rui, LIU Zishi, ZHANG Kangyou, YAN Yong, WEI Ling, ZEREN Wengmu, DINGZE Demi, HUANG Jianjun, WANG Li, WEI Yong. Isolation, Identification and Biological Characterization of Colletotrichum jasminigenum in Stems of Peanuts [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2206-2213. |
| [13] | QIN Yi, HU Wenjie, FANG Xiaowei, GUO Qian, TIAN Lanxin, LIU Fang, FANG Chun. Effect of Deletion of the Lipoteichoic Acid Synthase ltaS Gene on the Pathogenicity of Listeria monocytogenes [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 670-679. |
| [14] | WU Zihao, CAI Yilong, TUO Haixin, CHEN Wei. Pathogenicity Analysis of a PVL+ ST22 Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Equine Raw Milk [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 718-726. |
| [15] | CHEN Yuetong, LIU Xiaohan, WANG Zhiyang, ZHAO Yuxin, ZHOU Tiezhong, HU Zengjin, ZHU Yue, WANG Shaohui, TIAN Mingxing, DING Siyu, QI Jingjing, YU Shengqing. Isolation, Identification, Pathogenicity and Drug Susceptibility of Mycoplasma gallisepticum from Dead Chicken Embryos in Large-scale Chicken Farms in Guangdong Province [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(1): 290-299. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||