





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (7): 3105-3118.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.07.029
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Bohua LIU1( ), Hanyu FU1, Yuheng WANG2, Suolangsizhu1, Jiaqiang NIU1, Yuhua BAO2, Jiakui LI1,3, Yefen XU1,*(
), Hanyu FU1, Yuheng WANG2, Suolangsizhu1, Jiaqiang NIU1, Yuhua BAO2, Jiakui LI1,3, Yefen XU1,*( )
)
Received:2023-07-24
Online:2024-07-23
Published:2024-07-24
Contact:
Yefen XU
E-mail:484325625@qq.com;xzlzxyf@163.com
CLC Number:
Bohua LIU, Hanyu FU, Yuheng WANG, Suolangsizhu, Jiaqiang NIU, Yuhua BAO, Jiakui LI, Yefen XU. Isolation, Identification and Genome Analysis of Type B Pasteurella multocida Isolated from Yak in Tibetan Nakchu City[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3105-3118.
Table 1
Primers for PCR identification of Pasteurella multocida"
| 基因 Gene | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequence (5′→3′) | 产物大小/bp Product size | 退火温度/℃ Annealing temperature |
| 16S rRNA | Pm-16s | F: AGAGTTTGATCATGGCTCAG R: AAGGAGGTGATCCAACC | 1 534 | 55 |
| Kmt1 | Pm-Kmt1 | F: ATCCGCTATTTACCCAGTGG R: GCTGTAAACGAACTCGCCAC | 460 | 55 |
| hyaD-hyaC | A型 | F: TGCCAAAATCGCAGTCAG R: TTGCCATCATTGTCAGTG | 1 044 | 53 |
| bcbD | B型 | F: CATTTATCCAAGCTCCACC R: GCCCGAGAGTTTCAATCC | 760 | 53 |
| dcbF | D型 | F: TTACAAAAGAAAGACTAGGAGCCC R: CATCTACCCACTCAACCATATCAG | 657 | 53 |
| ecbJ | E型 | F: TCCGCAGAAAATTATTGACTC R: GCTTGCTGCTTGATTTTGTC | 511 | 53 |
| fcbD | F型 | F: AATCGGAGAACGCAGAAATCAG R: TTCCGCCGTCAATTACTCTG | 852 | 53 |
Table 2
Detection results of Pasteurella multocida in yaks in some areas of Tibet"
| 采样年份 Sampling year | 地区 District | 样本数量/头 Sample number | 阳性数/头 Positive number |
| 2020 | 西藏自治区林芝市 | 59 | 0 |
| 2020 | 西藏自治区拉萨市 | 63 | 0 |
| 2020 | 西藏自治区那曲市 | 61 | 6 |
| 2021 | 西藏自治区林芝市 | 77 | 0 |
| 2021 | 西藏自治区拉萨市 | 62 | 0 |
| 2021 | 西藏自治区那曲市 | 87 | 5 |
| 2022 | 西藏自治区林芝市 | 30 | 0 |
| 2022 | 西藏自治区那曲市 | 24 | 2 |
| 2023 | 西藏自治区林芝市 | 35 | 0 |
| 总计Total | 498 | 13 |
Table 4
Results of drug sensitivity test for isolated strains"
| 抗生素 Antibiotic | 药物名称 Antimicrobial agents | 判定标准Criterion | 平均直径/mm Mean diameter | 结果 Result | ||
| R | I | S | ||||
| 青霉素类 Penicillins | 青霉素Penicillin | ≤10 | 10~15 | ≥15 | 5.96 | R |
| 苯唑西林Oxacillin | ≤14 | 15~22 | ≥23 | 6.45 | R | |
| 氨苄西林Ampicillin | ≤13 | 14~16 | ≥17 | 13.31 | I | |
| 羧苄西林Carbenicillin | ≤13 | 14~16 | ≥17 | 21.11 | S | |
| 哌拉西林Piperacillin | ≤17 | 18~20 | ≥21 | 18.5 | I | |
| 头孢菌素类 Cephalosporins | 头孢氨苄Cephalexin | ≤14 | 14~18 | ≥19 | 17.09 | I |
| 头孢唑林Cefazolin | ≤14 | 14~18 | ≥19 | 22.13 | S | |
| 头孢拉定Cefradine | ≤14 | 14~18 | ≥19 | 14.62 | I | |
| 头孢呋辛Cefuroxime | ≤14 | 14~18 | ≥19 | 19.41 | S | |
| 头孢他啶Ceftazidime | ≤14 | 15~17 | ≥18 | 19.96 | S | |
| 头孢哌酮Cefoperazone | ≤15 | 16~20 | ≥21 | 23.76 | S | |
| 头孢曲松Ceftriaxone | ≤13 | 14~20 | ≥21 | 26.62 | S | |
| 大环内酯类 Macrolides | 红霉素Erythromycin | ≤13 | 14~22 | ≥23 | 6.62 | R |
| 麦迪霉素Medemycin | ≤10 | 11~15 | ≥16 | 5.95 | R | |
| 氨基糖苷类 Aminoglycosides | 阿米卡星Amikacin | ≤14 | 15~16 | ≥17 | 20.66 | S |
| 庆大霉素Gentamicin | ≤12 | 13~14 | ≥15 | 8.19 | R | |
| 卡那霉素Kanamycin | ≤13 | 14~17 | ≥18 | 17.92 | I | |
| 新霉素Neomycin | ≤17 | 18~21 | ≥22 | 18.92 | I | |
| 四环素类 Tetracycline | 四环素Tetracycline | ≤11 | 12~14 | ≥15 | 6.47 | R |
| 多西环素Doxycycline | ≤9 | 10~12 | ≥13 | 8.37 | R | |
| 米诺环素Minocycline | ≤12 | 13~15 | ≥16 | 9.42 | R | |
| 喹诺酮类 Quinolones | 诺氟沙星Norfloxacin | ≤12 | 13~16 | ≥17 | 28.27 | S |
| 氧氟沙星Ofloxacin | ≤13 | 14~16 | ≥17 | 31.03 | S | |
| 环丙沙星Ciprofloxacin | ≤15 | 16~20 | ≥21 | 31.55 | S | |
| 多肽类 Polypeptide | 万古霉素Vancomycin | ≤10 | 11~16 | ≥17 | 15.26 | I |
| 多黏菌素B Polymyxin B | ≤11 | ― | ≥12 | 11.91 | I | |
| 磺胺类 Sulfonamides | 复方新诺明 Cotrimoxazole | ≤9 | 10~16 | ≥17 | 22.93 | S |
| 呋喃类Furans | 呋喃唑酮Furazolidone | ≤13 | 14~22 | ≥23 | 14.50 | I |
| 氯霉素类 Chloramphenicol | 氯霉素 Chloramphenicol | ≤12 | 13~17 | ≥18 | 26.30 | S |
| 林可酰胺类 Lincoamides | 克林霉素 Clindamycin | ≤10 | 11~15 | ≥16 | 6.44 | R |
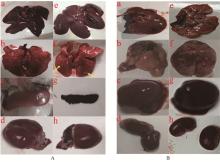
Fig. 4
Pathological changes of autopsy A. Pathological changes of rabbits; B. Pathological changes of mice; a-d. Liver, lung, spleen and kidney of the control groups, respectively; e-h. Liver, lung, spleen and kidney of the experimental group, respectively; Yellow arrow. Tissue lesion bleeding point"


Fig. 5
Pm whole genome circle map The outermost circle marks the size of the genome, each scale is 5 kb; The second circle and the third circle are the genes on the positive and negative chains of the genome respectively, and different colors represent different functional classifications of COG. The fourth circle is repeated sequence; The fifth circle is tRNA and rRNA, blue is tRNA, purple is rRNA; The sixth circle is the GC content, the light yellow part indicates that the GC content of this region is higher than the average GC content of the genome, the higher the peak value, the greater the difference between the average GC content, and the blue part indicates that the GC content of this region is lower than the average GC content of the genome. The innermost ring is GC-skew, with dark gray representing regions with more G than C and red representing regions with more C than G"

| 1 | MOSTAAN S , GHASEMZADEH A , SARDARI S , et al. Pasteurella multocida vaccine candidates: a systematic review[J]. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol, 2020, 12 (3): 140- 147. |
| 2 |
CUEVAS I , CARBONERO A , CANO D , et al. Antimicrobial resistance of Pasteurella multocida type B isolates associated with acute septicemia in pigs and cattle in Spain[J]. BMC Vet Res, 2020, 16 (1): 222.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02442-z |
| 3 |
IDER M , MADEN M . Biomarkers of infectious pneumonia in naturally infected calves[J]. Am J Vet Res, 2022, 83 (8)
doi: 10.2460/ajvr.21.10.0172 |
| 4 |
MOCHIZUKI Y , ISHIKAWA H , SATO A , et al. Pasteurella multocida-induced endophthalmitis after a cat scratch[J]. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep, 2020, 18, 100711.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2020.100711 |
| 5 | 王方国, 耿尚景超, 颜新敏, 等. 西藏那曲牦牛BRDC细菌病原核酸检测与分析[J]. 西北农业学报, 2021, 30 (11): 1603- 1610. |
| WANG F G , GENGSHANG J C , YAN X M , et al. Nucleic acid detection and analysis of BRDC bacteria in Nagqu yak, Xizang Province[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2021, 30 (11): 1603- 1610. | |
| 6 | 李家奎, 索朗斯珠, 贡嘎, 等. 牦牛重要传染病和寄生虫的防治与展望[J]. 中国奶牛, 2012, (1): 30- 33. |
| LI J K , SOLANG S Z , GONG G , et al. Prevention and treatment of infectious diseases and parasitic in yak and its prospects[J]. China Dairy Cattle, 2012, (1): 30- 33. | |
| 7 | PENG Z , WANG X R , ZHOU R , et al. Pasteurella multocida: genotypes and genomics[J]. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev, 2019, 83 (4): e00014- 19. |
| 8 | 刘朋, 陈萌, 程子龙, 等. 奶牛荚膜血清A型巴氏杆菌的分离鉴定及致病性[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2018, 38 (8): 1548- 1552. |
| LIU P , CHEN M , CHENG Z L , et al. Isolation, identification and pathogenicity of the serotype a Pasteurella multocida in cow[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2018, 38 (8): 1548- 1552. | |
| 9 | 尹媛媛, 何芳, 赵光夫, 等. 多杀性巴氏杆菌主要毒力因子研究进展[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2021, 41 (6): 1210- 1218. |
| YI Y Y , HE F , ZHAO G F , et al. Research progress on the main virulence factors of Pasteurella multocida[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2021, 41 (6): 1210- 1218. | |
| 10 | 许文博, 吴丽梅, 刘鑫, 等. 1株多杀性巴氏杆菌的全基因组序列及致病相关基因分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53 (6): 1858- 1869. |
| XU W B , WU L M , LIU X , et al. Analysis on complete genome sequence and pathogenic genes of a Pasteurella multocida strain[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53 (6): 1858- 1869. | |
| 11 | CHOUDHARY M , CHOUDHARY B K , CHANDRA GHOSH R , et al. Cultivable microbiota and pulmonary lesions in polymicrobial bovine pneumonia[J]. Microb Pathog, 2019, 134, 103577. |
| 12 | 王子杰, 操义恒, 马雪, 等. Beltex羊肺源多杀性巴氏杆菌和溶血曼氏杆菌的分离鉴定及耐药性分析[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2022, 42 (9): 1823-1829, 1850. |
| WANG Z J , CAO Y H , MA X , et al. Isolation, identification and drug resistance analysis of Pasteurella multocida and Mannheimia haemolyticus from Beltex sheep lung[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2022, 42 (9): 1823-1829, 1850. | |
| 13 | HOLSCHBACH C L , AULIK N , POULSEN K , et al. Prevalence and temporal trends in antimicrobial resistance of bovine respiratory disease pathogen isolates submitted to the Wisconsin Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory: 2008-2017[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2020, 103 (10): 9464- 9472. |
| 14 | LIN L , LI C H , WANG F , et al. Complete genome sequence of Pasteurella multocida HuN001, a capsular type a strain from a human[J]. Microbiol Resour Announc, 2021, 10 (26): e0039521. |
| 15 | LIVINGSTONE M , AITCHISON K , DAGLEISH M , et al. De novo whole-genome sequencing and annotation of pathogenic bovine Pasteurella multocida type a: 3 strains[J]. Microbiol Resour Announc, 2020, 9 (49): e01078- 20. |
| 16 | GUAN L J , SONG J J , XUE Y , et al. Immune protective efficacy of China's traditional inactivated and attenuated vaccines against the prevalent strains of Pasteurella multocida in mice[J]. Vaccines (Basel), 2021, 9 (10): 1155. |
| 17 | 阚威, 王谢忠, 李兆才, 等. 牛源荚膜血清型A型多杀性巴氏杆菌的分离鉴定及其种特异性基因的序列分析[J]. 中兽医医药杂志, 2019, 38 (4): 18- 22. |
| KAN W , WANG X Z , LI Z C , et al. Isolation and identification of bovine capsular type A Pasteurella mutocida and sequence analysis of its species-specific genes[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 38 (4): 18- 22. | |
| 18 | HUMPHRIES R , BOBENCHIK A M , HINDLER J A , et al. Overview of changes to the clinical and laboratory standards institute Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, M100, 31st Edition[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2021, 59 (12): e0021321. |
| 19 | 井郁金, 金映红, 汪萍, 等. 绵羊源荚膜血清A型多杀性巴氏杆菌的分离鉴定及其生物学特性研究[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2020, 50 (8): 1012- 1017. |
| JING Y J , JIN Y H , WANG P , et al. Isolation and identification of Pasteurella multocida capsule serotype A and partial biological characteristics from sheep[J]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 2020, 50 (8): 1012- 1017. | |
| 20 | KUTZER P , SZENTIKS C A , BOCK S , et al. Re-emergence and spread of haemorrhagic septicaemia in Germany: the wolf as a vector?[J]. Microorganisms, 2021, 9 (9): 1999. |
| 21 | CUEVAS I , CARBONERO A , CANO D , et al. First outbreak of bovine haemorrhagic septicaemia caused by Pasteurella multocida type B in Spain-Short communication[J]. Acta Vet Hung, 2020, 68 (1): 8- 11. |
| 22 | ALHAMAMI T , ROY CHOWDHURY P , VENTER H , et al. Genomic profiling of Pasteurella multocida isolated from feedlot cases of bovine respiratory disease[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2023, 283, 109773. |
| 23 | 马弘财, 王冬经, 元振杰, 等. 西藏当雄县牦牛巴氏杆菌病血清流行病学调查[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2021, 38 (9): 17-19, 23. |
| MA H C , WANG D J , YUAN Z J , et al. Seroepidemiological investigation on pasteurellosis in yaks in Damxung County of Tibet[J]. China Animal Health Inspection, 2021, 38 (9): 17-19, 23. | |
| 24 | GORSKI L. Serotype assignment by sero-agglutination, ELISA, and PCR[M]//FOX E M, BIERNE H, STESSL B. Listeria Monocytogenes. New York: Humana, 2021: 57-78. |
| 25 | 陈建春, 索朗斯珠, 罗润波, 等. 我国牦牛主产区巴氏杆菌流行病学调查与危险因素分析[J]. 甘肃畜牧兽医, 2018, 48 (4): 72- 74. |
| CHEN J C , SOLANG S Z , LUO R B , et al. Epidemiological investigation and risk factors analysis of Pasteurella in major yak producing areas in China[J]. Gansu Animal Husbandry and Veterinary, 2018, 48 (4): 72- 74. | |
| 26 | 陈建春, 王一飞, 周赛赛, 等. 西藏那曲牦牛源多杀巴氏杆菌荚膜分型及其毒力基因检测[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2019, 24 (9): 88- 97. |
| CHEN J C , WANG Y F , ZHOU S S , et al. Capsule type identification and virulence gene detection of Pasteurella multocida derived from yaks in Naqu, Tibet[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2019, 24 (9): 88- 97. | |
| 27 | SUDARYATMA P E , MEKATA H , KUBO M , et al. Co-infection of epithelial cells established from the upper and lower bovine respiratory tract with bovine respiratory syncytial virus and bacteria[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2019, 235, 80- 85. |
| 28 | ALHAMAMI T , CHOWDHURY P R , GOMES N , et al. First emergence of resistance to macrolides and tetracycline identified in Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida isolates from beef feedlots in Australia[J]. Microorganisms, 2021, 9 (6): 1322. |
| 29 | KANNAKI T R , PRIYANKA E , HAUNSHI S . Research Note: disease tolerance/resistance and host immune response to experimental infection with Pasteurella multocida A: 1 isolate in Indian native Nicobari chicken breed[J]. Poult Sci, 2021, 100 (8): 101268. |
| 30 | DOYLE-BAKER D , NGELEKA M , JANZEN E , et al. Septicemic pasteurellosis causing peracute death and necrotizing myositis in a beef heifer calf (Bos taurus) in Alberta, Canada[J]. Can Vet J, 2020, 61 (12): 1303- 1306. |
| 31 | VU-KHAC H , TRINH T T H , NGUYEN T T G , et al. Prevalence of virulence factor, antibiotic resistance, and serotype genes of Pasteurella multocida strains isolated from pigs in Vietnam[J]. Vet World, 2020, 13 (5): 896- 904. |
| 32 | PRAJAPATI A , YOGISHARADHYA R , MOHANTY N N , et al. Comparative genome analysis of Pasteurella multocida serogroup B: 2 strains causing haemorrhagic septicaemia (HS) in bovines[J]. Gene, 2022, 826, 146452. |
| 33 | HE F , QIN X B , XU N , et al. Pasteurella multocida Pm0442 affects virulence gene expression and targets TLR2 to induce inflammatory responses[J]. Front Microbiol, 2020, 11, 1972. |
| 34 | JIAN Z H , ZENG L , XU T J , et al. Antibiotic resistance genes in bacteria: occurrence, spread, and control[J]. J Basic Microbiol, 2021, 61 (12): 1049- 1070. |
| 35 | GUAN L J , ZHANG L , XUE Y , et al. Molecular pathogenesis of the hyaluronic acid capsule of Pasteurella multocida[J]. Microb Pathog, 2020, 149, 104380. |
| 36 | ISHIZAWA J , ZARABI S F , DAVIS R E , et al. Mitochondrial ClpP-mediated proteolysis induces selective cancer cell lethality[J]. Cancer Cell, 2019, 35 (5): 721- 737.e9. |
| 37 | PETROCCHI-RILO M , GUTIÉRREZ-MARTÍN C B , PÉREZ-FERNÁNDEZ E , et al. Antimicrobial resistance genes in porcine Pasteurella multocida are not associated with its antimicrobial susceptibility pattern[J]. Antibiotics (Basel), 2020, 9 (9): 614. |
| [1] | Ruiqi ZHANG, Yanqin PANG, Zaishan LI, Xiuguo SHANG, Ganqiu LAN, Jinbiao GUO, Yunxiang ZHAO. Research on Feeding Capacity Selection of Lactating Sows Based on Intelligent Precision Feeding [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2890-2900. |
| [2] | Milan MA, Qi WANG, Qiu YAN, Tianan LI, Xingxu ZHAO, Yong ZHANG. Expression of HIG1 Hypoxia Inducible Domain Family Member 1C in Cryptorchidism of Yak and Its Regulatory Mechanism [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 2983-2994. |
| [3] | Huanqin ZHENG, Xiaomin JIANG, Hong YUE, Baoyan WANG, Yang LIU, Xingxiao ZHANG, Jianlong ZHANG, Hongwei ZHU. Isolation, Identification and Partial Biological Characteristics Analysis of Feline Herpesvirus-1 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3040-3048. |
| [4] | Weizhe LIU, Chenggang LUO, Rong YUAN, Yijie LIAO, Yimin WEN, Ying SUN, Enbo YU, Sanjie CAO, Xiaobo HUANG. Isolation and Identification of a Highly Pathogenic Strain of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3049-3063. |
| [5] | Jitong LI, Tong ZHU, Junfeng LÜ, Yuehua GAO, Feng HU, Kexiang YU, Minxun SONG, Jianlin WANG, Yufeng LI. Isolation and Identification of Novel Picornavirus from Ducks and Whole Genome Sequence Analysis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3075-3084. |
| [6] | Wangqing BAN MA, Xi CHEN, Yi YUE, Yurong SU, Hua YUE, Cheng TANG. Isolation, Identification and Partial Biological Characteristics of a Bovine Respiratory Coronavirus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(7): 3094-3104. |
| [7] | Kun YANG, Jingwen MA, Xinrui ZHOU, Liezhu LUO, Zhe LIU, Ziqiang HU, Xingchen WU, Libin LIANG, Shimin GAO. Pathogenicity of Three Recombinant Strains of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2550-2559. |
| [8] | Ning ZHOU, Cheng TANG, Jia XU, Hua YUE, Xi CHEN. Pathogenicity and Genomic Characteristics of Feline Panleukopenia Virus A91S Variant in Cats [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(6): 2560-2568. |
| [9] | CUI Shengdi, WANG Kai, ZHAO Zhenjian, CHEN Dong, SHEN Qi, YU Yang, WANG Junge, CHEN Ziyang, YU Shixin, CHEN Jiamiao, WANG Xiangfeng, TANG Guoqing. Identification of Candidate Genes for Pork Texture Traits Using GWAS Combined with Co-localisation of DNA Methylation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 1945-1957. |
| [10] | XIONG Ting, HE Xianming, ZHAO Xiya, ZHUANG Tingting, HUANG Meizhen, LIANG Shijin, YU Chuanzhao, LIANG Xuejing, CHEN Ruiai. Whole Genome Analysis of Three Predominant Epidemic Strains of Chicken Infectious Bronchitis Virus and Their Pathogenicity [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2109-2122. |
| [11] | LUO Ting, HAN Zhu, XU Yefen, CAI Lin, SUOLANG Sizhu, XU Jinhua, NIU Jiaqiang. Whole Genome Sequencing and Sequence Analysis on T10 of Mycoplasma bovis Strain from Yaks in Xizang [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2154-2167. |
| [12] | ZHENG Rui, LIU Zishi, ZHANG Kangyou, YAN Yong, WEI Ling, ZEREN Wengmu, DINGZE Demi, HUANG Jianjun, WANG Li, WEI Yong. Isolation, Identification and Biological Characterization of Colletotrichum jasminigenum in Stems of Peanuts [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2206-2213. |
| [13] | HUANG Xianpeng, XING Jiayi, BAI Yuanyuan, JIANG Yuting, MA Zhiwei, FU Wei, LAN Daoliang. Cloning of Six Pluripotent Related Transcription Factors OSKMNL in Yak and Construction of Polycistron Lentiviral Vector [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1579-1591. |
| [14] | SHANG Kaiyuan, JIANG Mingfeng, GUAN Jiuqiang, AN Tianwu, ZHAO Hongwen, BAI Qin, WU Weisheng, LI Huade, XIE Rongqing, SHA Quan, LUO Xiaolin, ZHANG Xiangfei. Effects of Maternal Nutritional Regulation in Transition Period on Growth and Development, Serum Biochemistry and Immune Function of Yak Calves [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1638-1648. |
| [15] | TIAN Rui, XU Sixiang, XIE Feng, LIU Guangjin, WANG Gang, LI Qingxia, DAI Lei, XIE Guoxin, ZHANG Qiongwen, LU Yajing, WANG Guangwen, WANG Jinxiu, ZHANG Wei. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Genome of Clostridium perfringens Isolated from Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1707-1715. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||