





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (2): 900-911.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.02.038
• Basic Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Ruiling( ), LI Yuchen, TANG Rongfeng, YANG Qian*(
), LI Yuchen, TANG Rongfeng, YANG Qian*( )
)
Received:2024-03-20
Online:2025-02-23
Published:2025-02-26
Contact:
YANG Qian
E-mail:lrl33316407@163.com;zxbyq@njau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
LIU Ruiling, LI Yuchen, TANG Rongfeng, YANG Qian. Preliminary Study on the Mechanism of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection Affecting Small Intestinal Goblet Cells[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(2): 900-911.
Table 1
Primer sequences of the target genes"
| 基因Gene | 引物对序列(5′→3′) Primer pairs sequence |
| PEDV-N | CGGAACAGGACCTCACGCC/ACAATCTCAACTACGCTGGGAAG |
| β-actin | AAGGATTCCTATGTGGGCGAC/CGTACAGGGATAGCACAGCC |
| Muc2 | ATGCCCTTGCGTCCATAACA/AGGAGCAGTGTCCGTCAAAG |
| SPDEF | CAAGCTGCTCAACATCACCG/GGAACTGCTCCTCCGACAT |
| TFF3 | GTGCCTTGGTGTTTCAAGCC/GAAGAACTGTCCTCGGGTGG |
| MAPK1 | GGCTGTTCCCAAATGCTGAC/AACTTGAATGGTGCTTCGGC |
| MAPK3 | ACCTACAGTCTCTGCCCTCC/CAGCCGCTCCTTAGGTAGGT |
| MAPK8 | CTCGCTACTACAGAGCACCC/TGTGGCAAACCATTTCTCCC |
| MAP2K1 | GCACATGGATGGAGGTTCTC/GCTGACCCCAAAGTCACAGA |
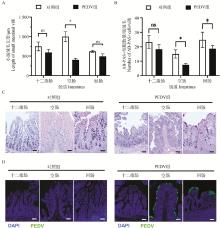
Fig. 1
Effect of PEDV infection on mucus secretion in the small intestine of piglets A. Length of intestinal villi in duodenum, jejunum and ileum of blank piglets and piglets infected with PEDV; B. Number of goblet cells in duodenum, jejunum and ileum of blank piglets and piglets infected with PEDV; C. AB-PAS staining of goblet cells (bluish violet) in duodenal, jejunal and ileal tissues of blank and PEDV-infected piglets; D. Immunofluorescence staining of PEDV infection in duodenal, jejunal and ileal tissues of blank and PEDV-infected piglets; Scale: 50 μm; ns. No significant difference, *. P < 0.05"

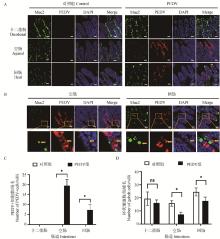
Fig. 2
Effect of PEDV infection on the goblet cells in the small intestine of piglets A. Immunofluorescence staining of duodenal, jejunal and ileal tissues of blank and PEDV-infected piglets for PEDV infection and number of goblet cells; B. Immunofluorescence staining showed that the goblet cells infected with PEDV in jejunum and ileum of piglets were infected with PEDV; C. Number of PEDV positive cells (red) in the duodenum, jejunum and ileum tissues of blank and PEDV-infected piglets; D. Number of goblet cells (green) in duodenum, jejunum and ileum of blank piglets and piglets infected with PEDV; Scale: 50 μm; ns. No significant difference, *. P < 0.05"

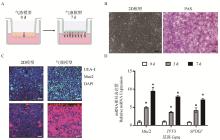
Fig. 3
Establishment of pig small intestinal goblet cell culture model A. Air-liquid interface differentiation model of porcine jejunal organs; B. Light microscope observation and PAS staining of 2D organs; C. Laser confocal display of mucin expression; D. The expression of goblet cell-related genes increased with time in the gas-liquid interface differentiation model; scale: 50 μm; *. P < 0.05"

| 1 |
LI H J , GAO D S , LI Y T , et al. Antiviral effect of lithium chloride on porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in vitro[J]. Res Vet Sci, 2018, 118, 288- 294.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2018.03.002 |
| 2 |
TAN L , LI Y L , HE J Y , et al. Epidemic and genetic characterization of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains circulating in the regions around Hunan, China, during 2017-2018[J]. Arch Virol, 2020, 165 (4): 877- 889.
doi: 10.1007/s00705-020-04532-7 |
| 3 |
WICHT O , LI W T , WILLEMS L , et al. Proteolytic activation of the porcine epidemic diarrhea coronavirus spike fusion protein by trypsin in cell culture[J]. J Virol, 2014, 88 (14): 7952- 7961.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.00297-14 |
| 4 |
WANG H F , HUI P , UEMOTO Y , et al. Metabolomic and proteomic profiling of porcine intestinal epithelial cells infected with porcine epidemic diarrhea virus[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24 (6): 5071.
doi: 10.3390/ijms24065071 |
| 5 |
JUNG K , SAIF L J . Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection: Etiology, epidemiology, pathogenesis and immunoprophylaxis[J]. Vet J (London, England: 1997), 2015, 204 (2): 134- 143.
doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2015.02.017 |
| 6 | LI Y C , WANG X Y , ZHANG E , et al. Calpain-1: a novel antiviral host factor identified in porcine small intestinal mucus[J]. mBio, 2022, 13 (5): e00358- 22. |
| 7 |
HANSSON G C . Role of mucus layers in gut infection and inflammation[J]. Curr Opin Microbiol, 2012, 15 (1): 57- 62.
doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2011.11.002 |
| 8 | DU J , LUO J Q , YU J , et al. Manipulation of intestinal antiviral innate immunity and immune evasion strategies of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus[J]. BioMed Res Int, 2019, 2019, 1862531. |
| 9 | LI L , FU F , GUO S S , et al. Porcine intestinal enteroids: a new model for studying enteric coronavirus porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection and the host innate response[J]. J Virol, 2019, 93 (5): e01682- 18. |
| 10 |
YANG J W , TIAN G , CHEN D W , et al. Dietary 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 supplementation alleviates porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection by improving intestinal structure and immune response in weaned pigs[J]. Animals, 2019, 9 (9): 627.
doi: 10.3390/ani9090627 |
| 11 |
VAN DIEP N , CHOIJOOKHUU N , FUKE N , et al. New tropisms of porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus (PEDV) in pigs naturally coinfected by variants bearing large deletions in the spike (S) protein and PEDVs possessing an intact S protein[J]. Transbound Emerg Dis, 2020, 67 (6): 2589- 2601.
doi: 10.1111/tbed.13607 |
| 12 |
NIEDERWERDER M C , HESSE R A . Swine enteric coronavirus disease: A review of 4 years with porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus and porcine deltacoronavirus in the United States and Canada[J]. Transbound Emerg Dis, 2018, 65 (3): 660- 675.
doi: 10.1111/tbed.12823 |
| 13 | YIN L D , CHEN J F , LI L , et al. Aminopeptidase N expression, not interferon responses, determines the intestinal segmental tropism of porcine deltacoronavirus[J]. J Virol, 2020, 94 (14): e00480- 20. |
| 14 |
JUNG K , MIYAZAKI A , HU H , et al. Susceptibility of porcine IPEC-J2 intestinal epithelial cells to infection with porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) and serum cytokine responses of gnotobiotic pigs to acute infection with IPEC-J2 cell culture-passaged PDCoV[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2018, 221, 49- 58.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.05.019 |
| 15 |
CHEN Y M , HELM E T , GABLER N , et al. Alterations in intestinal innate mucosal immunity of weaned pigs during porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection[J]. Vet Pathol, 2020, 57 (5): 642- 652.
doi: 10.1177/0300985820932140 |
| 16 |
LIANG J X , LI Y , YAN Z S , et al. Study of the effect of intestinal immunity in neonatal piglets coinfected with porcine deltacoronavirus and porcine epidemic diarrhea virus[J]. Arch Virol, 2022, 167 (8): 1649- 1657.
doi: 10.1007/s00705-022-05461-3 |
| 17 | 王娜, 唐雪婵. 黏蛋白-2与肠黏膜屏障损伤的研究进展[J]. 基础医学与临床, 2015, 35 (7): 985- 988. |
| WANG N , TANG X C . Research progress of mucin-2 and intestinal mucosal barrier damage[J]. Basic & Clinical Medicine, 2015, 35 (7): 985- 988. | |
| 18 |
STEDMAN A , BECK-CORMIER S , LE BOUTEILLER M , et al. Ribosome biogenesis dysfunction leads to P53-mediated apoptosis and goblet cell differentiation of mouse intestinal stem/progenitor cells[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2015, 22 (11): 1865- 1876.
doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.57 |
| 19 |
RENES I B , VERBURG M , VAN NISPEN D J P M , et al. Epithelial proliferation, cell death, and gene expression in experimental colitis: alterations in carbonic anhydrase I, mucin MUC2, and trefoil factor 3 expression[J]. Int J Colorectal Dis, 2002, 17 (5): 317- 326.
doi: 10.1007/s00384-002-0409-4 |
| 20 |
BOSHUIZEN J A , REIMERINK J H J , MALE A M K V , et al. Homeostasis and function of goblet cells during rotavirus infection in mice[J]. Virology, 2005, 337 (2): 210- 221.
doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.03.039 |
| 21 |
CORTEZ V , BOYD D F , CRAWFORD J C , et al. Astrovirus infects actively secreting goblet cells and alters the gut mucus barrier[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11 (1): 2097.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15999-y |
| 22 |
WANG X , YAMAMOTO Y , WILSON L H , et al. Cloning and variation of ground state intestinal stem cells[J]. Nature, 2015, 522 (7555): 173- 178.
doi: 10.1038/nature14484 |
| 23 |
LI H J , RAY S K , KUCUKURAL A , et al. Reduced Neurog3 gene dosage shifts enteroendocrine progenitor towards goblet cell lineage in the mouse intestine[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 11 (2): 433- 448.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2020.08.006 |
| 24 |
HUANG Z H , WU H M , FAN J J , et al. Colonic mucin-2 attenuates acute necrotizing pancreatitis in rats by modulating intestinal homeostasis[J]. FASEB J, 2023, 37 (7): e22994.
doi: 10.1096/fj.202201998R |
| 25 |
CHANG R M , WEN L Q , CHANG J X , et al. Repair of damaged intestinal mucosa in a mouse model of sepsis[J]. World J Emerg Med, 2013, 4 (3): 223- 228.
doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.issn.1920-8642.2013.03.012 |
| 26 |
PELASEYED T , BERGSTRÖM J H , GUSTAFSSON J K , et al. The mucus and mucins of the goblet cells and enterocytes provide the first defense line of the gastrointestinal tract and interact with the immune system[J]. Immunol Rev, 2014, 260 (1): 8- 20.
doi: 10.1111/imr.12182 |
| 27 |
GIPSON I K . Goblet cells of the conjunctiva: a review of recent findings[J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2016, 54, 49- 63.
doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2016.04.005 |
| 28 |
GRINAT J , KOSEL F , GOVEAS N , et al. Epigenetic modifier balances mapk and WNT signalling in differentiation of goblet and paneth cells[J]. Life Sci Alliance, 2022, 5 (4): e202101187.
doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101187 |
| 29 |
KANNO H , HORIKAWA Y , HODGES R R , et al. Cholinergic agonists transactivate EGFR and stimulate MAPK to induce goblet cell secretion[J]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2003, 284 (4): C988- C998.
doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00582.2001 |
| 30 |
JOHANSSON M E V , HANSSON G C . Immunological aspects of intestinal mucus and mucins[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2016, 16 (10): 639- 649.
doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.88 |
| 31 |
GUO J J , WANG D S , HUANG H T . Spontaneous remission of edema and regranulation of goblet cells in rat tracheae after capsaicin-induced acute inflammation[J]. Anat Embryol (Berl), 2003, 206 (4): 301- 309.
doi: 10.1007/s00429-002-0299-9 |
| 32 |
MADAS B G , DROZSDIK E J . Effects of mucus thickness and goblet cell hyperplasia on microdosimetric quantities characterizing the bronchial epithelium upon radon exposure[J]. Int J Radiat Biol, 2018, 94 (11): 967- 974.
doi: 10.1080/09553002.2018.1511931 |
| 33 |
WADDELL A , VALLANCE J E , HUMMEL A , et al. IL-33 induces murine intestinal goblet cell differentiation indirectly via innate lymphoid cell IL-13 secretion[J]. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md: 1950), 2019, 202 (2): 598- 607.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800292 |
| 34 |
DOLAN B , ERMUND A , MARTINEZ-ABAD B , et al. Clearance of small intestinal crypts involves goblet cell mucus secretion by intracellular granule rupture and enterocyte ion transport[J]. Sci Signal, 2022, 15 (752): eabl5848.
doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abl5848 |
| 35 |
FAN B C , ZHOU J Z , ZHAO Y X , et al. Identification of cell types and transcriptome landscapes of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus-infected porcine small intestine using single-cell rna sequencing[J]. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md: 1950), 2023, 210 (3): 271- 282.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2101216 |
| 36 |
ZHANG Y , CHEN H J , YU J , et al. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus epidemic and classical strains in IPEC-J2 cells[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2022, 273, 109540.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2022.109540 |
| 37 |
KAR S K , WELLS J M , ELLEN E D , et al. Organoids: a promising new in vitro platform in livestock and veterinary research[J]. Vet Res, 2021, 52 (1): 43.
doi: 10.1186/s13567-021-00904-2 |
| 38 |
HEUBERGER J , KOSEL F , QI J J , et al. Shp2/MAPK signaling controls goblet/paneth cell fate decisions in the intestine[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2014, 111 (9): 3472- 3477.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1309342111 |
| 39 |
CHOUDRY H A , MAVANUR A , O'MALLEY M E , et al. MEK-ERK pathway inhibition reduces mucin production in a murine xenograft model of pseudomyxoma peritonei[J]. Cancer Res, 2012, 72 (8_Supplement): 5253.
doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2012-5253 |
| 40 |
ZHANG B B , LI J , FU J L , et al. Interaction between mucus layer and gut microbiota in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: soil and seeds[J]. Chin Med J, 2023, 136 (12): 1390- 1400.
doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002711 |
| 41 |
LEE S I , KIM I H . Nucleotide-mediated SPDEF modulates TFF3-mediated wound healing and intestinal barrier function during the weaning process[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8 (1): 4827.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23218-4 |
| 42 | CHEN G Y , STAPPENBECK T S . Mucus, it is not just a static barrier[J]. Sci Signal, 2014, 7 (323): pe11. |
| 43 |
TANABE T , KANOH S , TSUSHIMA K , et al. Clarithromycin inhibits interleukin-13-induced goblet cell hyperplasia in human airway cells[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2011, 45 (5): 1075- 1083.
doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0327OC |
| [1] | Yue LI, Changchun ZHANG, Guangyu LIU, Mengyuan GAO, Chaojun FU, Jiabao XING, Sijia XU, Qiyuan KUANG, Jing LIU, Xiaopeng GAO, Heng WANG, Lang GONG, Guihong ZHANG, Yankuo SUN. Application and Analysis of Meta-transcriptomics Sequencing Technology in the Diagnosis of Viral Diarrhea Diseases in Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(8): 3579-3589. |
| [2] | XU Hong, SHANG Hongqi, ZHANG Xue, QIAN Jiali, WANG Chuanhong, SONG Xu, BAO Meiying, LIU Shiyu, ZHANG Gege, GUO Rongli, ZHAO Yongxiang, FAN Baochao, LI Bin. Inhibition Effect of C8orf4 Gene Encoding Protein on in vitro Replication of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2100-2108. |
| [3] | MA Yajuan, SU Kai, LIN Yidan, WANG Yawen, ZHANG Yanan, YUAN Hongxing, YUAN Chen, SONG Qinye. The Inhibitory Effect of Salinomycin on Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(4): 1661-1671. |
| [4] | XIAO Le, LIU Junyuan, ZENG Wenyu, WANG Qin, HAN Wenjue, LIU Yanling, FAN Yu, XU Yuting, YANG Beini, XIAO Xiong, WANG Zili. Microbiome and Transcriptome Analyses Revealed the Regulatory Mechanism of Xiangsha Liujunzi Decoction on Ileal Injury Induced by ETEC in Weaned Piglets with Diarrhea [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 797-808. |
| [5] | CHANG Weichen, LI Shuaiqi, LI Yan, YAN Wei, ZHANG Hongying, WANG Yanbin, YANG Mingfan, ZHANG Angke. Effect of Pulsatilla Powder Prescription Decoction Ferments on Intestinal Barrier Function of Piglets Infected with Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(10): 4403-4410. |
| [6] | ZHANG Zhicheng, CHEN Meijuan, AI Jun. Bayesian Inference and Simulation on True Prevalence of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus in American Swine Population [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(7): 2013-2024. |
| [7] | LIANG Jixiang, JIAO Zhe, YAN Zhishan, LI Yang, LI Dongqi, LIU Xiaoli, GU Changqin, HU Xueying, CHENG Guofu, ZHANG Wanpo. Effect of Porcine Deltacoronavirus Infection on the Number of Intestinal Goblet Cells and the Expression of Hes1 and MUC2 in the Small Intestine of Neonatal Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(3): 772-781. |
| [8] | CHANG Xinjian, ZHOU Jinzhu, YIN Jie, NIU Beibei, FAN Baochao, GUO Rongli, ZHAO Yongxiang, NIU Jiaqiang, HE Kongwang, LI Bin. Investigation on Pathogens of Major Viral Diarrhea in Pig Farms in East China from 2017 to 2019 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(12): 3141-3150. |
| [9] | LIN Chunfa, HAO Yongfeng, LIU Juan. Effect of Polysaccharides from ZhuKuQin on the Number of Intestinal Goblet Cell and the Transcription of MUC-2 and ITF-3 mRNA in the Small Intestine of Damp-heat Diarrhea Piglets [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2019, 50(6): 1301-1311. |
| [10] | SHEN Xiaojuan, LI Jingjiao, BIAN Jiang, ZHAO Tingting, HUA Xiuguo, CUI Li. Metagenomics Analysis of Feces from Diarrhea Piglets Reveals the Viral Composition and Epidemic Characteristics of Coronavirus [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2019, 50(3): 611-619. |
| [11] | WANG Long-bai, WANG Chen-yan, WU Xue-min, CHEN Qiu-yong, CHE Yong-liang, CHEN Ru-jing, ZHOU Lun-jiang. Prokaryotic Expression and Immunogenic Analysis of the Combined M and N Fusion Genes for Variant Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2018, 49(6): 1249-1255. |
| [12] | DONG Jian-guo, WANG Rui, QU Zhe-hui, ZHAO Yu, LIU Tao. Genetic Variations of S Gene of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus in Sourthern Henan Province from 2014 to 2015 [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2018, 49(4): 859-864. |
| [13] | ZHANG Ruo-xi, ZHANG Zhi, GU Wen-yuan, LIU Tian-ju, LI Chong, WANG Jian-chang, LI Bin, YUAN Wan-zhe, WANG Yu-qing, HAN Qing-an. Detection of Porcine Diarrhea Associated Virus and Genetic Variation Analysis of S Gene of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus in Hebei Province [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2018, 49(3): 597-605. |
| [14] | YAO Zuo-jun, HAO Da-ren, BAI Yun, YAN Guo-hua, WANG Hai-min, SONG Qin-ye, LI Tan-qing. Indirect ELISA for Detecting Antibody to Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus S1 Protein [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2017, 48(6): 1085-1091. |
| [15] | LI Hong-jie, WANG Xiao-xue, GAO Dong-sheng, HUANG Hui-min, CHEN Lu, CHANG Hong-tao, WANG Chuan-qing, LI Yong-tao, ZHAO Jun. Subcellular Localization and Effect on Type Ⅰ Interferon Response of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Nsp7 [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2017, 48(3): 501-507. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||