





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 417-429.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.01.038
• Basic Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Xinhe( ), LI Haonan, ZHOU Xiao, XU Jiajing, ZHANG Yuanshu*(
), LI Haonan, ZHOU Xiao, XU Jiajing, ZHANG Yuanshu*( ), HAN Zhengkang
), HAN Zhengkang
Received:2024-02-22
Online:2025-01-23
Published:2025-01-18
Contact:
ZHANG Yuanshu
E-mail:2021107033@stu.njau.edu.cn;zhangyuanshu@njau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
HUANG Xinhe, LI Haonan, ZHOU Xiao, XU Jiajing, ZHANG Yuanshu, HAN Zhengkang. Effects and Mechanism on the Synthesis of Milk Components and Cell Proliferation in Mouse Mammary Epithelial Cells by Phytoestrogen Daidzein[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(1): 417-429.
Table 1
Group of cell treatments"
| 组别 Group | 处理 Treatment |
| 对照组 Control group | 等体积不完全培养基 Equal volume of incomplete culture medium |
| 低浓度组(10 μmol·L-1) | 等体积不完全培养基+10 μmol·L-1 DZ |
| Low concentration group (10 μmol·L-1) | Equal volume of incomplete culture medium+10 μmol·L-1 DZ |
| 中浓度组(20 μmol·L-1) | 等体积不完全培养基+20 μmol·L-1 DZ |
| Medium concentration group (20 μmol·L-1) | Equal volume of incomplete culture medium+20 μmol·L-1 DZ |
| 高浓度组(40 μmol·L-1) | 等体积不完全培养基+40 μmol·L-1 DZ |
| High concentration group (40 μmol·L-1) | Equal volume of incomplete culture medium+40 μmol·L-1 DZ |
| 阳性对照组(E2) Positive control group (E2) | 等体积不完全培养基+5×10-4μmol·L-1 E2 Equal volume of incomplete culture medium+5×10-4μmol·L-1 E2 |

Fig. 1
Effects of DZ treatment at different concentrations and different time on the viability of mammary epithelial cells (n=6) Compared with the control group, ** means extremely significant difference (P < 0.01), * means significant difference (P < 0.05).The color pictures can be found by scanning the OSID code on the front page of the article, the same as below"


Fig. 4
Effect of DZ treatment on lipid droplet synthesis in mouse mammary epithelial cells A. Fluorescent staining of lipid droplets, scale bars=200 μm; B. Integral optical density analysis of lipid droplets, compared with the control group, ** means extremely significant difference (P < 0.01).The color pictures can be found by scanning the OSID code on the front page of the article, the same as below"


Fig. 6
Effect of DZ on cell cycle distribution in mouse mammary epithelial cells A-E. Cell cycle distribution after treatment with different concentrations of DZ and E2; F. The statistics of cell cycle distribution results. Compared with the control group, ** means extremely significant difference (P < 0.01), * means significant difference (P < 0.05).The color pictures can be found by scanning the OSID code on the front page of the article, the same as below"
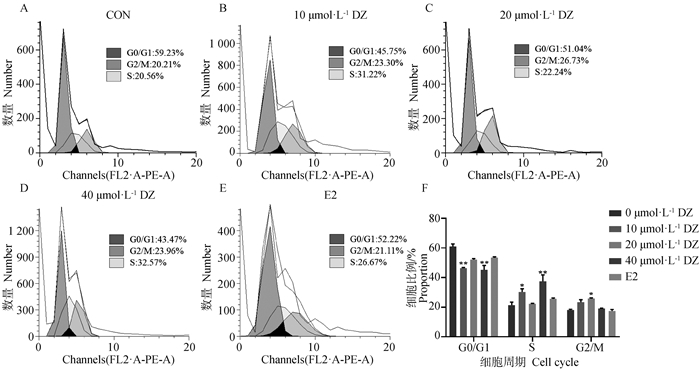

Fig. 7
Effect of DZ on apoptosis rate in mouse mammary epithelial cells Compared with the control group, ** means extremely significant difference (P < 0.01), * means significant difference (P < 0.05).The color pictures can be found by scanning the OSID code on the front page of the article, the same as below"

| 1 |
BOUTINAUD M , HERVE L , QUESNEL H , et al. Review: the cellular mechanisms underlying mammary tissue plasticity during lactation in ruminants[J]. Animal, 2019, 13, s52- s64.
doi: 10.1017/S1751731119000624 |
| 2 | 李庆章. 乳腺发育与泌乳生物学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009. |
| LI Q Z . Development and lactation biology of mammary gland[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009. | |
| 3 | SCULLY K M , GLEIBERMAN A S , LINDZEY J , et al. Role of estrogen receptor-α in the anterior pituitary gland[J]. Mol Endocrinol, 1997, 11 (6): 674- 681. |
| 4 |
CHU M Q , ZHAO Y , YU S , et al. MicroRNA-221 may be involved in lipid metabolism in mammary epithelial cells[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2018, 97, 118- 127.
doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.02.014 |
| 5 |
BURGOS S A , DAI M , CANT J P . Nutrient availability and lactogenic hormones regulate mammary protein synthesis through the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2010, 93 (1): 153- 161.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2009-2444 |
| 6 |
TUCKER H A . Hormones, mammary growth, and lactation: a 41-year perspective[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2000, 83 (4): 874- 884.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(00)74951-4 |
| 7 |
ALSHEHRI M M , SHARIFI-RAD J , HERRERA-BRAVO J , et al. Therapeutic potential of isoflavones with an emphasis on daidzein[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021, 2021, 6331630.
doi: 10.1155/2021/6331630 |
| 8 |
TSUGAMI Y , SUZUKI N , SUZUKI T , et al. Regulatory effects of soy isoflavones and their metabolites in milk production via different ways in mice[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2020, 68 (21): 5847- 5853.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c01288 |
| 9 | 谢娜娜, 闫书平, 张崇昊, 等. 植物雌激素大豆黄酮对牛乳腺上皮细胞增殖及细胞周期的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2022, 34 (4): 2645- 2653. |
| XIE N N , YAN S P , ZHANG C H , et al. Effects of phytoestrogen daidzein on proliferation and cell cycle of bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2022, 34 (4): 2645- 2653. | |
| 10 |
刘春龙, 李忠秋, 张帆, 等. 大豆黄酮和染料木素对体外培养奶牛乳腺上皮细胞增殖及抗氧化水平的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2008, 39 (11): 1517- 1522.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0366-6964.2008.11.011 |
|
LIU C L , LI Z Q , ZHANG F , et al. Effect of daidzein and genistein on proliferation and antioxidation of mammary epithelial cell of dairy cow in vitro[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2008, 39 (11): 1517- 1522.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0366-6964.2008.11.011 |
|
| 11 |
KUMAR V , CHAUHAN S S . Daidzein induces intrinsic pathway of apoptosis along with ER α/β ratio alteration and ROS production[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2021, 22 (2): 603- 610.
doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.2.603 |
| 12 |
LI W , LONG X Y , LI F , et al. Lysine stimulates the development of the murine mammary gland at puberty via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling axis[J]. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl), 2022, 106 (6): 1420- 1430.
doi: 10.1111/jpn.13756 |
| 13 |
SHERR C J . Surprising regulation of cell cycle entry[J]. Science, 2019, 366 (6471): 1315- 1316.
doi: 10.1126/science.aaz4043 |
| 14 |
FAN L , BI T H , WANG L X , et al. DNA-damage tolerance through PCNA ubiquitination and sumoylation[J]. Biochem J, 2020, 477 (14): 2655- 2677.
doi: 10.1042/BCJ20190579 |
| 15 | 王雯竞, 吴霄, 臧旭鹏, 等. 哺乳动物乳腺发育调控机制的研究进展[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2022, 54 (1): 137- 143. |
| WANG W J , WU X , ZANG X P , et al. Progress in research on the regulation mechanism of mammary gland development in mammals[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 54 (1): 137- 143. | |
| 16 |
GUO J L , WANG Q L , ZHANG Y , et al. Functional daidzein enhances the anticancer effect of topotecan and reverses BCRP-mediated drug resistance in breast cancer[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2019, 147, 104387.
doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104387 |
| 17 |
YU M M , QI H , GAO X J . Daidzein promotes milk synthesis and proliferation of mammary epithelial cells via the estrogen receptor α-dependent NFκB1 activation[J]. Anim Biotechnol, 2022, 33 (1): 43- 52.
doi: 10.1080/10495398.2020.1763376 |
| 18 | METCALFE A D , GILMORE A , KLINOWSKA T , et al. Developmental regulation of Bcl-2 family protein expression in the involuting mammary gland[J]. J Cell Sci, 1999, 112 (Pt 11): 1771- 1783. |
| 19 |
ZHU C , WANG L L , ZHU J R , et al. OGR1 negatively regulates β-casein and triglyceride synthesis and cell proliferation via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in goat mammary epithelial cells[J]. Anim Biotechnol, 2021, 32 (5): 627- 636.
doi: 10.1080/10495398.2020.1737099 |
| 20 | 任发政. 乳的营养与健康[J]. 中国食品学报, 2020, 20 (7): 1- 9. |
| REN F Z . Advances in milk nutrition and human health[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2020, 20 (7): 1- 9. | |
| 21 |
GŁĄB T K , BORATYŃSKI J . Potential of casein as a carrier for biologically active agents[J]. Top Curr Chem (Cham), 2017, 375 (4): 71.
doi: 10.1007/s41061-017-0158-z |
| 22 |
TSUGAMI Y , MATSUNAGA K , SUZUKI T , et al. Isoflavones and their metabolites influence the milk component synthesis ability of mammary epithelial cells through prolactin/STAT5 signaling[J]. Mol Nutr Food Res, 2017, 61 (10): 1700156.
doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201700156 |
| 23 |
SHAHBAZKIA H R , AMINLARI M , TAVASOLI A , et al. Associations among milk production traits and glycosylated haemoglobin in dairy cattle; importance of lactose synthesis potential[J]. Vet Res Commun, 2010, 34 (1): 1- 9.
doi: 10.1007/s11259-009-9324-2 |
| 24 |
SUNEHAG A L , LOUIE K , BIER J L , et al. Hexoneogenesis in the human breast during lactation[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2002, 87 (1): 297- 301.
doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.1.8171 |
| 25 |
BEN CHEDLY H , LACASSE P , MARNET P G , et al. Use of milk epithelial cells to study regulation of cell activity and apoptosis during once-daily milking in goats[J]. Animal, 2011, 5 (4): 572- 579.
doi: 10.1017/S1751731110002284 |
| 26 |
LI N , ZHAO F , WEI C J , et al. Function of SREBP1 in the milk fat synthesis of dairy cow mammary epithelial cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2014, 15 (9): 16998- 17013.
doi: 10.3390/ijms150916998 |
| 27 |
ZHANG M , ZHANG S Q , HUI Q , et al. β-Hydroxybutyrate facilitates fatty acids synthesis mediated by sterol regulatory element-binding protein1 in bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2015, 37 (6): 2115- 2124.
doi: 10.1159/000438569 |
| 28 | 陈坤琳, 钱勇, 蒋临正, 等. SIRT7对奶牛乳腺上皮细胞乳蛋白、乳脂和乳糖合成关键基因表达的调控[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2019, 42 (5): 917- 923. |
| CHEN K L , QIAN Y , JIANG L Z , et al. Effects of SIRT7 on the expression of key genes involved in lactoprotein, milk fat and lactosesynthesis in dairy cow mammary epithelial cells[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2019, 42 (5): 917- 923. | |
| 29 |
LIU L L , LIN Y , LIU L X , et al. Regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma on milk fat synthesis in dairy cow mammary epithelial cells[J]. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim, 2016, 52 (10): 1044- 1059.
doi: 10.1007/s11626-016-0059-4 |
| 30 |
MU T , HU H H , MA Y F , et al. Regulation of key genes for milk fat synthesis in ruminants[J]. Front Nutr, 2021, 8, 765147.
doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.765147 |
| 31 |
ERSAHIN T , TUNCBAG N , CETIN-ATALAY R . The PI3K/AKT/mTOR interactive pathway[J]. Mol BioSyst, 2015, 11 (7): 1946- 1954.
doi: 10.1039/C5MB00101C |
| 32 |
HINZ N , JÜCKER M . Distinct functions of AKT isoforms in breast cancer: a comprehensive review[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2019, 17 (1): 154.
doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0450-3 |
| 33 |
PONNUSAMY A , SINHA S , HYDE G D , et al. FTI-277 inhibits smooth muscle cell calcification by up-regulating PI3K/Akt signaling and inhibiting apoptosis[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13 (4): e0196232.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196232 |
| 34 |
YU M M , WANG Y , WANG Z , et al. Taurine promotes milk synthesis via the GPR87-PI3K-SETD1A signaling in BMECs[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2019, 67 (7): 1927- 1936.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b06532 |
| 35 |
JIN X , SUN J , YU B , et al. Daidzein stimulates osteogenesis facilitating proliferation, differentiation, and antiapoptosis in human osteoblast-like MG-63 cells via estrogen receptor-dependent MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt activation[J]. Nutr Res, 2017, 42, 20- 30.
doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2017.04.009 |
| [1] | LIU Chun-long;;LI Zhong-qiu;ZHANG Fan;JIANG Wen-bo;XU Yan;SHAN An-shan. Effect of Daidzein and Genistein on Proliferation and Antioxidation of Mammary Epithelial Cell of Dairy Cow in vitro [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2008, 39(11): 1517-1522. |
| [2] | NI Ying-dong;HONG Wen-jie;REN Ling-zhi;HU Yan;DAI Jing;RAO Kai-qing;CHEN Jie;ZHAO Ru-qian. Effects of Dietary Daidzein on Egg Quality and Meat Quality of the Offspring of Broiler Breed Hens during the Late Period of Laying Cycle [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2007, 38(11): 1188-1194. |
| [3] | MA Hai-tian;HOU Zong-mei;HAN Zheng-kang;YAO Wen;WANG Guo-jie;ZOU Si-xiang. Effect of Daidzein on Membrane Digestion of Disaccharide in Piglet [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2005, 36(6): 625-626. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||