





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (11): 5925-5935.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.11.047
• Clinical Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHEN Haoyi( ), ZHAO Yiran(
), ZHAO Yiran( ), SHI Jingwen, LEI Binrong, QIAN Ruolin, YUAN Hong, REN Ge, YAO Hua, ZHANG Hua*(
), SHI Jingwen, LEI Binrong, QIAN Ruolin, YUAN Hong, REN Ge, YAO Hua, ZHANG Hua*( )
)
Received:2024-11-28
Online:2025-11-23
Published:2025-11-27
Contact:
ZHANG Hua
E-mail:13621277161@139.com;zhaoyiran0917@icloud.com;huazhang0914@163.com
CLC Number:
SHEN Haoyi, ZHAO Yiran, SHI Jingwen, LEI Binrong, QIAN Ruolin, YUAN Hong, REN Ge, YAO Hua, ZHANG Hua. Analysis of Antibacterial Activity and Synergistic Effect of Natural Plant Essential Oils Combined with Potassium Monopersulfate[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5925-5935.
Table 1
The MIC and MBC results of eight essential oils and potassium monopersulfate against S. aureus and E. coli μg ·mL-1"
| 试剂 Reagent | 金黄色葡萄球菌(ATCC 29740) S. aureus (ATCC 29740) | 大肠杆菌(CVCC 1450) E. coli(CVCC 1450) | |||
| MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | ||
| 国产茶树精油 Domestic tea tree oil | 7.81 | 15.63 | 62.50 | 125.00 | |
| 澳洲茶树精油 Australian tea tree oil | 3.91 | 7.81 | 31.25 | 62.50 | |
| 国产尤加利精油 Domestic eucalyptus oil | 31.25 | 62.50 | 125.00 | 250.00 | |
| 澳洲尤加利精油 Australian eucalyptus oil | 31.25 | 62.50 | 31.25 | 62.50 | |
| 国产洋甘菊精油 Domestic chamomile oil | 15.63 | 31.25 | 15.63 | 31.25 | |
| 澳洲洋甘菊精油 Australian chamomile oil | 7.81 | 15.63 | 250.00 | 500.00 | |
| 国产薰衣草精油 Domestic lavender oil | 1.95 | 3.91 | 15.63 | 31.25 | |
| 澳洲薰衣草精油 Australian lavender oil | 1.95 | 3.91 | 125.00 | 250.00 | |
| 过硫酸氢钾复合盐 Potassiumperoxymonosulfate sulfate | 0.000 6 | 0.001 2 | 0.000 6 | 0.001 2 | |
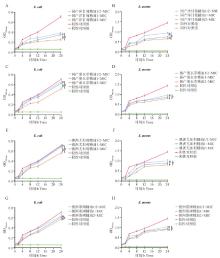
Fig. 1
Different concentrations of highly antibacterial plant essential oil time-antibacterial curve In the figure, * indicates statistically significant differences between different concentrations of essential oil treatment groups, 0.01 < P < 0.05; ** indicates highly statistically significant difference between different concentrations of essential oil treatment groups, P < 0.01; ns indicates no significant difference between different concentrations of essential oil treatment groups, P>0.05"

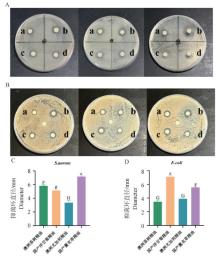
Fig. 2
Results of in vitro drug sensitivity test A. Drug sensitivity test results of four highly antibacterial plant essential oils against Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 29740). B. Drug sensitivity test results of four highly antibacterial plant essential oils against Escherichia coli (CVCC 1450). C, D. Quantitative results of the inhibition zones of four highly antibacterial plant essential oils. In Figures A and B: a. Sterile drug sensitivity disc of diluted Australian tea tree essential oil; b. Sterile drug sensitivity disc of diluted domestic chamomile essential oil; c. Sterile drug sensitivity disc of diluted Australian eucalyptus essential oil; d. Sterile drug sensitivity disc of diluted domestic lavender essential oil. In Figures C and D, different lowercase letters indicate a statistically significant differences with 0.01 < P < 0.05, and different uppercase letters indicate highly statistically significant difference with P < 0.01"

Table 2
Evaluation of the combined antibacterial effects of four highly antibacterial plant essential oils and potassium monopersulfate"
| 菌株 Bacterial strain | 试剂 Reagent | MIC/(μg·mL-1) | 联合抑菌指数 FICI | 作用方式 Mode of action | |
| 单用 Single use | 联合 Combined | ||||
| 金黄色葡萄球菌 S. aureus | 澳洲尤加利精油 过硫酸氢钾复合盐 | 31.25 0.000 6 | 31.25 0.001 2 | 3 | 拮抗 |
| 大肠杆菌 E. coli | 澳洲尤加利精油 过硫酸氢钾复合盐 | 31.25 0.000 6 | 62.50 0.000 6 | 3 | 拮抗 |
| 金黄色葡萄球菌 S. aureus | 澳洲茶树精油 过硫酸氢钾复合盐 | 3.91 0.000 6 | 3.91 0.000 3 | 1.5 | 无关 |
| 大肠杆菌 E. coli | 澳洲茶树精油 过硫酸氢钾复合盐 | 31.25 0.000 6 | 31.25 0.000 6 | 2 | 无关 |
| 金黄色葡萄球菌 S. aureus | 国产薰衣草精油 过硫酸氢钾复合盐 | 1.95 0.000 6 | 1.00 0.000 3 | 1 | 相加 |
| 大肠杆菌 E. coli | 国产薰衣草精油 过硫酸氢钾复合盐 | 15.63 0.000 6 | 7.81 0.000 3 | 1 | 相加 |
| 金黄色葡萄球菌 S. aureus | 国产洋甘菊精油 过硫酸氢钾复合盐 | 15.63 0.000 6 | 3.91 0.000 3 | 0.5 | 协同 |
| 大肠杆菌 E. coli | 国产洋甘菊精油 过硫酸氢钾复合盐 | 15.63 0.000 6 | 3.91 0.000 3 | 0.5 | 协同 |
| 1 | 青格尔. 茶树和薰衣草精油体外抑菌及对皮肤开放性损伤修复的影响[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2020. |
| QING G E. Effects of tea tree and lavender essential oil on bacteriostasia and repair in open skin injury[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| 2 | 王颖, 李琳, 胡静. 基于山苍子精油的复配筛选及协同抗菌性能[J]. 精细化工, 2023, 40 (1): 146-152, 199. |
| WANG Y , LI L , HU J . Compound screening and synergistic antibacterial properties of litsea cubeba essential oils[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2023, 40 (1): 146-152, 199. | |
| 3 |
JU J , XIE Y , GUO Y , et al. Application of edible coating with essential oil in food preservation[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2019, 59 (15): 2467- 2480.
doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1456402 |
| 4 |
SELLAMUTHU P S , SIVAKUMAR D , SOUNDY P , et al. Essential oil vapours suppress the development of anthracnose and enhance defence related and antioxidant enzyme activities in avocado fruit[J]. Postharvest Biol Tec, 2013, 81, 66- 72.
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2013.02.007 |
| 5 |
CHELLAPPANDIAN M , VASANTHA-SRINIVASAN P , SENTHIL-NATHAN S , et al. Botanical essential oils and uses as mosquitocides and repellents against dengue[J]. Environ Int, 2018, 113, 214- 230.
doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.12.038 |
| 6 | 胡文杰, 戴彩华, 周升团. 油樟叶精油馏分的主要成分、抑菌活性及其主要单体成分抑菌机理研究[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2019, 25 (15): 14- 19. |
| HU W J , DAI C H , ZHOU S T . Research on major constituents, bacteriostatic effect and antibacterial mechanism of fractions from cinnamomum longepaniculatum leaves essential oils and its major monomer components[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 25 (15): 14- 19. | |
| 7 | 包志碧, 陈仁伟, 刘旺景, 等. 植物提取物的防腐作用及其机理研究进展[J]. 饲料工业, 2018, 39 (12): 58- 64. |
| BAO Z B , CHEN R W , LIU W J , et al. Research progress of the preservative effect of plant extracts on food and its mechanism[J]. Feed Industry, 2018, 39 (12): 58- 64. | |
| 8 | 汤友军, 鲁晓翔. 植物精油稳定性的改善及其在食品中应用研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技, 2020, 41 (7): 353- 357. |
| TANG Y J , LU X X . Research progress on stability improvement of plant essential oil and its application in food[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41 (7): 353- 357. | |
| 9 |
BARBOSA L C A , FILOMENO C A , TEIXEIRA R R . Chemical variability and biological activities of eucalyptus spp. essential oils[J]. Molecules, 2016, 21 (12): 1671.
doi: 10.3390/molecules21121671 |
| 10 | 苏乐文, 李洋, 纪培煜, 等. 几种香辛料的体外抑菌效果研究[J]. 现代农业科技, 2022 (16): 175- 180. |
| SU L W , LI Y , JI P Y , et al. Study on antibacterial effect of several spices in vitro[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022 (16): 175- 180. | |
| 11 | 邹月, 黄金凤, 魏琴, 等. 不同提取时间的艳山姜挥发油组分分析及其抑菌活性研究[J]. 中国调味品, 2020, 45 (3): 62-66, 72. |
| ZOU Y , HUANG J F , WEI Q , et al. Analysis of volatile oil components of alpinia zerumbet at different extraction time and study on their antibacterial activity[J]. China Condiment, 2020, 45 (3): 62-66, 72. | |
| 12 |
MOON S E , KIM H Y , CHA J D . Synergistic effect between clove oil and its major compounds and antibiotics against oral bacteria[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2011, 56 (9): 907- 916.
doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2011.02.005 |
| 13 | 王雅如, 赵丹, 杨翼航, 等. 十种中草药对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌体外抑菌效果研究[J]. 生物化工, 2022, 8 (4): 90-92, 105. |
| WANG Y R , ZHAO D , ZHANG Y H , et al. In vitro bacteriostatic effects of ten Chinese herbal medicines on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Biological Chemical Engineering, 2022, 8 (4): 90-92, 105. | |
| 14 | 李文茹, 施庆珊, 谢小保, 等. 植物精油化学成分及其抗菌活性的研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2016, 43 (6): 1339- 1344. |
| LI W R , SHI Q S , XIE X B , et al. Progress on the antimicrobial properties of essential oils[J]. Microbiology China, 2016, 43 (06): 1339- 1344. | |
| 15 | 吴克刚, 罗敏婷, 魏浩. 8种植物精油对肠道常见微生物体外抑菌效果的研究[J]. 现代食品科技, 2017, 33 (6): 133-141, 93. |
| WU K G , LUO M T , WEI H . Evaluation of the in vitro antimicrobial effects of eight plant essential oils against common intestinal microorganisms[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2017, 33 (6): 133-141, 93. | |
| 16 | 魏磊, 李晓, 王伟, 等. 12种植物精油主要成分及对鸡源致病菌的抑菌作用研究[J]. 饲料研究, 2016 (12): 53- 56. |
| WEI L , LI X , WANG W , et al. Study on the main components of 12 kinds of plant essential oils and their antibacterial effects on chicken-derived pathogenic bacteria[J]. Feed Research, 2016 (12): 53- 56. | |
| 17 |
CHEN J , TANG C , ZHANG R , et al. Metabolomics analysis to evaluate the antibacterial activity of the essential oil from the leaves of Cinnamomum camphora (Linn.) Pres[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 253, 112652.
doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112652 |
| 18 | 罗鹏, 熊海涛, 杨晓晨, 等. 植物精油的体外抗菌活性及替抗性能初步探究[J]. 广西畜牧兽医, 2024, 40 (4): 143- 145. |
| LUO P , XIONG H T , YANG X C , et al. Preliminary investigation on the in vitro antibacterial activity and antibiotic replacement performance of plant essential oils[J]. Guangxi Journal of Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 40 (4): 143- 145. | |
| 19 | 谢姊欢, 叶正明, 刘宇, 等. 四种植物精油对草莓致病菌的协同抑制作用研究[J]. 精细化工中间体, 2021, 51 (5): 51-58, 77. |
| XIE Z H , YE Z M , LIU Y , et al. Synergistic antimicrobial effect of four plant essential oils against strawberry pathogen[J]. Fine Chemical Intermediates, 2021, 51 (5): 51-58, 77. | |
| 20 | 吴慧娟, 黄杨名, 陈科廷, 等. 神农香菊全草精油的化学成分及抑菌机理研究[J]. 食品科学, 2012, 33 (17): 35- 39. |
| WU H J , HUANG Y M , CHEN K T , et al. Chemical composition and antimicrobial mechanism of essential oil from Dendranthema indicum var. aromaticum[J]. Food Science, 2012, 33 (17): 35- 39. | |
| 21 |
NGUYEN L , DEVICO B , MANNAN M , et al. Tea tree essential oil kills Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus epidermidis persisters[J]. Biomolecules, 2023, 13 (9): 1404- 1404.
doi: 10.3390/biom13091404 |
| 22 | 朱月星, 尹思雨, 皮汨源, 等. 罗马洋甘菊精油含量及成分分析[J]. 绿色科技, 2024, 26 (8): 271- 275. |
| ZHU Y X , YIN S Y , PI M Y , et al. Analysis of essential oil content and composition of roman chamomile[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2024, 26 (8): 271- 275. | |
| 23 | 高永生, 金斐, 朱丽云, 等. 植物精油及其活性成分的抗菌机理[J]. 中国食品学报, 2022, 22 (1): 376- 388. |
| GAO Y S , JIN F , ZHU L Y , et al. Antimicrobial mechanism of plant essential oils and its active ingredients[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2022, 22 (1): 376- 388. | |
| 24 | 郝渊鹏, 李静一, 杨瑞, 等. 芳香植物精油的抗菌性及在动物生产中的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55 (5): 644- 657. |
| HAO Y P , LI J Y , YANG R , et al. Antimicrobial activity of aromatic plant essential oils and their application in animal production[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55 (5): 644- 657. | |
| 25 | 萨仁高娃, 胡文忠, 冯可, 等. 植物精油及其成分对病原微生物抗菌机理的研究进展[J]. 食品科学, 2020, 41 (11): 285- 294. |
| SA R G W , HU W Z , FENG K , et al. Antimicrobial mechanisms of essential oils and their components on pathogenic bacteria: a review[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41 (11): 285- 294. | |
| 26 | 王梦阳, 李博洋, 张珍珍, 等. 两种提取方法的新会柑皮精油化学成分分析及抑菌效果的比较[J]. 饮料工业, 2025, 28 (4): 10- 16. |
| WANG M Y , LI B Y , ZHANG Z Z , et al. Chemical composition and antibacterial effect comparison of essential oil from xinhui citrus peel by two extraction methods[J]. Beverage Industry, 2025, 28 (4): 10- 16. | |
| 27 | 张金君, 钟愧, 韩世范, 等. 植物精油单独应用和联合应用的药理作用研究[J]. 农产品加工, 2024 (16): 93- 97. |
| ZHANG J J , ZHONG K , HAN S F , et al. Study on pharmacological effects of plant essential oil applied alone and in combination[J]. Agricultural Products Processing, 2024 (16): 93- 97. | |
| 28 | 张艳东, 张艳俊, 李腾飞. 植物精油的提取及其生理活性研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2023, 44 (9): 203- 210. |
| ZHANG Y D , ZHANG Y J , LI T F . Plant essential oil extraction and physiological activities[J]. Food Research and Development, 2023, 44 (9): 203- 210. | |
| 29 | 张桂枝, 杨雪茹, 陈旭勃, 等. 植物精油与有机酸盐联合对曲霉菌的抑制作用[J]. 现代牧业, 2022, 6 (4): 30- 36. |
| ZHANG G Z , YANG X R , CHEN X B , et al. Bacteriostasis of plant essential oil combined with organic acid salt on Aspergillus[J]. Modern Animal Husbandry,, 2022, 6 (4): 30- 36. | |
| 30 | 赵琛, 丁健, 李艳玲. 植物精油的生物活性及其在畜禽免疫上的应用[J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32 (9): 4070- 4077. |
| ZHAO C , DING J , LI Y L . Biological activity of plant essential oils and their application in animal immunity[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32 (9): 4070- 4077. |
| [1] | WANG Linwei, WANG Jing, HAN Saibo, LI Hanchuan, WANG Panpan, GUO Gang, JIANG Linshu. Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Essential Oils on Serum Immune and Biochemical Indicators in Suckling Calves [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(8): 3872-3892. |
| [2] | ZHANG Yuan, LI Mingyang, LIANG Yue, YU Xiangqian, WANG Yan, CHEN Jiyi, LIU Haixia, LIAN Xue, QIAN Yingjuan. Analysis of the Effect of Artemisia argyi Essential Oil on the Inhibition of the Proliferation of Chicken Marek's Disease Virus in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(11): 5901-5911. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yan, OU Niantao, LIU Mengzhe, WANG Kai, JIA Huixin, YU Wenjing, LI Yanling. In vitro Anti-inflammatory Activity of Cinnamon Essential Oil and Cinnamaldehyde, and the Protective Effect against LPS-induced Inflammatory Injury in RAW 264.7 cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(10): 5060-5071. |
| [4] | Ling LIU, Wanyu SHI, Xiumei LI, Minghua WANG, Xianghe ZHAI, Weiwei ZHOU. Intervention of Essential Oils from Citrus reticulata Blanco on Lipopolysaccharide- induced Inflammation in RAW264.7 Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(9): 4153-4160. |
| [5] | FU Xuezhen, LI Xincan, QIAN Hongyu, LÜ Hong, WU Chanyu, WANG Xiaohan, WANG Xiaohua, WANG Zhiying, ZHOU Zuoyong. Antibacterial Effect and Mechanism of Bergamot Essential Oil on Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(3): 1217-1227. |
| [6] | Jiajie LIN, Zixue LIN, Lijia WANG, Guowei WANG, Yanping HUANG, Yu ZHANG, Taoni ZHANG, Yinghao JIN, Meilan MO. Effect of Plant Essential Oil on Prevention and Treatment of Chicks Artificially Infected with Infectious Bronchitis Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(10): 4605-4619. |
| [7] | CHENG Xiangning, ZHANG Yun, HE Jiawei, CHEN Zhengkun, JIN Meilan, DING Honglei, WANG Qinghua. Isolation, Identification and Antifungal Susceptibility Analysis of Candida albicans Isolated from Pigeons [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(7): 3002-3011. |
| [8] | BAI Yan, LANG Xia, WANG Cailian, LIANG Tingyu, LIU Ting, GONG Xuyin, GAO Liangshuang, SHI Xiaolei, WU Jianping. Effects of Oregano Essential Oil and Monensin in Diet on Serum Biochemical Parameters, Digestive Enzyme Activities and Ruminal Microflora of Holstein Calves [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2019, 50(12): 2458-2469. |
| [9] | WANG Shui-ping. The Research Progress of Plant Extracts to Manipulate Rumen Fermentation [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2015, 46(1): 12-19. |
| [10] | SHI Chao-feng, YIN Zhong-qiong,WEI Qin,JIA Ren-yong. Bacteriostatic Action and Mechanism of α-terpineol on Escherichia coli [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2013, 44(5): 796-801. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||