





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (11): 4819-4828.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.11.004
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Quanjun CHEN( ), Zuo WANG*(
), Zuo WANG*( ), Fachun WAN, Weijun SHEN
), Fachun WAN, Weijun SHEN
Received:2024-01-26
Online:2024-11-23
Published:2024-11-30
Contact:
Zuo WANG
E-mail:2766272687@qq.com;zuowang@hunau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Quanjun CHEN, Zuo WANG, Fachun WAN, Weijun SHEN. Functional Characteristics and Related Regulation of Glucose Sensing Receptors and Transporters in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Ruminants[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(11): 4819-4828.
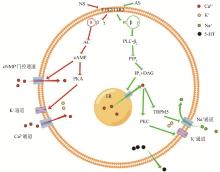
Fig. 2
T1R2/ T1R3-mediated signal transduction pathway[15](Draw on Figdraw platform) T1R2/T1R3. Taste 1 receptor 2 and 3; AC. Adenylate cyclase; cAMP. Cyclic AMP; PKA. Protein kinase A; PLC-β2. Phospholipase C-β2; PIP2. Phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-bisphosphate; IP3. Inositol trisphosphate; DAG. Diacylglycer; TRPM5. Transient receptor potential melastatin; PKC. Protein kinase C; 5-HT. 5-hydroxy tryptamine; ER. Endoplasmic reticulum; NS. Natural sweetener; AS. Artificial sweetener"
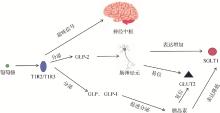
Fig. 4
Regulation of Gastrointestinal Hormones on SGLT1 and GLUT2 T1R2/T1R3. Taste 1 receptor 2 and 3; SGLT1. Sodium-coupled glucose transporter1; GLUT2. Facilitative glucose transporter2; GLP-1. Glucagon-like peptide-1; GLP-2. Glucagon-like peptide-2; GLP. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide"
| 1 |
MORANA W,AL-RAMMAHIM,ZHANGC,et al.Sweet taste receptor expression in ruminant intestine and its activation by artificial sweeteners to regulate glucose absorption[J].J Dairy Sci,2014,97(8):4955-4972.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2014-8004 |
| 2 |
RANT,LIH Z,LIUY,et al.Expression of genes related to sweet taste receptors and monosaccharides transporters along the gastrointestinal tracts at different development stages in goats[J].Livest Sci,2016,188,111-119.
doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2016.04.010 |
| 3 |
DALYK,MORANA W,AL-RAMMAHIM,et al.Non-nutritive sweetener activation of the pig sweet taste receptor T1R2-T1R3 in vitro mirrors sweetener stimulation of the gut-expressed receptor in vivo[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2021,542,54-58.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.01.032 |
| 4 | 刘秋蕾,王飞,李磊,等.甜味分子与G蛋白偶联受体Tas1R2/3的相互作用及激活机制[J].生命的化学,2014,34(4):500-505. |
| LIUQ L,WANGF,LIL,et al.The interaction and activation mechanism between G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) Tas1R2/3 and various sweeteners[J].Chemistry of life,2014,34(4):500-505. | |
| 5 |
PEREZ-AGUILARJ M,KANGS G,ZHANGL L,et al.Modeling and structural characterization of the sweet taste receptor heterodimer[J].ACS Chem Neurosci,2019,10(11):4579-4592.
doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00438 |
| 6 |
SUKUMARANS K,PALAYYANS R.Sweet taste signaling: the core pathways and regulatory mechanisms[J].Int J Mol Sci,2022,23(15):8225.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23158225 |
| 7 |
LAFFITTEA,BELLOIRC,NEIERSF,et al.Functional characterization of the Venus flytrap domain of the human TAS1R2 sweet taste receptor[J].Int J Mol Sci,2022,23(16):9216.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23169216 |
| 8 |
VON MOLITORE,RIEDELK,KROHNM,et al.An alternative pathway for sweet sensation: possible mechanisms and physiological relevance[J].Pflugers Arch,2020,472(12):1667-1691.
doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02467-1 |
| 9 |
DEPOORTEREI.Taste receptors in the gut tune the release of peptides in response to nutrients[J].Peptides,2015,66,9-12.
doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2015.01.013 |
| 10 |
RAKAF,FARRS,KELLYJ,et al.Metabolic control via nutrient-sensing mechanisms: role of taste receptors and the gut-brain neuroendocrine axis[J].Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab,2019,317(4):E559-E572.
doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00036.2019 |
| 11 |
GERSPACHA C,STEINERTR E,SCHÖNENBERGERL,et al.The role of the gut sweet taste receptor in regulating GLP-1, PYY, and CCK release in humans[J].Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab,2011,301(2):E317-E325.
doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00077.2011 |
| 12 |
NAKAGAWAY,OHTSUY,NAGASAWAM,et al.Glucose promotes its own metabolism by acting on the cell-surface glucose-sensing receptor T1R3[J].Endocr J,2014,61(2):119-131.
doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ13-0431 |
| 13 | 李蕾蕾,张根华,邓少平.甜味识别与转导机理[J].动物医学进展,2006,27(8):12-14. |
| LIL L,ZHANGG H,DENGS P.Sweet perception and transduction mechanism[J].Progress in Veterinary Medicine,2006,27(8):12-14. | |
| 14 |
LIUB,HAM,MENGX Y,et al.Functional characterization of the heterodimeric sweet taste receptor T1R2 and T1R3 from a New World monkey species (squirrel monkey) and its response to sweet-tasting proteins[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2012,427(2):431-437.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.09.083 |
| 15 | THOMPSONM D,COLED E C,JOSEP A,et al.G protein-coupled receptor accessory proteins and signaling: pharmacogenomic insights[J].Methods Mol Biol,2014,1175,121-152. |
| 16 |
KREUCHD,KEATINGD J,WUT Z,et al.Gut Mechanisms linking intestinal sweet sensing to glycemic control[J].Front Endocrinol (Lausanne),2018,9,741.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00741 |
| 17 |
DEPOORTEREI.Taste receptors of the gut: emerging roles in health and disease[J].Gut,2014,63(1):179-190.
doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305112 |
| 18 |
YANGZ M,WANGY,CHENS Y.Astragalus polysaccharide alleviates type 2 diabetic rats by reversing the glucose transporters and sweet taste receptors/GLP-1/GLP-1 receptor signaling pathways in the intestine-pancreatic axis[J].J Funct Foods,2021,76,104310.
doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.104310 |
| 19 |
MORANA W,AL-RAMMAHIM A,DALYK,et al.Consumption of a natural high-intensity sweetener enhances activity and expression of rabbit intestinal Na+/glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) and improves Colibacillosis-induced enteric disorders[J].J Agric Food Chem,2020,68(2):441-450.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b04995 |
| 20 |
SHIRAZI-BEECHEYS P,DALYK,AL-RAMMAHIM,et al.Role of nutrient-sensing taste 1 receptor (T1R) family members in gastrointestinal chemosensing[J].Br J Nutr,2014,111(S1):S8-S15.
doi: 10.1017/S0007114513002286 |
| 21 |
MORANA W,DALYK,AL-RAMMAHIM A,et al.Nutrient sensing of gut luminal environment[J].Proc Nutr Soc,2021,80(1):29-36.
doi: 10.1017/S0029665120007120 |
| 22 |
KOKRASHVILIZ,MOSINGERB,MARGOLSKEER F.Taste signaling elements expressed in gut enteroendocrine cells regulate nutrient-responsive secretion of gut hormones[J].Am J Clin Nutr,2009,90(3):822S-825S.
doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2009.27462T |
| 23 |
ABBASZ,SAMMADA,HUL R,et al.Glucose Metabolism and dynamics of facilitative glucose transporters (GLUTs) under the influence of heat stress in dairy cattle[J].Metabolites,2020,10(8):312.
doi: 10.3390/metabo10080312 |
| 24 |
LOHRENZA K,DUSKEK,SCHÖNHUSENU,et al.Glucose transporters and enzymes related to glucose synthesis in small intestinal mucosa of mid-lactation dairy cows fed 2 levels of starch[J].J Dairy Sci,2011,94(9):4546-4555.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2011-4333 |
| 25 |
SHIRAZI-BEECHEYS P,HIRAYAMAB A,WANGY,et al.Ontogenic development of lamb intestinal sodium-glucose co-transporter is regulated by diet[J].J Physiol,1991,437,699-708.
doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018620 |
| 26 |
LESCALE-MATYSL,DYERJ,SCOTTD,et al.Regulation of the ovine intestinal Na+/glucose co-transporter (SGLT1) is dissociated from mRNA abundance[J].Biochem J,1993,291,435-440.
doi: 10.1042/bj2910435 |
| 27 |
CHENL Q,CHEUNGL S,FENGL,et al.Transport of Sugars[J].Annu Rev Biochem,2015,84,865-894.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060614-033904 |
| 28 |
KOEPSELLH.Glucose transporters in the small intestine in health and disease[J].Pflugers Arch,2020,472(9):1207-1248.
doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02439-5 |
| 29 |
RÖDERP V,GEILLINGERK E,ZIETEKT S,et al.The role of SGLT1 and GLUT2 in intestinal glucose transport and sensing[J].PLoS One,2014,9(2):e89977.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089977 |
| 30 |
KUHRER E,FROSTC R,SVENDSENB,et al.Molecular mechanisms of glucose-stimulated GLP-1 secretion from perfused rat small intestine[J].Diabetes,2015,64(2):370-382.
doi: 10.2337/db14-0807 |
| 31 |
GOLDSTEINN,MCKNIGHTA D,CARTYJ R E,et al.Hypothalamic detection of macronutrients via multiple gut-brain pathways[J].Cell Metab,2021,33(3):676-687.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.12.018 |
| 32 | 卢垚,孙佩佩,宋代军.肠道上皮主要葡萄糖转运载体及其作用机制[J].动物营养学报,2018,30(1):50-58. |
| LUY,SUNP P,SONGD J.Intestinal epithelium major glucose transporters and their action mechanisms[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2018,30(1):50-58. | |
| 33 |
KELLETTG L,BROT-LAROCHEE,MACEO J,et al.Sugar absorption in the intestine: the role of GLUT2[J].Annu Rev Nutr,2008,28,35-54.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.28.061807.155518 |
| 34 |
DANIELH,ZIETEKT.Taste and move: glucose and peptide transporters in the gastrointestinal tract[J].Exp Physiol,2015,100(12):1441-1450.
doi: 10.1113/EP085029 |
| 35 | 谭碧娥,印遇龙.胃肠营养化学感应及其生理效应[J].动物营养学报,2013,25(2):231-241. |
| TANB E,YINY L.Gut nutrient chemosensing and its physiology effects[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2013,25(2):231-241. | |
| 36 |
STEINHOFF-WAGNERJ,ZITNANR,SCHÖNHUSENU,et al.Diet effects on glucose absorption in the small intestine of neonatal calves: importance of intestinal mucosal growth, lactase activity, and glucose transporters[J].J Dairy Sci,2014,97(10):6358-6369.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2014-8391 |
| 37 |
ZHANGM,YANGH Y,YANGE W,et al.Berberine decreases intestinal GLUT2 translocation and reduces intestinal glucose absorption in mice[J].Int J Mol Sci,2021,23(1):327.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23010327 |
| 38 |
GORBOULEVV,SCHÜRMANNA,VALLONV,et al.Na+-D-glucose cotransporter SGLT1 is pivotal for intestinal glucose absorption and glucose-dependent incretin secretion[J].Diabetes,2012,61(1):187-196.
doi: 10.2337/db11-1029 |
| 39 |
CHENL H,TUOB G,DONGH.Regulation of intestinal glucose absorption by ion channels and transporters[J].Nutrients,2016,8(1):43.
doi: 10.3390/nu8010043 |
| 40 |
STEARNSA T,BALAKRISHNANA,RHOADSD B,et al.Rapid upregulation of sodium-glucose transporter SGLT1 in response to intestinal sweet taste stimulation[J].Ann Surg,2010,251(5):865-871.
doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181d96e1f |
| 41 |
MARGOLSKEER F,DYERJ,KOKRASHVILIZ,et al.T1R3 and gustducin in gut sense sugars to regulate expression of Na+-glucose cotransporter 1[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2007,104(38):15075-15080.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706678104 |
| 42 |
RAMSANAHIEA,DUXBURYM S,GRIKSCHEITT C,et al.Effect of GLP-2 on mucosal morphology and SGLT1 expression in tissue-engineered neointestine[J].Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol,2003,285(6):G1345-G1352.
doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00374.2002 |
| 43 |
DALYK,AL-RAMMAHIM,ARORAD K,et al.Expression of sweet receptor components in equine small intestine: relevance to intestinal glucose transport[J].Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol,2012,303(2):R199-R208.
doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00031.2012 |
| 44 |
LEEW Y,LOFLINP,CLANCEYC J,et al.Cyclic nucleotide regulation of Na+/glucose cotransporter (SGLT1) mRNA stability.Interaction of a nucleocytoplasmic protein with a regulatory domain in the 3'-untranslated region critical for stabilization[J].J Biol Chem,2000,275(43):33998-34008.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005040200 |
| 45 |
SINGHS K,BARTOOA C,KRISHNANS,et al.Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) stimulates transepithelial glucose transport[J].Obesity (Silver Spring),2008,16(11):2412-2416.
doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.393 |
| 46 |
SHIRAZI-BEECHEYS P,MORANA W,BATCHELORD J,et al.Glucose sensing and signalling; regulation of intestinal glucose transport[J].Proc Nutr Soc,2011,70(2):185-193.
doi: 10.1017/S0029665111000103 |
| 47 |
MCCAULEYH A.Enteroendocrine regulation of nutrient absorption[J].J Nutr,2020,150(1):10-21.
doi: 10.1093/jn/nxz191 |
| 48 |
MORANA W,AL-RAMMAHIM A,BATCHELORD J,et al.Glucagon-like peptide-2 and the enteric nervous system are components of cell-cell communication pathway regulating intestinal Na+/Glucose Co-transport[J].Front Nutr,2018,5,101.
doi: 10.3389/fnut.2018.00101 |
| 49 |
AUA,GUPTAA,SCHEMBRIP,et al.Rapid insertion of GLUT2 into the rat jejunal brush-border membrane promoted by glucagon-like peptide 2[J].Biochem J,2002,367,247-254.
doi: 10.1042/bj20020393 |
| 50 |
SMITHK,AZARIE K,LAMOIAT E,et al.T1R2 receptor-mediated glucose sensing in the upper intestine potentiates glucose absorption through activation of local regulatory pathways[J].Mol Metab,2018,17,98-111.
doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.08.009 |
| 51 |
TOBINV,LE GALLM,FIORAMONTIX,et al.Insulin internalizes GLUT2 in the enterocytes of healthy but not insulin-resistant mice[J].Diabetes,2008,57(3):555-562.
doi: 10.2337/db07-0928 |
| 52 |
TIANC X,WUJ,JIAOJ Z,et al.Short communication: a high-grain diet entails alteration in nutrient chemosensing of the rumen epithelium in goats[J].Anim Feed Sci Technol,2020,262,114410.
doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2020.114410 |
| 53 |
SHAY Z,HUJ,SHIB G,et al.Supplementary feeding of cattle-yak in the cold season alters rumen microbes, volatile fatty acids, and expression of SGLT1 in the rumen epithelium[J].PeerJ,2021,9,e11048.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.11048 |
| 54 |
HARMOND L.Understanding starch utilization in the small intestine of cattle[J].Asian-Australas J Anim Sci,2009,22(7):915-922.
doi: 10.5713/ajas.2009.r.08 |
| 55 | 燕爱飞,周芳芳,康劲翮,等.高、低淀粉饲粮对山羊小肠甜味受体信号通路基因表达的影响[J].动物营养学报,2021,33(4):2278-2289. |
| YANA F,ZHOUF F,KANGJ H,et al.Effects of high and low starch diets on gene expressions of key elements of sweet taste receptor signaling pathway in goats[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2021,33(4):2278-2289. | |
| 56 |
LIAOS F,HARMOND L,VANZANTE S,et al.The small intestinal epithelia of beef steers differentially express sugar transporter messenger ribonucleic acid in response to abomasal versus ruminal infusion of starch hydrolysate[J].J Anim Sci,2010,88(1):306-314.
doi: 10.2527/jas.2009-1992 |
| 57 |
LIANGZ Q,JINC J,BAIH X,et al.Low rumen degradable starch promotes the growth performance of goats by increasing protein synthesis in skeletal muscle via the AMPK-mTOR pathway[J].Anim Nutr,2023,13,1-8.
doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2022.10.006 |
| 58 |
HANX Y,LEIX J,YANGX X,et al.A Metagenomic insight into the hindgut microbiota and their metabolites for dairy goats fed different rumen degradable starch[J].Front Microbiol,2021,12,651631.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.651631 |
| 59 |
RAHMADANIM,SUSANTOI,PRASETYAR D D,et al.Modification of dietary rumen degradable starch content by chemical processing of feed ingredients: a meta-analysis[J].Anim Sci J,2023,94(1):e13834.
doi: 10.1111/asj.13834 |
| 60 |
MUSCHER-BANSEA S,PIECHOTTAM,SCHRÖDERB,et al.Modulation of intestinal glucose transport in response to reduced nitrogen supply in young goats[J].J Anim Sci,2012,90(13):4995-5004.
doi: 10.2527/jas.2012-5143 |
| [1] | ZHANG Lihuan, ZHANG Ruonan, JIA Hao, MA Yueyue, ZHU Zhiwei, LI Huifeng, CHEN Yuanyu. Effects of Probiotics Interaction on Growth Performance, Intestinal Digestion and Absorption, and Sugar Transporter GLUT2 in Broilers [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(9): 2165-2176. |
| [2] | WEN Yan-qiao, YAO Wan-ling, YANG Chao-xue, MA Qi, ZHANG Xiao-song, JI Peng, HUA Yong-li, WEI Yan-ming. Effects of Yujin Powder on Gastrointestinal Hormone in Serum and Intestinal Tissue of Large Intestine Dampness-heat Syndrome Rat Model [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2017, 48(6): 1140-1149. |
| [3] | WANG Xiu-qi;TAN Hui-ze;SHU Gang;SU Hai-lin;CHEN Li-long;JIANG qing-yan;FENG Ding-yuan. Study on Tissuespecific Expression of SGLT1 and GLUT2 mRNA in Chicken Intestine [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2006, 37(1): 12-17. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||