





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (10): 5007-5017.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.10.021
• Animal Biotechnology and Reproduction • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHOU Xinyi1( ), YANG Lidan2, GAO Chen1, WEI Xinhua1, HUO Haonan2, ZOU Huiying1, YU Dawei1, DU Weihua1,*(
), YANG Lidan2, GAO Chen1, WEI Xinhua1, HUO Haonan2, ZOU Huiying1, YU Dawei1, DU Weihua1,*( )
)
Received:2025-03-21
Online:2025-10-23
Published:2025-11-01
Contact:
DU Weihua
E-mail:15055636012@163.com;duweihua@caas.cn
CLC Number:
ZHOU Xinyi, YANG Lidan, GAO Chen, WEI Xinhua, HUO Haonan, ZOU Huiying, YU Dawei, DU Weihua. Establishment of Wild Boar Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Line with X Chromosome-Targeted Integration of GFP Cassette[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(10): 5007-5017.
Table 1
Sequence of primers"
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primers sequence |
| HIT-EF1α-GFP-F | GACACTATAGAACTCGACCACTAGTTTTGAGATCGAGTGCCGCATCACGGGCTCGAG- |
| TCGTCGTGAGGCTCCGGTGCCCG | |
| HIT-EF1α-GFP-R | GGCACTCGATCTCAAAGGCCGGCGCGCCTAAGATACATTG |
| PH-I-sgRNA1-F | CACCGTTGAACTCATGCGGAAAGGG |
| PH-I-sgRNA1-R | AAACCCCTTTCCGCATGAGTTCAAC |
| PH-I-sgRNA2-F | CACCGGCACACTCAGGGTCCAGTA |
| PH-I-sgRNA2-R | AAACTACTGGACCCTGAGTGTGCC |
| PH-I-F | GAGGACCAAATTCTCACTTCAAC |
| PH-I-R | TAGGGGTCAAATCAGAGCTACAG |
| EF1α-R | TAGGCACCGGTTCAATTGCCGA |
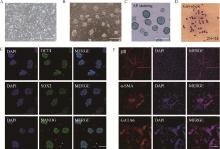
Fig. 1
Establishment and pluripotency identification of iPSCs in wild boars A. Wild boar fibroblasts at P2; B. Wild boar iPSCs at P35; C. AP staining of wild boar iPSCs; D. Karyotype of wild boar iPSCs; E. Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous pluripotency factors in wild boar iPSCs; F. Immunostaining of β Ⅲ, α-SMA and GATA6 in cells differentiated from wild boar iPSCs in vitro. Scale bar=100 μm"
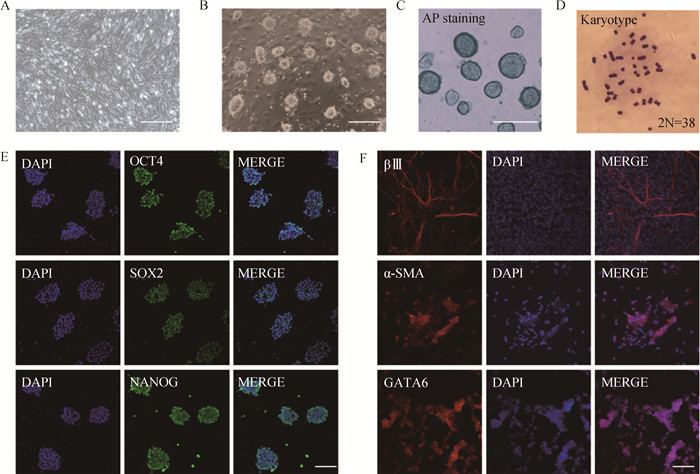
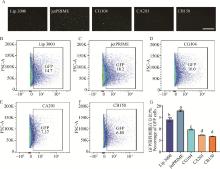
Fig. 2
Selection of transfection methods for iPSCs in wild boars A. Wild boars iPSCs at 24 h after transfection of PB-EF1a-GFP by different electroporation methods under fluorescence microscope, scale bar=100 μm; B. Transfection efficiency of iPSCs at 48 h with Lip 3000; C. Transfection efficiency of iPSCs at 48 h with jeatPRIME; D. Transfection efficiency of iPSCs at 48 h with electroporation CG104 program; E. Transfection efficiency of iPSCs at 48 h with electroporation of CA201; F. Transfection efficiency of iPSCs at 48 h with electroporation of CB150; G. Transfection efficiency for different methods (different letters indicate significant difference, P < 0.001, the same as below)"
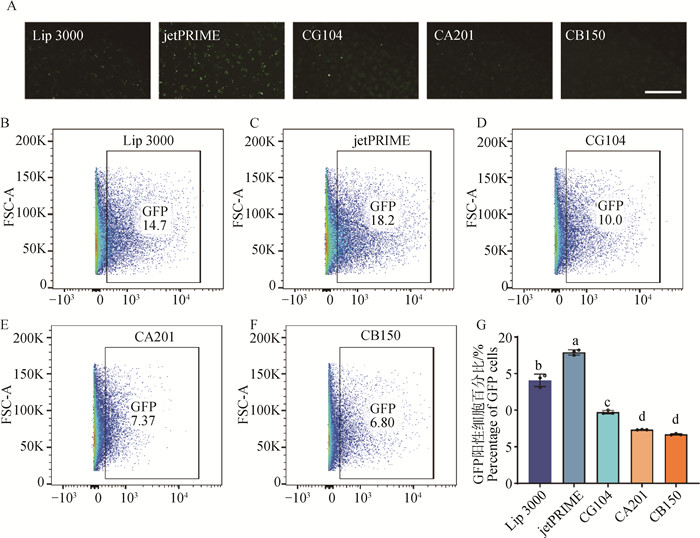
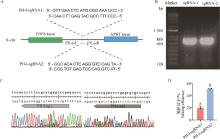
Fig. 3
Screening of sgRNAs targeting X chromosome of iPSCs in wild boars A. Schematic diagram of sgRNAs targeting the PHF6 and HPRT genes on the X chromosome of wild boar; B. Amplified target gene fragment containing PH-I-sgRNA from the genome of wild boar iPSCs; C. Sequencing results of target sites in gene edited cell; D. Analysis of sgRNA efficiency in wild pigs iPSCs"
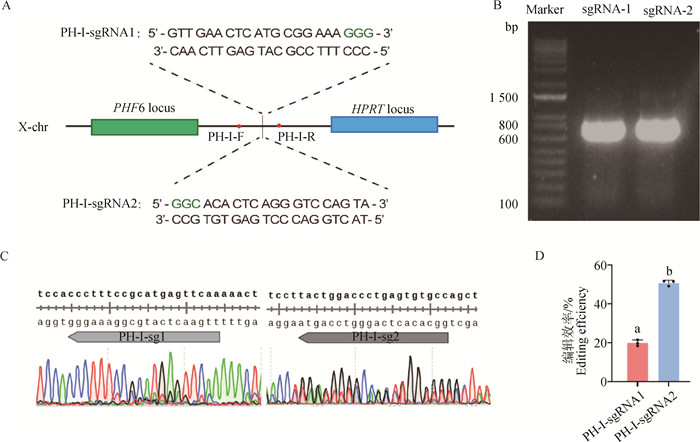
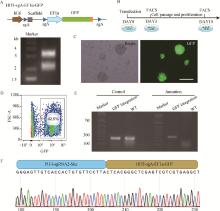
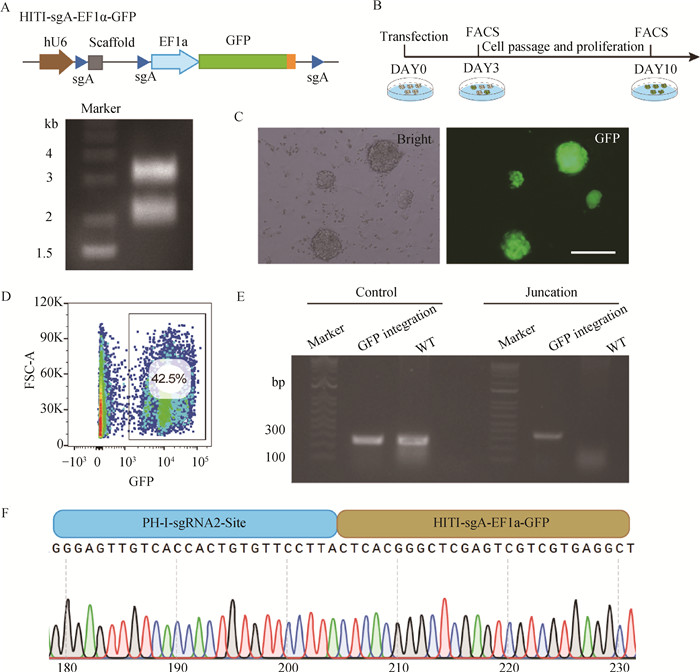
Fig. 4
Establishment of wild boar iPSCs with site-specific integration of GFP on the X chromosome A. Identification of vector HITI-sgA-EF1α-GFP double digestion; B. Experimental workflow for establishing wild boar iPSCs with targeted integration of GFP expression cassette; C. GFP-positive wild boar iPSCs after two rounds of flow cytometric sorting, scale bar=100 μm; D. The percentage of GFP-positive cells in wild boar iPSCs after the second round of flow cytometric sorting; E. Target fragment amplified by PCR after the GFP expression cassette integrated into PH-I-sgRNA-2 locus in wild boar iPSCs; F. Sequencing of target fragment after GFP expression cassette integrated into PH-I-sgRNA-2 locus in wild boar iPSCs"
| 1 |
CHOI S K , KIM K S , RANYUK M , et al. Asia-wide phylogeography of wild boar (Sus scrofa) based on mitochondrial DNA and Y-chromosome: Revising the migration routes of wild boar in Asia[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15 (8): e0238049.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238049 |
| 2 |
ZHANG M P , YANG Q , AI H S , et al. Revisiting the evolutionary history of pigs via de novo mutation rate estimation in a three-generation pedigree[J]. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics, 2022, 20 (6): 1040- 1052.
doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2022.02.001 |
| 3 |
KARAMATI S A , EFFATPANAH H , KHODAYARI M T , et al. Global prevalence of Neospora caninum in ddomestic pigs (Sus domesticus) and wild boars (Sus scrofa): a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Vet Med Sci, 2025, 11 (1): e70207.
doi: 10.1002/vms3.70207 |
| 4 |
LIU Y L , ZHANG S H , ZOU G Y , et al. Generation and characterization of giant panda induced pluripotent stem cells[J]. Sci Adv, 2024, 10 (38): eadn7724.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adn7724 |
| 5 |
WU Y R , WANG C W , FAN X Y , et al. The impact of induced pluripotent stem cells in animal conservation[J]. Vet Res Commun, 2024, 48 (2): 649- 663.
doi: 10.1007/s11259-024-10294-3 |
| 6 |
TAKAHASHI K , YAMANAKA S . Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors[J]. Cell, 2006, 126 (4): 663- 676.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.024 |
| 7 |
YAMANAKA S . Pluripotent stem cell-based cell therapy-promise and challenges[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2020, 27 (4): 523- 531.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.09.014 |
| 8 |
ZHANG Z W , BAO X Y , LIN C P . Progress and prospects of gene editing in pluripotent stem cells[J]. Biomedicines, 2023, 11 (8): 2168.
doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082168 |
| 9 |
ZHU G X , GAO D F , LI L Z , et al. Generation of three-dimensional meat-like tissue from stable pig epiblast stem cells[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14 (1): 8163.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44001-8 |
| 10 |
PACESA M , PELEA O , JINEK M . Past, present, and future of CRISPR genome editing technologies[J]. Cell, 2024, 187 (5): 1076- 1100.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.01.042 |
| 11 |
KIM T K , EBERWINE J H . Mammalian cell transfection: the present and the future[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2010, 397 (8): 3173- 3178.
doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-3821-6 |
| 12 |
FUS-KUJAWA A , PRUS P , BAJDAK-RUSINEK K , et al. An overview of methods and tools for transfection of eukaryotic cells in vitro[J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2021, 9, 701031.
doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.701031 |
| 13 | HAHN P , SCANLAN E . Gene delivery into mammalian cells: an overview on existing approaches employed in vitro and in vivo[J]. Top Curr Chem, 2010, 296, 1- 13. |
| 14 |
NASO M F , TOMKOWICZ B , PERRY W R , et al. Adeno-associated virus (AAV) as a vector for gene therapy[J]. BioDrugs, 2017, 31 (4): 317- 334.
doi: 10.1007/s40259-017-0234-5 |
| 15 | RAHIMI P , MOBARAKEH V I , KAMALZARE S , et al. Comparison of transfection efficiency of polymer-based and lipid-based transfection reagents[J]. Bratisl Lek Listy, 2018, 119 (11): 701- 705. |
| 16 |
MIDOUX P , PICHON C , AOUANC J J , et al. Chemical vectors for gene delivery: a current review on polymers, peptides and lipids containing histidine or imidazole as nucleic acids carriers[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2009, 157 (2): 166- 178.
doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00288.x |
| 17 |
LEAL A F , HERRENO-PACHON A M , BENINCORE-FLOREZ E , et al. Current strategies for increasing knock-in efficiency in CRISPR/Cas9-based approaches[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25 (5): 2456.
doi: 10.3390/ijms25052456 |
| 18 |
SUZUKI K , IZPISUA BELMONTE J C . In vivo genome editing via the HITI method as a tool for gene therapy[J]. J Hum Genet, 2018, 63 (2): 157- 164.
doi: 10.1038/s10038-017-0352-4 |
| 19 | FEBBRARO F , CHEN M , DENHAM M . Generation of human iPSCs by episomal reprogramming of skin fibroblasts and peripheral blood mononuclear cells[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2021, 2239, 135- 151. |
| 20 |
WANG J L , SUN S C , DENG H K . Chemical reprogramming for cell fate manipulation: methods, applications, and perspectives[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30 (9): 1130- 1147.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.08.001 |
| 21 |
ZHU Q Q , WANG F C , GAO D F , et al. Generation of stable integration-free pig induced pluripotent stem cells under chemically defined culture condition[J]. Cell Prolif, 2023, 56 (11): e13487.
doi: 10.1111/cpr.13487 |
| 22 |
BATISTA N T , POLAJZER T , MIKLAVCIC D . Cell death due to electroporation - a review[J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2021, 141, 107871.
doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2021.107871 |
| 23 |
HAMADA T , YOKOYAMA S , AKAHANE T , et al. Electroporation induces unexpected alterations in gene expression: a tip for selection of optimal transfection method[J]. Curr Issues Mol Biol, 2025, 47 (2): 91.
doi: 10.3390/cimb47020091 |
| 24 |
PAVLOV R V , AKIMOV S A , DASHINIMAEV E B , et al. Boosting lipofection efficiency through enhanced membrane fusion mechanisms[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25 (24): 13540.
doi: 10.3390/ijms252413540 |
| 25 |
CUESTA-GOMEZ N , VERHOEFF K , DADHEECH N , et al. Suspension culture improves iPSCs expansion and pluripotency phenotype[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2023, 14 (1): 154.
doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03382-9 |
| 26 | 胡暄, 王松, 于璐, 等. Cas9/sgRNA递送技术及其研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37 (11): 3880- 3889. |
| HU X , WANG S , YU L , et al. Advances of Cas9/sgRNA delivery system for gene editing[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 37 (11): 3880- 3889. | |
| 27 |
NAHAR S , SEHGAL P , AZHAR M , et al. A G-quadruplex motif at the 3' end of sgRNAs improves CRISPR-Cas9 based genome editing efficiency[J]. Chem Commun (Camb), 2018, 54 (19): 2377- 2380.
doi: 10.1039/C7CC08893K |
| 28 |
HEIDERSBACH A J , DORIGHI K M , GOMEZ J A , et al. A versatile, high-efficiency platform for CRISPR-based gene activation[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14 (1): 902.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36452-w |
| 29 |
GUO C T , MA X T , GAO F , et al. Off-target effects in CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing[J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2023, 11, 1143157.
doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1143157 |
| 30 |
JIN Y , HAN G C , GAO Y M , et al. Serum-tolerant polymeric complex for stem-cell transfection and neural differentiation[J]. Nat Commun, 2025, 16 (1): 2022.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57278-8 |
| 31 |
CHEN Q C , CHUAI G H , ZHANG H H , et al. Genome-wide CRISPR off-target prediction and optimization using RNA-DNA interaction fingerprints[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14 (1): 7521.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42695-4 |
| 32 |
BALKE-WANT H , KEERTHI V , GKITSAS N , et al. Homology-independent targeted insertion (HITI) enables guided CAR knock-in and efficient clinical scale CAR-T cell manufacturing[J]. Mol Cancer, 2023, 22 (1): 100.
doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01799-7 |
| 33 |
LU H X , LIU J , FENG T , et al. A HIT-trapping strategy for rapid generation of reversible and conditional alleles using a universal donor[J]. Genome Res, 2021, 31 (5): 900- 909.
doi: 10.1101/gr.271312.120 |
| 34 |
YAMAMOTO Y , GERBI S A . Making ends meet: targeted integration of DNA fragments by genome editing[J]. Chromosoma, 2018, 127 (4): 405- 420.
doi: 10.1007/s00412-018-0677-6 |
| 35 |
MENG X , JIA R X , ZHAO X P , et al. In vivo genome editing via CRISPR/Cas9-mediated homology- independent targeted integration for Bietti crystalline corneoretinal dystrophy treatment[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15 (1): 3773.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48092-9 |
| 36 |
KAWAMATA M , SUZUKI H I , KIMURA R , et al. Optimization of Cas9 activity through the addition of cytosine extensions to single-guide RNAs[J]. Nat Biomed Eng, 2023, 7 (5): 672- 691.
doi: 10.1038/s41551-023-01011-7 |
| 37 |
ZHANG M F , YI F , WU J J , et al. The efficient generation of knockout microglia cells using a dual-sgRNA strategy by CRISPR/Cas9[J]. Front Mol Neurosci, 2022, 15, 1008827.
doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1008827 |
| 38 |
VAKULSKAS C A , DEVER D P , RETTIG G R , et al. A high-fidelity Cas9 mutant delivered as a ribonucleoprotein complex enables efficient gene editing in human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells[J]. Nat Med, 2018, 24 (8): 1216- 1224.
doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0137-0 |
| 39 |
BRAVO J P K , LIU M S , HIBSHMAN G N , et al. Structural basis for mismatch surveillance by CRISPR-Cas9[J]. Nature, 2022, 603 (7900): 343- 347.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04470-1 |
| [1] | YANG Shubo, YUAN Qingxin, CHEN Qibai, WANG Pei, GAO Dongyang, LI He, SONG Jun. Preparation and Intracellular Antibacterial Activity of Liposomes Encapsulating Staphylococcus aureus Bacteriophage [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(9): 4638-4645. |
| [2] | TAN Juanjuan, YANG Beiying, WU Qianyue, HUA Huiying, CAO Huabin, YAN Hui, ZHANG Jinhua. Diversity Analysis of Wild Boar Flora in Jiangxi Region and the Isolation and Identification of Clostridium perfringens Carried by Wild Boar [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1876-1886. |
| [3] | ZHAO Wenxuan, GAO Xue, YU Dawei, GAO Chen, LI Junya. Establishment and Pluripotency Analysis of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from Mengshan Cattle [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1731-1743. |
| [4] | WANG Jiamei, HUANG Yongzhen, GAO Chen, LI Junliang, CHEN Yan, ZHU Bo, ZHANG Lupei, WANG Zezhao, GAO Huijiang, LI Junya, GAO Xue. Research Progress and Overview on Pluripotent Stem Cells in Livestock [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(4): 1473-1483. |
| [5] | WANG Hui, XU Mengyuan, LIU Lingkang, ZHENG Xibang, LI Gonghe, WU Wende. PhiC31 Integrase Triggers Site-specific Cassette Exchange in Chicken Fibroblast Cells through Electroporation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(6): 2330-2342. |
| [6] | LUO Ruijie, CAO Suying. Research Progress and Application Prospect of Livestock Pluripotent Stem Cells [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(10): 4003-4015. |
| [7] | ZHANG Wei, ZHANG Shao-peng, LI En-hong, CAO An, LIU Zhi-yu, HAN Jian-yong, CAO Su-ying. Porcine Extraembryonic Endoderm Stem Cell like Cells Induced by Overexpression of Gata6 [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2017, 48(12): 2314-2322. |
| [8] | ZHANG Haibin;ZHOU Mingdong;ZHOU Xia;HU Jingdong;ZHAO Hongkun; . Effect of Mature Chicken Interleukin-18 Protein on Its Immunoenhancement on Newcastle Disease Vaccine [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2012, 43(8): 1287-1291. |
| [9] | LI Zhong-qiu, LIU Chun-long, MA Hong, FU Bo, WANG Liang, PENG Fu-gang, MA Jian-zhang, LIU Di. Influence of Cold Stress on Transcription of HSP90 in Northeast Wild Boar Fibroblasts [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2012, 43(12): 1978-1983. |
| [10] | DU Shan;MA Baohua;LI Liangliang;LIU Jun;ZHAO Xiaoe;ZHANG Yong . Optimization of Electroporation for Transfection of Goat Mammary Epithelial Cells [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2012, 43(1): 159-166. |
| [11] | SONG Yong-li;HE Xiao-ning;HUA Song;LAN Jie;ZHENG Yue-mao;HE Xiao-ying;LI Ji-xia;QUAN Fu-sheng;ZHANG Yong . Culture of Bovine Fetal Skin Fibroblasts in vitro and Ipr1 Gene Transfection [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2011, 42(4): 585-592. |
| [12] | LIU Li-hua;MIN Ling-jiang;SHEN Wei;PAN Qing-jie. Analysis of Genetic Structure in Wild Boar and Their Crossbred Populations [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2009, 40(2): 173-179. |
| [13] | YANG Xiuqin;GUAN Qingzhi;YU Hao;GUO Lijuan;LIU Hui;LIU Di;. Cloning, Sequence Analysis and Expression of Two Transcript Variants of Wild Boar CAPN10 Gene [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2009, 40(11): 0-1614. |
| [14] | BAO Wenbin;WU Shenglong;CAO Jingjing;JU Huiping;ZHU Guoqiang;CHEN Guohong . <A href= [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2009, 40(10): 0-1554. |
| [15] | LI Xiao-lin;PAN Qing-jie;MIN Ling-jiang;SHEN Wei;LIU Di. Genetic Co-adaptability of Structural Genes in Wild Boars Populations [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2008, 39(3): 262-267. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||