





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (12): 5774-5783.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2024.12.039
• Basic Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
TIAN Yan( ), YANG Fusheng, LI Yan'e, LIANG Youping, FAN Jie, WU Fangyan, GU Xiaobin*(
), YANG Fusheng, LI Yan'e, LIANG Youping, FAN Jie, WU Fangyan, GU Xiaobin*( )
)
Received:2024-02-02
Online:2024-12-23
Published:2024-12-27
Contact:
GU Xiaobin
E-mail:2021203026@stu.sicau.edu.cn;guxiaobin198225@126.com
CLC Number:
TIAN Yan, YANG Fusheng, LI Yan'e, LIANG Youping, FAN Jie, WU Fangyan, GU Xiaobin. Effect of Recombinant Serpins of Psoroptes ovis on Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation in Mice[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(12): 5774-5783.
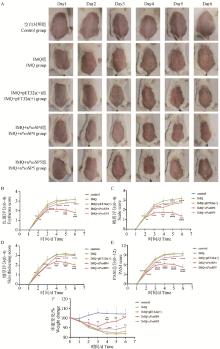
Fig. 2
Effect of rPsoSPs on morphological and weight in psoriasis skin inflammation of mice A. Representative photographs of dorsal skin of mice from a different group of animals during the experimental period from 1st to 6th day; B. Severity score of erythema in mice skin lesions; C. Severity score of scales in mice skin lesions; D. Severity score of thickness in mice skin lesions; E. Total PASI score of each group; F. Body weight changes in mice from 1st to 6th day. Compared with the control group, there were significant or extremely significant differences observed in both IMQ group and pET32a(+) group from 2nd to 6th day, which are not marked in the figure. The significance markers for IMQ+rPsoSP4 group and IMQ+rPsoSP5 group were as follows: *. P < 0.05, **. P < 0.01, ***. P < 0.001, ****. P < 0.000 1. Compared with the IMQ group, IMQ+pET32a(+) group and IMQ+rPsoSP5 group showed no significant difference from 2nd to 6th day, which are not marked in the figure. The significance markers for IMQ+rPsoSP4 group were as follows: #. P < 0.05, ##. P < 0.01, ###. P < 0.001, ####. P < 0.000 1"

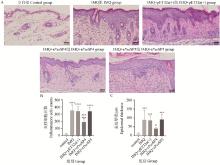
Fig. 3
Effect of rPsoSPs on histopathological change in psoriatic skin lesions of mice A. HE staining of the skin lesions of mice in each group on day 6(200×); B. Inflammatory cell counts of skin lesions in each group; C. Epidermal thickness of skin lesions in each group. Compared with control group, ***. P < 0.001, ****. P < 0.000 1;compared with IMQ group, #. P < 0.05, ###. P < 0.001"

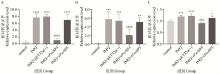
Fig. 4
Effect of rPsoSPs on inflammatory cytokines in psoriatic skin lesions of mice A. The effects of rPsoSPs on IL-1β mRNA levels in skin lesions tissue of mice; B. The effects of rPsoSPs on IL-6 mRNA levels in skin lesions tissue of mice; C. The effects of rPsoSPs on TNF-α mRNA levels in skin lesions tissue of mice. Compared with control group, *. P < 0.05, **. P < 0.01, ***. P < 0.001, ****. P < 0.000 1; compared with IMQ group, ###. P < 0.001, ####. P < 0.000 1"

| 1 |
LAW R H P , ZHANG Q W , MCGOWAN S , et al. An overview of the serpin superfamily[J]. Genome Biol, 2006, 7 (5): 216.
doi: 10.1186/gb-2006-7-5-216 |
| 2 |
MOLEHIN A J , GOBERT G N , MCMANUS D P . Serine protease inhibitors of parasitic helminths[J]. Parasitology, 2012, 139 (6): 681- 695.
doi: 10.1017/S0031182011002435 |
| 3 |
RANASINGHE S L , MCMANUS D P . Protease inhibitors of parasitic flukes: emerging roles in parasite survival and immune defence[J]. Trends Parasitol, 2017, 33 (5): 400- 413.
doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2016.12.013 |
| 4 | 宋伟宜, 王昕蕊, 于铭川, 等. 人兽共患带科绦虫丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂研究进展[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2021, 33 (6): 650- 654. |
| SONG W Y , WANG X R , YU M C , et al. Progress of researches on serine protease inhibitors for zoonotic cestode family Taeniidae[J]. Chinese Journal of Schistosomiasis Control, 2021, 33 (6): 650- 654. | |
| 5 |
TIRLONI L , KIM T K , COUTINHO M L , et al. The putative role of Rhipicephalus microplus salivary serpins in the tick-host relationship[J]. Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 2016, 71, 12- 28.
doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2016.01.004 |
| 6 |
XU Z M , LIN Z B , WEI N N , et al. Immunomodulatory effects of Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides serpin RHS2 on host immune responses[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2019, 12 (1): 341.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3607-4 |
| 7 |
WANG F Q , SONG Z Y , CHEN J , et al. The immunosuppressive functions of two novel tick serpins, HlSerpin-a and HlSerpin-b, from Haemaphysalis longicornis[J]. Immunology, 2020, 159 (1): 109- 120.
doi: 10.1111/imm.13130 |
| 8 |
PÁLENÍKOVÁ J , LIESKOVSKÁ J , LANGHANSOVÁ H , et al. Ixodes ricinus salivary serpin IRS-2 affects Th17 differentiation via inhibition of the interleukin-6/STAT-3 signaling pathway[J]. Infect Immun, 2015, 83 (5): 1949- 1956.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.03065-14 |
| 9 |
XU N , LIU X L , TANG B , et al. Recombinant Trichinella pseudospiralis serine protease inhibitors alter macrophage polarization in vitro[J]. Front Microbiol, 2017, 8, 1834.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01834 |
| 10 |
DE MARCO VERISSIMO C , JEWHURST H L , TIKHONOVA I G , et al. Fasciola hepatica serine protease inhibitor family (serpins): purposely crafted for regulating host proteases[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2020, 14 (8): e0008510.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008510 |
| 11 |
ZHANG C Y , GU X B , CHEN Y H , et al. Molecular characterization of four novel serpins in Psoroptes ovis var. cuniculi and their implications in the host-parasite interaction[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2021, 182, 1399- 1408.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.090 |
| 12 |
DUBERTRET L , MROWIETZ U , RANKI A , et al. European patient perspectives on the impact of psoriasis: the EUROPSO patient membership survey[J]. Br J Dermatol, 2006, 155 (4): 729- 736.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07405.x |
| 13 |
GUDJONSSON J E , ELDER J T . Psoriasis: epidemiology[J]. Clin Dermatol, 2007, 25 (6): 535- 546.
doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2007.08.007 |
| 14 |
STOECKLI M R , MCNEILLY T N , FREW D , et al. The effect of Psoroptes ovis infestation on ovine epidermal barrier function[J]. Vet Res, 2013, 44 (1): 11.
doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-44-11 |
| 15 |
QIN D Q , MA L , QIN L . Potential role of the epidermal differentiation complex in the pathogenesis of psoriasis[J]. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2022, 27 (12): 325.
doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2712325 |
| 16 |
MONTERO-VILCHEZ T , SEGURA-FERNÁNDEZ-NOGUERAS M V , PÉREZ-RODRÍGUEZ I , et al. Skin barrier function in psoriasis and atopic dermatitis: transepidermal water loss and temperature as useful tools to assess disease severity[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10 (2): 359.
doi: 10.3390/jcm10020359 |
| 17 |
BURGESS S T , FREW D , NUNN F , et al. Transcriptomic analysis of the temporal host response to skin infestation with the ectoparasitic mite Psoroptes ovis[J]. BMC Genomics, 2010, 11, 624.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-624 |
| 18 |
ZHOU W , HU M M , ZANG X H , et al. Luteolin attenuates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in BALB/c mice via suppression of inflammation response[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 131, 110696.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110696 |
| 19 |
COUTINHO M L , BIZZARRO B , TIRLONI L , et al. Rhipicephalus microplus serpins interfere with host immune responses by specifically modulating mast cells and lymphocytes[J]. Ticks Tick Borne Dis, 2020, 11 (4): 101425.
doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2020.101425 |
| 20 |
TIRLONI L , KIM T K , BERGER M , et al. Amblyomma americanum serpin 27 (AAS27) is a tick salivary anti-inflammatory protein secreted into the host during feeding[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2019, 13 (8): e0007660.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007660 |
| 21 |
XU J , WU L , YU P , et al. Effect of two recombinant Trichinella spiralis serine protease inhibitors on TNBS-induced experimental colitis of mice[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2018, 194 (3): 400- 413.
doi: 10.1111/cei.13199 |
| 22 |
CHEN Z Z , CLAEREBOUT E , CHIERS K , et al. Dermal immune responses against Psoroptes ovis in two cattle breeds and effects of anti-inflammatory dexamethasone treatment on the development of psoroptic mange[J]. Vet Res, 2021, 52 (1): 1.
doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-00874-x |
| 23 |
HUNTLEY J F , VAN DEN BROEK A , MACHELL J , et al. The effect of immunosuppression with Cyclosporin A on the development of sheep scab[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2005, 127 (3-4): 323- 332.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2004.10.021 |
| 24 |
GRIFFITHS C E , BARKER J N . Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis[J]. Lancet, 2007, 370 (9583): 263- 271.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61128-3 |
| 25 |
EL MALKI K , KARBACH S H , HUPPERT J , et al. An alternative pathway of imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in the absence of interleukin-17 receptor a signaling[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2013, 133 (2): 441- 451.
doi: 10.1038/jid.2012.318 |
| 26 |
MATSUNAGA Y , KIDO H , KAWAJI K , et al. Inhibitors of chymotrypsin-like proteases inhibit eosinophil peroxidase release from activated human eosinophils[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 1994, 312 (1): 67- 74.
doi: 10.1006/abbi.1994.1281 |
| 27 |
PEJLER G , RÖNNBERG E , WAERN I , et al. Mast cell proteases: multifaceted regulators of inflammatory disease[J]. Blood, 2010, 115 (24): 4981- 4990.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-01-257287 |
| 28 |
YOUNG C N , KOEPKE J I , TERLECKY L J , et al. Reactive oxygen species in tumor necrosis factor-α-activated primary human keratinocytes: implications for psoriasis and inflammatory skin disease[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2008, 128 (11): 2606- 2614.
doi: 10.1038/jid.2008.122 |
| 29 |
CAI Y H , XUE F , QUAN C , et al. A critical role of the IL-1β-IL-1R signaling pathway in skin inflammation and psoriasis pathogenesis[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2019, 139 (1): 146- 156.
doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.07.025 |
| 30 |
HERNÁNDEZ-QUINTERO M , KURI-HARCUCH W , GONZÁLEZ ROBLES A , et al. Interleukin-6 promotes human epidermal keratinocyte proliferation and keratin cytoskeleton reorganization in culture[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2006, 325 (1): 77- 90.
doi: 10.1007/s00441-006-0173-9 |
| 31 |
KIM N H , LEE M Y , PARK S J , et al. Auranofin blocks interleukin-6 signalling by inhibiting phosphorylation of JAK1 and STAT3[J]. Immunology, 2007, 122 (4): 607- 614.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02679.x |
| 32 |
HUNTINGTON J A . Serpin structure, function and dysfunction[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2011, 9, 26- 34.
doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04360.x |
| 33 |
GETTINS P G W , OLSON S T . Exosite determinants of serpin specificity[J]. J Biol Chem, 2009, 284 (31): 20441- 20445.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.R800064200 |
| 34 |
CHUNG H S , KIM J S , LEE S M , et al. Role of the P2 residue of human alpha 1-antitrypsin in determining target protease specificity[J]. PLoS ONE, 2017, 12 (9): e0185074.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185074 |
| [1] | HUANG Cuirui, HAO Guiying, ZHOU Yu, TIAN Yan, YANG Fusheng, TANG Li, YANG Guangyou, XIE Yue, HE Ran, XU Jing, GU Xiaobin. Recombinant Arginine Kinase of Psoroptes ovis Induces Cutaneous Eosinophil Recruitment in Rabbit [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(5): 2186-2194. |
| [2] | GE You, ZHENG Jing, PU Shanqiu, ZHOU Yu, HUANG Cuirui, YANG Guangyou, XIE Yue, HE Ran, XU Jing, GU Xiaobin. The Transcription Level of MMP2 in Psoroptes ovis var. cuniculi and Establishment of the Indirect ELISA Based on Its Recombinant Protein [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(2): 567-575. |
| [3] | ZHENG Youle, CHEN Yuhang, XIE Yue, YANG Guangyou, HE Ran, GU Xiaobin. The Effects of Recombinant Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor of Psoroptes ovis on the Characteristic Molecules of Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg Type Immune Responses in Rabbits Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(3): 594-601. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||