





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (7): 3423-3432.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.07.034
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Zhuoqi1,2( ), FAN Liyuan2, ZHONG Chunyan5, YU Yanfei2, LI Jizong2,3,4,*(
), FAN Liyuan2, ZHONG Chunyan5, YU Yanfei2, LI Jizong2,3,4,*( ), LI Bin2,3,4,*(
), LI Bin2,3,4,*( ), YUAN Xiaomin1,*(
), YUAN Xiaomin1,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-05
Online:2025-07-23
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
LI Jizong, LI Bin, YUAN Xiaomin
E-mail:475846734@qq.com;lijizong22@sina.com;libinana@126.com;yxm1230@hunau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
CHEN Zhuoqi, FAN Liyuan, ZHONG Chunyan, YU Yanfei, LI Jizong, LI Bin, YUAN Xiaomin. The Inhibitory Effect of Transcription Factor CEBPB on the Replication of Porcine Deltacoronavirus in vitro[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(7): 3423-3432.
Table 1
Primer and siRNA sequences"
| 基因名称 Gene name | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequences (5′→3′) |
| PDCoV N | PDCoV-N-F | ATCGACCACATGGCTCCAA |
| PDCoV-N-R | CAGCTCTTGCCCATGTAGCTT | |
| PDCoV-probe | CACACCAGTCGTTAAGCATGGCAAGCT | |
| GAPDH | GAPDH-F | TCACTGCCACCCAGAAGACT |
| GAPDH-R | ATGACCTTGCCCACAGCCTT | |
| CEBPB | CEBPB-F | CTGGAGACGCAGCATAAGGT |
| CEBPB-R | TGCTTGAACAAGTTCCGCAG | |
| siCEBPB | siRNA-sense | CGCCUGCCUUUAAAUCCAUTT |
| siRNA-antisense | AUGGAUUUAAAGGCAGGCGTT | |
| si-NC | siRNA-sense | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT |
| siRNA-antisense | ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT |
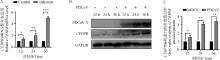
Fig. 1
Effect of PDCoV infection on CEBPB expression A. CEBPB mRNA expression levels at 12, 24, and 36 h post PDCoV infection; B. CEBPB protein expression levels at 12, 24, and 36 h post PDCoV infection; C. Gray value analysis of CEBPB protein expression levels at 12, 24, and 36 h post PDCoV infection; *. P < 0.05; **. P < 0.01; ***. P < 0.001, the same as below"
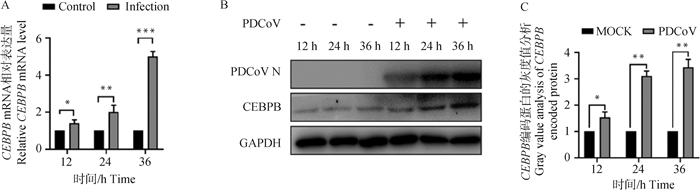
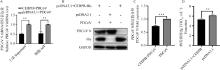
Fig. 2
Overexpression of CEBPB-encoded protein inhibits PDCoV replication A. PDCoV mRNA expression was detected after overexpression of CEBPB protein; B. PDCoV protein expression level was detected after overexpression of CEBPB protein; C. Gray value analysis of PDCoV protein expression levels determined after overexpression of the CEBPB protein; D. Virus titers were detected by TCID50 after overexpression of CEBPB protein; **. P < 0.01; ***. P < 0.001; ****. P < 0.000 1"
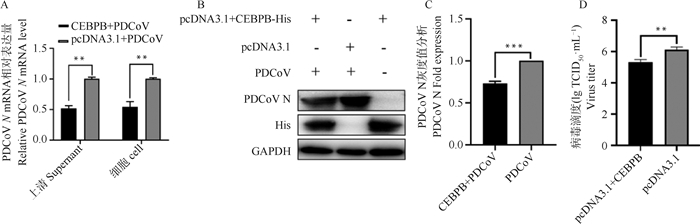
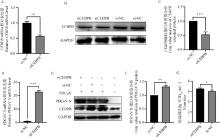
Fig. 3
Promoting PDCoV replication by interfering with CEBPB A. The mRNA level of CEBPB was detected by qPCR after transfection with siCEBPB. B. The protein level of CEBPB was detected by Western blot after transfection with siCEBPB. C. The grayscale value of CEBPB protein expression was analyzed by Western blot after transfection with siCEBPB. D. The mRNA expression level of PDCoV-N was detected by qPCR after transfection with siCEBPB and subsequent infection with PDCoV. E. The expression levels of PDCoV N and CEBPB coding proteins were detected after transfection with siCEBPB and subsequent infection with PDCoV. F. The grayscale values of PDCoV N and CEBPB coding protein expression levels were analyzed after transfection with siCEBPB and subsequent infection with PDCoV; G. Virus titer was detected by TCID50 after transfection with siCEBPB"
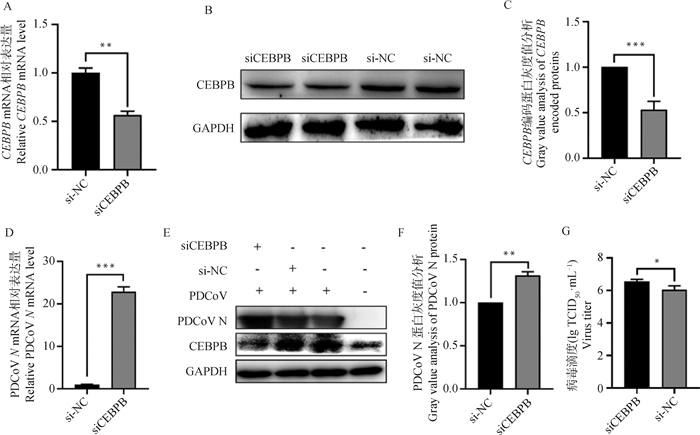
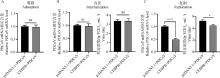
Fig. 4
Effect of CEBPB protein on PDCoV replication cycle A. The mRNA content of PDCoV in the adsorption phase of the virus was determined by qPCR. B. The mRNA content of PDCoV and viral titers in the internalization phase were measured using qPCR and TCID50 assays. C. The mRNA content of PDCoV and viral titers in the replication phase were measured using qPCR and TCID50 assays. ns. No sigaificant difference"
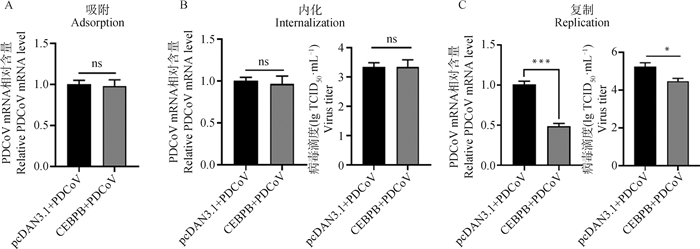
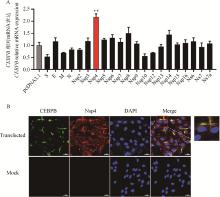
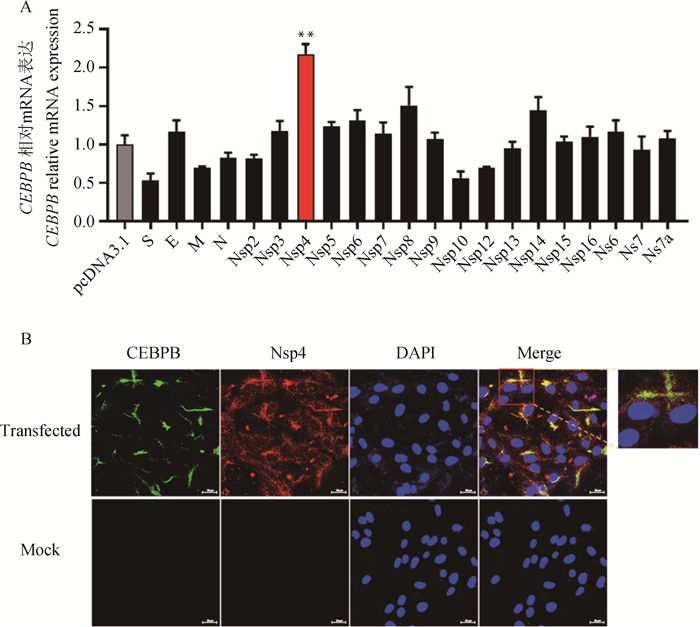
Fig. 5
Nsp4 raised CEBPB mRNA level and positioning analysis A. The mRNA level of CEBPB was detected by qPCR after transfection of PDCoV structural protein and non-structural protein overexpression plasmid. B. The CEBPB protein was detected in the cytoplasm after 24 h of co-transfection with the overexpressed plasmid of Nsp4 and CEBPB. A representative confocal image shows the colocalization of Nsp4 (red), CEBPB (green), and DAPI (blue)"
| 1 | LI J , ZHAO S , ZHANG B , et al. A novel recombinant S-based subunit vaccine induces protective immunity against porcine deltacoronavirus challenge in piglets[J]. J Virol, 2023, 97 (11): e0095823. |
| 2 | 朱向东, 高冉. 猪德尔塔冠状病毒的流行、传播及防控策略[J]. 猪业科学, 2023, 40 (8): 70- 72. |
| ZHU X D , GAO R . The prevalence, transmission, and prevention strategies of porcine delta coronavirus[J]. Swine Industry Science, 2023, 40 (8): 70- 72. | |
| 3 | LORSIRIGOOL A , SAENG-CHUTO K , TEMEEYASEN G , et al. The first detection and full-length genome sequence of porcine deltacoronavirus isolated in Lao PDR[J]. Arch Virol, 2016, 161 (10): 2909- 2911. |
| 4 | LEE S , LEE C . Complete genome characterization of Korean porcine deltacoronavirus strain KOR/KNU14-04/2014[J]. Genome Announc, 2014, 2 (6): e01191- 14. |
| 5 | OTRANTO D , SAKRU N , TESTINI G , et al. Case report: First evidence of human zoonotic infection by Onchocerca lupi (Spirurida, Onchocercidae)[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2011, 84 (1): 55- 58. |
| 6 | SONG D , ZHOU X , PENG Q , et al. Newly emerged porcine deltacoronavirus associated with diarrhoea in swine in China: Identification, prevalence and full-length genome sequence analysis[J]. Transbound Emerg Dis, 2015, 62 (6): 575- 580. |
| 7 | MCBRIDE R , VAN ZYL M , FIELDING B C . The coronavirus nucleocapsid is a multifunctional protein[J]. Viruses, 2014, 6 (8): 2991- 3018. |
| 8 | FANG P , FANG L , LIU X , et al. Identification and subcellular localization of porcine deltacoronavirus accessory protein NS6[J]. Virology, 2016, 499, 170- 177. |
| 9 |
汤荣锋, 范前进, 郭龙军, 等. 猪丁型冠状病毒S1-CTD相互作用宿主蛋白的筛选和鉴定[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53 (7): 2260- 2267.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.07.022 |
|
TANG R F , FAN Q J , GUO L J , et al. Screening and identification of host proteins interacting with PDCoV S1-CTD[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53 (7): 2260- 2267.
doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.07.022 |
|
| 10 | BOLEY P A , ALHAMO M A , LOSSIE G , et al. Porcine deltacoronavirus infection and transmission in poultry, United States1[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2020, 26 (2): 255- 265. |
| 11 | LIANG Q , ZHANG H , LI B , et al. Susceptibility of chickens to porcine deltacoronavirus infection[J]. Viruses, 2019, 11 (6): 573. |
| 12 | LIU Y , WANG B , LIANG Q Z , et al. Roles of two major domains of the porcine deltacoronavirus S1 subunit in receptor binding and neutralization[J]. J Virol, 2021, 95 (24): e0111821. |
| 13 | WANG X , FANG L , LIU S , et al. Susceptibility of porcine IPI-2I intestinal epithelial cells to infection with swine enteric coronaviruses[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2019, 233, 21- 27. |
| 14 | WANG Q , VLASOVA A N , KENNEY S P , et al. Emerging and re-emerging coronaviruses in pigs[J]. Curr Opin Virol, 2019, 34, 39- 49. |
| 15 | 瞿欢, 胡靖飞, 李施倩, 等. 不同动物源性细胞系对猪丁型冠状病毒的易感性[J]. 微生物学报, 2022, 62 (2): 672- 685. |
| QU H , HU J F , LI S Q , et al. Susceptibility of cell lines from different animal species to porcine deltacoronavirus[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2022, 62 (2): 672- 685. | |
| 16 | 朱培英, 冉李艳, 杨莎莎, 等. 猪德尔塔冠状病毒病原学特征与致病机制研究进展[J]. 现代畜牧兽医, 2023 (5): 88- 92. |
| ZHU P Y , RAN L Y , YANG S S , et al. Research progress on etiological characteristics and pathogenesis of porcine Delta Coronavirus[J]. Modern Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2023 (5): 88- 92. | |
| 17 | YANG X , KONG N , QIN W , et al. PGAM5 degrades PDCoV N protein and activates type Ⅰ interferon to antagonize viral replication[J]. J Virol, 2023, 97 (11): e0147023. |
| 18 | QU H , WEN Y , HU J , et al. Study of the inhibitory effect of STAT1 on PDCoV infection[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2022, 266, 109333. |
| 19 | LI Z , DUAN P , QIU R , et al. HDAC6 degrades nsp8 of porcine deltacoronavirus through deacetylation and ubiquitination to inhibit viral replication[J]. J Virol, 2023, 97 (5): e0037523. |
| 20 | 胡晟, 苏玉虹. 转录因子C/EBPβ的功能与调控[J]. 辽宁医学院学报, 2009, 30 (2): 186- 189. |
| HU S , SU Y H . Function and regulation of transcription factor C/EBPβ[J]. Journal of Liaoning Medical College, 2009, 30 (2): 186- 189. | |
| 21 | VAN DER KRIEKEN S E , POPEIJUS H E , MENSINK R P , et al. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β in relation to ER stress, inflammation, and metabolic disturbances[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2015, 2015, 324815. |
| 22 | RAMJI D P , FOKA P . CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: structure, function and regulation[J]. Biochem J, 2002, 365 (Pt 3): 561- 575. |
| 23 | KERSHAW E E , SCHUPP M , GUAN H P , et al. PPARgamma regulates adipose triglyceride lipase in adipocytes in vitro and in vivo[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2007, 293 (6): E1736- E1745. |
| 24 | AKIRA S , KISHIMOTO T . IL-6 and NF-IL6 in acute-phase response and viral infection[J]. Immunol Rev, 1992, 127, 25- 50. |
| 25 | NIU L , ZHENG Z , XUE Q , et al. Two coupled mutations abolished the binding of CEBPB to the promoter of CXCL14 that displayed an antiviral effect on PRRSV by activating IFN signaling[J]. FASEB J, 2020, 34 (8): 11257- 11271. |
| 26 | LEDNICKY J A , TAGLIAMONTE M S , WHITE S K , et al. Independent infections of porcine deltacoronavirus among Haitian children[J]. Nature, 2021, 600 (7887): 133- 137. |
| 27 | LIU S , FANG P , KE W , et al. Porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) infection antagonizes interferon-λ1 production[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2020, 247, 108785. |
| 28 | WESTIN E R , KHODADADI-JAMAYRAN A , PHAM L K , et al. CRISPR screen identifies CEBPB as contributor to dyskeratosis congenita fibroblast senescence via augmented inflammatory gene response[J]. G3 (Bethesda), 2023, 13 (11): jkad207. |
| 29 | REN Y , GUO W , QIAO B . Abnormal expression of CEBPB promotes the progression of renal cell carcinoma through regulating the generation of IL-6[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9 (10): e20175. |
| 30 | BECHARA R , AMATYA N , BAILEY R D , et al. The m6A reader IMP2 directs autoimmune inflammation through an IL-17-and TNFα-dependent C/EBP transcription factor axis[J]. Sci Immunol, 2021, 6 (61): eabd1287. |
| 31 | MARANTO J , RAPPAPORT J , DATTA P K . Role of C/EBP-β, p38 MAPK, and MKK6 in IL-1β-mediated C3 gene regulation in astrocytes[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2011, 112 (4): 1168- 1175. |
| 32 | NERLOV C . The C/EBP family of transcription factors: a paradigm for interaction between gene expression and proliferation control[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2007, 17 (7): 318- 324. |
| 33 | FAN B , PENG Q , SONG S , et al. Nonstructural protein 1 of variant PEDV plays a key role in escaping replication restriction by complement C3[J]. J Virol, 2022, 96 (18): e0102422. |
| 34 | DUAN C , GE X , WANG J , et al. Ergosterol peroxide exhibits antiviral and immunomodulatory abilities against porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) via suppression of NF-κB and p38/MAPK signaling pathways in vitro[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 93, 107317. |
| 35 | WU Y , SHI Z , CHEN J , et al. Porcine deltacoronavirus E protein induces interleukin-8 production via NF-κB and AP-1 activation[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2022, 274, 109553. |
| 36 | HUAN C C , WANG H X , SHENG X X , et al. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus nucleoprotein contributes to HMGB1 transcription and release by interacting with C/EBP-β[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7 (46): 75064- 75080. |
| 37 | RANGANATHAN P N , KHALILI K . The transcriptional enhancer element, kappa B, regulates promoter activity of the human neurotropic virus, JCV, in cells derived from the CNS[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 1993, 21 (8): 1959- 1964. |
| 38 | MAYREDDY R P , SAFAK M , RAZMARA M , et al. Transcription of the JC virus archetype late genome: importance of the kappa B and the 23-base-pair motifs in late promoter activity in glial cells[J]. J Virol, 1996, 70 (4): 2387- 2393. |
| 39 | ZHANG B , LI S , CHEN Z , et al. Phosphorylation of G3BP1 is involved in the regulation of PDCoV-induced inflammatory response[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2024, 293, 110070. |
| 40 | COYLE-RINK J , SWEET T , ABRAHAM S , et al. Interaction between TGFbeta signaling proteins and C/EBP controls basal and Tat-mediated transcription of HIV-1 LTR in astrocytes[J]. Virology, 2002, 299 (2): 240- 247. |
| 41 | YU Y , FU Q , LI J , et al. E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1-mediated CEBPB ubiquitination regulates the inflammatory response of macrophages in sepsis-induced myocardial injury[J]. Mamm Genome, 2024, 35 (1): 56- 67. |
| 42 | FEHR A R , PERLMAN S . Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2015, 1282, 1- 23. |
| 43 | KAWAI T , AKIRA S . TLR signaling[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2006, 13 (5): 816- 825. |
| [1] | XU Hong, SHANG Hongqi, ZHANG Xue, QIAN Jiali, WANG Chuanhong, SONG Xu, BAO Meiying, LIU Shiyu, ZHANG Gege, GUO Rongli, ZHAO Yongxiang, FAN Baochao, LI Bin. Inhibition Effect of C8orf4 Gene Encoding Protein on in vitro Replication of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2024, 55(5): 2100-2108. |
| [2] | LI Houwei, WANG Lei, ZHANG Xianfeng, HU Hui, ZHANG Zhenzhen, ZHANG Yunfei, LIU Lintao, JI Xingyu, HU Yonghao. Analysis of the Proliferation Characteristics of Porcine Deltacoronavirus on Suspension Cultured Porcine Kidney Cell LLC-PK1 [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(6): 2024-2028. |
| [3] | LIU Hejuan, SHI Chenxi, WANG Jing, WANG Meile, WANG Donghan, WEI Zhanyong, YIN Sugai. Exploration on the Potential Mechanism of Baicalein on Porcine Deltacoronavirus Infection Based on Network Pharmacology [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(11): 4097-4109. |
| [4] | LIANG Jixiang, JIAO Zhe, YAN Zhishan, LI Yang, LI Dongqi, LIU Xiaoli, GU Changqin, HU Xueying, CHENG Guofu, ZHANG Wanpo. Effect of Porcine Deltacoronavirus Infection on the Number of Intestinal Goblet Cells and the Expression of Hes1 and MUC2 in the Small Intestine of Neonatal Piglets [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(3): 772-781. |
| [5] | FENG Yu, YIN Xinhuan, YANG Xiaoyu, XU Lei, XU Zhiwen, ZHU Ling. Establishment and Application of an Indirect ELISA Based on Recombinant M Protein against Porcine Deltacoronavirus [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(7): 1710-1718. |
| [6] | HOU Linshan, JIA Jingliang, GU Wenyuan, LIU Baojing, SHI Qiankai, YUAN Guangfu, CHEN Shaojie, FAN Jinghui, ZUO Yuzhu. Establishment and Application of an Indirect ELISA Based on Recombinant S1 Protein for the Detection of Antibodies against Porcine Deltacoronavirus [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2019, 50(8): 1642-1648. |
| [7] | ZHENG Lanlan, ZHU Jingjing, WANG Pan, SHU Yan, LIANG Qingqing, LI Bingxiao, WANG Chaoqun, WEI Zhanyong. Development and Application of a TaqMan based Real-time Fluorescent RT-PCR for Specific Detection of Porcine Deltacoronavirus [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2019, 50(6): 1261-1267. |
| [8] | WANG Dan-yang, ZHANG Kang, WANG Xu-rong, WANG Hai-rui, WANG Lei, ZHANG Kai, ZHANG Jing-yan, LI Jian-xi, WANG Xue-zhi. Inhibitory Effects of Extracts from Terminalia chebula, Corydalis hendersonii, Aconitum tanguticum on Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus in vitro [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2018, 49(9): 2036-2043. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||