





Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (10): 5060-5071.doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2025.10.026
• Animal Nutrition and Feeds • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Yan( ), OU Niantao, LIU Mengzhe, WANG Kai, JIA Huixin, YU Wenjing, LI Yanling*(
), OU Niantao, LIU Mengzhe, WANG Kai, JIA Huixin, YU Wenjing, LI Yanling*( )
)
Received:2024-11-08
Online:2025-10-23
Published:2025-11-01
Contact:
LI Yanling
E-mail:zhangyan2302@163.com;yanl_li@163.com
CLC Number:
ZHANG Yan, OU Niantao, LIU Mengzhe, WANG Kai, JIA Huixin, YU Wenjing, LI Yanling. In vitro Anti-inflammatory Activity of Cinnamon Essential Oil and Cinnamaldehyde, and the Protective Effect against LPS-induced Inflammatory Injury in RAW 264.7 cells[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2025, 56(10): 5060-5071.
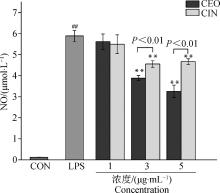
Fig. 3
Effect of different EOs on NO content of LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells Data were presented as "mean±SD". ##. P < 0.01, represent the NO content in RAW264.7 cells treated with LPS was very significantly different from the control group. **. P < 0.01, represent the NO content in RAW264.7 cells treated with CEO and CIN was very significantly different from the LPS group. Comparison of NO content in RAW264.7 cells between the CEO and CIN groups at the same concentration was directly presented as Pvalues, and P < 0.01 represented a very significant difference"
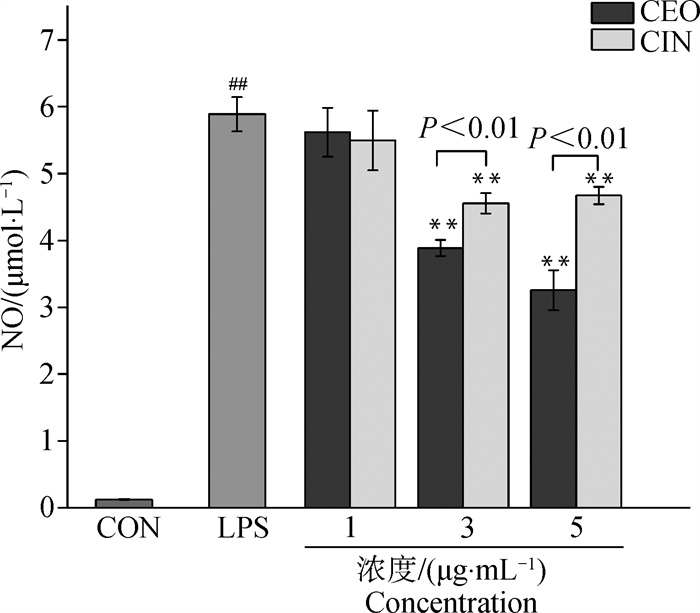
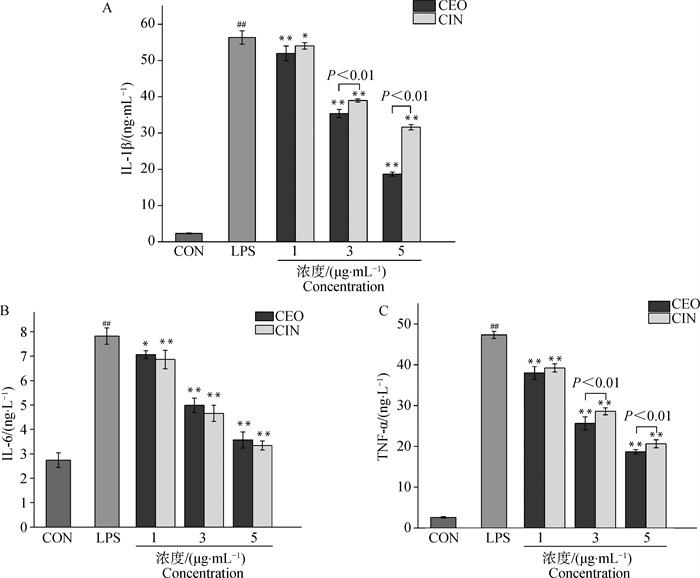
Fig. 4
Effect of different EOs on inflammatory factor IL-1β (A), IL-6 (B) and TNF-α (C) content of LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells Data were presented as "mean±SD". ##. P < 0.01, represent the inflammatory factor content in RAW264.7 cells treated with LPS was very significantly different from the control group. *. P < 0.05, represent the inflammatory factor content in RAW264.7 cells treated with CIN was significantly different from the LPS group. **. P < 0.01, represent the inflammatory factor content in RAW264.7 cells treated with CEO and CIN was very significantly different from the LPS group. Comparison of inflammatory factor content in RAW264.7 cells between the CEO and CIN groups at the same concentration was directly presented as Pvalues, and P < 0.01 represented a very significant difference"
| 1 | NIUX,DINGY,CHENS,et al.Effect of immune stress on growth performance and immune functions of livestock: mechanisms and prevention[J].Animals (Basel),2022,12(7):909. |
| 2 |
MEDZHITOVR.Inflammation 2010: new adventures of an old flame[J].Cell,2010,140(6):771-776.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.006 |
| 3 |
PJ J,MANJUS L,ETHIRAJK R,et al.Safer anti-inflammatory therapy through dual COX-2/5-LOX inhibitors: A structure-based approach[J].Eur J Pharm Sci,2018,121,356-381.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2018.06.003 |
| 4 |
HORTELANOS,ZEINIM,BOSCAL,et al.Nitric oxide and cell viability in inflammatory cells: A role for NO in macrophage function and fate[J].Toxicol,2005,208(2):249-258.
doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2004.11.035 |
| 5 |
SINGHB,SINGHJ P,KAURA,et al.Insights into the chemical composition and bioactivities of citrus peel essential oils[J].Food Res. Int,2021,143,110231.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110231 |
| 6 |
PLASTINAP,APRIANTINIA,MEIJERINKJ,et al.In vitroanti-inflammatory and radical scavenging properties of Chinotto (Citrus myrtifolia Raf.) essential oils[J].Nutrients,2018,10(6):783.
doi: 10.3390/nu10060783 |
| 7 |
SHENO Y.Anti-inflammatory effect of essential oil from Citrus aurantium L. var.amara Engl[J].J Agric Food Chem,2017,65(39):8586-8594.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02586 |
| 8 |
STEVANOVÍCZ,BOŠNJAK-NEUMVLLERJ,PAJÍC-LIJAKOVÍCI,et al.Essential oils as feed additives—future perspectives[J].Molecules,2018,23(7):1717.
doi: 10.3390/molecules23071717 |
| 9 |
NEHMER,ANDRESS,PEREIRAR B,et al.Essential oils in livestock: From health to food quality[J].Antioxidants (Basel),2021,10(2):330.
doi: 10.3390/antiox10020330 |
| 10 | 张嘉琦,张会艳,赵青余,等.植物精油对畜禽肠道健康、免疫调节和肉品质的研究进展[J].动物营养学报,2021,33(5):2439-2451. |
| ZHANGJ Q,ZHANGH Y,ZHAOQ Y,et al.Research progress of plant essential oil on intestinal health, immune regulation and meat quality of livestock and poultry[J].Journal of Animal Nutrition,2021,33(5):2439-2451. | |
| 11 |
SHUC,GEL,LIZ,et al.Antibacterial activity of cinnamon essential oil and its main component of cinnamaldehyde and the underlying mechanism[J].Front Pharmacol,2024,15,1378434.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1378434 |
| 12 |
LIUS,ZHAOC,CAOY,et al.Comparison of chemical compositions and antioxidant activity of essential oils from litsea cubeba, cinnamon, Anise, and Eucalyptus[J].Molecules,2023,28(13):5051.
doi: 10.3390/molecules28135051 |
| 13 |
ZHAOC,CAOY,ZHANGZ,et al.Cinnamon and eucalyptus oils suppress the inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide in vivo[J].Molecules,2021,26(23):7410.
doi: 10.3390/molecules26237410 |
| 14 | CHOWDHURYS,MANDALG P,PATRAA K,et al.Different essential oils in diets of broiler chickens: 2. Gut microbes and morphology, immune response, and some blood profile and antioxidant enzymes[J].Anim Feed Sci Technol,2017,236,39-47. |
| 15 | PALHARESC J,GESTEIRAC S,BELLIA L,et al.Effects of a blend of essential oils in milk replacer on performance, rumen fermentation, blood parameters, and health scores of dairy heifers[J].PLoS One,2021,16(3):e231068. |
| 16 | OOIL S,LIY,KAMS L,et al.Antimicrobial activities of cinnamon oil and cinnamaldehyde from the Chinese medicinal herb cinnamomum cassia blume[J].Am J Chin Med,2006(3):34, 511-522. |
| 17 |
CHANGK S,TAKJ H,KIMS I,et al.Repellency of Cinnamomum cassiabark compounds and cream containing cassia oil to Aedes aegypti(Diptera: Culicidae) under laboratory and indoor conditions[J].Pest Manag Sci,2006,62(11):1032-1038.
doi: 10.1002/ps.1268 |
| 18 |
LUL,SHUC,CHENL,et al.Insecticidal activity and mechanism of cinnamaldehyde inC. elegans[J].Fitoterapia,2020,146,104687.
doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2020.104687 |
| 19 |
JIMENEZM J,BERRIOSR,STELZHAMMERS,et al.Ingestion of organic acids and cinnamaldehyde improves tissue homeostasis of piglets exposed to enterotoxic Escherichia coli(ETEC)[J].J Anim Sci,2020,98(2):skaa012.
doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa012 |
| 20 |
SAMPATHC,CHUKKAPALLIS S,RAJUA V,et al.Cinnamaldehyde protects againstP. gingivalis induced intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in IEC-6 cells via the PI3K/Akt-Mediated NO/Nrf2 signaling pathway[J].Int J Mol Sci,2024,25(9):4734.
doi: 10.3390/ijms25094734 |
| 21 |
NGUYENL,NGUYENN,TRANK N,et al.Anxiolytic-like effect of inhaled cinnamon essential oil and its main component cinnamaldehyde in animal models[J].Molecules,2022,27(22):7997.
doi: 10.3390/molecules27227997 |
| 22 |
SIMJ,KHAZANDIM,PIH,et al.Antimicrobial effects of cinnamon essential oil and cinnamaldehyde combined with EDTA against canine otitis externa pathogens[J].J Appl Microbiol,2019,127(1):99-108.
doi: 10.1111/jam.14298 |
| 23 |
STEVENSN,ALLREDK.Antidiabetic potential of volatile cinnamon oil: A review and exploration of mechanisms using in silico molecular docking simulations[J].Molecules,2022,27(3):853.
doi: 10.3390/molecules27030853 |
| 24 |
VENDRAMINI-COSTAD B,CARVALHOJ E.Molecular link mechanisms between inflammation and cancer[J].Curr Pharm Des,2012,18(26):3831-3852.
doi: 10.2174/138161212802083707 |
| 25 |
YARLAN S,BISHAYEEA,SETHIG,et al.Targeting arachidonic acid pathway by natural products for cancer prevention and therapy[J].Semin Cancer Biol,2016,40-41,48-81.
doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2016.02.001 |
| 26 |
SIMONL S.Role and regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 during inflammation[J].Am J Med,1999,106(5):37S-42S.
doi: 10.1016/S0002-9343(99)00115-1 |
| 27 |
FURIAE,NAPOLIA,TAGARELLIA,et al.Speciation of 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid with calcium(Ⅱ), magnesium(Ⅱ), and nickel(Ⅱ) cations in self-medium[J].J Chem Eng Data,2013,58(5):1349-1353.
doi: 10.1021/je400105c |
| 28 |
CERELLAC,SOBOLEWSKIC,DICATOM,et al.Targeting COX-2 expression by natural compounds: a promising alternative strategy to synthetic COX-2 inhibitors for cancer chemoprevention and therapy[J].Biochem Pharmacol,2010,80(12):1801-1815.
doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.050 |
| 29 |
MASHIMAR,OKUYAMAT.The role of lipoxygenases in pathophysiology; new insights and future perspectives[J].Redox Biol,2015,6,297-310.
doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.08.006 |
| 30 |
ZHENGM,ZHANGZ,ZHUW,et al.Essential structural profile of a dual functional inhibitor against cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX): molecular docking and 3D-QSAR analyses on DHDMBF analogues[J].Bioorg Med Chem,2006,14(10):3428-3437.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2005.12.062 |
| 31 | BILTEKINS N,DEMIRCIF.In vitroanti-inflammatory and anticancer evaluation of Mentha spicata L. essential oils[J].Adv Mater,2023,8(19):17143-17150. |
| 32 |
KHANA,PERVAIZA,ANSARIB,et al.Phytochemical profiling, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and in-silico approach of Cornus macrophyllabioss (bark)[J].Molecules,2022,27(13):4081.
doi: 10.3390/molecules27134081 |
| 33 | 王雪,刘燕,史玉柱,等.瘤果黑种草子总皂苷的抗炎和免疫调节作用[J].免疫学杂志,2023,39(2):120-127. |
| WANGX,LIUY,SHIY Z,et al.The anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of total saponins from seeds of nigella glandulifera[J].Immunological Journal,2023,39(2):120-127. | |
| 34 |
BOGDANC.Nitric oxide and the immune response[J].Nat Immunol,2001,2(10):907-916.
doi: 10.1038/ni1001-907 |
| 35 |
MONCADAS,HIGGSA.The L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway[J].N Engl J Med,1993,329(27):2002-2012.
doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312303292706 |
| 36 |
TUNGY T,CHUAM T,WANGS Y,et al.Anti-inflammation activities of essential oil and its constituents from indigenous cinnamon (Cinnamomum osmophloeum) twigs[J].Bioresour Technol,2008,99(9):3908-3913.
doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2007.07.050 |
| 37 |
LIUC,CHUD,KALANTAR-ZADEHK,et al.Cytokines: from clinical significance to quantification[J].Adv Sci (Weinh),2021,8(15):e2004433.
doi: 10.1002/advs.202004433 |
| 38 |
LEES C,WANGS Y,LIC C,et al.Anti-inflammatory effect of cinnamaldehyde and linalool from the leaf essential oil of Cinnamomum osmophloeum Kanehira in endotoxin-induced mice[J].J Food Drug Anal,2018,26(1):211-220.
doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2017.03.006 |
| 39 |
ZHANGK,HUANGQ,DENGS,et al.Mechanisms of TLR4-mediated autophagy and nitroxidative stress[J].Front Cell Infect Microbiol,2021,11,766590.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.766590 |
| 40 |
RADIR.Oxygen radicals, nitric oxide, and peroxynitrite: redox pathways in molecular medicine[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2018,115(23):5839-5848.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1804932115 |
| 41 |
LIS T,DAIQ,ZHANGS X,et al.Ulinastatin attenuates LPS-induced inflammation in mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells by inhibiting the JNK/NF-kappaB signaling pathway and activating the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway[J].Acta Pharm Sin B,2018,39(8):1294-1304.
doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.143 |
| 42 | 崔乔. 肉桂醛对育肥绵羊生长性能、消化代谢及血液指标的影响[D]. 晋中: 山西农业大学, 2021. |
| CUI Q. Effects of diet supplemented with cinnamaldehyde on growth performance, digestive metabolism and blood indicatorsin fattening lambs[D]. Jinzhong: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| 43 |
WANGL,HOUY,YID,et al.Beneficial roles of dietary oleum cinnamomi in alleviating intestinal injury[J].Front Biosci (Landmark Ed),2015,20(5):814-828.
doi: 10.2741/4339 |
| 44 |
LEALK W,LEALM,BREANCINIM,et al.Essential oils and capsaicin in the diet of Jersey cows at early lactation and their positive impact on anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and immunological responses[J].Trop Anim Health Prod,2024,56(7):247.
doi: 10.1007/s11250-024-04077-w |
| 45 |
MOHANTYD,PADHEES,SAHOOC,et al.Integrating network pharmacology and experimental verification to decipher the multitarget pharmacological mechanism of Cinnamomum zeylanicum essential oil in treating inflammation[J].Heliyon,2024,10(2):e24120.
doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24120 |
| 46 |
SCHINKA,NAUMOSKAK,KITANOVSKIZ,et al.Anti-inflammatory effects of cinnamon extract and identification of active compounds influencing the TLR2 and TLR4 signaling pathways[J].Food Funct,2018,9(11):5950-5964.
doi: 10.1039/C8FO01286E |
| 47 |
HOC L,LIL H,WENGY C,et al.Eucalyptus essential oils inhibit the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in RAW264.7 macrophages through reducing MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways[J].BMC Complement Med Ther,2020,20(1):200.
doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-02999-0 |
| 48 |
BENH A,GARGOURIM,DHIFIW,et al.Potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of Citrus aurantium essential oil against carbon tetrachloride-mediated hepatotoxicity: A biochemical, molecular and histopathological changes in adult rats[J].Environ Toxicol,2019,34(4):388-400.
doi: 10.1002/tox.22693 |
| 49 | LINW T,HEY H,LOY H,et al.Essential oil from Glossogyne tenuifolia inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation-associated genes in macro-phage cells via suppression of NF-kappaB signaling pathway[J].Plants (Basel),2023,12(6):1241. |
| [1] | LIU Xu, PAN Yinchuan, YANG Yajun, LIU Xiwang, MA Ning, LI Jianyong. Inhibiting Effect of Aspirin Eugenol Ester on Lipopolysaccharide-induced Inflammatory Response in Mouse Macrophages in vitro [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2022, 53(11): 4048-4057. |
| [2] | LUO Jia, XU Jinrui, LI Wu, WANG Yujiong. The Effect of BCG-induced RAW264.7 Cells Fatty Acid Oxidation on Autophagy and Pro-inflammatory Cytokines Expression [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(9): 2617-2625. |
| [3] | HE Shuangjiang, SONG Ruilong, CAO Ying, LIU Qingyang, ZHANG Chuang, LIU Zongping. Effects of Low Level Cadmium Exposure on Osteoclast Differentiation [J]. ACTA VETERINARIA ET ZOOTECHNICA SINICA, 2019, 50(3): 663-669. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||